Stabilization of Uncertain Fractional Memristor Chaotic Time-Delay System Based on Fractional Order Sliding Mode Control
Dawei Ding, Fangfang Liu, Nian Wang* and Dong Liang
(1.School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Anhui University, Hefei 230601, China; 2.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing, Ministry of Education, Hefei 230601, China)
Abstract: Based on Lyapunov theorem and sliding mode control scheme, the chaos control of fractional memristor chaotic time-delay system was studied. In order to stabilize the system, a fractional sliding mode control method for fractional time-delay system was proposed. In addition, Lyapunov stability theorem was used to analyze the control scheme theoretically, which guaranteed the stability of commensurate and non-commensurate order systems with or without uncertainties and disturbances. Furthermore, to illustrate the feasibility of controller, the conditions for designing the controller parameters were derived. Finally, the simulation results presented the effectiveness of the designed strategy.
Keywords: fractional order system; time-delay; chaos control; uncertainty; sliding mode control
1 Introduction
Memristor is one of the four basic electronic components in a circuit. In the early 1970s[1], Leon Chua[2]tried to build six different mathematical relationships connecting four pairs of basic circuit variables, such as the voltagev, the currenti, the chargeq, and the fluxφ. Chua found that five of these relationships are well known:
while one is undefined, which is the relation between the fluxφand the chargeq. According to his seminal paper published in 1971, he assumed that the fourth basic circuit element should exist, which is characterized by aq(φ) curve. Then, memristor was named as the abbreviation of “memory resistor”[3].
Fractional calculus is a mathematical subject with a history of more than 300 years, which acts as the generalization of integer calculus. It has attracted more and more researchers’ attention in the last few years[4-5]. Many systems can be expressed as fractional differential equations, for example, economic system[6], biological population model[7], financial system[8], chaotic and hyper-chaotic systems[9-12].
Time-delay usually exists in a variety of engineering systems, such as biology, chemical processes, and economical systems, while their forms are not the same. For example, when the feedback delay occurs in a closed-loop system, it manifests as transportation and communication lag. The dynamic behavior of the system is usually affected by such a tiny delay. Thus, more and more researchers have studied systems with time-delay, such as biology[13], economy[14], system control[15-17], and so on.
In addition, delayed fractional system is proved useful in signal processing[18], financial system[19], and biology[20], so that the research of fractional time-delay system must be considered. The fractional order delayed system has been studied by a lot of investigators[21-26]. In Ref. [22], the fractional delayed Hopfield neural networks were discussed, and two types of them were studied. In Ref. [23], the existence of solutions near the equilibrium point for fractional differential equations with time-delay was analyzed. In Ref. [24], explicit formulas and stability of bifurcation periodic solutions were derived based on central manifold reduction. Additionally, chaotic behavior of fractional time-delay systems has become one of the research hotspots[27-29]. In Ref. [27], the chaotic phenomena in Bloch model with time-delay were discussed. It was found that the delay has an effect on the stability of the system. The Hopf bifurcation of fractional memristor chaotic delayed systems was studied by taking the time-delay and fractional order as bifurcation parameters in Ref. [28]. In Ref. [29], the chaotic dynamics of fractional order logistic maps with delays were analyzed, and a discrete chaotic attractor was found.
On the other hand, sliding mode control (SMC) is such an effective nonlinear control technology that a large number of SMC methods have been developed in the past few decades. For many fractional order system control schemes, impulsive control[30], active control[31], passive control[32], pinning adaptive control[33], and generalized projective control[34]are included. Main characteristics of SMC are that it is insensitive to the changes or disturbances of the system parameters and it has rapid transient response. Therefore, scholars have studied the sliding mode control strategy in the last few years[35-38]. The control of the fractional systems was studied by SMC.
With the above discussions, the innovation of this paper lies in the combination of sliding mode technology and fractional calculus theory, where fractional sliding mode controller is designed to control chaos of fractional memristor time-delay system. Therefore, a fractional sliding mode method based on Lyapunov stability theory is proposed and a suitable control structure is designed. Although many studies have discussed the application of sliding mode controllers in fractional chaotic systems, few have studied them in fractional memristor delayed chaotic systems. The controller makes the state of the system asymptotically stable, and there are external disturbances in the systems of commensurate and non-commensurate order.
The organizational structures of the article are as follows: the second section gives the definitions for fractional calculus and memristor model. In the third section, a delayed chaotic system based on fractional memristor is discussed. On the basis of the sliding mode control strategy theory, the controller of fractional chaotic time-delay system is designed in the fourth section, and the design process of fractional sliding mode approximation is introduced. The simulation results are given in the fifth section. At last, the sixth section gives some conclusions.
2 Basic Definitions and Preliminaries
2.1 Definitions
Definition1The fractional Caputo derivative of fractionalqis defined as[39]
(1)
where Γ is a gamma function,

(2)
Γ(z+1)=zΓ(z)
(3)
Definition2The Laplace transform of Caputo derivative is defined as[40]
(4)
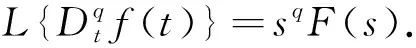
2.2 Memristors
The memristor is a circuit component used to display the relationship between flux (φ) and charge (z). The forms of memristor are as follows:
Firstly, flux-controlled memristor is defined as
(5)
whereW(φ) is the memductance.
