The competence of nursing students to prevent pressure injury - a scoping review
Si-Qi Xiong,Ming Sang,Yan-Qiu Huang,Hui-Ping Wang,Chang-De Jin
1Department of Graduate,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,China; 2Department of Nursing,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Pressure injury,Nursing student,Competency,Scoping review
Introduction
Pressure injury (PI),also called pressure ulcers,pressure sores or decubitus ulcers,was defined as“l(fā)ocalized injury to the skin and/or underlying tissue usually over a bony prominence,as a result of pressure,or pressure in combination with shear” by the European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel [1].It’s one of the globally concerned patient safety issues[2].
PI has been reported to result in significant suffering and morbidity to the patients [3],which also brings about huge economic burden on patients' families and the public health systems[4].It has been demonstrated that the cost of treating PI in Netherlands was between$3.22 and$2.8 billion per year[5],and the costs in UK of the health and social care system were estimated as£1.77 billion per year[6].
Currently,PI remains a significant burden for the European intensive care units,especially the impact of nursing workload [7].Pressure injury prevention (PIP)has been one of various nursing care priorities and the key indicator of the quality of nursing care.Sufficient knowledge of nursing students played a vital role in recognizing the risks of PI and the confidence had a significant impact on protecting the patients from potential harms or errors and avoidable injuries[8].
As the graduate students major in nursing education,we were interested in the nursing students’knowledge,attitudes,performances,skills,confidence and experiences in PIP.Therefore,scoping review were widely incorporated into the literature and the results were summarized in the present study.
Methods
The scoping review methodology was applied in our work,which was usually used to assess and synthesize the extent of the body of literature on a particular topic[9].Five steps of the scoping review guidelines reported by Arksey and O’Malley [10] were followed:1) identifying the research question,2) identifying relevant studies,3) defining a relevant study selection,4) charting the data and 5) collating,summarizing and reporting the results.
Identifying the research question
The research question of this study was to investigate the competency of nursing students in PIP and the needs for the prevention.
Identifying relevant studies
For a systematically medical literature survey,5 English databases (PubMed,CINAHL,Embase,Web of Science and Cochrane Library) and 3 Chinese databases (CNKI,Wanfang date and VIP date) were searched.The language was limited to English and Chinese,but no date limit was applied.Search strategies were developed by two members of the research teams (SM and WHP) and performed by the first author.
The following keywords were searched in various combinations:nursing student and pressure ulcers prevention,which were com-bined by the Boolean operators,AND or OR.The keywords were searched in different databases with appropriate thesaurus terms,and the deadline of the search was September 6,2018.As shown in Figure1,after removing the duplications,1416 studies were identified.
Defining a relevant study selection
