Enlightenment from WHO Pharmacovigilance in Construction of Chinese Materia Medica Pharmacovigilance System
Wei Ruili (魏瑞麗), Xie Yanming (謝雁鳴), Wang Lianxin (王連心)
Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
ABSTRACT With the widespread concern about the safety of Chinese materia medica, China urgently needs to build a Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance system that conforms to the national development policy and has the characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). A good job of pharmacovigilance of Chinese materia medica not only helps Chinese pharmaceutical companies to control their risks, but also guides them to use drugs safely and rationally. And it is also of great significance to the national drug regulatory work. Based on the monitoring of herbal safety in WHO pharmacovigilance system, the establishment of a Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance system was explored in order to provide a valuable reference for the risk control of Chinese pharmaceutical companies, the clinical use of Chinese materia medica, and the national drug regulatory work.
KEYWORDS: WHO pharmacovigilance; Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance; Adverse drug reaction
With the development of global economic integration, Chinese materia medica, as an important part of traditional medicine in China has always been valued for its safety. With the continuous improvement of science and technology, the types of Chinese materia medica preparations are increasing, and injections are being used more and more widely in clinical practice. In the Annual Report on the Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions in China, the monitoring of Chinese materia medica injections in 2015 involved 43.4% combined use of drugs,and severe reporting cases involved 56.5% combined use of drugs; in 2016, the adverse reactions/events of Chinese materia medica accounted for 16.6% of the total reported events; The blood-regulating formula, supplementing (and boosting) formula, and resuscitation formula were among the top three in terms of the number of Chinese materia medica injections reported for three consecutive years from 2014 to 2016[1-3]. The number of adverse reactions reported in Chinese materia medica and the number of varieties involved are on the increase year by year. This is related to the increase in sales and awareness of adverse reactions in recent years. The safety issues of Chinese materia medica injections and their clinical combined use have also attracted widespread attention. Combined application may increase the safety risk of Chinese materia medica injections. Therefore, it is quite necessary to promote the rational allocation of Chinese materia medica resources, deepen the formulation of a minimum risk control plan for Chinese materia medica production enterprises, increase the risk management of adverse drug reactions after the listing of Chinese materia medica,strengthen the rational use of clinical drugs, and establish a complete Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance system that meets the requirements of international relevant pharmacovigilance system.
In recent years, some scholars have interpreted the new version of the EU Pharmacovigilance Practice Guideline[4]from the aspects of legal basis,content structure, main content and key technical points, etc., which provide a good reference for the development and improvement of pharmacovigilance work in China. This paper refers to the relevant work of the WHO pharmacovigilance system to further explore the construction of Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance system.
DEFINITION AND SCOPE OF PHARMACOVIGILANCE
WHO clearly stated in the Significance of Pharmacovigilance: Monitoring of Drug Safety[5],pharmacovigilance is the science and activity of discovering, evaluating, recognizing, and preventing adverse drug effects or any other drug-related problems.Later published WHO Pharmacovigilance System Herbal Safety Monitoring Guide (hereinafter referred to as the WHO Herbal Safety Monitoring Guide) further expands the range of pharmacovigilance to Chinese materia medica, traditional and supplementary medicines, blood preparations, biological products, and medical care equipment and vaccines. Closely related to the discipline are: ① substandard drugs; ② medication errors; ③ lack of drug efficacy report; ④ in the absence of scientific data to expand the use of indication drugs; ⑤ acute and chronic poisoning case reports; ⑥ drug lethality estimates; ⑦ drug abuse and misuse; ⑧ adverse interactions with the use of chemicals, other drugs and food[6].
