Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Combination strategies
Alexander Claudius Jordan, Jennifer Wu
Alexander Claudius Jordan, Department of Internal Medicine, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY 10016, United States
Jennifer Wu, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Perlmutter Cancer Center, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, NY 10016, United States
Abstract
Key words: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver neoplasms; Antineoplastic agents; Immunological; Protein kinase inhibitors; Angiogenesis inhibitors
INTRODUCTION
Worldwide, liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer death and the seventh most common cancer in terms of incidence[1].The most common liver cancer subtype is hepatocellular carcinoma[1].Over the last 40 years, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) incidence has risen by approximately three-fold in the United States[2].Between 2000 and 2009, the incidence rose by approximately 4.5% per year and 0.7% per year from 2010 to 2012[3].Between the years 2018 and 2040, global liver cancer incidence is expected to rise by approximately 62%, while the number of liver cancer deaths worldwide will rise by 64%[2].If HCC is detected at an early stage (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0 or A), surgical resection or ablation can be performed in select groups of patients[4].Approximately 70% of patients will develop evidence of recurrence following resection[4,5].If patients are not candidates for surgical resection, liver transplantation is offered to patients who meet the Milan criteria and provides a possibility of cure[4,5].Patients who are not eligible for surgery or liver transplantation are candidates for locoregional therapies, including trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) and ablation, if they have early- or intermediate-stage disease (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0-B), or systemic therapies if they have advanced disease (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C)[4].Multiple options for systemic therapy exist (Table 1).The tyrosine kinase inhibitors sorafenib and lenvatinib are approved for use as first-line therapy[6].Ramucirumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2, and the tyrosine kinase inhibitors regorafenib and cabozantinib are approved for patients previously treated with sorafenib, however, candidates for ramucirumab therapy must also have an alphafetoprotein (AFP) level of 400 ng/mL or greater[6,7].With the exception of lenvatinib, which produced an objective response rate (ORR) of 24.1%, the rest of the approved systemic therapies could only achieve an ORR in the range of 2 to 11%[8-12].Sorafenib, ramucirumab, regorafenib and cabozantinib were directly compared to placebo and increased overall survival by only 1.2 to 2.8 months[8,10-12].
In hopes of discovering therapies that could produce greater responses, investigators began to utilize checkpoint inhibitors in HCC patients, given their success in other malignancies and the contribution of the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA4 pathways to creating an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment[13-15](Table 2).Nivolumab demonstrated an ORR of 15% and 20% in the dose-escalation and doseexpansion phases of the CheckMate 040 trial, respectively, while pembrolizumab produced an ORR of 17% in the KEYNOTE-224 trial[13,14].Both agents were then Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for use in patients who had previously received sorafenib[16,17].However, neither nivolumab or pembrolizumab demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in overall survival (OS) in patients with unresectable HCC when compared to sorafenib or placebo in phase III trials, respectively[18,19].Other checkpoint inhibitors studied in HCC patients in completed phase II trials include the PD-1 inhibitors camrelizumab, the PD-L1 inhibitor durvalumab, and the CTLA4 inhibitor tremelimumab[20-22].In a phase II multicenter study (NCT02989922) involving 217 patients from Chinese medical centers with HCC who had failed or could not tolerate prior systemic therapy who were treated with camrelizumab, the ORR was 13.8%, with a six-month OS rate of 74.7%[20].Durvalumab demonstrated an ORR of 10.3% with a median OS of 13.2 months in a multi-center phase I/II study in a cohort of 40 patients with HCC, most of whom had received prior sorafenib[21].In a phase II study of tremelimumab in 21 patients from Spanish medical centers with advanced HCC and chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, the ORR was 17.6% with a median OS of 8.2 months[22].Tremelimumab caused a decrease in AFP levels of more than 50% in slightly more than one-third of all patients, and a reduction in HCV viral load in most patients[22].

Table 1 List of systemic therapies utilized in combination therapy
The relatively modest benefits of currently-available systemic therapies for patients with advanced or unresectable HCC underscore the need for novel and improved therapies.Although nivolumab and pembrolizumab did not reach their endpoints in phase III trials, checkpoint inhibitors in general remain the focus of multiple active trials[18,19](Tables 3-6).Updated results from the KEYNOTE-224 trial demonstrated that median OS was much greater in patients who responded to pembrolizumab compared to non-responders at the time of the first post-treatment scan, and that 30.8% of patients were alive at a median follow-up of 31.2 months[23].These results suggest that patients who respond to checkpoint inhibitors may have a durable response.Combination therapies involving the use of both a checkpoint inhibitor and another therapy may provide a greater benefit than single-agent immunotherapy if they can substantially improve overall response rates.This review will outline the main types of combination therapies currently under investigation, discuss the rationale behind their design, and summarize the main clinical trials evaluating their safety and efficacy in HCC patients.
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH PD-1/PD-L1 INHIBITORS PLUS CTLA-4 INHIBITORS
The combination of nivolumab plus ipilimumab has proven successful in improving treatment responses in multiple malignancies when compared to standard-of-care therapy[24-27].As a first line regimen, the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab has demonstrated superior ORR, OS, and progression-free survival (PFS) when compared to either agent alone in patients with metastatic melanoma, even after 48 months of median follow-up[24,28].Given what is known regarding the immune microenvironment of HCC, these results raised the question about whether or not the combination of a PD-1 inhibitor and CTLA-4 inhibitor can demonstrate durable clinical responses in advanced HCC patients that are superior to those seen with single-agent checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapies in HCC patients.
