The Changes in Representatives of Specific Social Sectors of the CPPCC—A Perspective from the Political Absorptive Capacity of the CPC
Li Houqiang, Guo Dan, Chen Lanxin
Abstract: The establishment of the representatives of special social sectors of the CPPCC has to a greater degree guaranteed broad and in-depth participation for the people from all walks of life in the national political activities,providing an institutionalized platform for various social strata and social groups to systematically give their advice and suggestions. The establishment, adjustment, and changes in the sectors are of vital political significance not only in ensuring to the greatest extent that people from all walks of life widely participate in national political activities, and providing an institutionalized platform for people of all social strata and communities to systematically express their opinions and offer their advice,but also in manifesting the democratic absorption mechanism for the CPC to conduct democratic consultation and governance on the platform of democratic consultation. The more industries involved in the sectors, the more representative the sectors are, and the more reasonable the proportions of the sectors, the more likely it is to guarantee the level and quality of the democratic consultation and to solve more practical problems. This is why the establishment and changes of the CPPCC sectors are an important manifestation of the CPC’s political absorptive capacity. The CPPCC is an effective organizing form for the CPC to integrate society and an important platform for the governing party and society to maintain a social pattern of diversified interests and political stability, while the CPPCC sectors are the basic units for the governing party to promote the idea of participatory democracy.
Keywords: the CPPCC sectors; the CPC; political absorption
It has been sixty-eight years since the First Plenary Session of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC) in 1949.Charter of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (2004 Revision) gives a clear definition of the nature of the CPPCC. “The Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference is an organization of the united front of the Chinese people, an important institution of multi-party cooperation and political consultation under the leadership of the Communist Party of China, a major form for carrying forward socialist democracy in the political life of the country” (Editorial group of the book,2004, p. 8). The reason for this definition is that the CPPCC shoulders the great mission to integrate all the social forces to construct the socialist society in the primary stage of socialism.
It is a self-evident statement that democracy means participation. The citizens’ participation in political activities is not only a political system,but also a life style. Thus, how to bring the CPPCC into full play as an important platform for political participation has become a problem for which the governing party should attach great importance.The sectors of the CPPCC are mainly on the basis of social strata. Along with the deepening of reform,the social division of labor is becoming more and more specified, and there are various types of professions. People from all walks of life have shown their desires to have their opinions and wishes heard and to fulfill their obligation and deal with their interest demands. So, by involving all walks of life and all communities in the political consultation through developing different sectors, the CPPCC has organically brought the interest demands and political needs of different social classes into line with the existing political system and built a society of orderly interest expressions, and coordinated communications and political participation for the citizens, reflecting the wide scope of Chinese democracy. Sectors are the organizational basis for the CPPCC’s formation, existence and development,and are the basic units that make up the CPPCC,thus their establishment, adjustment, and changes are of vital political significance in ensuring, to the greatest extent, that people from all walks of life widely participate in national political life, providing an institutionalized platform for people of all social strata and communities to systematically express their opinions and offer their advice so that the democratic rights for the people can be secured,which is, at the same time, a manifestation of the democratic absorption mechanism for the CPC to conduct democratic consultation and governance on the platform of democratic consultation.Therefore, the more various and typical the types of professions contained in different sectors, and the more reasonable the proportions of sectors, the more likely it is to guarantee the level and quality of the democratic consultation and to solve more practical problems.
1. The development and changes of the CPPCC sectors since the founding of the People’s Republic of China
“Sector” has both a broad and a narrow sense.In its broad sense, it refers to all political parties,people’s organizations, public personages without party affiliation and other relevant elements who involved in the CPPCC. For instance, the CPPCC is composed of thirty-four sectors, in which the“sectors” are understood in the broad sense. In its narrow sense, “sector” refers to all the relevant elements except for political parties and people’s organizations involved in the CPPCC, such as the cultural art sector, the scientific art sector, the economic sector, the education sector, the ethnic minority sector and the religion sector. When talking about the distinction in sectors with respect to the CPPCC composition, the “sectors” here are usually understood in the broad sense (Editorial group of the book, 2004, pp. 76-77).
“Sector” is a distinctive term in the CPPCC, a specific form to divide the CPPCC’s participants into political parties, people’s organizations, ethnic groups, and people of all walks of life, and also an organizing form of the CPPCC. It reflects the organizational composition of the CPPCC, and at the same time the components of the patriotic united front (Xiong, 2010, pp. 57-60). Being made up of different sectors is not only a remarkable feature of the CPPCC, but also a basis and advantage for the CPPCC to exist and excise its power. Sector can be regarded as the foundation of the CPPCC,and a basis and bond for the CPPCC to develop political consultation, democratic supervision and participation in administration and discussion of state affairs; it is also a platform for the CPPCC committee members to give their full play to their subject roles, a bridge for the special committees to contact the members of CPPCC committees, and a basis for the CPPCC to play its integral role.
The establishment of sectors to some degree reflects the changes in the status and functions of the CPPCC. With political and economic development of society, the universality of the CPPCC system has been repeatedly confronted with challenges,and the development, differentiation, and pluralism of society have resulted in conflicts between different communities in their notions, interests,and propositions. Different social strata will come into being in different stages of social development and will devote themselves to participation in the political life. Therefore, correspondingly, the sectors of the CPPCC will also undergo constant changes in order to adapt to and meet the demands of people from the new strata.
