Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) for primary osteoporosis in the elderly: a clinical trial
Shen Zhi-fang (沈志方), Zhu Gao-feng (朱高峰), Qian Li-feng (錢立鋒), Fu Yuan-xin (付源鑫)
Acupuncture and Tuina Department, Jiaxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Jiaxing 314001, China
Osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation. It is a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue with a consequent increase in bone fragility and susceptibility of fractures. Primary senile osteoporosis is associated with the normal process of aging. It’s generally believed to be related to endocrine, nutrition and exercise.Individuals may experience pain, a shortened height,fractures and hunchback[1]. As the older population continues to grow, senile osteoporosis tends to affect more and more people. As a result, osteoporosisrelated pain, fracture and complications start to have a great impact on the quality of life in the aged population.
To date, the treatments for osteoporosis can be divided into two types: medication and physiotherapy.However, the adverse reactions and expenses from long-term administration of medication have restricted its application and undermined the compliance.Physiotherapy has less adverse reactions, and is low-cost and easy-to-operate, but produces a significant efficacy. Thus, it has been gradually accepted by osteoporosis patients. During the recent years, we adopted Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) to treat primary osteoporosis in the elderly,and the report is as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnosis was made by referring to theExpert Consensus on Diagnosis Criteria of Chinese Osteoporosis(3rd draft, 2014)[1]: aged over 70 in men, or over 20 years after menopause in women; trabecular bone loss or cortical bone loss, related to aging but not to sex hormone dependence; dorsal pain; shortened height or hunchback; bone fracture, often in spine (multiplewedge) and hip (femoral neck, tuberosity); bone mineral density (BMD) of the proximal femur lower by over 2.5 standard deviations (SD) compared to normal young adults.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Conforming to the diagnostic criteria of osteoporosis above; informed consent form.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Complicated with fracture or severe underlying diseases, unsuitable for exercises; mental disorders;failed to follow the prescript treatment protocol, which affected the therapeutic efficacy; having received medications for osteoporosis within the latest 3 months.
1.4 Quality control
According to the characteristics of patients, proficient doctors demonstrated the exercises during the first 2 weeks, unified the time and intensity of practice, and stipulated the practice diary and health education pamphlet. Each participant was followed up and offered a notebook when they mastered the exercises, to ensure the practice frequency and quality.
1.5 Statistical analysis
The SPSS 13.0 version software was adopted for statistical analysis. Measurement data in normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviationand analyzed byt-test; those not conforming to normal distribution were analyzed by non-parametric test. Enumeration data and ranked data were treated by Chi-square test or rank-sum test.P<0.05 indicated a statistical significance.
1.6 General data
A total of eighty patients were recruited from the outpatient or ward of Acupuncture and Tuina Department, Jiaxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. The patients were randomized into a Yi Jin Jing group and a medication group. The general data were equivalent between the two groups, and the between-group differences were statistically insignificant (allP>0.05), indicating the comparability(Table 1).
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Yi Jin Jing group
Under the guidance of doctor, patients in this group practiced the simplified 12-movement Yi Jin Jing(Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises)[2-3]. Prior to the practice, patients were required to get themselves ready,wearing loose and comfortable clothes, specific shoes for exercise or soft-sole cloth shoes (Figure 1). During the practice, patients should clear away distracting thoughts and performed each movement in a stretching,slow and soft way instead of forceful. After practice,patients should keep warm and away from wind. The exercises were practiced twice a day, better to have slight sweating each time (Figure 2).
2.2 Medication group
Patients in this group were prescribed with oral administration of alendronate sodium tablet (Hangzhou MSD Pharmaceutical Company, China), once a week,70 mg per dose.
The two groups underwent efficacy evaluation after 6-month intervention.

Figure 1. Preparation posture
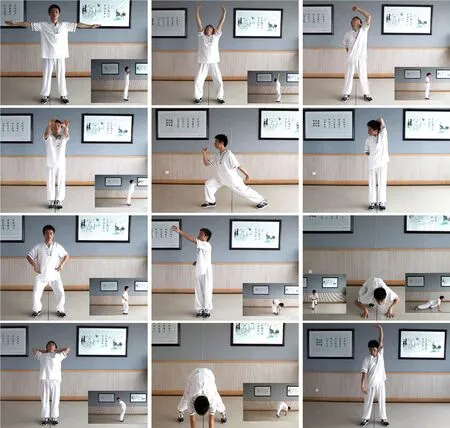

Figure 2. 12-movement Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises)
3 Observation of Therapeutic Efficacy
3.1 Items
3.1.1 BMD
The dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (Hologie QDR 4500W, USA) was adopted to measure the BMD of the proximal femur.
3.1.2 Visual analog scale (VAS)
A thread of 10 cm in length was marked 0 point at the left end standing for painless and 10 points at the right end for unbearable pain. 1-3 points represented mild pain; 4-6 points as moderate pain; 7-9 points as severe pain.
