Nutraceutical support for respiratory diseases
Yu-Ya Hwang,Yuan-Soon Ho
Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences,College of Medicine,Taipei Medical University,Taipei 10031,Taiwan,China
ABSTRACT Respiratory diseases have been a major health concern for human beings since several decades.Soothing the irritated nasal passages and airways had been a mutual necessity in multiple ancient cultures.In ancient China,herbs were largely used to help deal with cough and reduce mucus,thereby maintaining respiratory health.In India,knowledge of herb-related remedies passed down through generations.In the human society,freshly prepared herb ointments,including air-dried herbs,and boiled herbal soups have had a long history of combining botanical nutrients with local cuisine.
Keywords:Respiratory disease NPFP NPFA Nutrition Antioxidants
1.Introduction
The lung is a very special organ.It requires gentle diffusion capacities to accomplish pulmonary respiration.The levels of reactive oxygen species(ROS)in lung diseases are crucial to the quality of life of a patient (Fig.1).Indicators that help in evaluating the nutritional demands of respiratory diseases vary.Forced expiratory volume (FEV) and forced vital capacity (FVC) are the core indicators for lung function in patients [2].However,in animal models,levels of glutathione,glutathione peroxidase,and catalase and the contents of malondialdehyde and hydroxyproline in the lung are important physiological indicators.
Without correct dietary patterns,progression of fibrosis,mucus deposition,and inflammatory responses can both worsen the indicators and cause irreversible damages to the patient’s wellbeing.Since patients with respiratory diseases generally have a relatively low level of antioxidant defense ability,the redox balances are negatively influenced by the reduction in the antioxidant defense ability.Therefore,the best method to improve the patient’s health quality is to increase the intake of oxygen,enhance the contractile ability of the lung,or soothe the inflammatory responses.Therefore,clinicians have been focusing more on examining the serum levels of these indicators in patients with respiratory diseases.ROS levels,oxidative stress,alleviation of airway inflammatory responses,potent chemoattractant-based pathway blockages,and nanoparticle-induced lung injuries have also been receiving increasing research attention[3].