1.1 Changes in the size of the CPPCC sectors
In August of 1949, Zhou Enlai (1999) pointed out in a speech at the fourth meeting of the Standing Committee of the Preparatory Committee for the Political Consultative Conference, “The CPPCC is an organization of the united front, and the collective of the participating units.” (p. 30) The First CPPCC Plenary Session played an important role in exercising the functions and power of the National People’s Congress (NPC), which had not yet been established, representing the will of the whole nation, and declaring the founding of the People’s Republic of China. The National Committee of the first CPPCC was composed of 46 participating units,representatives from all walks of life, including 14 political units, 16 organizational units, 9 regional units, 6 military units, and specially invited personalities. For example, Chairman Mao Zedong’s signature on the attendance book of this conference read “The deputy to the CPC’s Delegate.” There is no concept of sector in the first CPPCC, but the returning mode of the deputies had already taken the attribute of sector that later came into being.
After the convention of the first NPC in 1954, the CPPCC no longer exercised the function and power of the NPC, and the Central Committee of the CPC in 1953 stipulated clearly that the CPPCC will still exist as an independent united front organization. In 1954, the national committee of the second CPPCC was composed of 28 units and specially invited personalities, including the CPC, the Revolutionary Committee of the Chinese Kuomintang, the China Democratic League, the China Democratic National Construction Association, public personages without party affiliation, the China Association for Promoting Democracy, the Chinese Peasants and Workers Democratic Party, the China Zhi Gong Party, the Jiusan Society, the Taiwan Democratic Self-Government League, the Communist Youth League of China, the Trade Union Federation, the peasants, the All-China Women’s Federation, the All-China Youth Federation, Cooperatives, the All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce, the China Federation of Literary and Art Circles, natural science groups, social science groups, the education sector, the press and publishing sector, the medicine and hygiene sector, the groups for friendship with foreign countries, social welfare groups, ethnic minority groups, returned overseas Chinese, and the religion sector. Regional representatives and military representatives were no longer represented at the CPPCC as a “unit”, but were brought into the NPC system. Since its second conference, the CPPCC national committee has gained its distinctive term“sector”, such as the education sector, the press and publishing sector, and the medicine and hygiene sector, but “sector” here mainly refers to the category of profession. It should be noted that “Cooperatives”was added to the range of sectors in this conference,obviously reflecting the traces of the collective economy in the initial construction stage after the founding of the People’s Republic of China. In the subsequent conferences, the CPPCC committees have undergone some changes. Some sectors were canceled, and some more were added to the original structure.
The fifth CPPCC (1978-1983) canceled the sector of “Cooperatives” and set up the “Sector of Sports”. The sixth CPPCC (1983-1988) set up two new sectors, the “All-China Federation of Taiwan Compatriots” and the “Compatriots of Hong Kong and Macao”, reflecting that the affairs of Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan had been put on the state agenda and the number of sectors of the national committee of the CPPCC amounted to 31. To highlight the significance of science and technology and the social status of the sci-tech talents, the eighth CPPCC (1993-1988) set up the sector of “China Association for Science and Technology”, to adapt to the development of the market economy, it set up “the Sector of Economics”, it also divided “compatriots of HK and Macao” into “compatriots of HK” and“compatriots of Macao”. From the 8th to the 12th CPPCC, the number of sectors was maintained at 34.
With the development of the CPPCC, the concept of “sector” has become more and more distinct. In his closing speech at the fourth session of the ninth CPPCC, Li Ruihuan pointed out, “The CPPCC is composed of sectors, and the committee members of the CPPCC are composed of deputies to those sectors... in some sense, the knowledge of the opinions from all the sectors means an overall knowledge of the majority of the people, and a probe of the conditions of the sectors means a general understanding of the whole society” (The Party Literature Research Center of the CPC Central Committee, 2001, p. 1731). In 2004, “Resolution on Amending the Charter of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference” adopted at the Second Session of the Tenth National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference. There appeared words like “develop a number of sectors”, “representative in its sector”,and “the developing of sectors,” which was the first use of “sector” in a formal charter to refer to all participating units of the CPPCC.
1.2 Changes in the names of the CPPCC sectors
In terms of the names of the CPPCC sectors, due to the changes in the constituent of the sectors, the names of the sectors have correspondingly undergone some changes. In the national committee of the third CPPCC (1959-1964), “The New Democratic Youth League of China” was changed to “Communist Youth League of China”; the connotation of “China Confederation of Literary and Art Circles” in the fourth CPPCC was extended to “the literary and art sector” in the fifth CPPCC and then to “the cultural art sector” in the sixth CPPCC; the fifth CPPCC(1978-1983) changed “China Association for Science and Technology” into “the sci-tech sector”, and“the social science groups” into “the social science sector”, breaking off the confinement of the “groups”and reflecting that these sectors involve not only the group representatives, but also other representative personages in those sectors. In agriculture, the sector of “the peasants” in the sixth CPPCC (1983-1988)was changed into the sector of “agriculture and forestry”, and then into “the agriculture sector” in the ninth CPPCC in 1998, the coverage of which was enlarged to the representatives of the first industry including agriculture, forestry, husbandry, and fishery. Considering the changes in the status and nature of Hong Kong and Macao, the ninth CPPCC in 1998 changed “compatriots of Hong Kong” into“specially invited personalities from Hong Kong”,and “compatriots of Macao” into “specially invited personalities from Macao”. In 2003, “the social welfare sector” was changed into “the sector of social welfare and social security” in the tenth CPPCC. The changes in the CPPCC sectors have reflected the demands of the social development in different stages in a larger scale and the universality of the CPPCC in different stages.