Traditional Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance thoughts are produced and developed along with people's understanding of the toxicity of Chinese materia medica. From the germination stage of the late Han Dynasty to the Weijin period to the long history of Ming and Qing Dynasties, the ancient doctors elaborated Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance from different aspects such as toxicity classification,medication alert and poisoning rescue, etc.[7]. With the development and changes of the times, Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance has been given new connotations. According to the definition of WHO pharmacovigilance, some scholars define the pharmacovigilance of Chinese materia medica as: "all the science and activities related to the safety of Chinese materia medica". The current understanding of the definitions and categories of Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance in China generally refers to the WHO pharmacovigilance related content, based on the existing problems of not systematic adverse reactions theory of Chinese materia medica, not standardize clinical medication, not refined Chinese materia medica related regulations, not perfect safety monitoring before and after the listing. In this paper, we propose to further clarify the specific content involved in "science" and "activity" in the category of pharmacovigilance for Chinese materia medica, such as basic research on the safety of Chinese materia medicas and clinical research, safety monitoring and evaluation, risk management research, and other related work. They are the activities to discover, evaluate,recognize, and prevent the adverse effects of Chinese materia medica or any other scientific activities related to Chinese materia medica. Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance should be the entire drug life process that runs through the use of Chinese materia medica products from resources, research and development,production, circulation, and distribution.
There are different incompatibilities in Chinese materia medica (eighteen incompatible medicaments and nineteen medicaments of mutual restraint), different origins, different processing methods, which lead to inconsistent active ingredients and toxic ingredients in the same variety, and other characteristics, such as syndrome contraindication, contraindications for pregnancy medications, and medications contraindications, effects of climate and solar terms on the use of Chinese materia medica, etc. In clinical practice, the combined use of Chinese patent medicines is easy to overlook drug interactions after combined use of drugs. It is an important measure for the sustainable development of Chinese medicine to correctly and rationally use of Chinese materia medica, introduce Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance concepts, and monitor the safety of Chinese materia medica with early warning.
LAWS AND REGULATIONS OF PHARMACOVIGILANCE
WHO Herbal Safety Monitoring Guide pointed out that in order to ensure the safety, quality, and efficacy of herbal medicines, the government should specify the national quality standards, Good Manufacturing Practices(GMP), labels, and licensing system of production, import and listing. For example, WHO has standardized the technical requirements for the selection and cultivation of medicinal plants in the Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GCP)[8].
Currently, relevant laws and regulations or regulatory documents have been developed in drug development, registration, production, labeling, and circulation in China, such as the Drug Administration Law of People's Republic of China, Administrative Measures for Drug Registration, and Drug Production Quality Management Specification, Administrative Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Drug Distribution,Management Regulations for Drug Instructions and Labels, Regulations for the Quality Management of Drug Business Quality, and Measures for the Administration of Pharmaceutical Trading Licenses and so on. In addition,there are special management standards for the production of Chinese materia medica, such as Regulations for Quality Management of Chinese Medicina Medica (Trial)and Regulations for the Protection of Varieties of Chinese Materia Medica.
Article 71 of the Drug Administration Law of People's Republic of China promulgated and implemented in 2001 clearly stipulates that "China implements a system for reporting adverse drug reactions", which indicates that China's monitoring of adverse reactions has entered the path of legalization[9]. In 2011, the Ministry of Health issued a new version of the Administrative Measures on the Reporting and Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions(Ministry of Health Order No. 81)[10]. It replaced the old version and clarified the purpose of legislation, scope of application, and responsibilities of the competent authority, detailed provisions on adverse reaction reports,monitoring, evaluation, control, information management,and legal responsibilities, as well as a clear definition of six terms such as "adverse reactions" on the basis of the old version[11]. Since the establishment of the National Adverse Reaction Monitoring Center in 1999, China has initially established an adverse reaction monitoring system. Over the years, China has invested a great deal of financial and material resources to promote the rapid development of the adverse reaction monitoring system. The National Drug Adverse Reaction Monitoring Information Network is a long-distance computer communication network for the day-to-day work and management of national adverse drug reaction monitoring centers for domestic and international organizations.At present, the network system has covered more than 280,000 medical institutions and pharmaceutical production and operation companies across the country,and all adverse reactions reported to them have functions of input editing, information transmission, preliminary causal analysis, summary statistics and search queries,and with advantages of real-time report transmission,unified data management. At the same time, the system can be networked directly with the International Drug Monitoring and Cooperation Center database for information exchange and technical cooperation of international drug monitoring and other aspects[12].