Secondly, charge-controlled memristor is defined as
(6)
whereM(z) is the memristance, andvM,iM,z, andφare the voltage, current, charge, and flux in the memristor, respectively.
3 Description of Fractional Order Delayed System
The memristor-based chaotic delayed system has been investigated in Ref.[41]. The circuit system includes nonlinear active memristor with time-delay and capacitor, as depicted in Fig.1. The following equations describe the system:
(7)
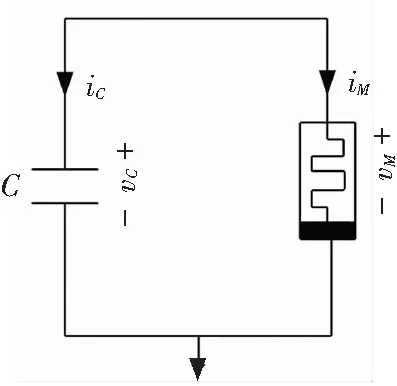
Fig.1 Chaotic circuit system based on delayed memristor
Then, Kirchhoff’s circuit law was applied to the system (Fig.1) and the following circuit equations were obtained:
(8)
wherexis the state variable through memristor,τis the time-delay, anda,b,c,α, andβare all constants. The equations were derived as follows:
(9)
wherey=vC(t),xτ=x(t-τ),m=-α/C, andn=-β/C.
Therefore, the time-delay system based on fractional memristor can be expressed by equations
(10)
whereq1andq2are fractional order of memristorMand capacitorC.
The analyses of chaotic dynamic based on the Lyapunov exponent are presented in Ref.[28].
4 Design of Fractional SMC
In order to stabilize the fractional memristor-based chaotic delayed system, control inputu(t) was added to Eq.(10) and the controlled system can be rewritten as
(11)
Then, fractional sliding mode controller was designed. First of all, fractional sliding mode surface was constructed, which indicates required system dynamics. Therefore, the following sliding mode surface was selected:
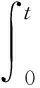
(12)
whereψ(t) is a function:
ψ(t)=my+nxy
(13)
The sliding mode surface and the derivative should meet the following conditions, which are on the basis of the sliding mode method:
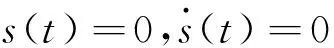
(14)
Thus, this conclusion is drawn:
Dq2y(t)+ψ(t)=0?Dq2y(t)=-ψ(t)
(15)
The next step was to develop a switching control method and drive any external state to the surface in a finite time[42-43]. The equivalent control law was deduced as
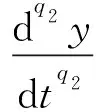
nxy=-2my-2nxy
(16)
The system was kept on a sliding manifold by using the switching control. In order to meet the sliding condition, the method of discontinuous reaching was selected as
ur(t)=Krsign(s)
(17)
whereKris the controller’s gain, and
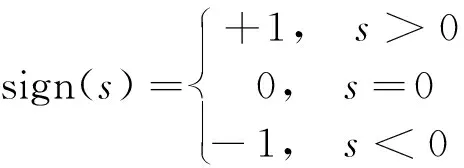
(18)
Thus, the total control method can be written as
u(t)=ueq(t)+ur(t)=-2my-2nxy+Krsign(s)
(19)
Theorem1Considering the chaotic time-delay system based on fractional order memristor (11) and the control law (19), the system is asymptotically stable when the controller’s gain satisfiesKr<0.
ProofChoose Lyapunov candidate as
(20)
Therefore,the time derivative is calculated as follows:
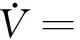
s·[my+nxy+u(t)+my+nxy]=
s·[2my+2nxy+u(t)]=
s·[2my+2nxy-2my-2nxy+Krsign(s)]=
s·Krsign(s)=Kr|s|<0
(21)
Theorem2If the controlled system (11) is disturbed by external interference, it can be expressed as follows:
(22)
whereΔf(x,y) andξ(t) are bounded that |Δf(x,y)|≤h1and |ξ(t)|≤h2. Under the sliding mode control (19), the chaotic system is asymptotically stable whenKr<-(h1+h2).
ProofWhen the Lyapunov candidate (20) is chosen, the floowing expression is obtained:
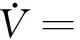
s·[2my+2nxy+Δf(x,y)+ξ(t)+u(t)]=s·[Δf(x,y)+ξ(t)+Krsign(s)]≤
|s|(h1+h2+Kr)<0
(23)
Thus, considering the uncertainties and disturbances, when the controller’s gainKr<-(h1+h2), the controller (19) can stabilize the system asymptotically.
Therefore, the two theorems are thoroughly proved.