1.3 Changes in the constituents of the CPPCC sectors
The present constituents of the CPPCC sectors are divided into four types: the party sector, the people’s organization sector, the profession sector,and the special sector. However, the structure of the CPPCC has undergone many changes during the CPPCC development. For example, due to the special historic status of the CPPCC in the initial socialist stage after the founding of the People’s Republic of China (PRC), the internal components of the CPPCC were divided into five types including the parties, the regions, the army, the organizations and the specially invited personalities. Stating with the second CPPCC, the types of internal structures have gradually stabilized and finally became fixed. But the proportion of the CPPCC committee members of the fixed four types has always been in fluctuation during the CPPCC development, reflecting the increasingly strengthened political absorptive and inclusive ability of the CPPCC. In general, the proportions of the party sector and the people’s organization sector are comparatively stable, but the numbers of their representatives are decreased,while the number and proportion of representatives from the profession sector have undergone greater changes, especially after the reform and opening-up,and have dramatically increased; at the same time,the number of the specially invited personalities has constantly decreased.
1.3.1 Changes in the party sector and the people’s organization sector
Among the types of CPPCC sectors, the party sector is the most highly organizational and systematic, and takes the most important position in the development of the CPPCC. Specifically, the party sector includes the CPC, various democratic parties and the public personages without party affiliation. The political consultation with the democratic parties is one of the important contents of the national political consultation. The public personages without party affiliation were produced during the specific historic conditions of the Chinese revolution, referring initially to personages without party affiliation in form but with party affiliation in nature, and later usually referring to the public personages with some social influence and academic achievements working hard for national independence, democracy and prosperity (Editorial group of the book, 2004, p. 81). In a regulation on the work of the united front released by the central committee of the CPC in 2015, it is clearly stipulated that the public personages without party affiliation refers to the people of some positive social contribution and influence, have both the desire for and the ability of political participation, the majority of whom being intellectuals.
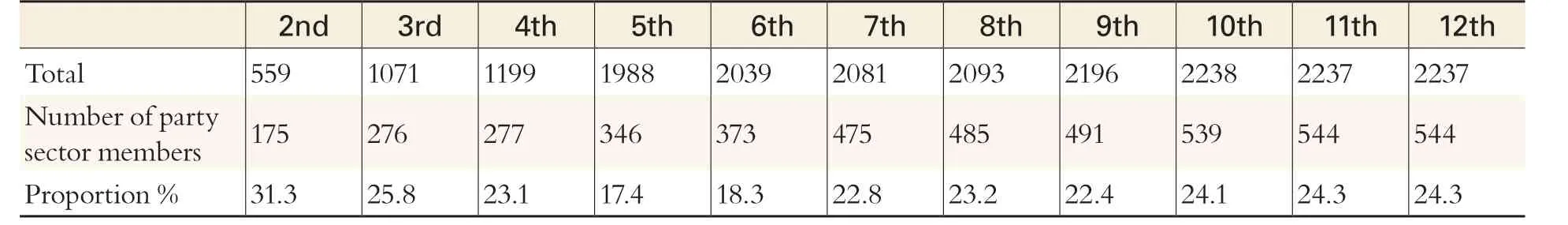
Table 1 The Proportion of the Party Sector Members in the CPPCC
In the initial stage of the newly founded PRC,there were eleven democratic parties participating in the first CPPCC. And in the second CPPCC,the two democratic parties, the “Chinese People’s Salvation Association” and “The Association of the Three People’s Principles”, were excluded from the participating democratic parties, and “Democratic Construction Association” was renamed as “China Democratic National Construction Association”and “The Democratic Promotion Association of the Chinese Kuomintang” as the “China Association for Promoting Democracy”, reflecting the political changes in the democratic parties after the establishment of the NPC system. In the fifth CPPCC, “the democratic personages without party affiliation” was changed into “the patriotic personages without party affiliation”, but in the subsequent sixth CPPCC, the former was restored and is still used today.
In terms of the specific proportion of representatives, the numbers of the party sector members participating in the second, third, fourth and fifth CPPCC respectively accounted for 31.3%,25.8%, 23.1% and 17.4%of the total committee members, with a constant decrease. Due to the expansion of the anti-rightest struggle in the 1950s and the political influence of the subsequent“Cultural Revolution”, the committee members of democratic parties suffered greatly and therefore,in the fifth CPPCC held in 1978, the committee members from the party sectors only accounted for 17.4% of the total, the historically lowest. Since the sixth CPPCC in 1983, thanks to the end of the tenyear “Cultural Revolution”, as well as the recovered development of various causes of China after the reform and opening-up, the CPPCC gradually regained steady development and the proportion of the party sector began to pick up, increasing to a permanent proportion of 22%-24% from the seventh CPPCC to the twelfth CPPCC, except for the 18.3%in the sixth CPPCC.
At present, the people’s organization sector is divided into eight specific sectors. They are the Communist Youth League of China, the All-China Federation of Trade Unions, the All-China Women’s Federation, the All-China Youth Federation, the All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce,the China Association for Science and Technology,the All-China Federation of Taiwan Compatriots,and the All-China Federation of Returned Overseas Chinese. During its development, many changes have occurred to the specific sectors of the people’s organizations. For instance, the Communist Youth League of China was called “The New Democratic Youth League of China” in the first and second CPPCC; the Taiwan Solidarity Union was given a seat in the sixth CPPCC, and the China Association for Science and Technology was given a seat in the eighth CPPCC. The All-China Federation of Trade Unions, the All-China Women’s Federation, the All-China Youth Federation, and the All-China Federation of Returned Overseas Chinese have been the common sectors since the second CPPCC,although their names have undergone slight changes.In 1953, the All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce was founded as the people’s organization and non-governmental chamber of commerce of the united front under the leadership of the CPC,with the privately-owned industrial and commercial enterprises as the main body and other industrialists and businessmen involved. Similar to the party sector, the people’s organization sector is of higher stability, but the proportion of their representatives has dropped in the total number of the committee members (Gao & Zhang, 2009, p. 62).