Next,the selection was performed in three stages.In the first stage,only the researches published in Chinese or English were retained.By reading the titles and abstracts of articles,irrelevant researches which were not involved in the connections between nursing students and prevention of PI were removed.There are 27 articles met the initial inclusion criteria.In the second stage,the full text were browsed and a variety of articles which had no records or measures of the attitudes and knowledge of nursing students on PI were eliminated,and the number of articles was reduced to 14.In the third stage,the references of all the included articles were also thoroughly explored to search for any additional papers discussing the competence of nursing students in PIP,and 4 related articles were added.In the end,17 related articles were finally collected in this study.
Charting the data
According to the research questions,Excel was adopted to sort out the key information of the articles,including author,publication year,research purpose,research methods,countries and main findings of the research,as represented in Table1 and Supplement Table1.
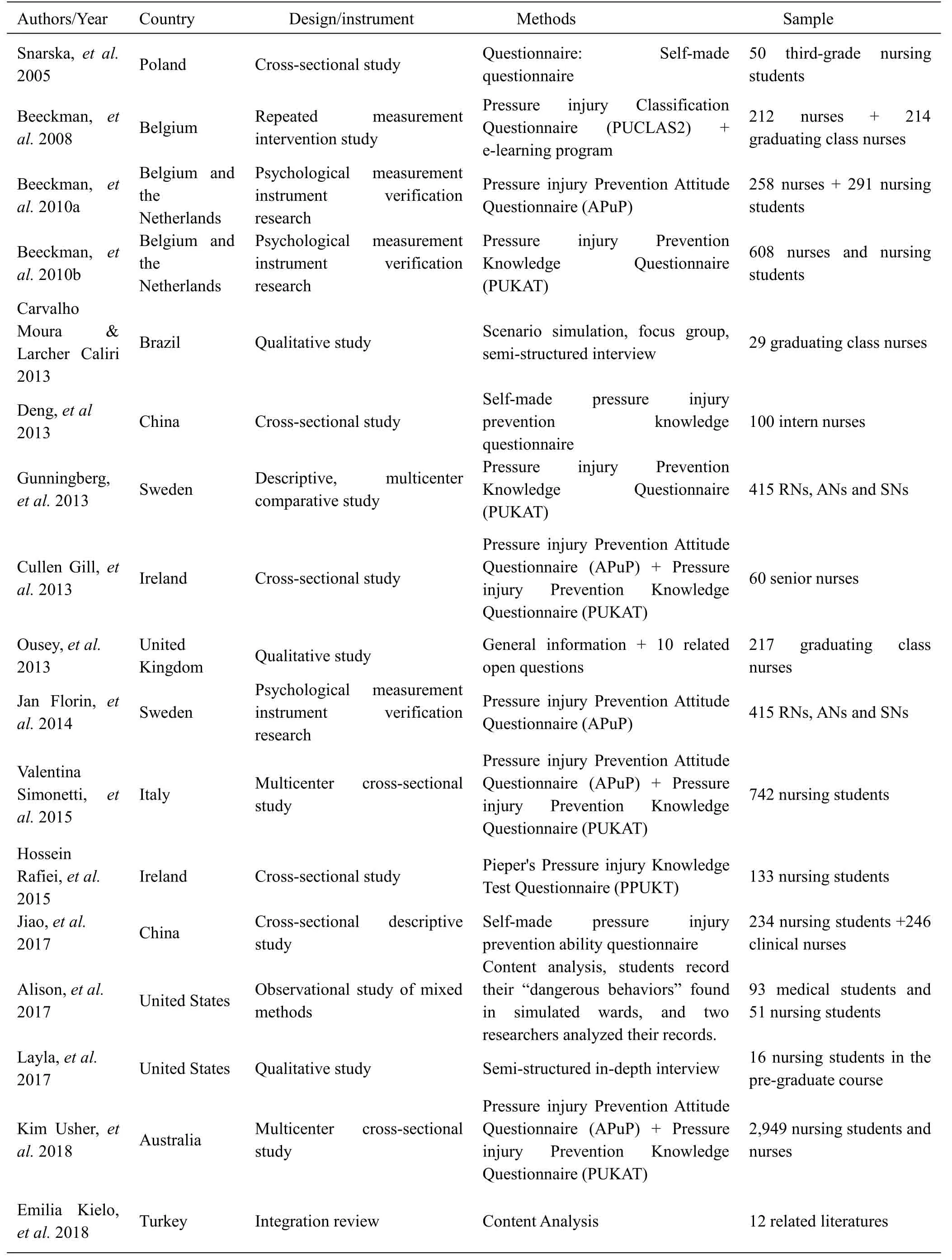
Table1 Basic information for inclusion in the study
Collating,summering,and reporting the results
Our research was represented in the form of structured reports.In order to ensure the consistency of the results,two researchers independently conducted thematic analyses of the literature.To sum up,the competency of PIP was described in three topics:“Knowledge and Attitude”,“Preparation for Nursing Students” and“Educational Situation and Needs”.
Results
General aspect of the literature
A total of 17 related studies were collected,with 3 qualitative studies,13 quantitative studies,and 1 comprehensive study.There was an intervention study and the rest were all descriptive studies.Furthermore,the related scales have been developed or validated in three studies.Self-made competency tests were applied to measure PIP knowledge or abilities of nursing students in three works.It was also reported in one study that observations were used to document the status of nursing students.Other effective assessment tools were involved in the remaining nine studies.Besides,there were studies comparing the differences between nursing students and the nurses.The focus groups and semi-structured interviews were adopted in the qualitative researches,with the sample sizes ranging from 29 to 217.
Special aspect of the literature
Knowledge and attitude.Hossein et al.[11] applied Pieper's pressure injury knowledge test questionnaire in their study,which stipulated that only those who correctly answer 90% or more questions were considered to be qualified.In the study,nursing students answered 67% of the questions correctly on average.The correct answer rate of the classification of PI was 50%.The PIP knowledge questionnaire(PUKAT) developed by Beeckman,et al.in 2010 [12]were adopted in another 5 studies.In these studies,the knowledge scores of nursing students varied between 10.2/26 [12] and 13.3/26 [13,14].No one could answer 100% correctly,and 92% of senior nursing students scored less than 18(18/26)[15].The scores of nursing students in the “nutrition” dimension were higher than that of other dimensions,the registered nurses and assistant nurses[13,16].The scoring rate in the “pressure/shear volume” dimension was low [13,14,16].
The stress ulcer prevention attitude scale developed by Beeckman,et al.[12] was involved in five researches.Among these studies,nursing students had a high PIP attitude score,with an average score of 40 to 46(total score of 52)[13,15,17].Students with two years or more clinical practice experiences scored dramatically higher than those with one year or less internship experiences [13].Kim,et al.revealed that there was a weak positive correlation between the total knowledge score and the total attitude score [13],while Cullen,et al.reported an inverse relationship between attitude and the knowledge score [15].It has also demonstrated that most nursing students rarely understood the risk factors,preventive measures and the classification of PI,and lacked the awareness of PIP[18,19].