5 Simulation Results
The dynamical behaviors and chaotic states of an uncontrolled fractional order memristor delayed system (10) in Ref. [28] were analyzed. Parameters for the system (10) are as follows:a=1,b=-2,c=5,m=0.5,n=-0.9. In this part, four cases are presented to prove the correctness of sliding mode control scheme. According to the improved Adams-Bashforth-Moulton predictor algorithm[44], the numerical simulation was carried out in this paper.
5.1 System without Uncertainties and Disturbances
5.1.1Commensurateordersystemwithoutuncertaintiesanddisturbances
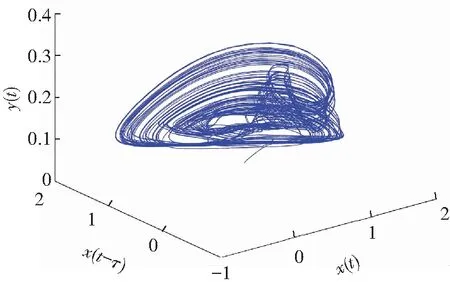
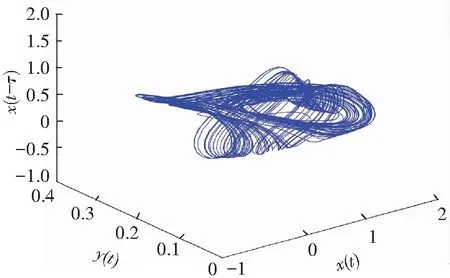
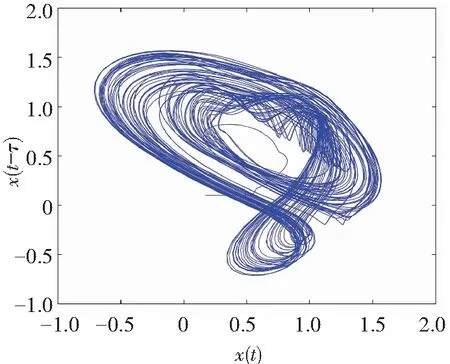
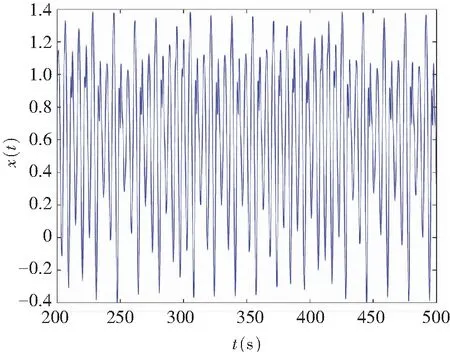
When it supposes the same derivative order in Eq.(10), i.e.,q1=q2=q, a commensurate order system can be obtained. The time-delay system based on fractional memristor is chaotic in case:q1=q2=0.88,(Figs.2-3).
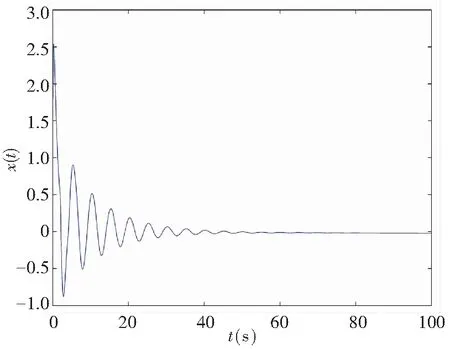
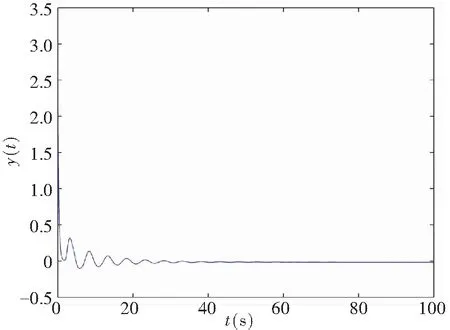
The controller’s gainKr=-1 was chosen in system (11) so as to satisfy Theorem 1. The control law (19) was used to stabilize the system, and the numerical simulations are shown in Fig.4. It proved that the theoretical results obtained are feasible for the system based on fractional order controlled time-delay memristor.