In 2013, China announced the Guidelines for Key Monitoring Work of Pharmaceutical Products of Manufacturing Enterprises to conduct focused monitoring of key drugs. The centralized monitoring of key varieties is active monitoring, which makes up for the underreporting of the conventional spontaneous reporting system. It can obtain comprehensive, timely and accurate adverse drug reaction information, and improve the accuracy of the calculation of adverse reaction rates. In order to strengthen the monitoring and evaluation of postmarket drug safety, and guide enterprises to conduct key drug monitoring and ensure the smooth implementation of key monitoring systems, the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) emphasizes that drug manufacturers are the main body and the implementing agency for focused monitoring of drugs, and has made clear provisions on key monitoring contents, technical requirements, monitoring plans and summary reports.
Although relevant departments have issued many management measures, the pharmacovigilance of Chinese materia medica still needs to be in line with international standards. The establishment of a comprehensive warning system for Chinese materia medica is conducive to the promotion and application of Chinese materia medica in the international arena, especially in line with "Belt and Road" policy of China.
ADVERSE REACTION REPORTS AND MONITORING
The monitoring of adverse reactions is an important part of the pharmacovigilance of Chinese materia medica.The relevant aspects of the WHO pharmacovigilance system for the monitoring of herbal safety are discussed from the following aspects.
Adverse reaction report source and monitoring scope
WHO Herbal Safety Monitoring Guide suggests that to achieve nationwide coverage of herbal medicine monitoring, according to the state of drug administration in various countries, the classification of herbal medicines can be attributed to prescription drugs, over-thecounter medicines, health care medicines, and health care professionals (including doctors, pharmacists and nurses), consumers/patients, manufacturing companies,etc., jointly submit reports of the same form to various national drug warning centers or drug administration departments. According to different national conditions of different countries, national poison centers, drug information centers, consumer organizations, clinical trials and research can also submit drug safety monitoring reports[13].
According to the Administrative Measures on the Reporting and Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions,the scope of the report on adverse drug reactions in China includes: domestic drug production during the new drug monitoring period and imported drugs within five years from the date of approval for import must submit all adverse drug reaction reports for the drug;Other domestically-produced drugs and imported drugs that have been granted for more than five years from the date of approval must submit new reports of adverse reactions. However, in view of the current actual situation, in order to avoid underreporting, the reporting principle is "suspected reporting"[14]. The Guidelines for Key Monitoring Work of Pharmaceutical Products of Manufacturing Enterprises require that the focus of drug monitoring is to observe the adverse reactions of listed drugs in the use of a wide range of people[15]. Some scholars have studied the principles for the selection of key varieties for monitoring the safety of Chinese materia medica, and proposed selection based on the principles of adverse reaction information, the characteristics of Chinese materia medica, and the characteristics of drug use[16]. The scope of adverse drug reaction monitoring in China has been comprehensive, including not only all adverse drug reports reported during the monitoring period of new drugs, new and severe adverse reaction reports not reported during the new drug monitoring period, but also including variety of adverse reaction reports. The principle of "suspected reporting" is also suitable for the monitoring of adverse reactions of all Chinese patent medicines.
The subjects reported in the adverse drug reaction report in China include medical institutions, drug companies, and drug manufacturers. The Annual Report on the Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions in China(2016) shows that 85.6% of reports from medical institutions, 12.8% of reports from pharmaceutical companies, 1.4% of reports from pharmaceutical manufacturers, and only 0.2% reports from individuals and other sources. From this we can see that medical institutions are still the main source of reports, and the number of reports produced by manufacturers is still low. Therefore, it is necessary to fully mobilize the enthusiasm and initiative reported by the drug manufacturers in the construction of Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance.
