Clinical experience of Xiangxi Liu’s infantile tuina for exogenous fever in children
Tang Wei (湯偉), Shao Xiang-ning (邵湘寧)
The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Pediatric Tuina; Common Cold; Fever; Infant; Child, Preschool
Infantile tuina, as a main external treatment method in pediatrics of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), has the advantages of simple operation, convenience,effectiveness and low cost.Therefore, it has been widely used for common diseases in children and also gained its popularity from children and their parents for its effectiveness, safety and painless.Currently, despite various schools of infantile tuina in China, exogenous fever in children has been generally accepted as a disease than can be well-treated by infantile tuina, and listed as a common disease by all schools[1].
Xiangxi (the western part of Hunan province) Liu’s infantile tuina has a long history of more than 300 years and a clear inheritance map.Its origin dates back to Qing dynasty and it has become one main school of current infantile tuina in China[2].The 4th generation inheritor of this school, professor Liu Kai-yun is a famous specialist of infantile tuina in the present age.He has made publication of the infantile tuina handed down from ancestors.Moreover, he pays attention to the clinical practice of infantile tuina, especially the treatment of children’s exogenous fever.We treated exogenous fever in children with Liu’s infantile tuina,and arranged related medical cases of this school.The report is now given as follows.
1 A Clear Diagnosis Is the Premise of Treatment
Fever is the most common clinical symptom in children and exists in the pathogenetic process of various diseases.Therefore, the premise of tuina is diagnosis.What is children’s exogenous fever? In TCM,it is commonly known as cold, equals to upper respiratory infection in modern medicine.At the same time, diseases including acute tonsillitis, acute pharyngitis, acute rhinitis, herpetic pharyngitis and common infectious diseases in the early stage such as measles, scarlatina, infantile acute skin rash all belong to this category[3-4].Whereas, children’s lower respiratory infection, such as infantile pneumonia,children’s bronchitis, and children’s infectious fever, is not included in this scope.
Besides, a differential diagnosis is required to distinguish children’s acute laryngitis from children’s exogenous fever.Fever is a common symptom in the early stage of children’s acute laryngitis, but this disease has a rapid onset and even causes laryngeal edema or even dyspnea in some children.According to our clinical experience, laboratory examinations such as the routine blood test, C-reaction protein test, procalcitonin test and mycoplasma detection are usually required for a clear diagnosis[5].
2 Syndrome Differentiation Is the First Step
With a confirmed diagnosis, exogenous fever in children can be treated with Liu’s pediatric tuina method[6-7].In Chinese medicine, exogenous fever is often differentiated into two patterns: the exterior syndrome of Wei-Defense and retention of pathogenic factors in the lung and stomach.
The exterior syndrome of Wei-Defense is characterized by simultaneous fever and aversion to cold.It can be subdivided into wind cold pattern and wind heat pattern.Characteristic signs and symptoms of wind cold are severe aversion to cold, mild fever,absence of sweating, no thirst, absence of red throat,and a superficial, tight pulse or red fingers.Characteristic signs and symptoms of wind heat are severe fever, mild aversion to cold, sweating, a dry mouth, a red throat, and a superficial, rapid pulse or purple fingers.For wind cold pattern, palpation feels a markedly cold sensation in the extremities, a warm sensation on the head and face and a mild warm sensation on the skin in the throat area.For wind heat pattern, palpation feels a mild cold sensation in the extremities, and a markedly warm sensation on the head, face and skin in the throat area.
Characteristic signs and symptoms of retention of pathogenic factors in the lung and stomach are a high-grade fever alone (without aversion to cold) and thirst.It can be subdivided into warm heat, food retention, and phlegm heat accumulating in the lung.Distinctive features of warm heat are a high fever,profuse sweating, excessive thirst, scanty urine and constipation.Distinctive features of food retention are a foul breath, abdominal pain and dry stools/constipation.Distinctive features of phlegm heat are cough, panting and phlegm sound in the throat/expectoration of yellow phlegm.For warm heat, palpation feels a burning sensation all over the body.For food retention,palpation feels a markedly burning sensation on the palms and abdomen, coupled with tenderness, and crying upon pressure.For phlegm heat, palpation feels a burning sensation in the skin around the throat area and pressing Tiantu (CV 22) causes coughing.
