Emerging and re-emerging human infectious diseases: A systematic review of the role of wild animals with a focus on public health impact
Marli C Cupertino, Michely B Resende, Nicholas AJ Mayers , Lorendane M Carvalho,, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista,2
1Medical School, Faculdade Dinamica do Vale do Piranga. Ponte Nova. Minas Gerais, Brazil
2Laboratory of Epidemiological and Computational Methods in Health, Department of Medicine and Nursing, Universidade Federal de Vi?osa. Minas Gerais, Brazil
3Department of Veterinary Medicine, Universidade Federal de Vi?osa. Vi?osa. Minas Gerais, Brazil
ABSTRACT Infectious diseases continue to impose unpredictable burdens on global health and economies, a subject that requires constant research and updates. In this sense, the objective of the present article was to review studies on the role of wild animals as reservoirs and/or dispersers of etiological agents of human infectious diseases in order to compile data on the main wild animals and etiological agents involved in zoonotic outbreaks. A systematic review was carried out using PRISMA guidelines, using the PubMed, Scopus and SciELO platforms as data banks. The descriptors used were“zoonosis”, “human infectious diseases” and “wild animals”.The results show that wild animals (mainly bats, birds and primates) play an important role in the dissemination of etiological agents (mainly viruses, as a new coronavirus called 2019 Novel Coronavirus) in extensive geographic regions. Moreover, these wild animal organisms can act as the site for essential biotic synergy among several pathogenic microorganisms, promoting a higher rate of adaptation, mutation and even genetic recombination, with consequent stimulation of new strains and subtypes, inducing new infectious agents with unknown virulent potential. In conclusion,the monitoring of these diseases and adequate preparation for possible epidemics and pandemics are fundamental conditions for the mitigation of their future impact. The zoonotic threat of these etiological agents and the impact on public health can be enormous as shown by the ongoing epidemic of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections.
KEYWORDS: Zoonosis; Epidemics; 2019-nCoV; Virology;Epidemiology
1. Introduction
Globally, there exists several ecosystems with rich biodiversity,which are gradually deteriorating due to an increase in anthropogenic activities[1]. The economic and technological advancement in agriculture & industrialization (directly and/or indirectly lead to an increase air and soil pollution), and population growth (incites unbridled urbanization of previously uninhabited natural areas), are a few determinant factors linked to the degradation of such environments. Correspondingly, these conditions encourage increased human-wildlife interactions,facilitating the dissemination of infectious & parasitic agents to new hosts & habitats, which consequently establishes new potentially harmful relationships, revamping the existent ecological niches in disease transmission cycles[1,2].
The emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) are those with an increased incidence in the past 20 years that could amplify in the near future. They can be caused by known etiological agents or newly identified strains of such; accounting for at least 12% of all human pathogens. Some examples are West Nile fever, influenza,Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and the current outbreak of viral pneumonia linked to a new coronavirus called 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). There are reemerging infections as well, like tuberculosis, which can be drug resistant[1-3].
Wild animal EIDs, can be classified in three groups, based on these fundamental epizootiological criteria: EIDs associated with“overflow” of domestic animals to wildlife populations living in their proximity; EIDs directly related to human intervention, through translocation of either host or parasite; and EIDs without evident involvement of domestic animals or humans. This situation has two important biological implications. Firstly, many wild species are reservoirs of several pathogens that threat the domestic animal and/or public health. Secondly, EIDs of wildlife represent a considerable menace to the preservation of global biodiversity[3].
Ebola, SARS, Nipah Virus Encephalitis (NiVE), and 2019-nCoV are some of the more prominent EIDs, originating from wildlife, presenting global epidemic risks, and generating, today,vast economic and social burdens to humanity[4]. Moreover, the transmission of these diseases to humans casts a significant burden on global health systems[5,6]. It is estimated that over a billion cases of zoonotic diseases occur annually. New emerging zoonoses are responsible for progressively encumbering health systems and global economies, particularly where populations are densely agglomerated,and hindering environmental resources[2].