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab
The CheckMate 040 study (NCT01658878) randomized 148 HCC patients who were previously treated with sorafenib to three separate arms comparing various treatment regimens utilizing ipilimumab and nivolumab[29,30].Patients in Arm A received nivolumab 1 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 3 mg/kg every three weeks for four doses followed by nivolumab 240 mg every two weeks, patients in Arm B received nivolumab 3 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 1 mg/kg every three weeks for four doses followed by nivolumab 240 mg every two weeks, and patients in Arm C received nivolumab 3 mg/kg every two weeks plus ipilimumab 1 mg/kg given every six weeks[29].Initial results indicated that 37% of patients developed grade 3 or 4 toxicity, with rash and pruritus being the most frequently reported adverse effect[29].The ORR was 31%, and after 24 months of follow-up, the OS rate was 40%[29].This study was updated at the International Liver Cancer Association Conference in Sep 2019[31].All 3 arms achieved a similar ORR (Arm A - 32%, Arm B - 31% and Arm C - 31%), while Arm A achieved the longest median OS (22.8 months vs 12.5 months for Arm B and 12.7 months for Arm C) and the highest OS rate at 30 months (44%)[31](Table 2).The study remains active[30].

Table 2 Reported results of successful clinical trials evaluating immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
The rather innovative study design allowed investigators to compare the impact of various doses of nivolumab and ipilimumab on treatment response[29-31].The dosing schedule in Arms A and B was similar, however, the dose of ipilimumab was three times higher in Arm A, and patients in Arm C received ipilimumab less frequently than the other two arms[29].The higher dose of ipilimumab received by patients in Arm A compared to patients in Arms B or C may have been responsible for the improved median overall survival[29].Unsurprisingly, Arm A also had the highest number of treatment-related adverse effects, possibly due to the larger doses of ipilimumab the patients received, highlighting the inherent toxicity of this combination[31].Twenty-two percent of patients discontinued the combination due to drug-related adverse events, compared to 6% and 2% of patients in Arms B and C, respectively[31].Based on the results of CheckMate 040, the FDA has granted a priority review for nivolumab plus ipilimumab in the treatment of patients with advanced HCC who progressed on sorafenib as of November 2019[32].
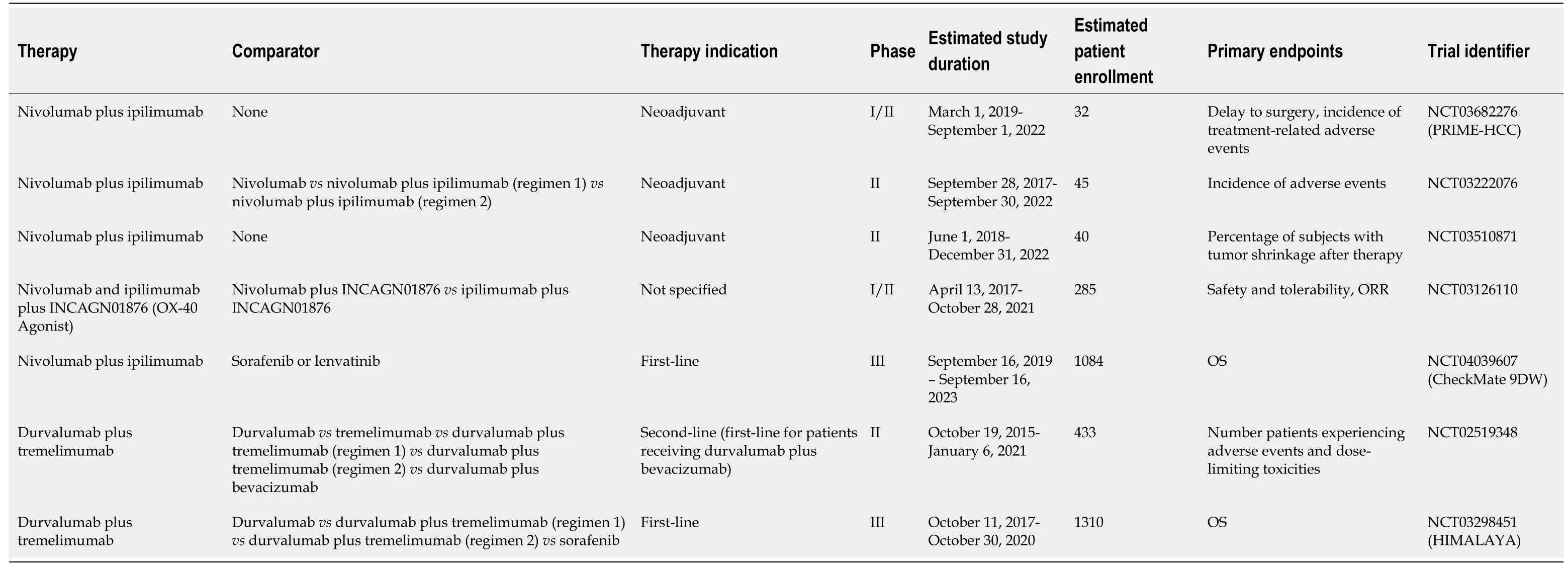
Table 3 Summary of active clinical trials evaluating checkpoint inhibitor combination therapy
There are multiple active clinical trials in addition to CheckMate 040 evaluating nivolumab plus ipilimumab for various treatment indications in HCC patients (Table 3).These include the phase III CheckMate 9DW clinical trial (NCT04039607) evaluating nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line therapy in comparison to sorafenib or lenvatinib in patients with advanced HCC[33].The primary endpoint is overall survival[33].If the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab demonstrates significantly improved OS compared to standard-of-care sorafenib or lenvatinib, it may become the new standard-of-care first-line therapy.However, the increased toxicity seen with this combination, especially if doses are similar to those used in Arm A of the CheckMate 040 trial, may lead to higher rates of therapy discontinuation[29].At least three separate studies will evaluate the safety and feasibility of neoadjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab administered prior to surgical resection[34-36].The phase II study (NCT03222076) sponsored by Anderson Cancer Center will randomize 45 patients with resectable HCC to receive adjuvant nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab prior to resection[34].If successful, further studies may explore whether neoadjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab can decrease the high recurrence rates observed after surgical resection[4,5].