1.3.2 Changes in the profession sector
The standard for the divisions in the profession sector is the type of profession. Compared with the party sector and the people’s organization sector, the profession sector has gone through greater changes and reflected the changes in the Chinese social strata and professions. The present profession sector is divided into eleven specific sectors including the literary and art sector, the science and technology sector, the social science sector, the economic sector,the agriculture sector, the education sector, the physical education sector, the press and publishing sector, the medicine and hygiene sector, the sector for peace and friendship with foreign countries,and the sector of social welfare and social security.The socialist market economy has accelerated the differentiation of social interests, and the social development contains the process in which the traditional professions are constantly disappearing,and new professions are emerging, thus, many newly emerged professions are constantly added to the CPPCC sectors, and some old-fashioned traditional sectors have perished with the development of the times. For example, the fifth CPPCC set up “sector of sports”; the sixth CPPCC canceled the “peasants sector” and set up “the sector of agriculture and forestry” which later was changed to “the sector of agriculture”; the eighth CPPCC set up “the sector of economics”.
During the period under the system of planned economy, the types of various social strata and industries were limited, therefore the number of committee members from the profession sector accounted for about 30% of the total over a long term. After the reform and opening-up, the number raised dramatically and increased to above 50%.Among committee members from the profession sector present at the first plenary session of the sixth CPPCC, 102 members are from “the agriculture and forestry sector”, the number of members from the cultural art sector, the science and technology sector,and the social science sector respectively increased from 65, 90, and 25 to 134, 271, and 78; while the number of members from the education sector, the press and publishing sector, and the medicine and hygiene sector increased respectively from 25, 14,and 50 to 160, 35 and 109. From the seventh CPPCC to today, for all the internal changes in the profession sector, the total number of committee members from the profession sector has always been kept at about 50% of the CPPCC committee members,①Source of data: The CPPCC Encyclopedia (Volume One), PP 743-797.which fully demonstrates that after the reform and openingup, the Chinese social and economic structure has experienced significant reforms, and with the differentiation of the interest communities and the emergence of the new profession types, the people from various industries and communities develop their own desires and demands, thus, it is necessary to enlarge the number of the committee members to voice their interest demands through the CPPCC.
1.3.3 Changes in the special sectors
Take the 12th CPPCC for example, the special sectors refers to five specific sectors including the ethnic minority sector, the religion sector, the specially invited HK personalities, the specially invited Macao personalities and other specially invited personalities, among which, the ethnic minority sector, the religion sector and the specially invited personalities have been CPPCC sectors since the first CPPCC in spite of their different initial names, while the other two were initially the sector of compatriots from Hong Kong and Macao which was later split into compatriots of HK and compatriots of Macao in the eight CPPCC and formally given their present names in the ninth CPPCC. The most remarkable changes occurred to “the specially invited personalities”. This sector refers to the representative figures in various fields of society. The components of this sector are not fixed, and the coverage of the specially invited personalities varies according to the changes in the adjustment of the CPPCC structure and its tasks during different periods of development (Editorial group of the book, 2004, p. 81).
Different from other sectors, the sector of specially invited personalities has a more extensive coverage, and the members are of more independence and participate in the CPPCC as an individual, unlike those of democratic parties who can form a unit and organize as a team. Thus, the number and the proportion of the specially invited personalities in different periods have presented instability which has served as an index to the close correlation between the specially invited personalities and the feature of the times. The specially invited personalities of the first CPPCC were chosen out of political considerations, and as a special community beneficial to the revolution and construction of China, they offered significantly useful advice for the Chinese socialist construction and played an important role in history. In the first session of the fifth CPPCC, the members of specially invited personalities accounted for nearly half of the total number of committee members,the highest in CPPCC history. Later, its proportion gradually decreased and is now kept at about 10%.Although they participate in the CPPCC as a sector,the significance of the representatives of specially invited personalities has gradually weakened because of their plural identities and the variance in their concerns at the time of participation.
2. The historic reasons for changes in the CPPCC sectors since the founding of the PRC
2.1 The arrangement of the sectors in the first CPPCC and its historic reasons
In 1948, the slogan released by the centralcommittee of the CPC to memorize May Day called for “all democratic parties, all people’s organizations and social elites to hold a political consultative conference and people’s deputes conference and establish a democratic coalition government”(General Office of the National Committee of the CPPCC, 1999, p.623), lift the curtain for the solidarity and cooperation between the CPC and other democratic parties to consult about the construction of China. The first CPPCC, at the same time, exercising the functions and power of the NPC to ensure both the leadership of the proletariat and the cooperation with the democratic parties and people without party affiliation. Thus, the adoption of the democratic consultation serves as a better means to realize the construction of the PRC. In the first CPPCC, 44% of the 662 committee members were communists, 26% were representatives of workers, peasants and people without party affiliation, and 30% were from democratic parties,①Source: The CPPCC Encyclopedia (Volume One), pp. 719-724.not only guaranteeing the leadership of the proletariat, but also uniting extensively with the centrists and the massive progressive forces.Therefore, the first CPPCC endeavored to invite representatives from various fields including democratic parties, people’s organizations, social elites, and ethnic minority groups. Regardless of sex, nationality, age, education, and religious belief, all the personages who had ever made some contribution to the Chinese democratic revolution and the people’s emancipation could be absorbed as the committee members of the newly established CPPCC, and in the central people’s government to be formed, three of the six vice presidents were democratic personages. Yet, the new CPPCC had a strict and definite political criterion, that is, “none of the reactionary parties and reactionaries within the system of the reactionary Kuomintang government is allowed to participate in the CPPCC” (Yang, Shi& Yuan, 1984, p.263).