Collection of adverse reaction reports
The collection of safety case reports in the WHO pharmacovigilance system was obtained by the Uppsala Monitoring Certre (UMC) through the Vigiflow reporting system to obtain worldwide ICH-E2B-formatted safety case reports (ICSRs), and stored in the Vigibase database.Data input has data quality standard rules, and the same information is converted into structured data by the term encoding, which can not only reduce and avoid data input errors, but also facilitate communication among member states[17]. In order to avoid the inconsistency of information on adverse reactions caused by geographical differences (such as the common name of the same herb in different parts of the world, or the variety of herbs in the same common name), UMC uses WHO Drug Dictionary (WHO-DD), Herbal Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification (HATC) and Herbal System Inventory to identify and record the herbal medicines[14].
The collection of adverse drug reaction reports in China is through the online reporting system of "National Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring Network". The collection of adverse drug reaction reports from Chinese materia medica has no exception. The adverse reaction monitoring centers in various provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities report electronic forms to the national adverse reaction monitoring center. In the monitoring project of key Chinese materia medica,the collection of adverse reaction information includes medical institutions (such as hospitals, community medical service organizations), pharmacies and other related drug use units. Usually, medical institutions should be the main channel for information collection, and a key monitoring project can be carried out in multiple medical institutions (multi-centers) at the same time. According to the different forms of information collection, key monitoring can be used for centralized monitoring of hospitalized patients, registration-returning interviews,and questionnaire surveys. Individual adverse drug reactions/events, group adverse drug reactions found in key monitoring cases shall be reported in accordance with the requirements of the Administrative Measures on the Reporting and Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions. In addition, on the basis of the existing system for reporting adverse drug reactions, a monitoring data collection and storage management subsystem for key Chinese materia medica varieties suitable for pharmaceutical production enterprises can be added.
Safety monitoring of Chinese materia medica started late and has less experience in China. There are still many shortages in the collection of adverse reactions of Chinese materia medica: lack of Chinese materia medica adverse reaction report form with Chinese materia medica characteristics; reporting process quality control standards need to unified, and the submitted adverse reaction report form is wrong reported and missed cases; The terminology of adverse reactions used for coding standardization is not yet sound, and there is no terminology for adverse reactions of Chinese materia medica; the relevant statements and coding categories basically copy the pattern of adverse reactions of chemical drugs, and the application of WHO-ATC classification to Chinese materia medica is not strong. Therefore, it is necessary to establish and improve the adverse reaction report form, terminology and coding classification method that conform to the laws of Chinese medicine as soon as possible.
Chinese materia medica adverse reaction report form that is as accurate and complete as possible and different from chemical drugs should be developed,and it can be generated based on the existing drug adverse reaction report form. The basic information of the patient, details of the suspicious Chinese materia medica products, the use of the drug, and the symptoms of adverse reactions should be included in the report.For example, patients related conditions should be added physical conditions (such as high sensitivity, tolerance or idiosyncrasy, etc.) and TCM differentiation of the disease;detailed information on suspected Chinese materia medica products should be combined with the characteristics of different Chinese materia medica to make corresponding supplements. For example, Chinese materia medica containing toxic ingredients should be supplemented with varieties of Chinese materia medica, medicinal parts, origin, collection time, storage conditions, methods of preparation, etc.; Medication part should be added whether the prescription is consistent with the syndrome,whether the compatibility is not appropriate, and whether decoction is appropriate. In addition, the names of drugs for combination use, reasons for combined use, and misuse and abuse of drugs should also be documented in detail.
Data mining and evaluation of adverse reaction report
The report on the WHO pharmacovigilance will be fed back after data mining and evaluation. UMC uses the data mining tool to generate the original signal, and the initial screening signal is formed after the original signal is filtered by the automatic screening strategy and tools.The Bayesian confidence propagation neural network(BCNPP) is used for signal mining of collected adverse reaction reports, and then a set of rigorous evaluation procedures will be followed. The signal first undergoes an artificial internal evaluation to generate a list of potential signals, and then the signal risk is determined after evaluation by external experts in different fields.In addition, UMC starts from the four principles of the relevance of adverse drug reactions and drug use time, biological rationality, contact strength, and other confounding factors, and classifies suspicious adverse reaction association evaluation criteria as "affirmative"and "very likely", "possible", "may not be relevant", "to be evaluated/not classified", "cannot be evaluated/not classified"[13].