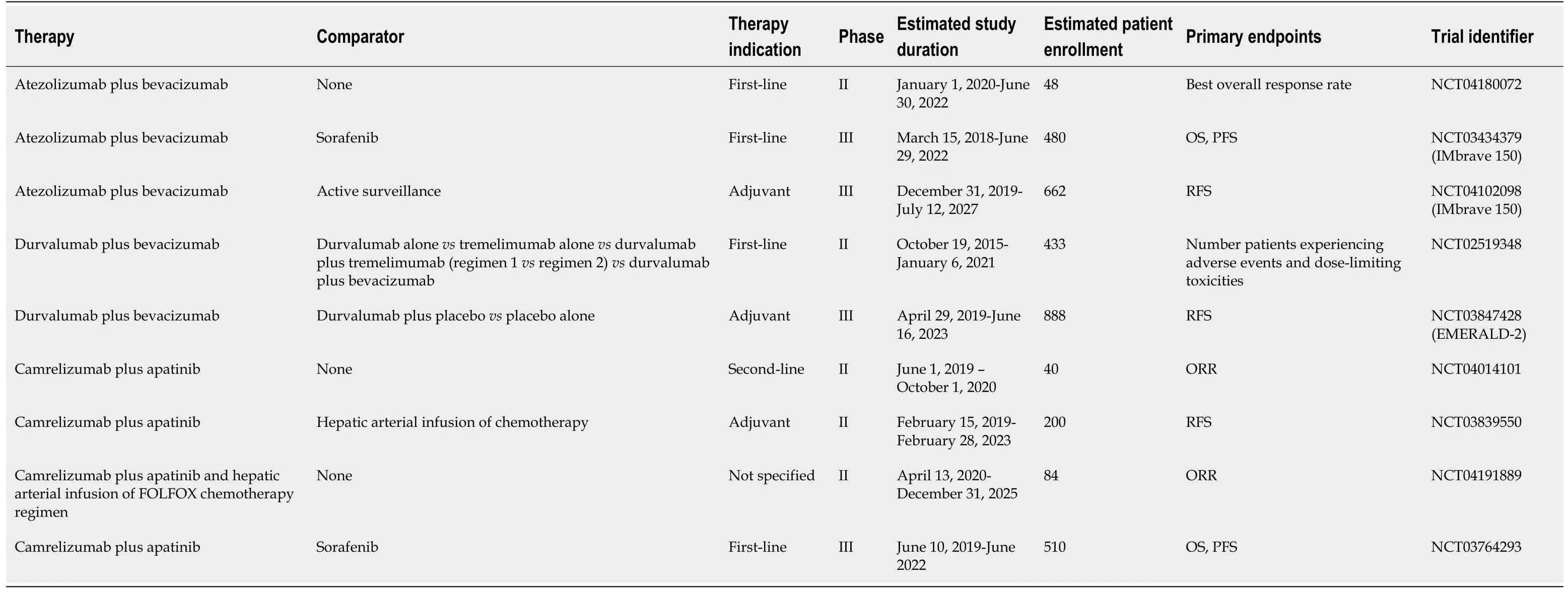
Table 4 Summary of active clinical trials evaluating combination therapy of checkpoint inhibitors plus vascular endothelial growth factor/factor receptor inhibitors
Durvalumab plus tremelimumab
The combination of durvalumab and tremelimumab was studied in a phase I/II trial (NCT02519348) in patients with unresectable HCC[37].The safety profile was deemed tolerable and an ORR of 15% was noted, according to results from the phase I portion of the study[37](Table 2).Common adverse effects included pruritus, fatigue, and elevated transaminases, which are similar to those noted in patients treated with durvalumab in phase II studies[21,37].The phase II portion of the study seeks to evaluate the safety and feasibility of durvalumab plus tremelimumab as second-line therapy[38](Table 3).This study will randomize 433 patients into five separate arms, in which patients with advanced HCC will receive either durvalumab or tremelimumab alone, durvalumab plus tremelimumab, or durvalumab plus bevacizumab[38].Two arms of the study will compare different regimens of durvalumab plus tremelimumab[38].Additional active studies involving this combination include the phase III HIMALAYA clinical trial (NCT03298451) which will compare durvalumab plus tremelimumab to sorafenib or durvalumab alone as first-line therapy in approximately 1310 advanced HCC patients from multiple countries[39](Table 3).Overall survival is the primary endpoint[39].
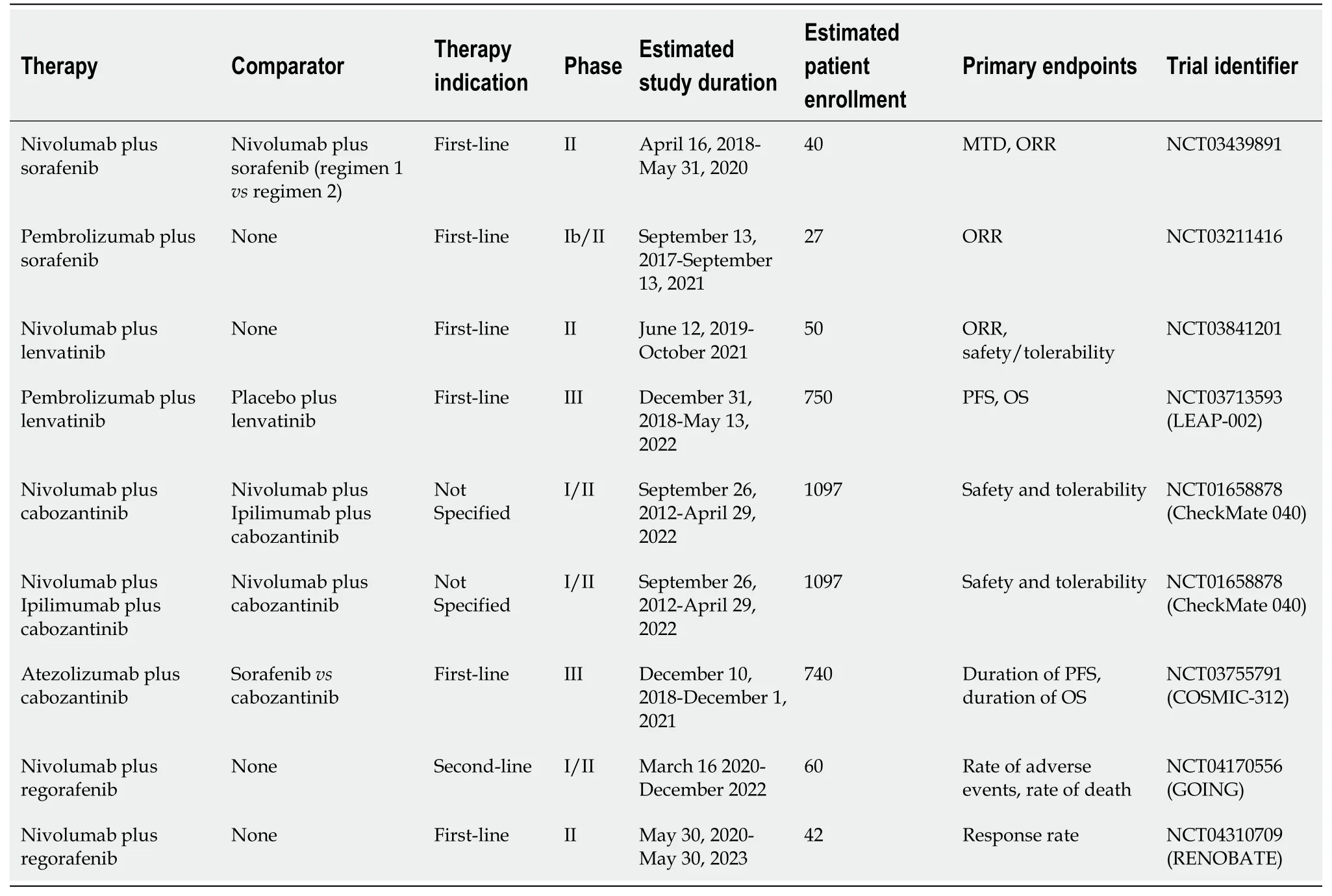
Table 5 Summary of active clinical trials evaluating combination therapy of checkpoint inhibitors plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors
It remains to be seen whether the combination of durvalumab plus tremelimumab will have a similar toxicity profile as nivolumab plus ipilimumab.If durvalumab plus tremelimumab can demonstrate a high ORR with a comparatively lower rate of immune-related adverse effects, then it may become a viable alternative for HCC patients who have failed prior systemic therapies and cannot tolerate nivolumab plus ipilimumab due to adverse effects.If the dosing schedule utilized in the phase I/II clinical trial (NCT02519348) is adopted, this may minimize toxicity given the relatively infrequent dosing schedule of every four weeks[37].Although the most common sideeffects seen in patients treated with either combination include liver function test abnormalities and skin ailments such as pruritus or rash, the CheckMate 040 study demonstrated that 22% of patients discontinued therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab due to treatment-related toxicity, compared to 7.5% of patients receiving durvalumab and tremelimumab in the NCT02519348 trial[31,37].Given the ability of tremelimumab to reduce HCV viral loads, this combination may be preferred for patients with chronic hepatitis C infections[22].
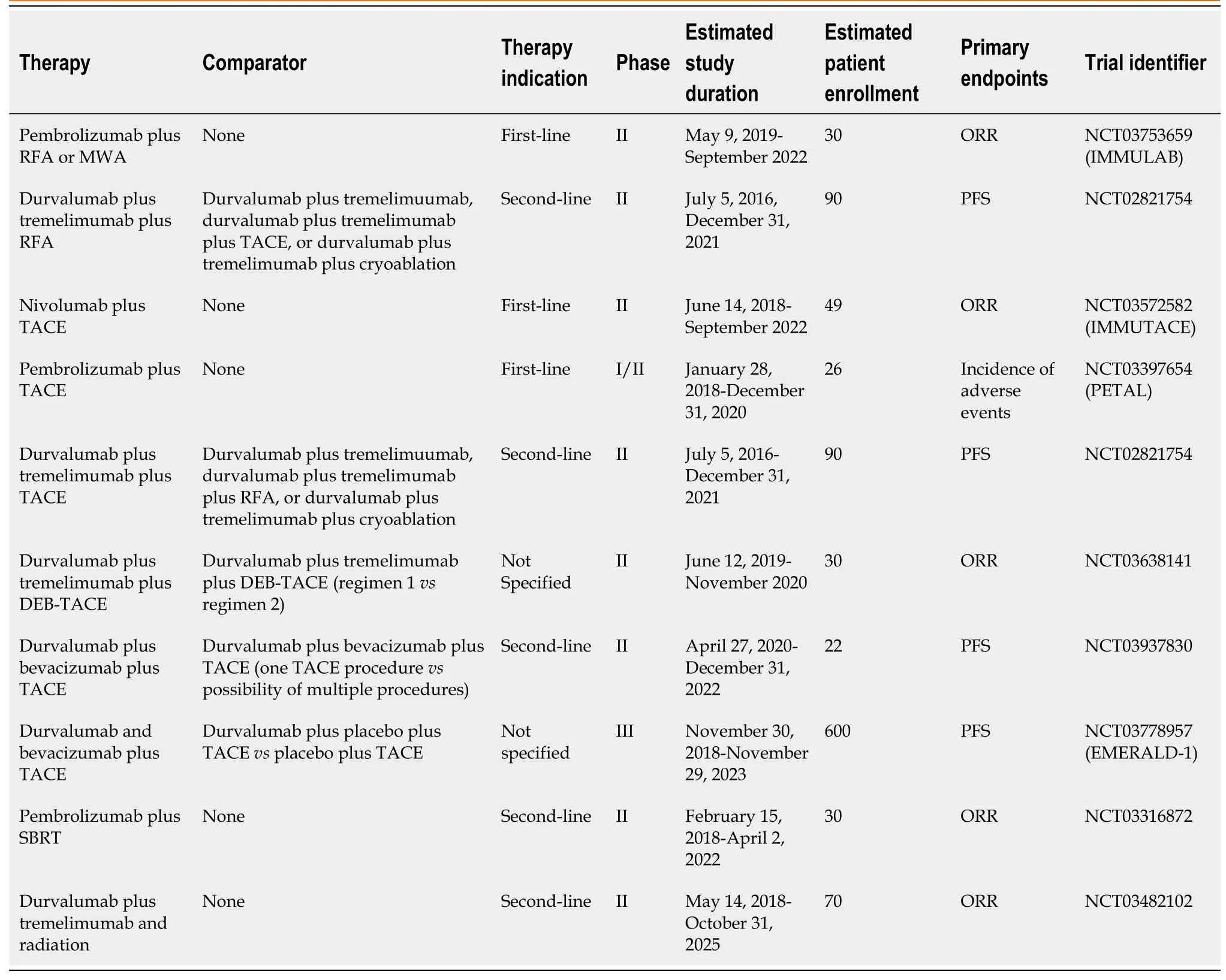
Table 6 Summary of active clinical trials evaluating combination therapy of checkpoint inhibitors plus ablation, trans-arterial chemoembolization, or radiation
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS PLUS OX40 AGONISTS
OX40 is a co-stimulatory receptor that is expressed by CD4 and CD8+ T-cells after antigen stimulation[40].Treg cells can also express OX40[40].OX40 agonists, which are monoclonal antibodies that bind OX40, induce T-cell expansion and persistence and may be able to suppress Treg activity[40].The clinical use of a monoclonal antibody targeting OX40 was deemed safe following a phase I study (NCT01644968) in 30 patients with various malignancies, with the most common adverse effects including fatigue, rash, lymphopenia, fever, and pruritus[41].Twelve patients in demonstrated a reduction in the size of at least one individual metastasis[41].