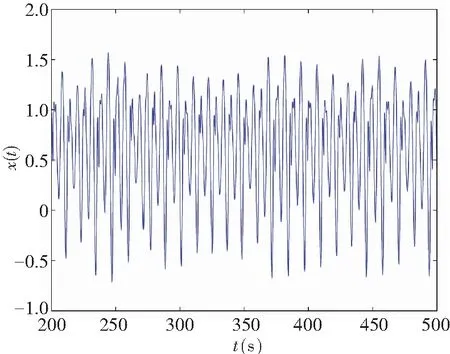
(a) Chaos on (x,t)-plane
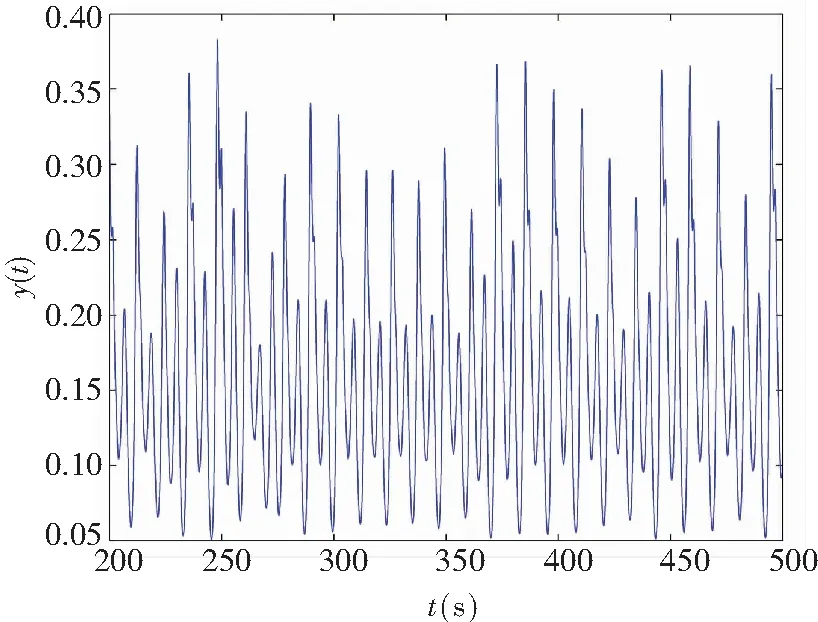
(b) Chaos on(y,t)-plane
However, when the gain of the controllerKr=0.01 was chosen in the system (11), it did not meet the conditions in Theorem 1. Fig.5 depicts the time domain of the delayed system under control, which is a mismatched control condition. It shows that the time domain curves are divergent. The counter example validated the feasibility of the designed control scheme.
5.1.2Non-commensurateordersystemwithoutuncertaintiesanddisturbances
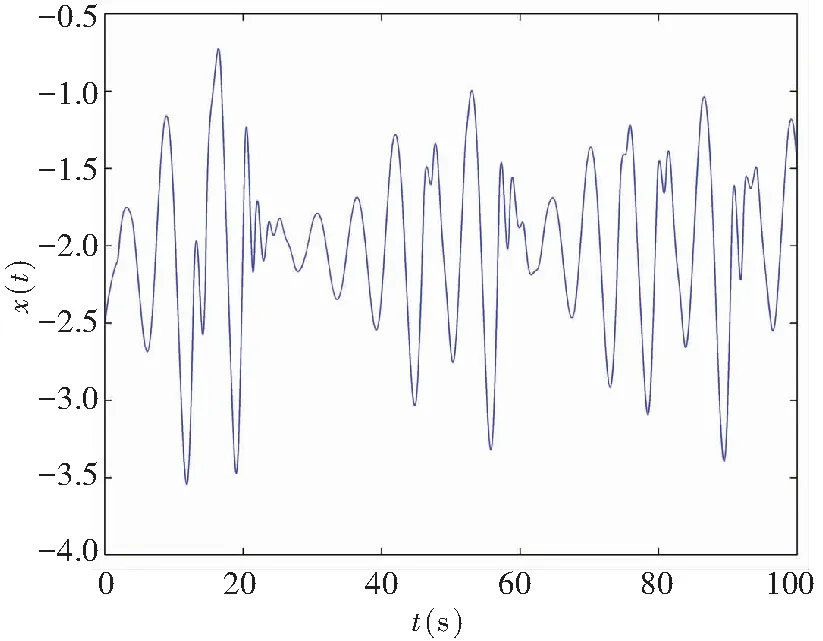
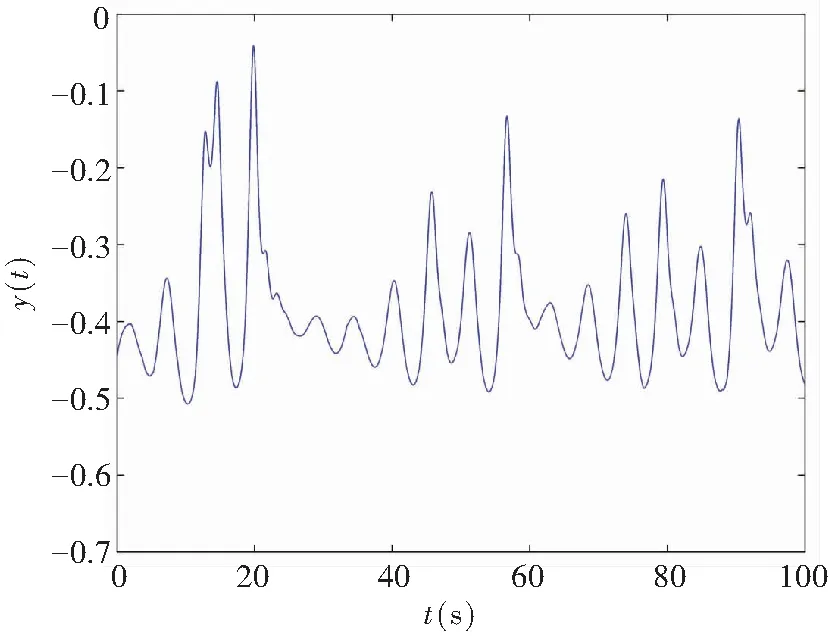
If the two orders of derivatives in Eq.(10) are different, for example,q1≠q2, then a non-commensurate order system is generally available. When the ordersq1=0.80 andq2=0.85, Figs.6-7 show some chaotic behaviors for the fractional memristor-based delayed system.