In China, CFDA drug evaluation center is responsible for drug safety signal management, which is divided into three steps: signal discovery, signal evaluation and signal processing. The signal is firstly discovered from the adverse event/event report table manually or using computer-aided excavation tools.Common data mining and assessment methods include decision tree method, Bayesian network model and Apriori algorithm. The second step is to evaluate the signal by combining clinical relevance, non-clinical data correlation, literature data, and expert consultation. The signal assessment process is not accomplished in an action. The potential risks of unclear signal indications need to be subsequently collected for more adverse reaction reports or supplemented by relevant studies to clarify. For a clear signal, risk minimization schemes or drug risk communication need to be developed. The last step is signal processing, which is risk control.The measures for controlling risks are various and there are information interventions (such as revision of specifications, formulation of patient medication guidelines, release of government announcements,etc.), behavioral interventions, and market interventions(such as recall, withdrawal, special supply, etc.). For examples, in the 61stand 67thissues of the Adverse Drug Reactions Bulletin, the risk of liver injury caused by oral administration of Radix Polygoni Multiflori and its preparations and the risks of adverse reactions of the Chinese and Western medicine compound preparations of Ganmaoqing Table (Capsule) and Naoluotong Capsule were reported and analyzed. The doctors' prescriptions and patients' medications were used for risk warning. The pharmaceutical manufacturers were advised to modify the instructions.
The data mining technique of Chinese materia medica safety information has achieved a lot, but it needs to be further improved. The decision tree method was used to analyze the Shuanghuanglian Injection and the Chuanhuning Injection in detail. The generated tree diagram model realized the visualization of the data rules.Its high accuracy and high efficiency were conducive to the discovery of deep hidden laws in the data[18].The Bayesian network model brings the evaluation of adverse reactions from the qualitative evaluation to the quantitative evaluation stage. Association rules are important for revealing the occurrence of adverse reactions. The relevance evaluation of adverse reaction reports in China uses the UMC evaluation criteria. After comparing the advantages and disadvantages of the world's four main data mining algorithms, some scholars predict that the improved random forest model, Bayesian logistic regression and association rules based on the decision tree will have guiding significance for the data mining of the combined drugs[19]. Future research and exploration of data mining algorithms will continue to be the focus and direction of efforts.
For the assessment of adverse reaction data,especially for key Chinese materia medica varieties,although China has issued the Key Monitoring Work Guide, there is still a lack of detailed evaluation indicators for key production monitoring reports submitted by drug manufacturers.
FEEDBACK AND COMMUNICATION OF PHARMACOVIGILANCE INFORMATION
WHO pharmacovigilance information are released through Uppsala Report, Uppsala Annual Report, WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter, Signal Magazine, Vigimed Forum and Vigibase Database and other methods (Table 1)for feedback and communication[20].
The domestic pharmacovigilance information feedback mechanism in China is released to the public free of charge on the official website of the CFDA through the Adverse Drug Reaction Information Bulletin,Pharmacovigilance News and the national annual report on adverse drug reaction monitoring. Up to now, the National ADR Monitoring 2016 Annual Report, 76 Issues of Adverse Drug Reaction Information Bulletin, and 177 Issues of Pharmacovigilance News have been published.The external feedback is mainly to submit a uniform format of adverse reaction report to UMC. Currently, the adverse reaction report submitted does not include the Chinese materia medica adverse reaction report.