A combination strategy utilizing OX-40 agonists in conjunction with checkpoint inhibitors may be a viable option in the treatment of HCC.PD-1/PDL1 or CTLA4 blockade and OX40 agonism administered together may produce a greater activation of the immune system due to the targeting of distinct pathways.The use of an OX-40 monoclonal antibody in conjunction with an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody in mice models of ovarian cancer produced responses that were superior than those from either agent alone[42].A phase I/II clinical trial (NCT03241173) was performed to determine whether this form of combination therapy is safe and effective in patients with solid malignancies including HCC[43].The study contained three separate arms, including two arms where nivolumab or ipilimumab alone were given with the OX-40 inhibitor INCAGN01949, and another arm where both checkpoint inhibitors and INCAGN01949 were administered together[43].Results are pending[43].An additional phase I/II trial sponsored by Incyte Biosciences (NCT03126110) is active and is similarly designed to the first trial, but is employing the OX40 agonist INCAGN01876 in patients with solid malignancies, including HCC[43,44](Table 3).
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS PLUS VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR OR VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR INHIBITORS
Anti-angiogenic agents have been a focus of research in HCC due to the relatively high vascularity of HCC tumors, however, studies suggest they may also have beneficial effects on the immune system[45-47].VEGF expression can modulate the immune systemviavarious mechanisms, leading to immunosuppression[46,47].VEGF molecules can inhibit leukocyte adherence to the endothelium, inhibit the development of dendritic cells, and promote Treg proliferation[46,47].The combination of checkpoint inhibitors and VEGF or vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitors may cause a greater net activation of the immune system than checkpoint inhibitors alone due to the added effect of VEGF inhibition.
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Bevacizumab, a VEGF inhibitor, is currently approved for the treatment of multiple malignancies, including metastatic colorectal cancer, non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer, and ovarian cancer[48].Bevacizumab was studied in a phase II trial in 46 patients with unresectable HCC and treatment resulted in a median PFS of 6.9 months and an OS rate of 53% at 1 year, 28% at 2 years, and 23% at 3 years[49].However, 11% of patients developed clinically significant bleeding, including one patient who suffered a variceal bleed that was ultimately fatal[49].Another phase II study evaluating singleagent bevacizumab in advanced HCC patients found that 9% of patients developed gastrointestinal bleeding[45].Atezolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets PD-L1 and prevents its binding to the PD-1 receptor and the B7.1 molecule[50].It has been approved either as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer, small-cell lung cancer, urothelial carcinoma, and breast cancer[51].The combination of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab demonstrated prolonged progression-free survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients in a phase III trial with an acceptable safety profile[52].
Initial data testing this combination in HCC patients originates from a phase Ib study (NCT02645531) evaluating this combination as first-line therapy in 26 patients with advanced HCC[53].Approximately 35% of patients developed grade 3-4 toxicities with hypertension being the most frequently reported adverse event, with an ORR of 62%[53].In late 2019, the study authors reported that patients who received the combination therapy in Arm F demonstrated significantly better median progressionfree survival (5.6vs3.4 months,P= 0.0108) when compared to atezolizumab alone[54].The most common side effects seen in the patients randomized to combination therapy included proteinuria, fatigue and rash[55].Patients in Arm A had a median overall survival of 17.1 months[55].Initial phase III data has been reported from the IMBRAVE 150 trial that randomized approximately 501 systemic treatment-na?ve patients with unresectable HCC to receive atezolizumab plus bevacizumab or sorafenib alone[56].Preliminary data published in November 2019 demonstrated an improved PFS (6.8vs4.3) and OS hazard ratio (0.58) with the combinationvssorafenib alone[56](Table 2).Recent quality-of-life data from IMbrave150 presented in January 2020 revealed that patients taking atezolizumab plus bevacizumab had delayed time to deterioration of quality-of-life[57].Patients in the combination arm reported greater time to deterioration of physical functioning, diarrhea, loss of appetite, fatigue, and pain[57](Table 4).
These data suggest that atezolizumab plus bevacizumab may become an alternative regimen for patients with advanced HCC due to its relatively acceptable toxicity profile when compared to a dual checkpoint inhibitor regimen, and improved efficacy when compared to sorafenib alone.The study remains active[58].