3.1.3 Activities of daily living (ADL)
A quantitative observation of patients’ ADL was conducted based on Barthel index (BI). ADL consisted of 10 items which all contained 2-4 questions. Each question was scored 0, 5, 10 or 15 points corresponding to the capacity, 100 points as the full score. <20 points was considered as extremely serious functional defect,and the living was completely dependent; 20-40 points meant that major help was needed; 40-60 points meant that minor help was needed; >60 points stood for substantially independent.
3.2 Results
3.2.1 Comparison of BMD of the proximal femur
There was no statistical difference in BMD of the proximal femur before the intervention between the two groups (P>0.05). After 6-month intervention, BMD of the proximal femur increased significantly in both groups (bothP<0.01), without a statistical betweengroup difference (P>0.05), (Table 2).
3.2.2 Comparison of VAS and ADL scores
There were no significant differences in VAS and ADL scores between the two groups before the intervention(bothP>0.05). After 6-month intervention, VAS and ADL scores improved significantly in both groups (allP<0.01),and the improvements in the Yi Jin Jing group were more significant compared to those in the medication group (bothP<0.01), (Table 3).
Table 2. Comparison of BMD of the proximal femurg/cm2)

Table 2. Comparison of BMD of the proximal femurg/cm2)
Note: Ⅰntra-group comparison, 1) P<0.01
?
Table 3. Comparison of VAS and ADL scores
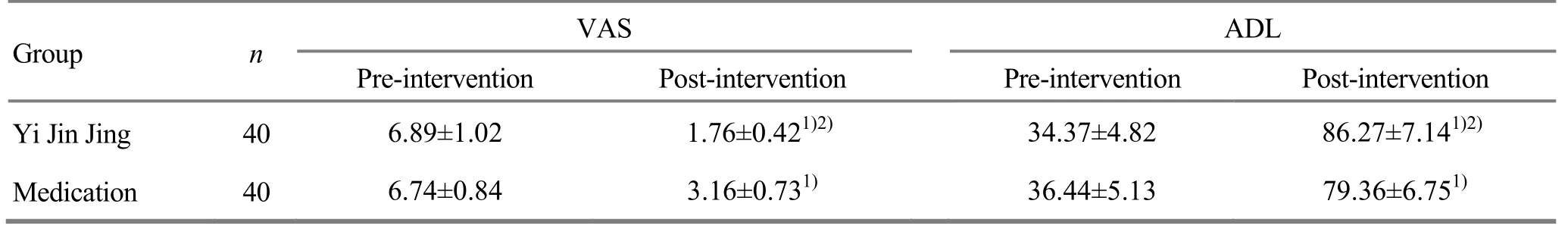
Table 3. Comparison of VAS and ADL scores
Note: Ⅰntra-group comparison, 1) P<0.01; compared with the medication group after the intervention, 2) P<0.01
?
4 Discussion
Senile primary osteoporosis, or degenerative osteoporosis, is a specific sign of aging in skeleton. The patients usually have lower quality of life in multiple dimensions compared to normal people, and the major causing factors are pain, fracture, decreased ADL and the subsequent negative emotions and fear. Thus, it has become the main targets to increase BMD, release pain,increase muscle force, improve balance, reduce the risk for fracture, enhance ADL, and eliminate negative feelings in the treatment of osteoporosis[3].
Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) is one of the Chinese Daoyin exercises. ‘Yi’ means change;‘Jin’ refers to muscles and sinews; ‘Jing’ means method.Generally, Yi Jin Jing refers to a method to change muscles and sinews. Taking body regulation, breath regulation and mind regulation as the principle, the practice of Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) emphasizes the integration of motion and stillness and combination of firmness and flexibility,with qi and attention guided by movements, external flexibility for stretching the body and internal firmness for protecting the heart and regulating the breath. The final aim is to release the spastic, fortify the weak,elongate the shrunken, and firm the rotten sinews[4-7].Galileo was the first one who noticed the relation between mechanical stress and bone mass in 1683. In 1892, Julius Wolf discovered the influence of mechanical stress on bone strength. Weinans H,et al[8]found that the mechanical load produced by muscle can trigger the osteoblasts to increase bone mass. Modern research has indicated that the reduction of skeleton muscle is a crucial inducing factor of osteoporosis.Practice of Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) can increase the flexibility and strength of skeleton muscle, fortify the function of skeleton muscle,improve the agility and balance of body, reduce falling accidents and the incidence of osteoporosis-induced fractures[9-13]. Meanwhile, through breath and mind regulations, Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) can ease the tension, and improve the anxiety and depressions states, hence effectively helping the mental health[14-17].
The current study showed that Yi Jin Jing (Sinewtransforming Qigong Exercises) effectively improved BMD of the proximal femur, as well as VAS and ADL scores, producing a more significant general efficacy compared to oral administration of alendronate sodium tablet. Therefore, Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) is suggested to improve BMD and living condition of senile osteoporosis patients. Moreover,since it’s easy-to-operate and produces no adverse reactions[18-20], this training is worth promoting in communities.