3 Qing-clearing Wujing Combining with Acupoint-selection According to Pattern Differentiation
Exogenous fever in children pertains to Feijing according to the meridian categorization and treatment principle of Liu’s infantile tuina; it also pertains to Feijing excess pattern since it is caused by external pathogenic factors.Tui-pushing Wujing is an essential manipulation in Liu’s infantile tuina system.To treat Feijing excess pattern, according to the engendering and restraining principle of the Zang-fu organs, the four-clearing and one-tonifying method is appropriate, namely Qing-clearing Feijing in the first place, Qing-clearing Pijing in the second, Qing-clearing Ganjing in the third,gently Qing-clearing Xinjing in the fourth and mildly Bu-reinforcing Shenjing in the fifth place[8].
For the exterior syndrome of Wei-Defense, pushing Wujing can clear evil in the lung Wei-Defense; for the pattern of retention of pathogenic factors in the lung and stomach, pushing Wujing can clear the accumulated heat in the lung and stomach.Acupoints combination scheme varies from pathogenic characters and pathogenesis.The major frame of the tuina prescription is pushing Wujing, pattern differentiationbased acupoint selection principle and opening orifices.
Prescription for Children’s exogenous fever in Liu’s infantile tuina: opening orifices-pushing Wujing (fourclearing and one-tonifying method, Figure 1-Figure 5)-combining acupoints (specific acupoints for inducing sweating and clearing heat)-opening orifices.
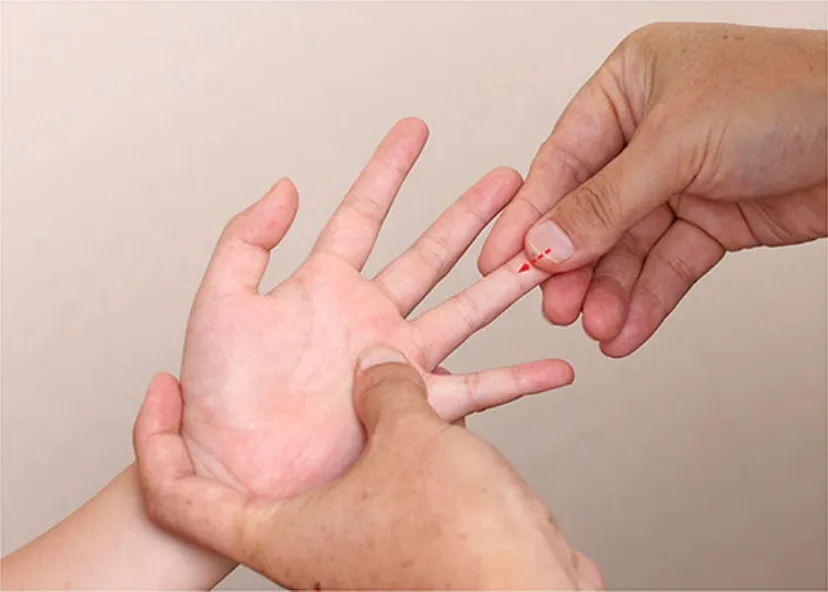

Figure 1.Qing-clearing Feijing
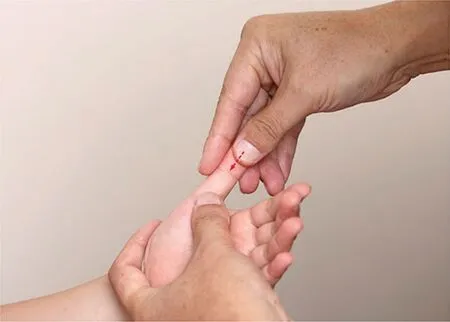
Figure 2.Qing-clearing Pijing
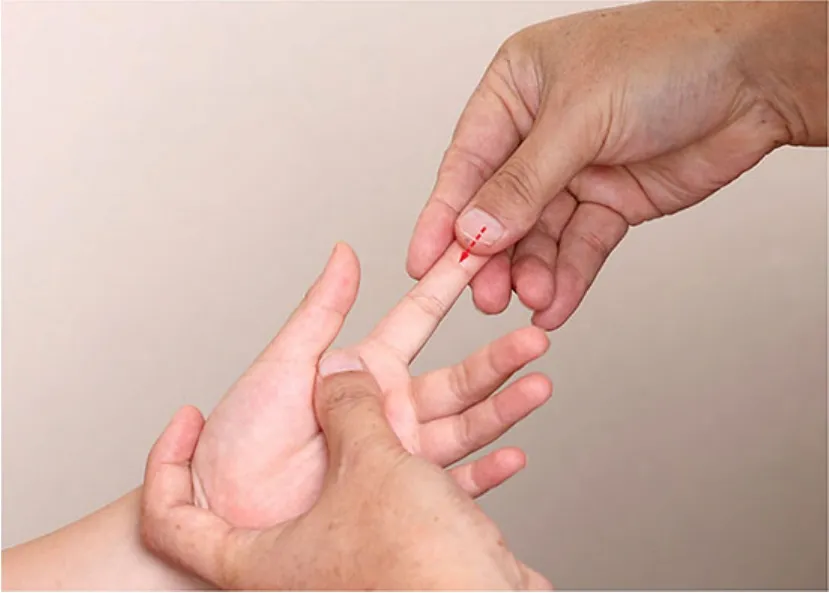
Figure 3.Qing-clearing Ganjing
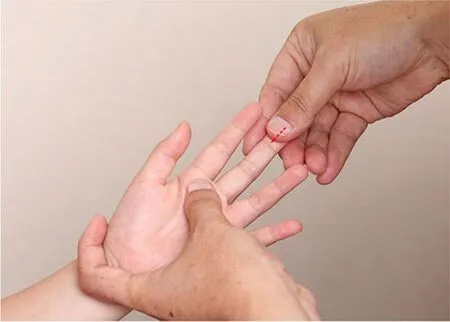
Figure 4.Qing-clearing Xinjing
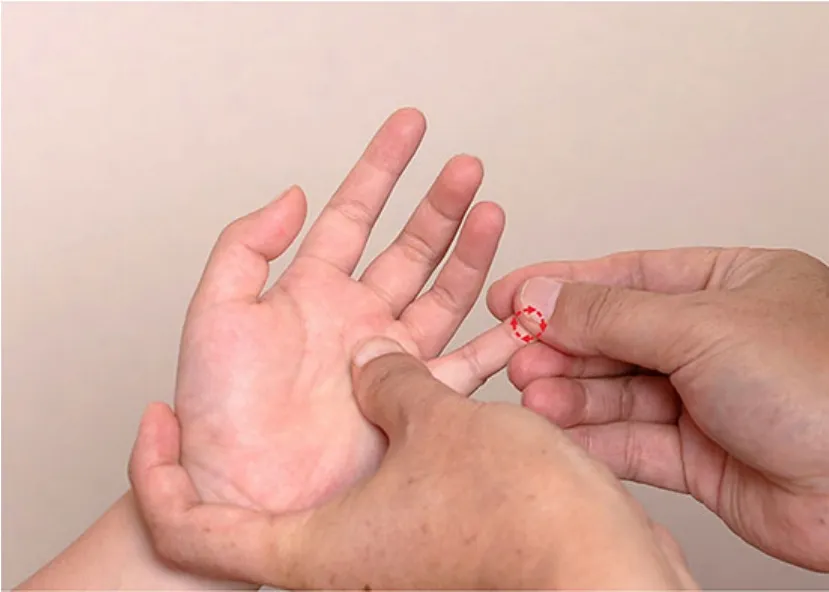
Figure 5.Bu-reinforcing Shenjing
4 Selecting Specific Acupoints by Referring to the Categories of Herbs
According to the therapeutic functions of different acupoints/locations in infantile tuina and referring to the classification method of herbs, Professor Liu Kai-yun has sorted acupoints/locations with the function of removing fever into 5 categories.
4.1 Promoting sweating to release the exterior and subdue fever
Including Yun-circularly pushing Taiyang, Qia-pinching Neilaogong, Rou-kneading Wailaogong, Qia-pinching Zongjin, Tui-pushing Sanguan and Ershanmen, and Na-grasping Hegu (LI 4) and Jianjing (GB 21).