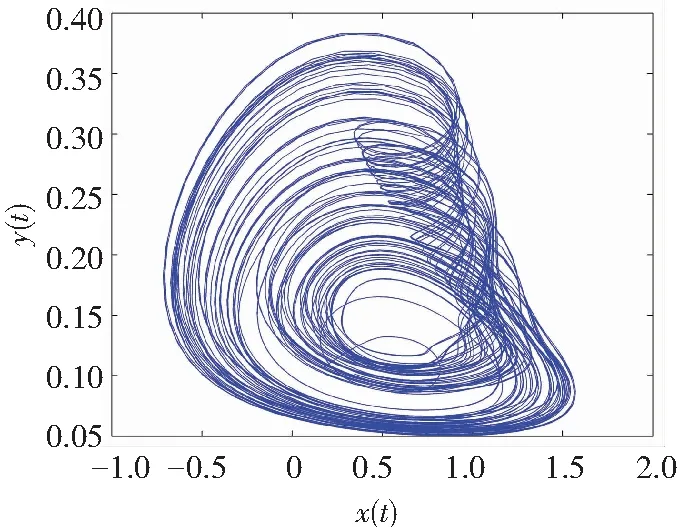
(a)Projection on (x,y)-plane
(c) Projection on (x,x(t-τ),y)-plane
(b) Projection on (x,y,x(t-τ))-plane
(d) Projection on (x,x(t-τ))-plane
(a)Projection on (x,t)-plane
(b) Projection on (y,t)-plane
(a)Projection on (x,t)-plane
(b) Projection on (y,t)-plane
(a)Chaos on (x,t)-plane
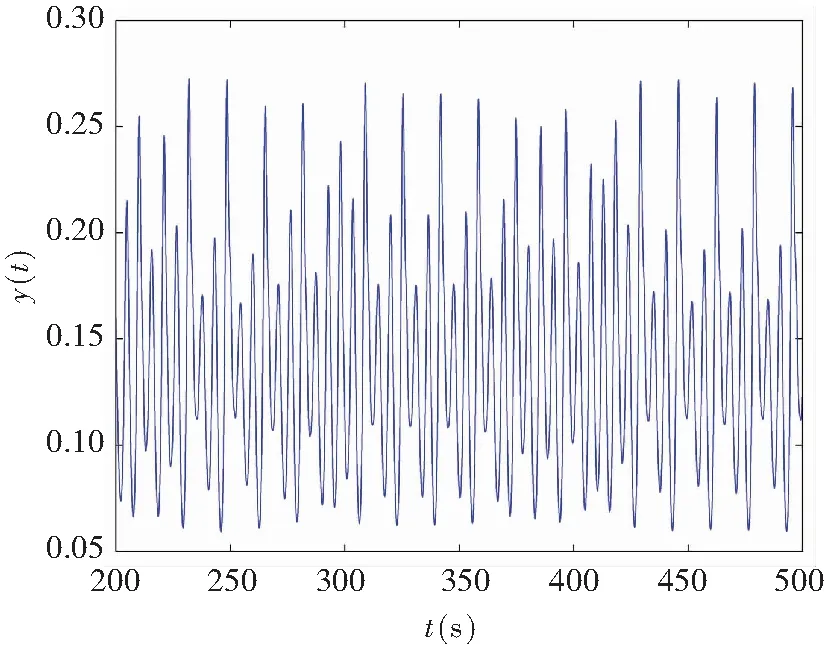
(b) Chaos on (y,t)-plane
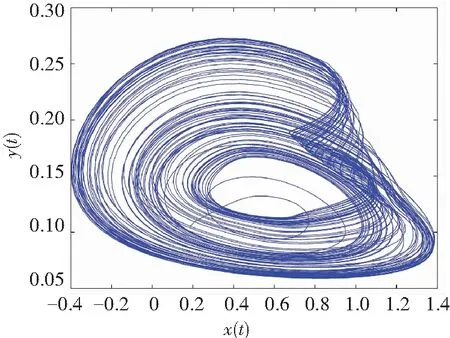
(a)Projection on (x,y)-plane
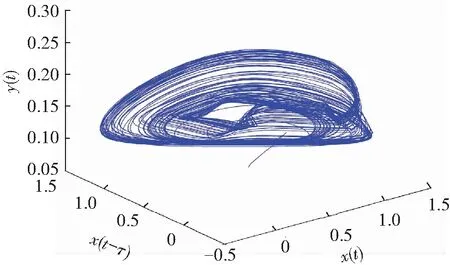
(c) Projection on (x,x(t-τ),y)-plane
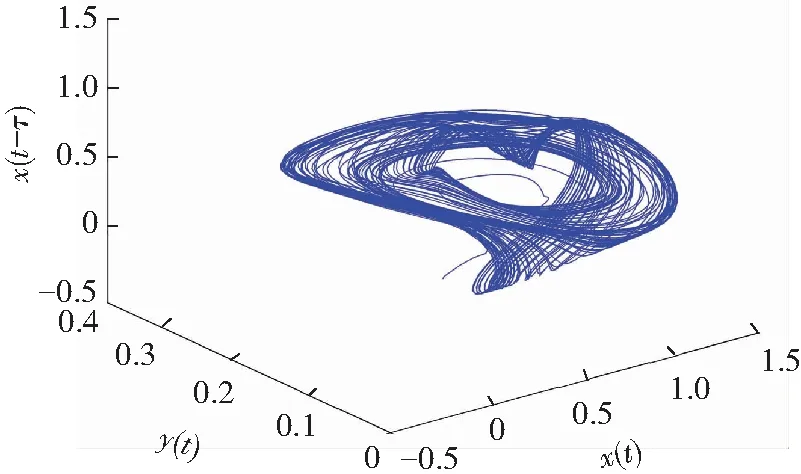
(b) Projection on (x,y,x(t-τ))-plane
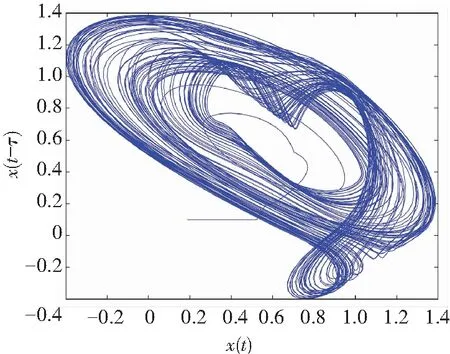
(d) Projection on (x,x(t-τ))-plane
When the controller’s gainKr=-1 was chosen in the system (11), it conformed to Theorem 1. The control law (19) was used to stabilize the system. Fig.8 