Despite the insistence on controlling these pests, focus must primarily be on disease prevention, and health & environmental education interventions. There is also the need for thorough investigation of the zoonotic epidemiology in high-risk animalhuman interfaces, in order to evaluate the prospective emergence of viral diseases and appropriate suitable prophylactic measures worldwide. The threat of a new human pandemic is probably more likely in high-risk interfaces, promoting the reemergence of former diseases. As for viral diseases, reliable data on the circumstances at the point of their dissemination does not exist for several viral species. Comprehensively, animal disease data is generally incomplete due to inaccurate surveillance of wild animals worldwide[5].
Characterizing the animals that act as reservoirs and, in general,surveying the antigenic variants of wild life origins, are extremely important. Furthermore, the environmental and anthropogenic risk factors that may influence the transmission of infectious diseases related to these animals must be determined, thereby increasing the efficacy of the designated prophylactic measures[7].
These infectious diseases continue to impose huge and unforeseeable burdens to the global health and economy. Thus,adequate surveillance of these diseases and preparation for potential epidemics and pandemics is fundamental to mitigate the impact of future outbreaks[8]. One of the challenges of controlling the dissemination of etiological agents is precisely the copious diversity of the animal reservoirs, making it easier for these agents to perpetuate in several habitats[2]. Because of both the lack of data around this theme and its importance to public health, the present study aims to review studies on the role of wild animals as reservoirs or dispersers of etiological agents of human infectious diseases in order to compile data on the main wild animals and etiological agents involved in zoonotic outbreaks.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Strategy to find and select the articles
To perform this study was used PRISMA guidelines. The PubMed,Scopus and SciELO databases were used to search articles,published up to April 2019, and premised on the wild animals acting as reservoirs of etiological agents of importance to public health. The search strategy was based on three components: (1) wild animals participating in the transmission or dispersion of etiological agents of human diseases; (2) zoonosis; (3) human infectious diseases which might have the participation of wild animals in their transmission cycle. The search filters were developed according to synonym dictionary of the MeSH terms (Medical Subject Headings)platform of the digital library PubMed/Medline (US National Library of Medicine National Institute of Health). After that, these descriptors were adapted to the Scopus and the SciELO (Scientific Electronic Library Online) platforms. The following descriptors and Boolean operators were used: “wild animals AND human infectious diseases”, “zoonosis AND human infectious diseases”, “zoonosis AND wild animals” and “animal reservoirs AND human infectious diseases”. Having then obtained an ample amount of data from these filters, there was a consensus reached as to which articles would meet the inclusion criteria. Neither language nor chronologic restrictions were applied when searching for the articles. The initial screening was carried out considering the title and abstract of all articles found.Duplicated studies were eliminated by contrasting authors, title, year and journal of publication. After this first selection, all potentially relevant studies were downloaded in their entirety to have their eligibility assessed.
2.2. Data extraction, exclusion, and inclusion criteria
The exclusion of the articles was based on well-defined criteria,as follows: (1) studies that discussed infectious diseases, but had no relation to wild animals, (2) zoonosis with no relation to wild life,and (3) studies with incomplete texts or secondary studies (such as editorials, editors’ letters, Master or Doctoral theses, book chapters,and articles whose complete text was unavailable). Reference lists of the selected articles were also examined to find potentially relevant documents. The criteria for including the articles were: (1) must be data analysis about zoonosis, and (2) must encompass in its study some relation between an infectious disease and wild animals in the transmission cycle of the etiological agent. Such criteria were defined with the goal of fulfilling the proposed objective: considering with greater depth the role of wild animals in the transmission cycle of human infectious diseases.