However,current correlational studies have neglected the fact that patient serum samples are not necessarily the definite answer to all respiratory disease pathologies.Correlation is not equivalent to association;correlation does not imply causation.In other words,reducing the concentrations of potassium and sodium in the blood or increasing the levels of antioxidant vitamins in blood circulation may not always be beneficial to patients.Although NPFAs do not have a positive impact on patient’s serum tests,NPFAs are adjuvant to the management of a patient’s disease as they may help interfere with deposition of collagen,α-smooth muscle actin,and extracellular matrix(ECM),which are also important elements in a patient’s diet.Therefore,in respiratory health,it is very important to review NPFPs and functional NPFAs simultaneously.
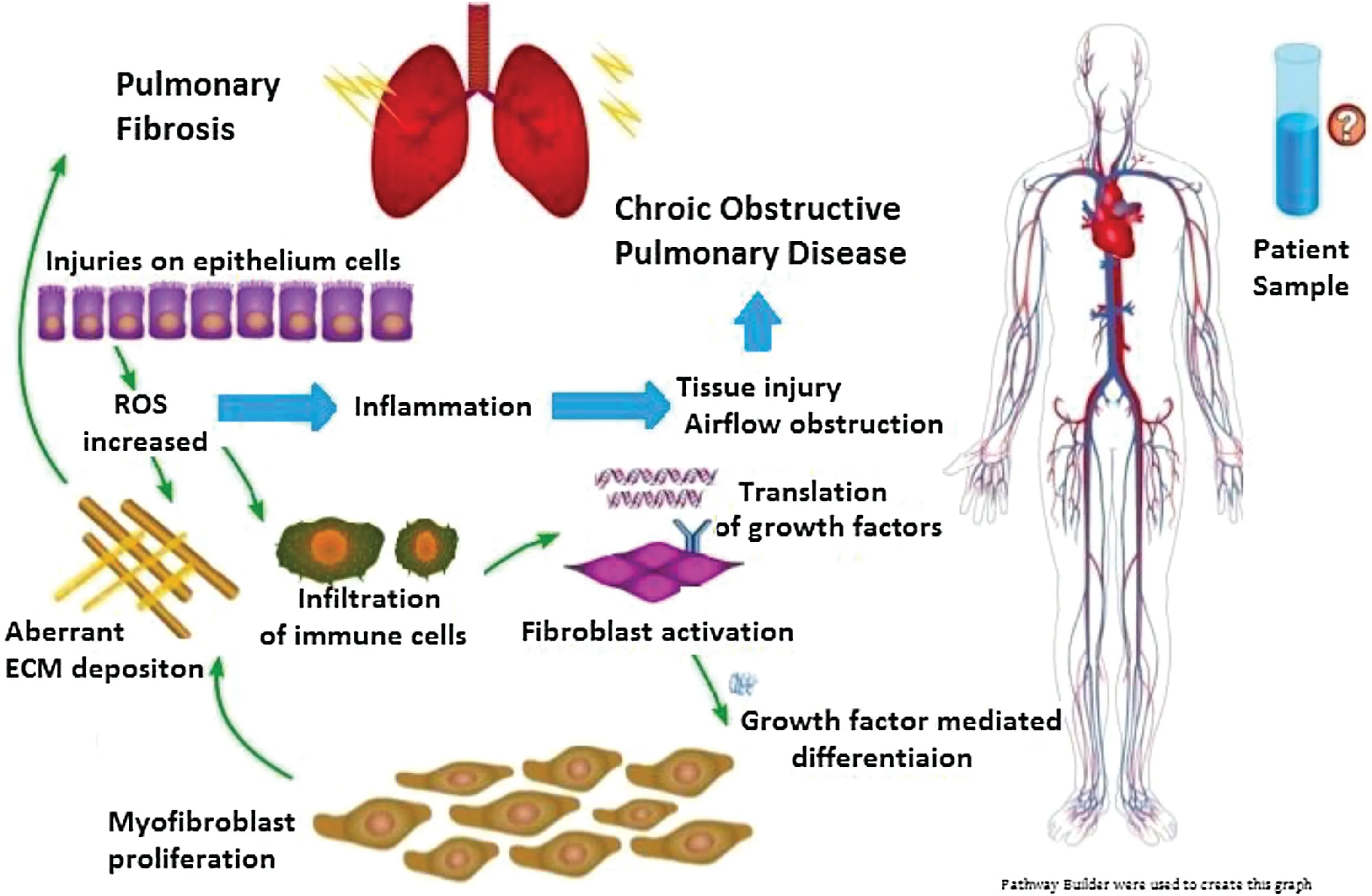
Fig.1.Respiratory diseases are often related to inflammatory responses.
2.Natural products from animals(NPFAs)
2.1.Fish oil
Fish oil is a good food source of omega-3 fatty acids,docosahexaenoic acid (DHA),and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).Omega-3 is a widely used anti-inflammatory nutrient[4]in patients with agerelated respiratory diseases.DHA and EPA are the primary elements that are considered as of value in fish oil by researchers.Multiple studies have indicated the role of high-energy food in inflammation and chronic diseases such as COPD and pulmonary fibrosis [5–7].DHA may contribute to the prevention of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis [8].EPA- and DHA-specific diets are good dietary options for the management of different types of lung disease progressions[9].
2.2.Heparin
According to the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines,heparin-based therapy is a safe and effective treatment strategy.Heparin is known for its capacity of altering the clotting responses in the human circulatory system[10].Heparin has received attention due to its surprising role in anticoagulant function and its potential in inhibiting procollagen fiber cross-linking.Therefore,it is considered to be a potential therapeutic option for fibrotic diseases[11].
Heparin has been approved by both FDA and WHO and has been commercialized as a drug and nutritional supplement; furthermore,it has been widely used to treat asthma and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.It has been reported that heparin could help patients with IPF to reduce discomfort or alleviate irritated responses [12].The mechanism underlying the action of heparin involves preventing the cross-linking of procollagen fibers by inhibiting lysyl oxidase.In the absence of the cross-linking of procollagen fibers,over-scarring and fibrotic progression could not continue.
3.Natural products from plants(NPFPs)
Oxygen interacts with lipids,protein,and nucleic acids both rapidly and conveniently.The ROS system requires sufficient oxidation-reducing factors such as metal nutrition and vitamin intake [13–15].Under certain amounts of the precursors of TGFβ,the number of macrophages will increase drastically.NPFPs have been reported to prevent chronic inflammatory responses,thereby easily activating the innate immune responses[16].