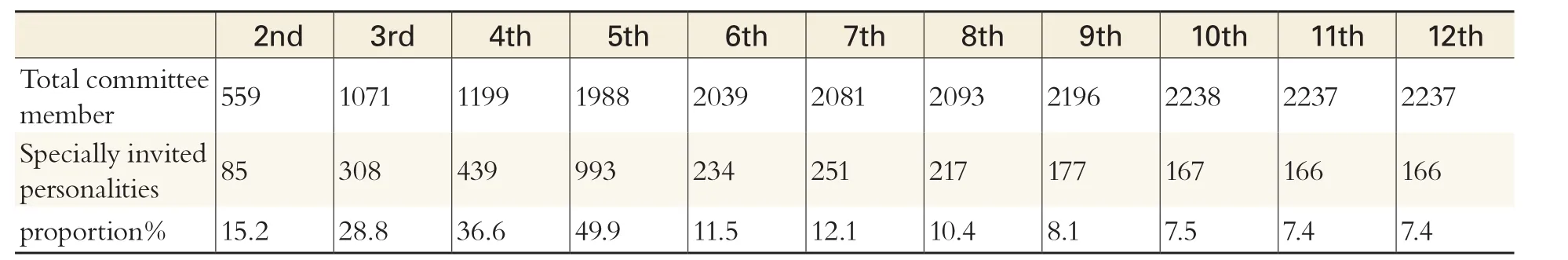
Table 2 The Proportion of the Specially Invited Personalities in the CPPCC
The most special constituent of the first CPPCC were the regional and military deputies,the former of which were the deputies to the liberated areas and the democratic personages from the liberated areas, while the latter were made up of the deputies to the field armies of the People’s Liberation Army. Both of these component units have historic reasons. First and foremost, the army was indispensable in further battles against the remaining forces of the Kuomintang and consolidating the power of the coalition government. And then, to further legalize the state power, the support from the democratic personages and the people of the liberated areas was a must. Since the second CPPCC in 1954, the regional deputies and the military deputies have been in line with the system of the NPC.
The first CPPCC was held in a special historic period and occupies a special historic status as a result. The development of the sectors was mainly to gain political legitimacy and unite all the forces that could be united to consolidate the newborn state power. To become the only governing party of the country, the CPC needed to absorb as many social elites as possible rather than focus only on the interests of the workers and peasants.Correspondingly, democratic parties and nonparty personages did not want to lose their political sayings. Thus, the establishment of a coalition government was the best choice for them to realize democracy and their political propositions through the CPPCC.
2.2 The development of the sectors from the second to the fourth CPPCC and its historic reasons
Since little disparity was found in the development of the sectors from the second to the fourth CPPCC, plus all of the three conferences were held in the period of the planned economy, it would be better to analyze them together. The Charter of the CPPCC issued in 1954 stipulates that the CPPCC should continue in existence as an organizing form of the people’s united democratic front to unite all the nationalities, democratic classes, democratic parties, people’s organizations, overseas Chinese,and other patriotic democratic personalities.Therefore, the CPPCC continued to exist as an organizing form of the people’s united democratic front until 1978.
In terms of the party sector, the CPC had a larger size than other democratic parties, for in the second,third, and fourth CPPCC, the committee members of the CPC respectively amounted to 40, 60, and 61,respectively accounting for 22.8%, 21.7%, and 22%of the total party sector. In comparison, democratic parties’ proportion was unevenly distributed,with the three major democratic parties―the Revolutionary Committee of the Chinese Kuomintang, the China Democratic League, and the China Democratic National Construction Association—having a larger proportion of about 15% and the minor parties like the Zhi Gong Party and the Taiwan Democratic Self-government League having a smaller proportion, below 4%.①Source: The CPPCC Encyclopedia (Volume One), PP 727-742.
The three great socialist reconstructions accomplished at the end of 1956 which realized the public ownership economy and formed “two classes and one stratum” (the workers class, the peasants class, and the stratum of the intellectuals).As a result, the structure of the state power had a tendency of centralization, inevitably suppressing the function of the CPPCC united front. Moreover,in the struggle against capitalism right-leaning in 1957, many internal contradictions among the people were handled as the contradictions between ourselves and the enemy. In January of 1958,Chairman Mao pointed out in his speech at the Supreme State Conference that the Rectification Movement should also be popularized in the democratic parties, and from then on, the CPPCC began its left-leaning political life and gradually“took class struggle as the key link” in various work. Later, consequently, the work of the CPPCC nearly came stagnation, and the fourth CPPCC adjourned after its first plenary session.Additionally, in terms of the profession sector,the three conferences had also seen few changes and were basically kept to the original structure.The committee members of the profession sector covered a variety of fields in society and were of higher professionalism, but in the above-mentioned three CPPCCs, the proportions of representatives had little variance, and even the proportion of some specific sectors continued to drop, dramatically weakening the non-governmental nature of the CPPCC. With the official voices drowning the nongovernmental voices, the CPPCC failed to reflect its superiority as an organization to communicate the issues of personages from the various fields of society.