Other active clinical trials evaluating this combination include the NCT04102098 phase III trial, a part of the IMbrave 150 study, which will randomize 662 patients with resectable HCC and a high risk of recurrence to receive atezolizumab plus bevacizumab or surveillance as adjuvant therapy[59](Table 4).Given the significant improvement in PFS seen when this combination is used as first-line therapy, it may also be successful as adjuvant therapy and reduce the high recurrence rates often seen post-resection[4-5,56,59].A single-arm phase II trial (NCT04180072) will enroll 48 patients with advanced HCC and chronic HBV infection, allowing the investigators to determine whether HBV infection has any significant effect on the safety and effectiveness of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab[60](Table 4).
Durvalumab plus bevacizumab
The results of the studies testing atezolizumab and bevacizumab may be generalizable to other checkpoint inhibitors, such as durvalumab, if used in combination with bevacizumab or other VEGF inhibitors given similar mechanisms of action.The combination of durvalumab plus bevacizumab is being studied in multiple different trials, including the aforementioned phase II study (NCT02519348) in patients with advanced HCC as first-line therapy[38](Table 3).The phase III EMERALD-2 trial (NCT03847428) will compare durvalumab plus bevacizumab to either durvalumab alone or placebo as adjuvant therapy after either ablation or resection in HCC patients with a high risk of recurrence[61](Table 4).
Durvalumab plus ramucirumab
A phase I trial (NCT02572687) is evaluating the safety of the combination of ramucirumab and durvalumab in patients with advanced gastrointestinal or thoracic malignancies including hepatocellular carcinoma[62].Although no reported phase II or III trials are currently active, if this combination proves to be safe with a tolerable sideeffect profile, further study is warranted based on the results of the REACH-2 trial to determine if this combination is most effective in patients with an AFP greater than 400[10].
Camrelizumab plus apatinib
Apatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of VEGFR2 that binds to its target with ten-fold more affinity than sorafenib, and is currently approved in China for use in advanced gastric cancer patients[63,64].Apatinib has demonstrated a tolerable safety profile with evidence of anti-tumor activity in HCC patients as single-agent therapy[64].In a murine model of lung cancer, the combination of apatinib and an anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody inhibited tumor growth in a synergistic fashion with a notable increase in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes[65].The combination of apatinib and camrelizumab was studied in a phase Ia and Ib trial (NCT02942329) that enrolled 43 Chinese patients with various gastrointestinal malignancies, including gastric cancer, esophagogastric junction cancer, and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[63].This combination was thought to have a tolerable safety profile, with the most common side-effects being hypertension and an elevated AST[63].Half of all HCC patients demonstrated a partial response, a response similar in magnitude to results from the initial Phase 1b trial (NCT02715531) testing first-line atezolizumab and bevacizumab[53,63].Multiple studies are evaluating this combination in distinct HCC patient populations[66-69](Table 4).A phase II study (NCT04014101) seeks to determine whether camrelizumab plus apatinib is safe and effective in patients with advanced HCC as second-line therapy[66].Another phase II study (NCT03839550) will determine whether this combination is superior to hepatic arterial infusion of chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting, with recurrence-free survival as the primary endpoint[67].The phase II TRIPLET study (NCT04191889) will evaluate the safety and efficacy of the combination of FOLFOX chemotherapy infused directly into an artery perfusing the tumors, followed by camrelizumab and apatinib in 84 patients with advanced HCC[68].A phase III study (NCT03764293) evaluating camrelizumab and apatinib as first-line therapy in advanced HCC patients will report both OS and PFS as primary endpoints[69].The aforementioned studies are primarily being carried out in Chinese medical centers, which will limit the external validity of the results and require additional studies before their findings can be generalized to other patient populations[66-69].
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS PLUS MULTITARGETED TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS
Sorafenib, lenvatinib, cabozantinib, and regorafenib all have activity against VEGF receptors and may mitigate the immunosuppressive activity of VEGF[6].Although the exact mechanisms of action are unclear, TKIs can modulate the immune system[70-72].Sorafenib decreased the populations of Tregs and CD8+ T cells that expressed PD-1 in the tumors of mice models of HCC[70].Anin-vitrostudy demonstrated that sorafenib could increase effector-T cell activation and inhibit Treg suppression of effector-T cells, albeit at sub-pharmacologic doses[71].Sorafenib has also been shown to restore the ability of dendritic cells to activate T cellsin vitro[72].In mouse models of HCC, lenvatinib demonstrated greater antitumor activity in immunocompetent mice when compared to sorafenib but not in immunodeficient mice, suggesting that the increase in activity may be related to immunomodulatory effects[73].
Given that the mechanism of action of TKIs differs from that of checkpoint inhibitors, pairing a TKI with a checkpoint inhibitor may produce responses that are either additive or synergistic.Additionally, responses to combination therapy with checkpoint inhibitors and TKIs may be more effective than responses to VEGF or VEGFR inhibitors alone because TKIs inhibit multiple distinct signaling pathways.If these combination therapies are proven effective, their safety may be of concern.Common toxicities observed with the various TKIs include diarrhea, skin rashes, fatigue, nausea, elevated aspartate aminotransferase levels, and rash[8,9,11,12].The sideeffect profiles of checkpoint inhibitors partially overlap with those of the TKIs, and it is unclear whether this may lead to greater toxicity when compared to single-agent regimens[13,14,24,31].
Sorafenib plus checkpoint inhibitors
The safety and effectiveness of sorafenib plus pembrolizumab as first-line therapy will be evaluated in 27 patients with advanced or metastatic HCC participating in a phase Ib/II study (NCT03211416) by the Roswell Park Cancer Institute[74](Table 5).One phase II trial (NCT03439891) will study the combination of nivolumab plus sorafenib as firstline therapy in patients with advanced HCC[75](Table 5).ORR is one of the primary endpoints for both studies[74,75].