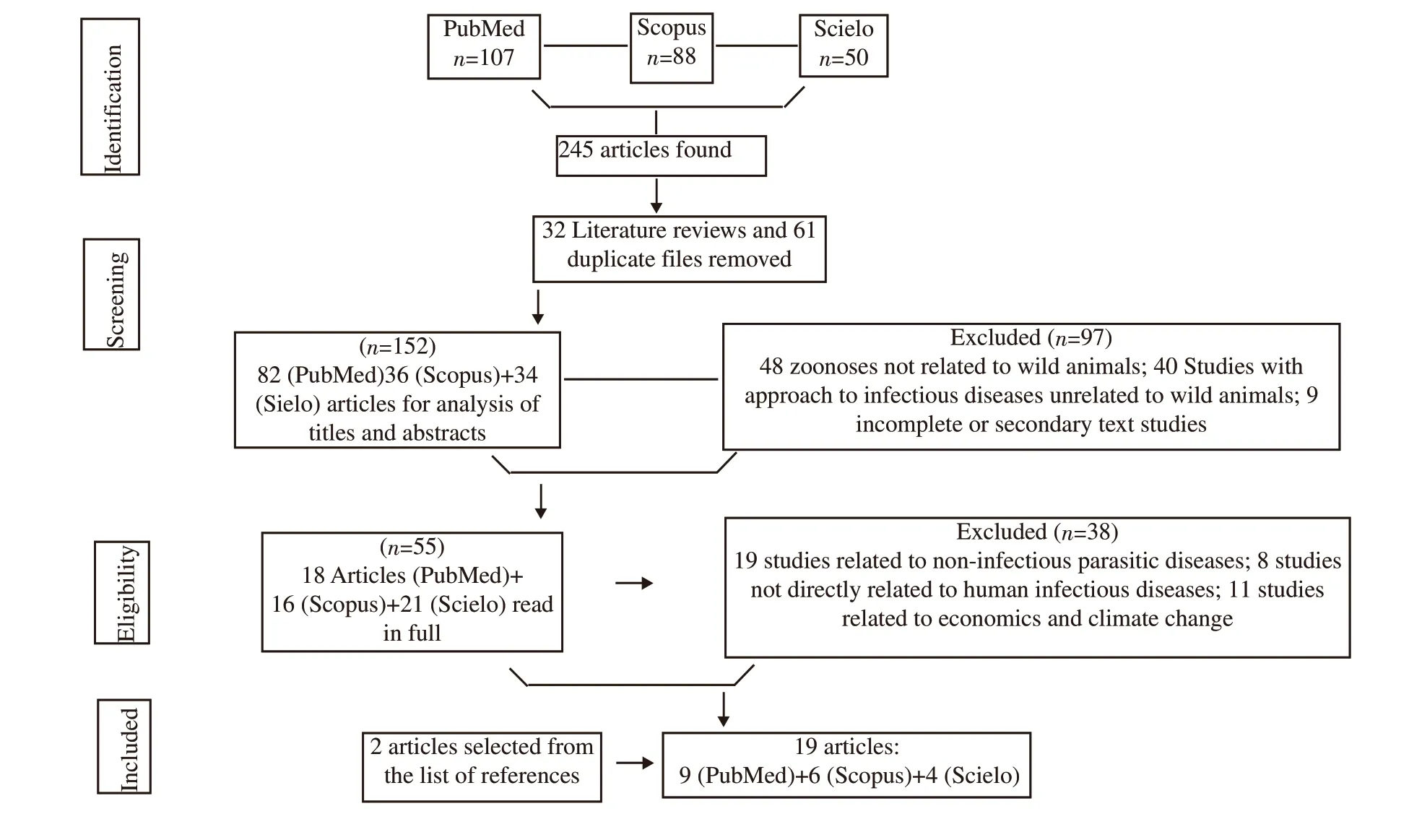
Figure 1. Flow diagram of review survey results, based on items from preferred reports for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes: The PRISMA Statement.