2.3 The particularity of the arrangement of the fifth CPPCC sectors and its historic reasons
The first session of the fifth CPPCC was held in Beijing on February 24, 1978. As with the first CPPCC held in the time when China entered a new stage of reform and opening-up and socialist modernized construction, the CPPCC, under the correct guide-line, was gradually getting back on track after the Cultural Revolution. To involve more personages from various circles of society in the national restoration and construction, the fifth CPPCC saw a dramatic increase in the number of representatives, the total number of the national committee members having reached 1,988, an increase of 65.8% compared with the 1,199 of the fourth CPPCC.
It should be noted that the number of specially invited personalities in the national committee members of the fifth CPPCC amounted to 993,accounting for 49.95% of the total. Because of the disruption of the national political and social orders caused by the ten-year Cultural Revolution,the CPPCC was closed for over a decade. In the fifth CPPCC, Deng Xiaoping specially invited a large corps of veteran cadres, intellectuals, and patriotic personalities to participate in the political consultation, and categorized them into the sector of “specially invited personalities”. It was also due to the disruption of the original sector system into which the newly absorbed committee members could not be clearly categorized and thus had to be grouped as a new sector called specially invited personalities.
2.4 The sixth to the twelfth CPPCC on the track of development
From the sixth CPPCC, the development of the CPPCC began to get back on track, increasing gradually from the 2,038 committee members in the sixth CPPCC to 2,196 in the ninth CPPCC,over 100 above the number of the eighth CPPCC,and in the subsequent conferences from the tenth to the twelfth CPPCC, the number of committee members was basically fixed, amounted respectively to 2,238, 2,237, and 2,237. In terms of the structure of the sectors, the number of sectors from the eighth CPPCC to the twelfth CPPCC was basically fixed at 34, and the proportions of each sector were also comparatively stable; the number and proportion of the representatives from the profession sector were stabilized at about 50%,rising to the top among the four major sectors, a true reflection of the huge changes in the social strata of China since the 1990s.
The adjustment of the names of the sectors can reflect the changes in the features of some specific profession sectors, and the inclusiveness of the CPPCC to constantly absorb more newborn forces.For instance, the eighth CPPCC was the first to add the economic sector, the number of representatives from which increased to 83, and constantly increased to 151 in the twelfth CPPCC which was held in 2013. The number of representatives from other specific profession sectors were basically kept stable with a slight increase. With the establishment of the basic economic system in the primary stage of socialism with public ownership as the mainstay and the common development of multiple ownerships, more and more personages from the private ownership enterprises were absorbed into the CPPCC. According to the statistics, there were 20 private entrepreneurs participating in the eighth CPPCC in 1993, and over 40 in the ninth CPPCC in 1998 (Liu & Chen, 1998, May 2), and the number increased to 65 in the tenth CPPCC in 2003 (Wu,2004, p. 224).
Professor Lu Xueyi (2004) from the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences divides Chinese society into ten major social strata in accordance with the division of labor, hierarchy of authority, production relations, and institutional segmentation. They are state and social administrators, managers, private entrepreneurs, professional and technical personnel,clerical staff, individual industrial and commercial households, commercial service salesmen, industrial workers, agricultural laborers, and the jobless,unemployed and partially unemployed (p. 8). As a major form to promote socialist democracy in Chinese political life, the CPPCC is obliged to unite and mobilize all the social strata to actively participate in the national construction of modernization. Accordingly, the central committee of the CPC adjusted the relevant united front policy,thus the amended Constitution of the People’s Republic of China and the Charter of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (2004 Revision) added expression “builders of the socialist cause”. The CPPCC also moderately adjusted the structure of its sectors according to the ever-changing situation. The 2004 Charter of the CPPCC interprets the organization of the patriotic united front as “a most extensive patriotic united front of all socialist workers, builders of the socialist cause, patriots supporting socialism and patriots supporting the reunification of the fatherland under the leadership of the Communist Party of China and participated in by the democratic parties, public personages without party affiliation, people’s organizations,ethnic minorities and patriotic personalities from all walks of life, including compatriots of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, compatriots of the Macao Special Administrative Region, Taiwan compatriots and overseas Chinese” (Editorial group of the book, 2004, p. 7). The stipulation of the Constitution and the Charter of the CPPCC has developed the patriotic united front to the leagues of “The Four” (the workers, the builders, the two kinds of patriots), enlarging solidarity, enhancing inclusiveness, and promoting harmony among the communities of various social strata. This also serves as the real motive for the CPPCC to readjust its sectors.
3. Changes in the CPPCC sectors and the political absorptive capacity of the CPC
Political absorption usually refers to “the institutionalizing and integrating the new interest groups’ power demands and political participation in the process of the social changes into the political system” (Jing & Zhang, 2012, p. 114). Some scholars believe that the concept of “political absorption”mainly comes from the concept of “administrative absorption”. Professor Jin Yaoji (1997) put forward it to interpret Hong Kong’s governance before it returned to the fatherland, referring to “a process in which the government absorbs the political theories represented by social elites or elite groups into the political decision-making structure and thus accomplished some degree of ‘elite integration’thus bestowing legitimacy on the ruling power so that a slack but integrated political society can be established”. The main body of political absorption includes not only the state, but also the parties,especially the governing party. The concept of political absorption is further defined by Professor Lang Youxing (2009) on the basis of administrative absorption, that is, political absorption mainly refers to a political structure established by the governing party to have the political will voiced and to enable some social communities or social strata to express their political wills so as to guarantee their interests(pp.108-115).