4.2 Clearing visceral heat
Including Qing-clearing Pijing, Qing-clearing Feijing,Qing-clearing Ganjing, Qing-clearing Xinjing and Qing-clearing Houxi (SI 3).
4.3 Clearing interior heat
Including Tui-pushing Liufu, Large Tui-pushing Tianheshui (the first Liu’s manipulation to remove fever,Figure 6), Da Ma Guo Tianhe (Tui-pushing Tianheshui Like Horse Jump) (the second Liu’s manipulation to remove fever, Figure 7), Shui Di Lao Yue (Fishing up the Moon in the Water) (the third Liu’s manipulation to remove fever, Figure 8) and Tui-pushing vertebrae, and Tui-pushing Dazhui (GV 14).
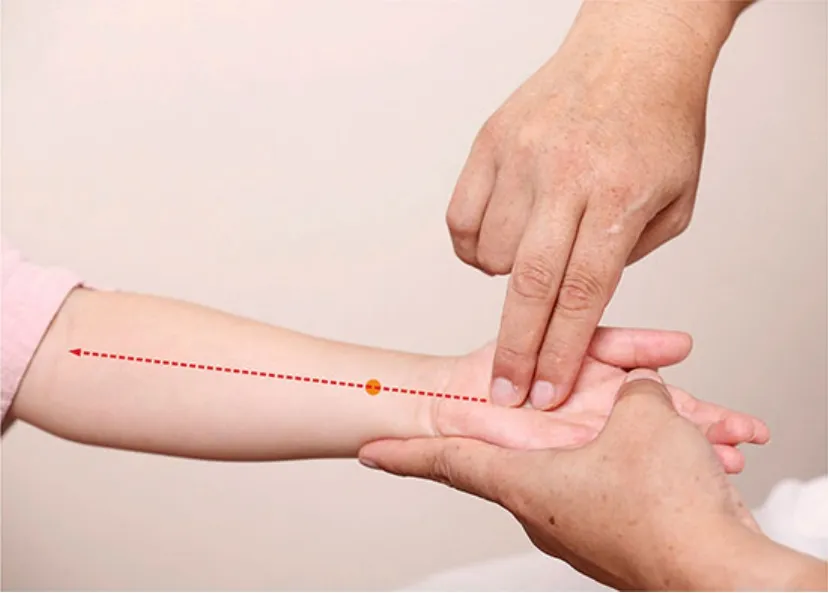
Figure 6.Large Tui-pushing Tianheshui
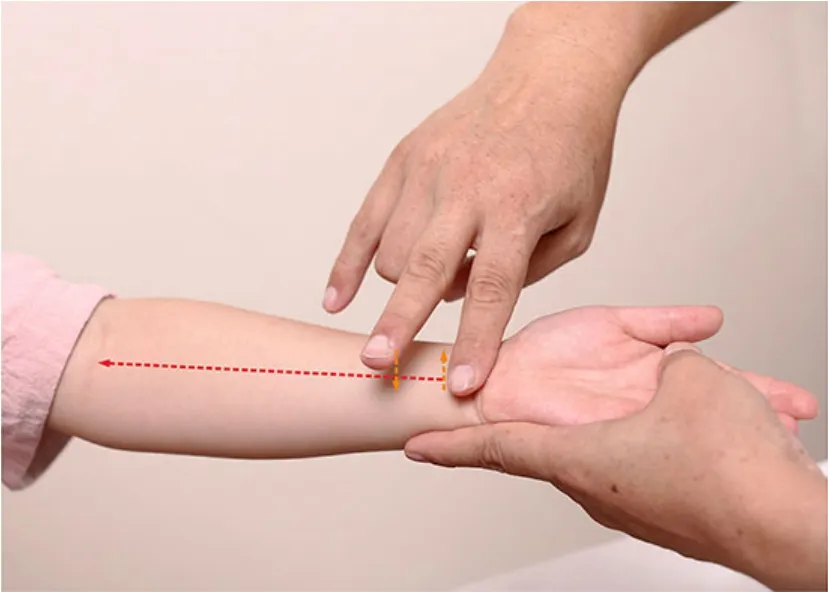
Figure 7.Da Ma Guo Tianhe(Tui-pushing Tianheshui Like Horse Jump)
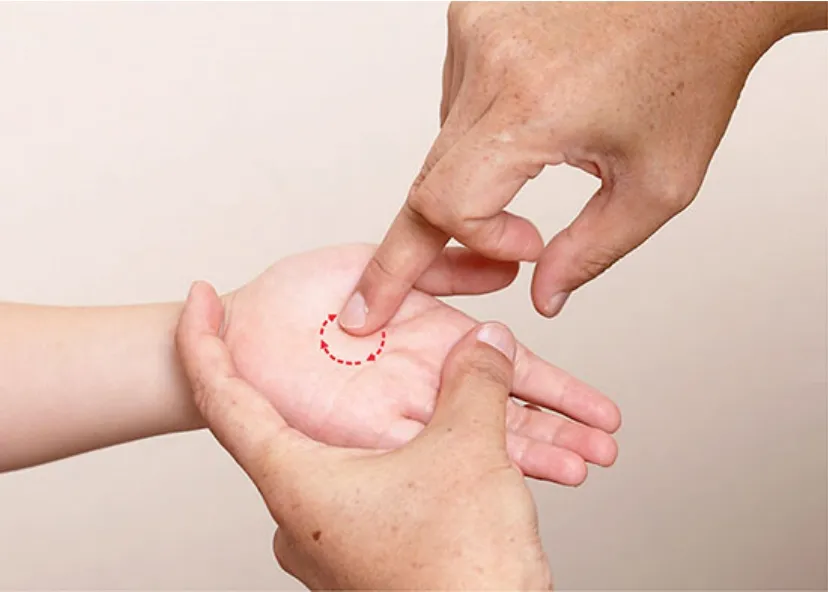
Figure 8.Shui Di Lao Yue(Fishing up the Moon in the Water)
4.4 Clearing deficiency heat
Including Rou-kneading Erma and Rou-kneading An-pressing Yongquan (KI 1).
4.5 Clearing dampness-heat in lower jiao
Namely Tui-pushing Jimen[9-10].
For wind cold pattern, Sanguan and Ershanmen can be used to disperse wind-cold and release the exterior pathogen with pungent-warm nature.For wind heat pattern, Liufu, vertebrae and Hegu (LI 4) can be used to disperse wind-heat and release the exterior with pungent-cool nature.For high fever due to retention of pathogenic factors in the lung and stomach, Large Tui-pushing Tianheshui, Da Ma Guo Tianhe (Tui-pushing Tianheshui Like Horse Jump) and Shui Di Lao Yue(Fishing up the Moon in the Water) can be used.Regarding the intensity of fever-removing function of those methods from high to low, professor Liu Kai-yun holds the order should be Da Ma Guo Tianhe(Tui-pushing Tianheshui Like Horse Jump), Large Tui-pushing Tianheshui and Shui Di Lao Yue (Fishing up the Moon in the Water).All the three methods above should be accompanied by blowing motion[11].