Qualitative data was extracted from all the selected articles. The data extraction was classified as follows: (1) characteristics of the publication: author, year, journal and country; (2) characteristics of the animal: species; (3) characteristics of the disease: viral, bacterial,parasitic, cases in humans; and (4) main results of the study.
3. Results
In total, 245 articles were found. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the present study, 19 articles were selected for the review[3,5,7-23], as shown by Figure 1. The description of the qualitative data extracted from the studies included in this reviewcharacteristics of the publication: author, year, country, and main conclusion; kind of the wild animal; characteristics of the disease:species, and cases in humans - are shown in the Table 1.
The majority of zoonoses cited in the studies, with the aforementioned specific descriptors, had links to mammals(n=16). The types of mammals, more expressively, were bats and primates (Non-Human Primates[3,5,16,23], Cercocebus atys[12,15], Pan troglodytes[12,14,15], and Gorilla gorilla[14]), and, less expressively,wild rodents[5], Dromedary camels[8], African buffalos[15], wild boars[18,22]. The second largest group of animals identified as reservoirs or dispersers of etiological agents of human infectious diseases were wild birds (n=7). There was one report of disease related to arthropods (ticks)[22] and another to amphibians(salamanders)[3].
Furthermore, research affirmed that the main etiological agents were viral (n=16), with the minority being bacteria (n=2)[17,22]and parasites (n=1)[23]. Among the etiological agents found included: Influenza Virus, Coronavirus, Nipah Virus, Ebola Virus,Paramyxovirus, Rhabdovirus, Hendra Virus, Menangle Virus, West Nile Virus, Bird Influenza, Filovirus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Orthohantavirus/Hantavirus, Human Type-4 Cells Lymphotropic Virus, Hepatitis E Virus, Leptospirosis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Marburg Virus, Rift Valley Fever Virus, Parvovirus,Arbovirus, and gastrointestinal parasites in general.
The data shows the epidemiological circumstances involved in the zoonotic overflow, amplification and dissemination of several etiologic agents (Figure 2), that can be transmitted directly to humans, without the need for wild animal reservoirs (Figure 2A). Nevertheless, in some cases, these wild animals function as reservoirs and dispersers of etiological agents (Figure 2B). As the microorganisms do not trigger symptomology in the wild animals,they remain long periods in nature, being dispersed expansively across geographical regions. This along with epidemiological surveillance failures can substantiate the reemergence of particular disease outbreaks in these areas[3,8,16,18] (Figure 2C). Another factor that promotes the emergence of new infectious diseases isthe perpetuation of the virus in accidental hosts. The maintenance of viruses inside the body of an unusual host may increase the possibility of error in the process of RNA duplication and emergence of mutation in a relative short period. This fact can triggers changes in virus morphology, creating new infectious agents with unknown virulent potential, using new adaptive strategies and resistance to vaccines, consequently increasing the transmission rate of the virus in vulnerable populations (Figure 2D).