The process of political absorption should begin with its establishment within an open political system. Only by opening up, encouraging various views and eliminating political exclusion can it be possible to effectively expand the channels for political participation, unite all forces that can be united, effectively and orderly absorb the majority of the members of the society into the national political life and form a community of powerful cohesiveness. The political absorption is also a process of exploring and restructuring legitimate resources. In terms of its nature, the governing party is also a social institution, and only by comprehensively winning social recognition and support can a party gain a broad social foundation to take the lead of the country, and only by effectively mobilizing and integrating society can a party earn the social support and establish its extensive and solid governing foundation (Lin, 2001, pp. 37-44). Among the political systems of China, the establishment of the CPPCC system can reflect to the greatest extent how the political systems absorb the social elite organizations. Moreover,from the perspective of politics, political absorption manifests the interaction between political systems and the social environment. Only by keeping a constant positive interactive relationship with the social environment can political systems respond effectively to society and gain the constant feedback necessary to strengthen self-vitality and pave a legitimate foundation for their survival and development.
3.1 The CPPCC is an effective organizing form for the CPC to integrate society
Modernized political systems focus on the governing party’s social effective absorptive and regulatory capacity, which mainly manifest in the governing party’s social integration capacity and political absorptive function. The CPPCC is an important institution of multiparty cooperation and political consultation under the leadership of the Communist Party of China, and a major form for carrying forward socialist democracy in the political life of the country. As the representative of the CPC, about the nature of the CPPCC after the establishment of the National People’s Congress,Chairman Mao (1999) once pointed out, “The CPPCC shall not be run as a state organ, for the NPC and the State Council are respectively a state power organ and a state administrative organ.So, if the CPPCC is run as a state organ, then it will be a binary structure, and this repetition and decentralization will lead to no democratic centralism. The CPPCC is not only a people’s organization, but also a party organ, an organ for the consultation of various parties” (p. 61).
The distinctive superiority of the CPPCC in integrating society is mainly embodied in its extensive representation and immense inclusiveness as an organization of the most extensive united front.Its implementation of the guideline of “massive solidarity, massive unification, and involvement of all the representatives,” unite all the political parties,important people’s organizations, public personages without party affiliation, ethnic minorities and representatives from all walks of life, Taiwan compatriots, compatriots of HK and Macao and the returned overseas Chinese. The National Committee of the CPPCC is composed of 34 sectors, and has absorbed a large corps of influential political,economic, social, and intellectual elites who are of both immense political and social influence and professionalism to put forward scientific advice and suggestions that are of great assistance to the governing party’s effective governance. In the course of the political absorption, the governing party usually gives some political assignment to social elites and bestows on their political identities and status in order to rely on their influential power to promote social cohesion, while at the same time,the social elites are very pleased to depend on the political systems to air their advice, suggestions and demands. That is also why “star Committee Members” in some industries gained particular attention in the annual national committee of the CPPCC.
Besides, the distinctive organizing form of the CPPCC system — sectors with its characteristics of having great flexibility and adaptability can provide a vast organizing space for absorbing new social groups into the systems. By combining with the political systems, the CPPCC absorbs and integrates new social strata and social forces emerging in the course of reforms and openingup so as to realize a highly organized plural social structure and stable political system (Hu, 2010,pp. 57-63). The 17th CPC National Congress put forward that the deputies to the newly emerging social strata and economic organizations should be appointed, for those new economic organizations are in possession of a huge amount of the private ownership economic resources as well as a large number of social and human capital, and thus cannot be overlooked by the political parties.Therefore, to adopt effective political absorptive strategies and increase the representatives’proportion of this sector, to make the newly emerging social elites a part of the system and enhance their political recognition, is beneficial to social stability. Of course, an additional important function of granting social elites a formal institutional identity is to prevent the governmental functionaries from abusing power and protect the business activities and property of the enterprises against any infringement so that the political identities can participate in the political activities and legally and publicly safeguard the interests of their enterprises (Gao, 2006, pp. 132-133).
3.2 The CPPCC is an important platform for the governing party and society to maintain diversified interests and political stability
Samuel P. Huntington (2008) pointed out,“Modernity breeds stability, but modernization breeds instability” (p. 31). There are four major root causes of political instability. They are too rapid modernization, unbalanced political participation,an enlarged city-country disparity, and widespread political corruption. These four aspects are closely related to China in its rapid development and should they be handled inappropriately China might slide into political instability. Political stability is in reality a kind of political order, which “depends in part on the relationship between the development of political institutions and the mobilization of new social forces into politics” (Huntington, 1968, Preface).The most important sign to measure whether a country is modern or traditional is whether its people can participate in politics through a largescale organization and exert political influence.So political stability “depends on the relationship between the level of political participation and the level of political institutionalization” (Huntington,2008, p. 60). Hence, political stability should be regarded as the supreme goal of a modernizing country.