Cabozantinib plus checkpoint inhibitors
Studies testing treatment regimens involving cabozantinib plus immunotherapy include the aforementioned CheckMate 040 study (NCT01658878), which contains two separate arms in which patients are receiving nivolumab plus cabozantinib and nivolumab and ipilimumab plus cabozantinib[30](Table 2).Initial data from this portion of the CheckMate 040 study has been reported[76].Seventy-one patients with advanced HCC who were sorafenib-na?ve or who had previously been treated with sorafenib were randomized to receive nivolumab plus cabozantinib or nivolumab plus ipilimumab and cabozantinib[76].The ORR was 26%vs17% for those who received all three drugs or nivolumab plus cabozantinib, respectively[76](Table 2).Median PFS was 6.8 for the three-drug regimen arm and 5.5 for the two-drug regimen arm[76](Table 2).The three-drug regimen caused significantly more toxicity, with 71% of patients in that arm reporting grade 3-4 adverse effects,vs42% of patients in the two-drug arm[76].Approximately 20% of patients in the three-drug arm discontinued the drug secondary to toxicity, compared with 3% of the patients in the two-drug arm[76].Although the three-drug regimen demonstrates promise based on these early results, its high rate of toxicity may prohibit widespread adoption as standard-of-care therapy.Other checkpoint inhibitors, such as atezolizumab, are being studied as part of combination regimens involving cabozantinib[76](Table 5).The phase III COSMIC-312 trial (NCT03755791) will study the combination of cabozantinib and atezolizumabvssorafenib as first-line therapy in a multi-national group of patients with advanced HCC[77](Table 5).
Lenvatinib plus checkpoint inhibitors
A phase 1b trial (NCT03006926) in which 18 patients were given a combination of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab demonstrated an acceptable safety profile, with hypertension and poor appetite reported as the most common adverse effects[78].One phase II study (NCT03841201) will test the combination of lenvatinib and nivolumab in a cohort of patients from a German medical center with ORR and safety and tolerability measures as the primary endpoints[79](Table 5).A phase III study (NCT03713593) sponsored by Merck will test the combination of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in an international cohort of approximately 750 patients with advanced HCC with PFS and OS as the primary endpoints[80].Patients will be randomized to receive either lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or lenvatinib plus placebo[80](Table 5).
Regorafenib plus checkpoint inhibitors
Multiple studies evaluating regorafenib in conjunction with PD-1 inhibitors are active.They include a phase Ib trial sponsored by Bayer[81]that will elucidate the safety profile of regorafenib plus pembrolizumab.Recent results were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium in January 2020[82].Thirty-five patients had been treated, with 29 in the dose-defining cohort and 6 in the dose-expansion cohort[82].Fifteen patients had discontinued treatment, with either clinical or radiologic disease progression as the most common reason[82].Eighty-nine percent of patients experienced grade 3 or 4 treatment-emergent adverse events[82].The multi-center phase II (GOING) trial (NCT04170556) and the single-center phase II (RENOBATE) trial from South Korea will evaluate the combination of regorafenib and nivolumab as second-line and first-line therapy, respectively[83,84](Table 5).
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS PLUS LOCOREGIONAL THERAPIES
Locoregional therapies can activate the immune system through various mechanisms[85-87].
Treatment with either radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or TACE can stimulate the expansion of T-cells recognizing tumor-associated antigens, while RFA can lead to natural killer cell activation[85-87].The ability of locoregional therapies to stimulate the immune system makes them potential candidates for an effective combination strategy with checkpoint inhibitors[85-87].The side-effect profiles of immunotherapy and these locoregional therapies differ significantly, which may lead to relatively low toxicity compared to other combination regimens previously discussed[14,15,31,88,89].
Checkpoint inhibitors plus ablation
Patients who will likely be eligible for combination therapies involving ablation will have tumors 3 cm or less with early-stage, BCLC class 0 or A disease who are not candidates for surgical resection[4,5].Although multiple types of ablation exist, RFA is the usual standard of care and adverse events may include intraperitoneal bleeding, intrahepatic abscess, grounding pad burns, bile duct injury, thermal damage to organs in close proximity to the tumor, pneumothorax, pain, and tumor seeding of tissues[4,88].RFA is not optimal for tumors that are larger than 5 cm, numerous with 3 or more lesions, poorly visibleviaultrasound, or adjacent to structures such as the biliary tree, bowel, and vital organs such as the heart[4,5,90].
Multiple studies evaluating combinations of radiofrequency ablation and immunotherapy are ongoing[91-93](Table 6).Patients with unresectable HCC underwent treatment with tremelimumab and radiofrequency ablation or chemoablation in a phase I study in which 32 patients were enrolled[91].A partial response was noted in 5 out of 19 patients, and 12 out of 14 patients with confirmed HCV infection were noted to have a decrease in their viral load, consistent with prior studies involving tremelimumab[22,91].The phase II clinical trial (NCT02821754) sponsored by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) includes an arm where patients with advanced HCC will receive durvalumab plus tremelimumab and RFA, and another where patients will receive cryoablation in conjunction with the checkpoint inhibitors as second-line therapy[92].Progression-free survival is the primary outcome[92].Studies involving pembrolizumab include the IMMULAB phase II study (NCT03753659), which will test the combination of RFA or microwave ablation plus pembrolizumab in 30 patients who had not received prior systemic therapy and report ORR as the primary outcome[93].
Checkpoint inhibitors plus TACE
TACE plus immunotherapy may be appropriate for patients with intermediate-stage disease, including those with BCLC class B disease based on current indications for TACE[4].Some patients who are ineligible for RFA, such as those with larger tumors, multiple lesions, or smaller tumors which cannot be safely ablated may be candidates for TACE[4].Potential adverse events of TACE therapy include damage to the hepatic artery, bile duct injury, acute liver failure, variceal bleeding, and cholecystitis[89,94].Specific protocols for performing TACE may differ, and the types of chemotherapy, embolic agents, and schedule of TACE sessions may vary between institutions, among other factors[89].This variation in how TACE is performed may lead to variation in side-effect profiles, and could affect the efficacy of combination therapies when compared across medical centers[89].