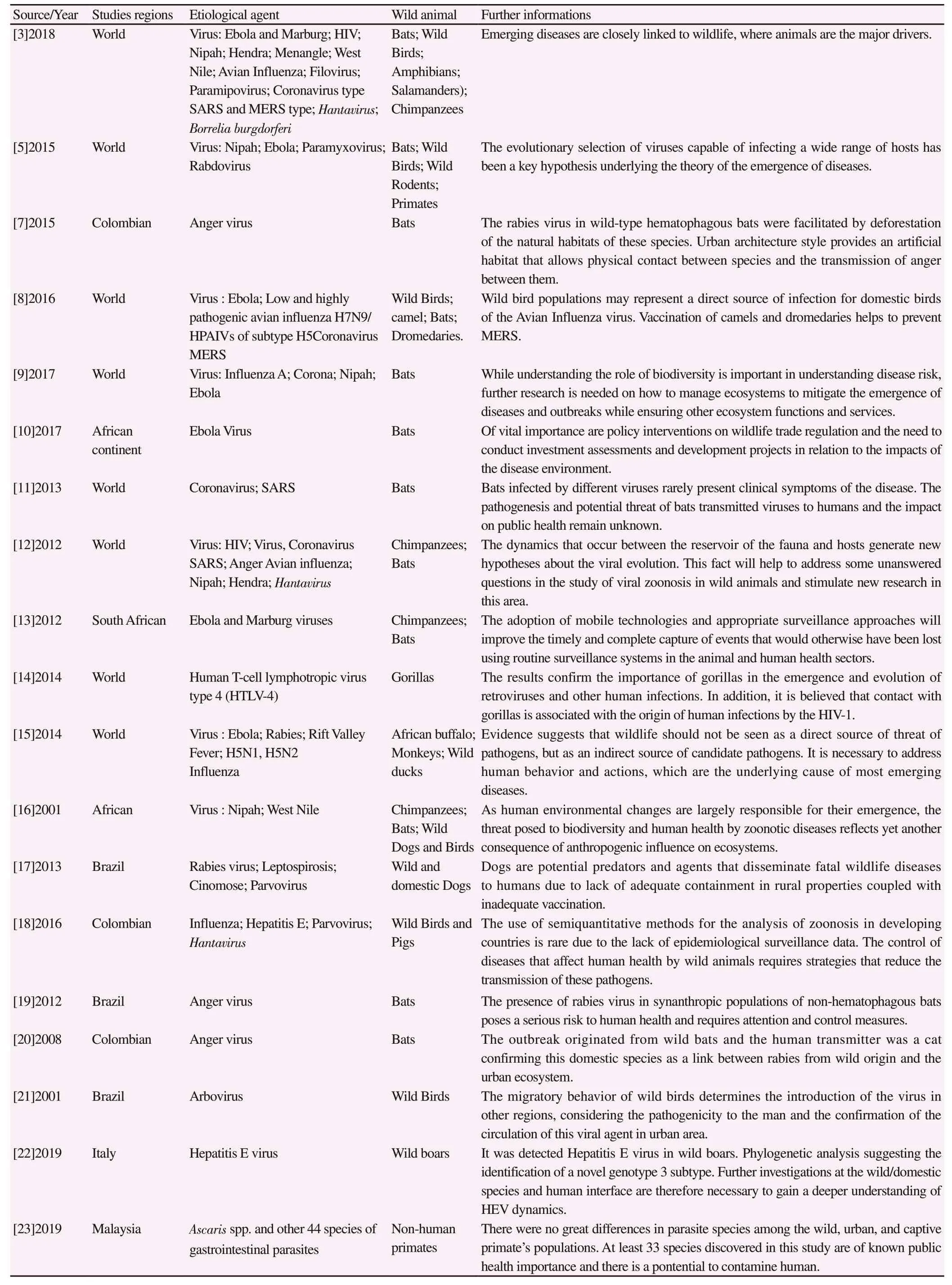
Table 1. Description of the qualitative data extracted from the studies included in this review: characteristics of the publication: author, year, and country; main conclusion; kind of the wild animal; characteristics of the disease: species, and cases in humans (all studies shows human cases).