5 Discussion
Xiangxi Liu’s infantile tuina has a history of more than 300 years.In 2004, it had been chosen as the first batch of TCM Inheritance Workhouse Construction Project by the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine and had been approved by the expert group of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2016.Besides, this school had won the comment that a good school that has maintained the original infantile tuina of Ming and Qing dynasties, by experts in the textbook ofInfantile Tuinacompiled under the guidance of the 13th Five-year Plan of pediatric tuina unified textbook[12].The primary academic characteristic is Tui-pushing Wujing.In clinical practice, it stresses visceral syndrome differentiation and the engendering and restraining relationship of the viscera, and takes the infantile physiological and pathological characteristics into consideration.Based on the above contents, the supplementing and reducing methods and the selection of the Wujing can be determined[13].According to the viewpoint of this school’s 4th generation inheritor professor Liu Kai-yun and his student (Professor Fu Ming-jin), Liu’s infantile tuina for treating fever caused by exogenous pathogens can completely remove fever in 24 h in the most cases.Normally, the fever-removal time is 2-3 h after the midnight hour (23:00-01:00) of the day of the treatment.If the fever remains, tuina manipulation can be conducted one more time on the second day[14-15].Besides, by follow-up visit of the parents, the fever removal time is largely after 03:00 am in the morning.Moreover, the therapeutic effect is better if the tuina treatment is conducted in the afternoon rather than in the morning.