3.1.Green tea
Consumption of green tea has been proven to be beneficial to patients with type 2 diabetes and lung cancer;in addition,green tea possesses strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) has been considered to be the most important nutritional element of green tea playing a role in pulmonary fibrosis [17].EGCG has significant potential in inhibiting chemoattractants and regulating inflammatory responses in multiple fibrotic diseases.In addition,in vivo studies have confirmed that EGCG is beneficial in ameliorating the lung injuries of rats exposed to cigarette smoke [18].Therefore,EGCG has a high potential in improving the well-being of patients with respiratory diseases.
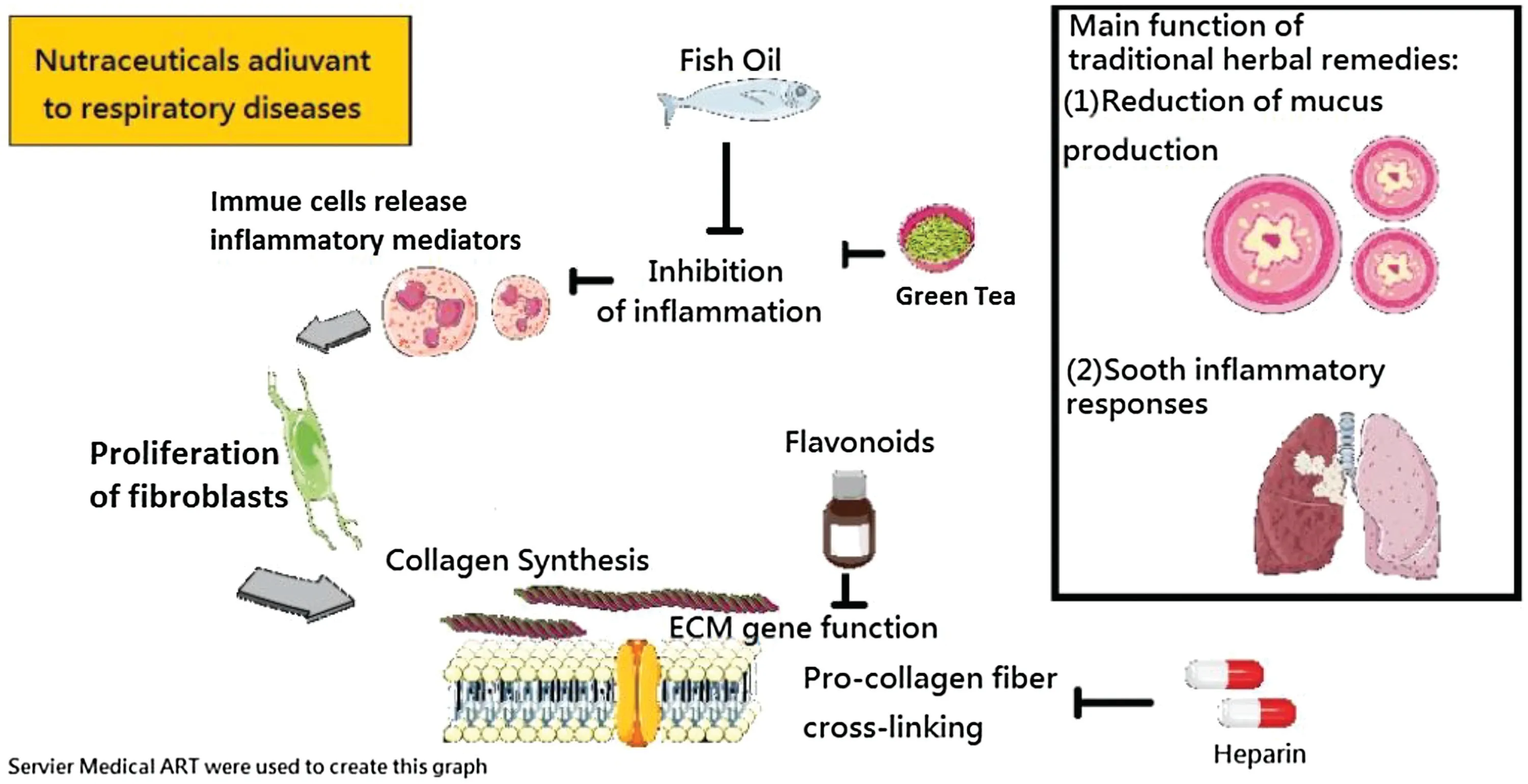
Fig.2.Both NPFP and NPFA are beneficial in respiratory diseases.