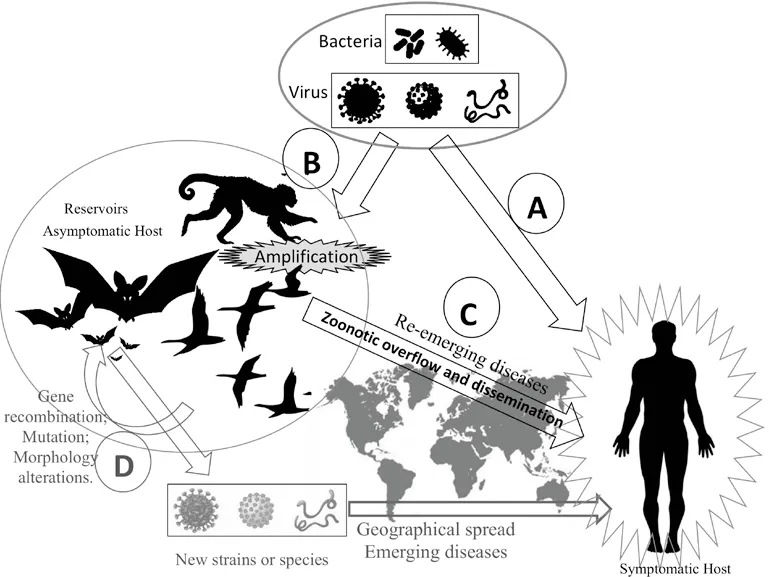
Figure 2. Role of wild animals on amplification and dissemination of etiological agents that cause human infectious diseases, and epidemiological circumstances involved in the zoonotic overflow, and biotic interactions that trigger the emergence of new etiological agents with potential impact to public health.
4. Discussion
There is discontinuity in scientific knowledge about the real role of wild animals in times of outbreaks of human infectious diseases.All selected studies treated wild animals as reservoirs or geographic dispersers of etiological agents that caused cases of infectious diseases in humans. However, some e etiologic agents even today have unknown sources of contamination; as with the case of human infection by the MERS-CoV or 2019-nCoV. About MERS-CoV molecular investigation indicated that bats may contribute to it’s transmission amongst anthropoids. Nonetheless, the data on this association is still mitigated and rudimentary[25-27]. 2019-nCoV is one of the cases where there may have been gene recombination, a mutation triggering to morphological changes in the coronavirus that naturally infects wild animals, possibly snakes or bats, according to recent research[6,28,30]. This shows that despite the ample literature on the role wildlife plays in the dissemination and transmission of human infectious disease, there’s still no direct link correlating it with serious human diseases.
Recognizing the epidemiological circumstances involved in the zoonotic overflow, amplification and dissemination, is pertinent in prioritizing adequate surveillance and predictive techniques for the emergence of new pathologies with potential impact to public health[3,5,6]. Since most etiological agents of human infectious diseases do not develop symptoms in the disperser animals, how they act as reservoirs is not often researched and/or diagnosed appropriately[5,6]. Therefore, this knowledge gap should induce the convergence of research in this field for the purpose of training knowledgeable professionals, to aid in the orientation of appropriate preventive health practices, according to each etiological agent’s distinct characteristic.
According to the analyzed data, the viruses present greater risk of becoming more perilous, considering they can coexist with several viral species within the same organism[28-33]. This increases the probability of these viruses undergoing recombination, culminating in wild-type strains with potential risk to the general public health[34,35].For example, bats are described as hosts of arenaviruses, herpesviruses,lyssaviruses, paramyxoviruses and filoviruses[3,36-38]. As a single animal can be a reservoir of several types of virus, genetic material exchange (by gene recombination) between them is plausible.Recombination is defined as the process of intermolecular exchange of genetic elements. From this can derive new strains, subtypes and even new virus species, generating diseases with unknown pathogenicity[34,35]. Prime examples are the Ebola, H1N1 Influenza and a new subtype of Hepatitis E virus described in wild boars[22].
Several viral agents, discussed in this review, were involved in important outbreaks emphasizing the importance of the etiological agents of emerging and re-emerging diseases, on public health, in the global sanitary context. For example, 2014 Ebola virus outbreak was conspicuous. It circulated through many African nations, provoking 21 759 cases with over 8 600 deaths[29]. In China, the current 2020 outbreak of viral pneumonia linked to a new coronavirus 2019-nCoV,that originated there in December 2019[6]. Its persistence can be associated with gene recombination, the mutation triggering distinct morphological changes in the coronavirus that naturally infects wild animals, even snack or bats, according to recent researches[28,30].Areas where there are agglomerations of animal species coexisting,under high stress conditions, as in the Chinese wet markets, have already been responsible for infectious diseases epidemics in China and Southeast Asia, including the virus responsible for SARS, which killed almost 800 people worldwide in 2003[1,36]. This environment can be a catalyst for immune systems disorders within these animals, being a favorable circumstance for inconspicuous viral recombination and mutations, which then generates etiologic agents with unknown pathogenicity, triggering catastrophes to global public health. The sanitary authorities might have implemented researching the origins of the outbreak and its relation to wild animal reservoirs,had there been more supporting studies on the dissemination of such diseases[39-41].