shows the numerical simulations. Its results show that the obtained theoretical conclusions are effective for fractional order memristor-based delayed system under control.
In addition, controller’s gainKr=0.01 was chosen to prove the correctness of Theorem 1, but it did not meet Theorem 1. Fig.9 depicts the time state for the chaotic delayed system under control, which does not match the given control conditions. It can be concluded that the time domain curves are unstable.
5.2 System with Uncertainties and Disturbances
5.2.1Commensurateordersystemwithuncertaintiesanddisturbances
In this part, the memristor-based chaotic delayed system was disturbed by uncertaintyΔf(x,y)=0.45sin(πx)cos(πy) and disturbanceξ(t)=0.5sin(πt), where |Δf(x,y)|≤h1=0.45 and |ξ(t)|≤h2=0.5. Fig.10 depicts the system state response with the control law (19) when the controller’s gainKr=-1, and it satisfies Theorem 2.
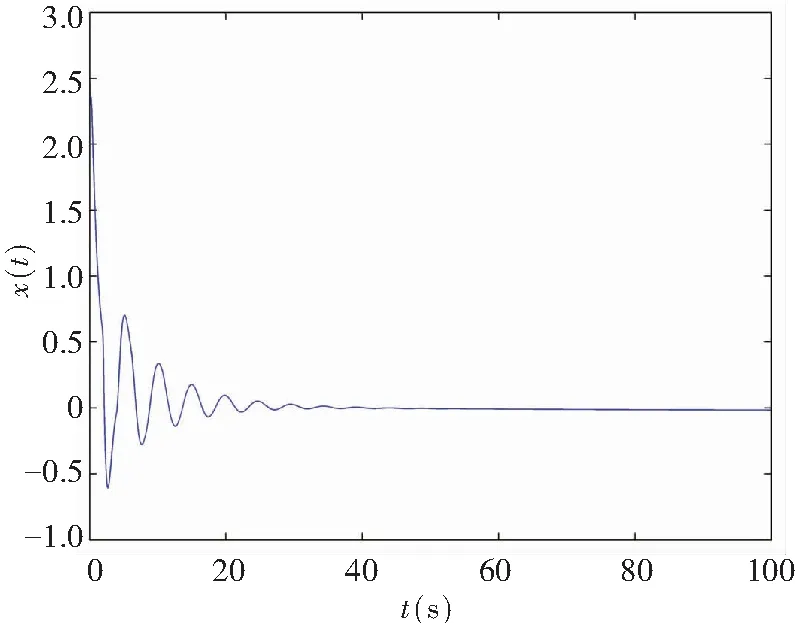
(a)Projection on (x,t)-plane
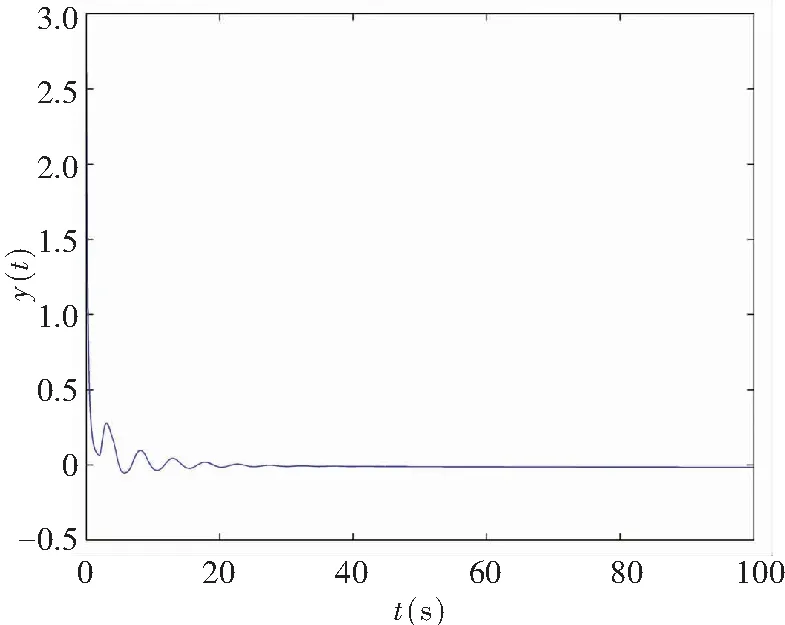
(b) Projection on (y,t)-plane

(a)Projection on (x,t)-plane
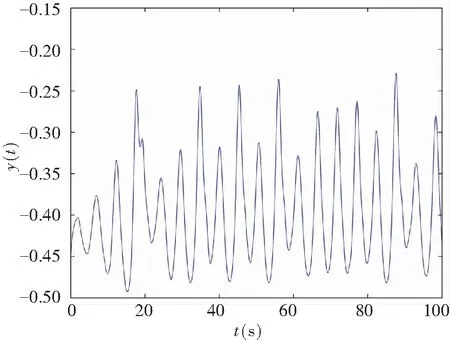
(b) Projection on (y,t)-plane
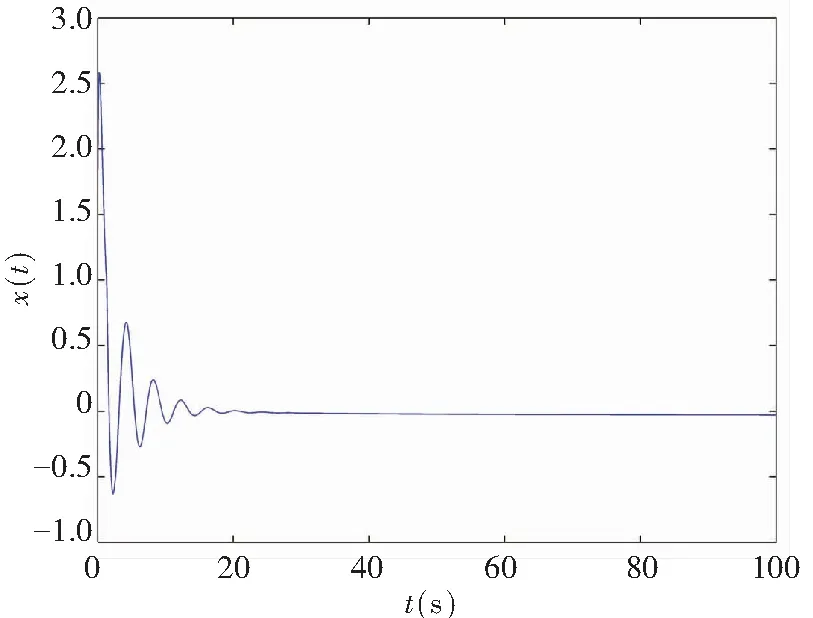
(a)Projection on (x,t)-plane
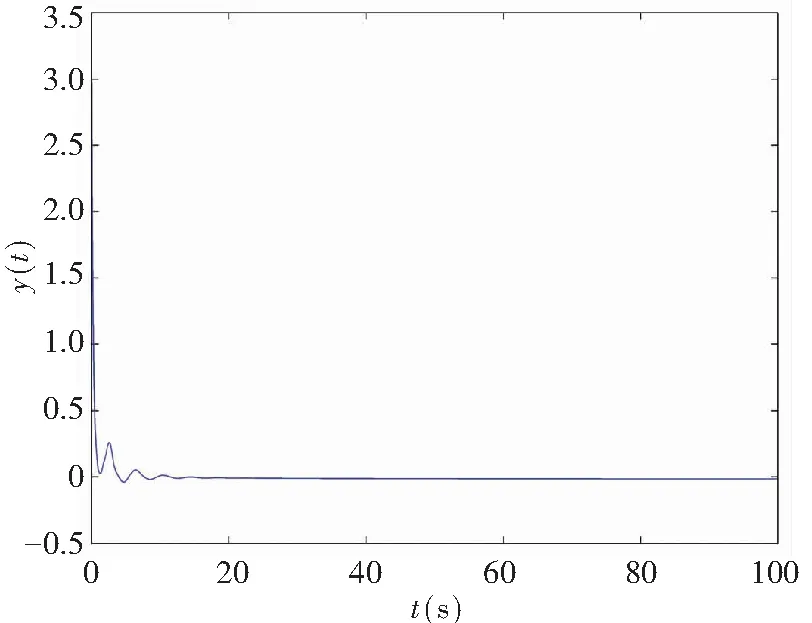
(b) Projection on (y,t)-plane
5.2.2Non-commensurateordersystemwithuncertaintiesanddisturbances
The memristor-based chaotic delayed system was disturbed by uncertaintyΔf(x,y)=0.45sin(πx)·cos(πy) and disturbanceξ(t)=0.5sin(πt), where |Δf(x,y)|≤h1=0.45 and |ξ(t)|≤h2=0.5. In the case of control law (19), the system time response is depicted in Fig.11 when the controller’s gainKr=-1, and it satisfies Theorem 2.