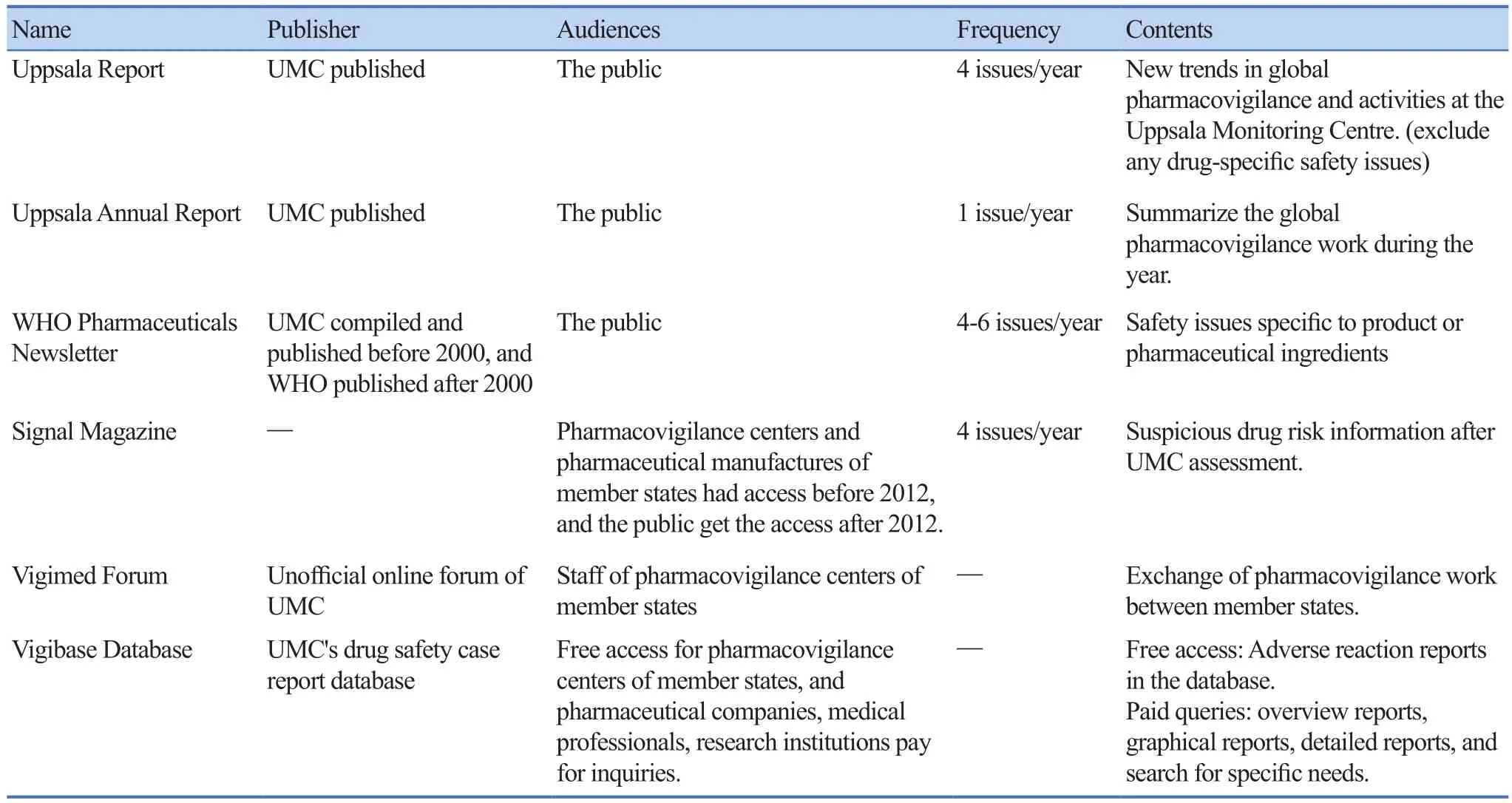
Table 1. Feedback and Communication of WHO pharmacovigilance information
The feedback mechanism of Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance information is still insufficient and information is asymmetric. For example, by taking advantage of "Internet Plus", the pharmacovigilance information can be released through mainstream media communication tools; strengthening contact with consumer associations to promote the collection and feedback of safety information for Chinese medicine products; and sending emails directly to physicians or pharmacists in the event of emergency Chinese materia medica adverse reactions, etc. These are all very effective means and methods.