5.1 To estimate the prognosis according to sweating
One important treatment principle for exogenous fever is promoting sweating to release the exterior.Therefore, the attention should be paid to the sweating condition of the children to estimate the prognosis.
Infantile tuina manipulates directly on skin.Therefore,the skin is both the application site and the location of disease.Thus, tuina treatment can reach directly the disease location to remove fever via sweating.Generally speaking, for wind cold pattern, signs including gentle sweating like drizzling rain and gradual warming hands and feet are considered a favorable prognosis, in which,fever will disappear after 1-2 treatments.For wind heat pattern, signs including sweating like thin and unceasing rain and a cold sensation on the back after sweating are considered a favorable prognosis, in which, fever will disappear after 2-3 treatments.
5.2 To adjust tuina scheme according to individual,disease and pattern
In clinical practice, factors including the intensity of manipulation, treatment frequency and single treatment duration should be adjusted with varied conditions.For exterior syndrome, the manipulation should be gentle with a slight floating force to induce sweating to dispel the exogenous evil.The frequency is once a day; for the pathogen stagnated in the lung and stomach, the manipulation should be strong with a slight sinking force to expel the evil and clear the heat in Yangming.The frequency is twice a day.
The therapeutic effect is also affected by patients’constitution, disease condition and disease category.Generally speaking, the effect is better in children with a good constitution; otherwise, if the patient is weak or long-term dependent on drug assistant for fever, the single tuina treatment may not receive a satisfactory effect.Besides, for patients with complicated disease,single tuina treatment is not enough, and drugs or other treatment targeting at the cause of the disease will be required.Moreover, we should also obey the development tendency of the disease during tuina treatment.For example, in the case of purulent tonsillitis, fever is not obvious in the early stage.But, in the purulent period, patients usually manifest high fever.Therefore, tuina treatment should not only focus on fever removal.It should also focus on facilitating blood and qi circulation as well as warming meridians,removing blood stasis and dispelling putridity.Tui-pushing Sanguan, Rou-kneading Wailaogong with warming effect should be used to promote healing.
5.3 To prohibit the overuse of acupoints for clearing heat
In the pattern differentiation process of exogenous fever, the cold or heat nature should be made clear to further determine the treatment principle.Though cold may transform into heat, acupoints with function of clearing heat should not be used for a long time or frequently, such as Shui Di Lao Yue (Fishing up the Moon in the Water), Large Tui-pushing Tianheshui and Da Ma Guo Tianhe (Tui-pushing Tianheshui Like Horse Jump).This aims to protect infantile yang qi and prevent adverse reactions such as unceasing sweating after fever removal or affecting appetite.The special physiological characteristic of children is the fragile viscera, especially the stomach and spleen[16-17].The cold manipulations may harm stomach and spleen, so tuina manipulation should be stopped immediately once symptoms are alleviated.At the same time,manipulations regulating the spleen and stomach can be added, such as Bu-reinforcing Pijing, Yun Shui Ru Tu(Yun-transferring Water into Earth), and Rou-kneading Zhongwan (CV 12).
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年5期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年5期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical observation of Zhen’ai needling method in Nei Jing (Classic of Internal Medicine) on improving quality of life in patients with allergic rhinitis
- Effect of acupoint massage plus acupoint sticking therapy for the stress reaction during postoperative anesthesia recovery period in patients undergoing nasal endoscopic surgery
- Effect of modified Qing Long Bai Wei needling on the levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and INF-α in synovial fluid of knee osteoarthritis patients
- Clinical observation of sinew-regulating and bone-setting manipulation combined with functional exercise to treat rotator cuff injury
- Therapeutic observation of acupuncture plus tuina for cervical vertigo
- Experimental study on the influence of pressing force and time on thermal effect of An-pressing manipulation