In regards to Brazil, one should allude to the reported cases of the Hantavirus infections in the frontier regions, which revealed the probable existence and distribution of the disease reservoir in that region. Population growth, unbridled and unplanned urbanization with social exclusion and invasion of previously uninhabited natural areas, are anthropogenic activities that result in destabilization of varying ecosystems, and facilitate the approximation/exposure of humans to exotic pathologic agents[31,42-44].
The infectious diseases whose microbial transmission benefits from diverse environmental factors, through adapting & building resistance, usually attack humans after they have established themselves in these ecosystems[32,45,46]. The origins of this kind of transmission are influenced by ecological components, such as climatic variations, fauna and flora[31,47-52]. Thus, one has to confront the capricious efficacy of prophylactic strategies, since they are required to complement the dynamic pace of the mechanisms involved in the human-health-environment equilibrium[48]. When considering the prevention of epidemics and pandemics, keeping blockades in ports, airports and roads are of little to no effect without the constant surveillance of viral, bacterial, fungal and parasitic loads from migrant birds and wild animals that might traverse from affected to unaffected areas[49-52].
There are considerable difficulties in controlling the dissemination of etiological agents, because they become increasingly diversified as anthropogenic biomes develop; in such context, many species of birds and mammals notably emerge to the forefront[2,47,50].The fragmented context of knowledge has been challenged, and the integration of varying expertise has become fundamental to maintaining the balance among vital processes in changing environments[48,50-53]. Understanding that human health and animal health is a single entity (“One Health”)[8,10,37,46,48,53], promotes incentives for research on animals that will fill gaps in the science that directly affects global sectors, as described in this review.
There is a huge gap in the scientific knowledge on the actual role of wild animals in human infectious diseases outbreaks. There are many challenges to identifying which wild animals are reservoirs to specific etiological agents. Another challenge is determining the possible biotic interactions that trigger the emergence of new efficient subtypes and/or strains.
It was identified that viruses are the main etiological agents involved in this process and the principal wild animals are birds and mammals, due to their genetic proximity to humans, although these agents do not trigger symptomatology in these animals, nonetheless,there is insignificant research and diagnostic data.
Surveys need to be constant and perennial. Only then, will the predictability of complex biotic relationships between these distinct pathogens and their wild animal reservoirs be more analogous. This lack of adequate research leads to failure in Eco-epidemiological control strategies of the diseases, allowing for greater occurrence throughout major geographical zones, and the development of new diseases with a detrimental impact to public health.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thanks the support received from the Faculdade Dinamica do Vale do Piranga (FADIP), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Funda??o de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG).
Authors’ contributions
MCC and RSB conceived of the presented idea and supervised the findings of this work. MCC, MDR, NAJM and LMC developed the theory, performed the data collection, and wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年3期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年3期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Dose prediction of lopinavir/ritonavir for 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)infection based on mathematic modeling
- Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) update: What we know and what is unknown
- Imported cases of 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections in Thailand:Mathematical modelling of the outbreak
- Molecular isolation and identification of Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis in Didelphis virginiana from Hidalgo, Mexico
- Blastocystis incidence, spontaneous clearance, persistence and risk factors in a rural community in Thailand: A prospective cohort study
- Etiologies of tropical acute febrile illness in West Pahang, Malaysia: A prospective observational study