Conflict of Interest
There was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
This work was supported by Appropriate Technology Cultivation Projects for Science and Technology Plan of Chinese Medical in Zhejiang Province (浙江省中醫(yī)藥科技計劃適宜技術(shù)培育項目, No. 2014ZP013, No.2016ZB123).
Statement of Informed Consent
Ⅰnformed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
[1] Osteoporosis Commission of Gerontological Society of China. Expert consensus on diagnosis criteria of Chinese osteoporosis (3rd draft, 2014). Zhongguo Guzhishusong Zazhi, 2014, 20(9): 2007-1010.
[2] Management Center of Health Qigong, General Administration of Sport of China. Health Qigong: Yi Jin Jing. Beijing: People’s Sports Press, 2003.
[3] Shen ZF, Zhu GF, Shen QH, Wu YJ, Xu J. Effect of Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) plus tuina on scapulohumeral periarthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017,15(4): 285-289.
[4] Ding C, Sun Q. Research progress of relevant problems for senile osteoporosis. Zhongguo Guzhishusong Zazhi, 2016,22(3): 372-375.
[5] Xiao B, Yuan SX. Ⅰnvestigation on sinew changing technique. Shanghai Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2002, 36(7): 40-41.
[6] Yang Q. Popularization and application of Daoyin Qigong Yi Jin Jing in clinical practice. Anmo Yu Kangfu Yixue,2013, 4(7): 198-199.
[7] Zhang ZB. Textual research on the illustrations in ancient versions of Yi Jin Jing. Zhonghua Yishi Zazhi, 2015, 45(5):299-305.
[8] Weinans H, Huiskes R, Grootenboer HJ. Trends of mechanical consequences and modeling of a fibrous membrane around femoral hip prostheses. J Biomech, 1990,23(10): 991-1000.
[9] Zheng Y. Good effect of Yi Jin Jing on human body. Hebei Lianhe Daxue Xuebao (Yixue Ban), 2012, 14(2): 175-176.
[10] Gong L, Yan JT, Liu YC, Fang L, Zhang H, Xu J, Cheng JF.Effects of sinews-strengthening training on isokinetic muscle strength in old patients with sarcopenia. Shanghai Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2011, 25(3): 55-58.
[11] Wang B, Ma SR, Hu Y. Effect of health Qigong Yi Jin Jing exercise for sarcopenia patients’ rehabilitation efficacy.Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi, 2016, 36(2): 898-899.
[12] Hu WM, Gong L, Qian YM, Hu H. Effect of different tuina Yi Jin Jingpractice on the knee muscle strength of the elderly. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zazhi, 2013, 32(9):775-779.
[13] Liu YC, Wang ZY, Fang L, Yan JT, Fang M, Zhu QG,Zhang H, Shang Y, Zhang HB.Effect of Yi Jin Jing on dynamic balance of patients with senile sarcopenia. Hebei Zhongyiyao Xuebao, 2014, 29(4): 9-11.
[14] Jin DP, Xu J, Zhao JZ, Hu Y, Wang DY. Effect of Yi Jin Jingon daily living function and physical function of sarcopenia patients. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi,2011, 18(1): 14-16.
[15] Gu YH, Zhang SN, Guo AS. Health Qigong exercise to enhance the role of mental health research and analysis.Zhong Wai Yiliao, 2008, 28(30): 6-7.
[16] Zhang WC, Zhong ZB, Wu QH, Chen XF, Wang SY,Zhang Y. A research on health Qigong-Yi Jin Jing for slowing down intelligence decline of the aged. Zhongguo Xingwei Yixue Kexue, 2006, 15(9): 827-828.
[17] Zhang CH, Song AQ, Qiu YJ, Pang XD, Li AM. Effect of simple Yi Jin Jing (twelve poses) on elders’ self-rating anxiety scale. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zazhi, 2005, 24(3):340-342.
[18] Zhu GF, Shen ZF, Shen QH, Jin YQ, Lou ZY. Effect of Yi Jin Jing (Sinew-transforming Qigong Exercises) on skeletal muscle strength in the elderly. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017,15(6): 434-439.
[19] Li JH, Gong L, Hu WM, Fang M. Clinical study on tuina plus Yi Jin Jing exercise in treating knee osteoarthritis.Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi, 2010, 37(9): 1793-1795.
[20] Fan YZ, Wu YC, Wang JX, Zhang JF. Effect of tuina exercise on quadriceps femoris muscle strength of patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2012, 10(5):321-328.
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年2期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年2期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effect of acupuncture on hippocampal mitochondrial proteome expression in SAMP8 mouse model with Alzheimer disease
- Effect of acupuncture in intervening heroin-induced brain damage via regulating ubiquitin-proteasome pathway
- Effect of An-pressing manipulation on the serum levels of T-AOC and CK-MM in volunteers with delayed onset muscle soreness in biceps brachii
- Effect of acupuncture plus Tai Ji Quan on the recovery of neurological function and depression state in post-stroke depression patients
- Observation on clinical effect of tuina plus Western medication for functional dyspepsia due to liver qi stagnation and spleen deficiency
- Clinical observation on cervical chiropractic for cervical spondylosis of vertebral artery type