The human liver can help in metabolizing EGCG into theaflavins.Thealfavin is a natural phenol extracted from black tea; it is formed through the fermentation of green tea.Several NPFPs exert their anti-inflammatory effects by interfering with inflammationrelated pathways and activator protein 1(AP1) and the nuclear factor(NF)-kB pathway[19].By consuming green tea,patients can simultaneously receive the nutritional benefits of both EGCG and theaflavins.
3.2.Flavonoids
Flavonoids are known for their capability of reducing the expression of ECM genes.In general,flavonoids work as managers in the human body [14,20].It has been reported that quercetin is a key modulating flavonoid[21,22].Quercetin can disturb the redox balance in pulmonary fibrosis.The key element of this modulation is Nrf2.Quercetin can help increase the Nrf2 activity,thus elevating the antioxidant response accordingly[23].Therefore,increasing the intake of vegetables and fruits not only increases the intake of flavonoids[24]but also decreases the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-8 and TNF-α.
4.Conclusion
Blood has always been an important indicator in our medical system;it has helped scientists to identify hundreds of thousands of diseases.From circulating cell-free DNA to hematological flow cytometry,modern medical examinations have a high regard for the representative capacities of human serum samples and nasal swab tests.However,our understanding of serum samples is not always beneficial to our awareness of health conditions as we may neglect several aspects of nutritional needs and focus solely on serum compositions,especially when the human lung is recently being re-examined carefully by the public owing to its newly discovered function,i.e.,the production of blood.Therefore,rather than reviewing the traditional herbs and botanical compounds,this review has described the potentials of NPFAs and NPFPs simultaneously.From in vivo experiments to current FDA-approved nutritional supports,NPFAs are crucial to a patient’s dietary pattern.
Nutrients are flexible supplements,not fixed therapeutic packages,and they can be combined with different dietary patterns,cooking styles,and cultural backgrounds.Therefore,although all the NPFAs and NPFPs are beneficial to respiratory health,combining them wisely may be the best fit for patient care.By interfering actively with dietary patterns,they might gradually improve the patient’s health conditions and survival [25].However,regarding NPFAs such as heparin,they might actually inhibit the progression of diseases and prolong the patient’s prognosis without the need for artificial drugs or interventions(Fig.2).
Respiratory diseases are highly related to inflammation [7].Therefore,ameliorating the dysregulated inflammatory responses in the lung can directly soothe the patient’s condition [26].By decreasing the ROS levels actively,focusing on antioxidant levels[13],and blocking the inflammatory response-related signaling pathways,dietary pattern management can help in preventing the disease progression[27].
DHA,EPA,and heparin are all popular NPFAs that are beneficial in the management of disease progression.For instance,fish oil deals with the inflammatory signaling pathways,while heparin disrupts the fibrotic progression by procollagen cross-linking.
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Health and Welfare surcharge of tobacco products grant (MOHW107-TDU-B-212-114014),by TMU Research Center of Cancer Translational Medicine from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education(MOE)in Taiwan,by the Ministry of Science and Technology,Taiwan (MOST105-2320-B-038-053-MY3 awarded to Dr.Ho,MOST106-2314-B-038-053-MY3).
 食品科學(xué)與人類(lèi)健康(英文)2018年3期
食品科學(xué)與人類(lèi)健康(英文)2018年3期
- 食品科學(xué)與人類(lèi)健康(英文)的其它文章
- Behavioral assessment of hippocampal function following dietary intervention
- Study of interaction between metal ions and quercetin
- Prophylactic effect of Kudingcha polyphenols on oxazolone induced colitis through its antioxidant capacities
- Role of calpain system in meat tenderness:A review
- Corn phytochemicals and their health benefits
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