DISCUSSION
Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance must adapt to the development of the times, better integrate with the country's current medical and health care system, and be in line with international advanced pharmacological alertness levels, and it needs continuous improvement.
At the level of pharmaceutical production enterprise, different pharmaceutical companies need to establish a comprehensive Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance system based on their own production and development characteristics, and strictly control the entire drug life cycle of resources, R&D, production, and circulation of Chinese medicine products after they are listed and marketed, and improve the quality control of Chinese materia medica and ensure the consistency of product quality.
At the level of medical institutions, the training of clinicians, nurses and pharmacists on the rational use of drugs should be strengthened, and the quality of practitioners should be improved. Relevant policies,regulations and professional knowledge on Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance should be popularized to avoid the overuse of Chinese materia medica specified in instructions. The awareness of adverse reaction reporting should be strengthened, and the content of adverse reactions, and report the flow should be standardized to avoid missed reports, and improve the quality of adverse reaction reports.
At the level of patient, it is necessary to strengthen education and raise people's awareness of safe drug use so as to avoid unreasonable and abuse of drugs. Adverse drug reactions are reported to the relevant regulatory authorities through relevant public channels.
At the level of national regulatory, the first is to continuously strengthen and improve the relevant laws and regulations on Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance. On December 6, 2016, the White Paper of Chinese Medicine in China was published. This is the first time that the Chinese government has issued a white paper to systematically introduce the development context and characteristics of Chinese medicine, the national policy and major measures for the development of Chinese medicine in China, and demonstrated the scientific value and cultural characteristics of Chinese medicine. The Law of the People's Republic of China on Traditional Chinese Medicine was formally implemented on July 1, 2017[21]. The second is to clarify the scope of Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance, and in line with international standards. Pharmacovigilance does not mean monitoring of adverse drug reactions. The range of pharmacovigilance is greater and more extensive. The third is system optimization. The adverse drug reaction monitoring system should further expand the collection scope of the adverse drug reaction monitoring network(such as direct reports of patients and their families,forensic medical reports, etc.), and reports of adverse reactions of single and compound preparations can be separately reported, which is beneficial to the analysis and evaluation of adverse reaction reports; The re-registration system can require drug manufacturers to continue to follow up on product safety and efficacy data, submit comprehensive reports and review regularly; establish mechanisms for compensation for drug damages.
In short, the concept of Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance has been introduced into China's drug regulatory field and is in line with international standards, making it essential for the healthy and sustainable development of Chinese medicine. It is imperative to establish a complete Chinese materia medica pharmacovigilance system and issue relevant guidelines to guide the Chinese materia medica companies in their risk control over Chinese patent medicines, the rational use of drugs by medical institutions, the safety of common people's medications, and the national drug supervision.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been funded by General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China(NO.81473798): Study on allergic reaction mechanism of post-marketing Chinese medicine injections with active monitoring and network target monitoring; National Science and Technology Major Project of "Development Program of Significant New Drug" (2015ZX09501004-001-002/009); Entrusted Project of China Center for Food and Drug International Exchange, The State Food and Drug Administration: International promotion of Chinese medicine safety.
 World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2018年3期
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2018年3期
- World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- World Integrated Medicine Master Han Jisheng
- Consensus on Epigastralgia Diagnosis and Treatment of Chinese Medicine (2017)
- Effect of Qiangli Dingxuan Tablet on Cerebral Hemodynamics and Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potentials in Vertigo Patients with Posterior Circulation Ischemia
- Clinical Study on the Treatment of Neonatal Jaundice with Lidan Tuihuang Formula Combined with Bifid Lriple Viable and Blue Ray Irradiation
- Quality Evaluation on Traditional Chinese Medicine Nursing Plan for Stroke in Acute and Recovery Phases
- Profiling the Change of Key Chemical Ingredients in Combination of Aconitum carmichaeli Debx. and Bletilla striata (Thunb.)Reichb.f. by UPLC-QTOF/MS with Multivariate Statistical Analysis