Preparedness of nursing students.The main concern for the preparation of nursing students entering the clinic was the senior nursing students.99% of nursing students believed that participating in the training programs of PIP clinical practices played crucial roles in accumulating the related knowledge [18].While 50% of the nursing students demonstrated that their PIP knowledge came from the basic nursing courses in schools,and most nursing students seldom participate in the PIP courses [19].It has been reported that 68%of the nursing students received less than 10 hours of formal instruction on skin integrity in schools [19].However,70% of them indicated that their existing knowledge and skills were enough to keep the skin intactness of patients in clinical practices [19].Alison,et al.illustrated that both nursing students and medical students had low recognition of hospitalization related hazards,and 54% of them could not identify the presence of PI[20].
Education and needs.It has been revealed in the present study that the PIP knowledge of junior nursing students with little clinical practice experiences was lower than that of senior nursing students and nurses,and their knowledge was enriched with the increase of practices in different departments [12,13,16,21]Nursing students who participated in extracurricular activities or sought information online scored higher in the pressure sore knowledge test than those who lacked the above experiences [22].Besides,the E-learning intervention also improved the PIP knowledge of nursing students [23].Nursing students indicated that observing the behaviors of wound nurses and others engaged in PIP practices can enhance their sense of responsibility and enthusiasm for PIP[24].
Discussion
Our review comprehensively summarized the PIP competence of nursing students,which has been extensively studied in the global quantitative and qualitative literature,mainly in Europe.However,the present study paid more attention to the PIP knowledge and attitude of nursing students,because as the successor of clinical nursing staff,nursing student'knowledge reserve and attitude towards diseases had a guiding effect on the clinical practices[25].
The knowledge of nursing students in PIP was insufficient,which was consistent with the conditions of nurses who also hardly dealt with PIP[16].Nursing students especially lack the knowledge of “preventive measures to reduce stress/shear force”,which may cause by the neglect of the PI risk factors in the teaching materials and the lack of opportunities to contact patients suffered from PI in school,therefore,they cannot learn related experiences from practices to cope with PI.At present,the knowledge assessment tool used by most researchers was PUKAT developed by Beeckman,et al.in 2010,which can comprehensively evaluate the knowledge of nursing students and has been applied in Australia,Italy and other countries.The sinicization of PUKAT was introduced in 2016 [26],but it has not been broadly applied in China,which was suggested to be applied in the further studies.
For the emotional aspect,nursing student showed a positive attitude towards PIP.Most nursing students feel confident to manage most of the wound care and become more active with the improvement of learning grade and the increase of clinical practice experiences.School education and clinical practices throughout the beginning and end of study made nursing students pay more attention to PIP,and qualify themselves as having the basic skills to prevent PI.However,due to the lack of practical experiences,they believed that the prevention procedures for PI were complicated,leading to the low confidence.Negative attitude was reported to be one of the causes of PI,thus,it was important to have a positive attitude towards PI [27].Therefore,for the future teaching programs,it is necessary to strengthen the practices of nursing students and increase the chances of communication between nursing students and clinical nurses,especially the nurses dealing with PI,so that they can be familiar with the clinical nursing works as soon as possible,which may help in correcting their attitudes.
The readiness of nursing students to prevent PI has been controversial for a long time.Some nursing students believed that their abilities and confidence to prevent PI were insufficient,while others indicated that their present knowledge was sufficient to deal with clinical PI.This may be resulted from the various questionnaires in each study,and the time and region of the questionnaires were also different.In addition,the results of the self-assessment reports were rather subjective,and the awareness of the nursing students on themselves would affect their assessments of the abilities.Therefore,it is strongly recommended that qualitative re-search designs can be used in the future researches in order to clearly and accurately describe the abilities of nursing students to prevent PI.
Nursing students were not educated about complete PIP or wound care treatments during their study programs.However,it was believed that the education they received has enabled them to cope with clinical difficulties.Electronic intervention can improve the knowledge of PIP in nursing students.Since half of the relevant knowledge of nursing students came from school teaching,the basic nursing knowledge in school was the premise of entering clinical work.However,
with the developed information technology and rapid communication strategy,the update speed of knowledge in books was far behind the network information,which can no longer meet the needs of nursing students.Through clinical practices and self-study,the lack of knowledge of nursing students can be supplemented in time.In the future teaching processes,novel teaching methods will be explored and the clinical practices of nursing students will be increased,so as to supplement the deficiencies of traditional teaching and improve the abilities of nursing students.
Conclusion
The present review revealed that the knowledge of nursing students to prevent PI was insufficient and their consciousness was also weak,however,their attitudes was positive.So far,there has been the controversy about the readiness of nursing students to prevent PI,and the relationship between the related knowledge and the attitude was not yet clear.Besides,the current school education did not meet the needs of nursing students.Better education methods,more clinical practices chances,and more opportunities to communicate with clinical staff were urgently needed for the nursing students.Additionally,appropriate measurement tools or hybrid methods should be adopted to accurately assess all aspects of the nursing profession.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Critical reflection on the role of senior staff nurse
- Nursing as a profession:Undergraduate female students’perception
- Current situation and influencing factors of classroom situation deviant behavior of undergraduate nursing students in colleges of traditional Chinese medicine
- Application of "Internet+" question-based teaching mode in the teaching of characteristic nursing of Dai medicine