Because of the enhanced level of the people’s social expectations as a result of modernization,to maintain political stability is to a larger extent determined by the degree of openness in the political systems, especially the degree of inclusiveness of social elites. In pursuit of their own goals, the people will resort to the expression of their political demands when confronted with difficulties, thus blocked channels for their expression will result in pressure over the political systems and lead to political instability. The new social forces produced by modernization should be institutionalized into politics as this is an effective way to realize the institutionalization and political stability in the pluralistic socialist structure (Wang& Xie, 2001, pp. 3-8). Therefore, to absorb social elites into political institutions and organizations can, on the one hand, help to truly understand the political demands of all walks of life, while on the other hand guarantee the political authority of the government through the influence of social elites on policy making so as to realize the dynamic stability of the entire political system. “Modernization also brings into existence and political consciousness and activity social and economic groups which either did not exist in traditional society or were outside the scope of politics in traditional society. Either these groups are assimilated into the political system or they become a source of antagonism and revolution against the political system. The achievement of a political community in a modernizing society thus involves both the‘horizontal’ integration of communal groups and the ‘vertical’ assimilation of social and economic classes” (Huntington, 2008, p. 332).
At present, the CPPCC is the largest platform for consultative governance. In the 1990s, the CPPCC system had gradually refined a theoretical form of its own for consultative governance. Opinions of the CPC Central Committee on Strengthening the Work of the CPPCC in 2006 again emphasized the positive practical significance of consultative politics and consultative democracy to China, and this was echoed by the wave of research on consultative democracy in the academic world. In 2007, The China’s Political Party System further stressed that“One major feature of China’s socialist democracy is the combination of democratic election and democratic consultation.”①Retrieved from: http//www.scio.gov.cn/zfbps/ndhf/2007/Document/307872/307872_3.htm.It was the first time the concept of consultative democracy appeared in the documents of the Central Committee of the CPC. The Report at the Eighteenth CPC National Congress directly elevated “consultative democracy” from a form of democracy to a form of institution, and proposed an overall layout for promoting its extensive, multilevel, and institutionalized development, having achieved the integration of theory and practice in recognizing the development of consultative democracy. In practice, the consultative governance of China had been put into multi-layer practice. The function of the CPPCC as the national-layer platform of the consultative governance had been strengthened,and the manifestation of the interactive consultative relationship among the governing party, organs of state and participating parties, and sectors from all walks of life had been achieved through forms like the plenary sessions of the CPPCC, conferences of the Standing Committee, the chairmen’s meeting,the standing committee members, symposiums, and meetings of the special committees (Zhang, 2016,pp. 5-10).
4. The CPPCC sectors are the basic units for the governing party to carry forward the idea of participatory democracy
Based on representative democracy,participatory democracy advocates a participatory pattern to formulating public policies and solving public affairs through citizens’ discussion and consultation. Modern politics generally believes participatory democracy is an effective complement to representative democracy. First, participatory democracy can effectively complement the deficiencies of representative elite politics. Second,participatory democracy emphasizes the process of citizens’ participation in political activities and in making public policies, that is, to solve practical problems through consultation and discussion, while representative democracy stresses the election and often overlooks the formation and implementation of the policies. Third, participatory democracy is a more extensive social democracy that has gone deep into every field of society. Its fundamental requirement is to build a participatory society, and with this premise a democratic government might have a possibility to be founded.
The CPPCC members are returned not by regional constituencies but by consultation of each sector. In this way the committee members will not be confined by region and populace proportion.Instead, they can extensively involve representative personalities from every field, making the CPPCC the most extensively representative and most inclusive in politics with the function of expressing the interests of various sectors. The organized composition of the CPPCC fully displays the CPPCC as the most extensive united front organization.Sectors as the components of the CPPCC can involve all the people or organizations from all social classes and strata; that the members of the CPPCC are composed of representatives of various social strata is a characteristic and advantage of the CPPCC, and serves as an organizational foundation and organizational guarantee for the CPPCC to carry forward socialist democracy and earnestly perform its functions (Zheng, 2016, pp. 9-13). The CPPCC sectors exactly reflect the participation of all walks of life in the political and social life of the country. There is no high or low position in their status, no difference in politics, and no leadership among them. All sectors can absorb the public sentiment and participate in state affairs by participating in the CPPCC, submitting proposals,attending hearings, discussing issues and conducting special investigations. The CPPCC committee members can either express their opinions as an individual or give their group propositions on behalf of their sectors and industries. The CPPCC sectors have gathered from all walks of life the elites of a strong professionalism and higher education who can offer constructive advice and have a say in their specialties. As the main body performing the function of the CPPCC, the committee members are the only political force to perform their duties as sector representatives. The identity of being a sector representative of the CPPCC is the key to the broad representation and immense inclusiveness of the CPPCC. The CPC, through the platform of the CPPCC, is unremittingly in pursuit of absorbing,uniting, and influencing all democratic parties,people’s organizations and representatives of all walks of life and making full use of various political resources, mobilizing the enthusiasm of all aspects for the realization of the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation. The exertion of the sector function is directly related to the realization of the socialist democratic form of the CPPCC, to the political status of the CPPCC, and to the consolidating of the CPC’s position as the governing party, to the improvement of its governing ability, and to the realization of its objectives. The importance of the CPPCC sectors should never be ignored.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2018年3期
Contemporary Social Sciences2018年3期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- The Placement of “Nostalgia” and Protection of Folk Culture in the Context of Urbanization
- Phased Analysis of the Evolution of the Ecological Civilization Concept—A Historical Review from a Global Perspective
- A Miracle of Human Development in China (1950-2030)
- Digital Preservation: A New Approach to Protecting Historical and Cultural Towns and Villages
- Population Quality-based Demographic Dividend, Industrial Transformation and Sustainable Development of the Chinese Economy and Society
- New Approaches to Targeted Poverty Alleviation in the Age of Big Data—On Improving the Results of Targeted Poverty Alleviation Programs (10)