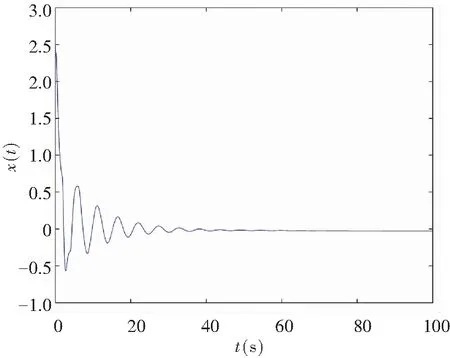
(a)Projection on (x,t)-plane
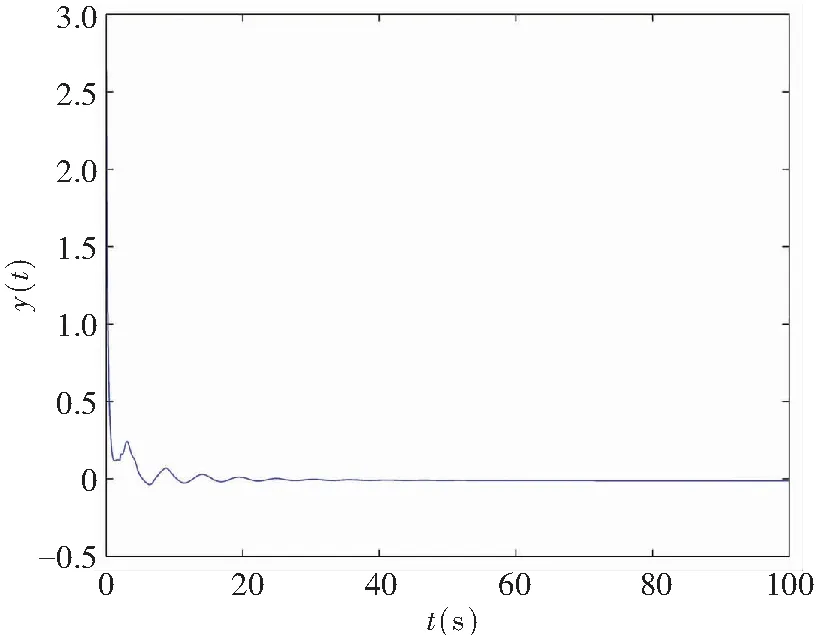
(b) Projection on (y,t)-plane
6 Conclusions
This paper investigated the chaotic time-delay system based on fractional memristor.A fractional sliding mode control method was designed to control chaotic behavior of the system.On the basis of Lyapunov theorem, the proposed control scheme could make the fractional delayed memristor-based chaotic system asymptotically stable, which proves that the designed control scheme is theoretically sound and robust.In the case of uncertainties and disturbances, the method was also applicable to the commensurate and non-commensurate order systems.The simulation results indicate that sliding mode control scheme has anti-interference ability.Finally, numerical simulations show that the designed control scheme can make the fractional order memristor-based time-delay system stable in finite time.Two counterexamples were used to verify correctness of the designed sliding mode control scheme.
 Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology(New Series)2020年4期
Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology(New Series)2020年4期
- Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology(New Series)的其它文章
- Design of a Reflective Intensity Optical Fibre Bundle Displacement Sensor
- Fingerprint Database Updating Using Crowdsourcing in Indoor Bluetooth Positioning System
- Effects of Environments on the Noise of Atomic Force Microscopy Cantilevers
- Microbial Community Profiles Related to Volatile Fatty Acids Production in Mesophilic and Thermophilic Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge Pretreated by Enzymolysis
- Characterisation of Bacteria-Based Concrete Crack Rejuvenation by Externally Applied Repair
- Nano-Silica Production by Rice Husk Combustion in a 0.7 MW Double-Circulating Fluidized Bed after Acid Pretreatment