Multiple studies testing the safety of treatment combinations involving checkpoint inhibitors and TACE are active[95-99](Table 6).The phase II, single-arm IMMUTACE study from Germany (NCT03572582) will study the effectiveness and safety of nivolumab plus TACE for patients with intermediate-stage HCC who have not received prior systemic therapy or TACE, with ORR as the primary endpoint[95].The combination of TACE and pembrolizumab will be studied as first-line therapy in the phase I/II, single-arm PETAL trial (NCT03397654), which will report the incidence of adverse effects as the primary outcome measure[96].A phase II clinical trial (NCT03638141) will evaluate the combination of durvalumab plus tremelimumab and drug-eluting bead TACE (deb-TACE) in approximately 90 patients with advanced HCC[97].Patients with active HCV infection will be excluded, which may hinder the ability to detect any effects of the combination therapy on HCV viral load possibly due to tremelimumab[22,97].The previously mentioned NCT02821754 phase II trial sponsored by the NCI contains an arm in which patients will receive durvalumab plus tremelimumab and TACE[92].The combination of durvalumab plus bevacizumab and TACE will be evaluated as second-line therapy in a phase II trial (NCT03937830) sponsored by the NCI in 22 patients with advanced HCC[98].The combination of durvalumab, bevacizumab and TACE will be compared to TACE alone or TACE plus durvalumab in the phase III, multi-center EMERALD-1 clinical trial (NCT03778957) which will report PFS as a primary outcome measure[99].Secondary outcome measures include overall survival[99].
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS PLUS RADIATION
The effect of checkpoint inhibitors on T-cells can be amplified by radiation[100].Radiation therapy (RT) has been shown to induce antitumor immune responses through the formation of antitumor antibodies[100].RT directed at one tumor site can induce responses in other tumor sites not directly targeted, a phenomenon known as the abscopal effect, which is related to immune system activation[100,102,103].In mouse models of melanoma, radiation therapy can increase both antigen presentation to Tcells recognizing tumor antigens and infiltration of tumors by those T-cells[101].RT can increase the expression of MHC-1 (major histocompatibility complex-1) molecules in tumors and increase T-cell and natural killer cell tumor infiltration[102,103].Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) can be used to treat early-stage, BCLC A disease that is not amenable to treatment with RFA, and can achieve local control rates of approximately 80% or greater[90].SBRT is a possible alternative treatment option after TACE has been unsuccessful, with local control rates of approximately 87%-99% in multiple studies[90].Adverse events as a result of SBRT may include upper gastrointestinal bleeding from esophageal varices or gastric and duodenal ulcers, and biliary strictures[104].SBRT generally has a more tolerable side-effect profile when compared to TACE, with rates of grade 3 or higher toxicity estimated at 6% to 27% in patients with unresectable HCC who receive SBRT[90,104].If proven safe, SBRT plus immunotherapy could become a reasonable treatment option for HCC patients who are not candidates for RFA or who have failed TACE.
Multiple studies testing the combination of ionizing radiation and immunotherapy are ongoing in patients with unresectable HCC[105-107](Table 6).One phase I study (NCT03203304) will enroll 50 participants with advanced HCC who will first receive SBRT[105].Patients will be randomized into two arms, one of which will receive nivolumab alone after SBRT, while the second will receive nivolumab and ipilimumab[105].If the results from this study suggest that administering nivolumab plus ipilimumab after SBRT is safe, better responses may be seen with that combination than with nivolumab alone given after SBRT due to the synergistic effects of nivolumab plus ipilimumab[24,28,105].A phase II study (NCT03482102) sponsored by Massachusetts General Hospital will evaluate the safety and efficacy of durvalumab and tremelimumab administered in combination with radiation as second-line therapy[106].As with prior studies examining durvalumab plus tremelimumab, a central question of the NCT03482102 study is whether this combination will be less toxic than those utilizing nivolumab plus ipilimumab in addition to SBRT, and whether tremelimumab will lower the viral load in patients infected with HCV[22,31,106].Another phase II study will report the overall response rate after enrolling approximately 30 patients, and treating them with pembrolizumab and SBRT in the second-line setting[107].Both radiation dosing and the time intervals between radiation treatment and immunotherapy treatment may affect the efficacy of combination therapies, and should be considered when the results of these various studies are available[108].
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
PD-1 and PT-112 inhibitors
PT-112 is a platinum-based drug of the phosphaplatin class currently under development by Phosphaplatin Therapeutics with reported anti-tumor effects bothinvivoandin-vitro[109-111].It promotes apoptosis in tumor cells and may have antiangiogenic effects[110].Anin-vitrostudy demonstrated that PT-112 treatment led to increased phosphorylation of a wide variety of targets, including VGFR1, EGFR, and CDC2, suggesting it may have activity against multiple distinct pathways[111].Tumor cells may not be able to evade the drug’s antitumor effects through traditional drug resistance pathways because it binds to transmembrane proteins rather than DNA[110,112].Anin-vitrostudy in ovarian cancer cells demonstrated that cisplatin enters cells more readily than phosphaplatins, and may suggest that phosphaplatin treatment may produce fewer side-effects when compared to cisplatin therapy due to reduced intracellular accumulation[113].A phase I clinical trial involving 62 patients receiving PT-112 (NCT2266745) demonstrated no maximum tolerated dose, with fatigue as the most frequently-reported adverse event[114].A patient with small cell lung cancer who progressed after prior treatment with both a CTLA-4 inhibitor and PD-1 inhibitor was progression-free at 7.5 months, while a patient with non-small cell lung cancer who progressed on a PD-1 inhibitor was progression-free at 6 months, indicating the potential benefit of PT-112 therapy[114].The ORR was approximately 10.7%[114].A phase I/II trial testing PT-112 in patients with advanced solid tumors, including patients with advanced HCC, remains active[115].The safety and efficacy of combining PD-1 therapy and PT-112 is being explored in a multi-center, non-randomized, phase I/II trial (NCT03409458) by Phosphaplatin Therapeutics that will administer PT-112 in combination with avelumab in patients with solid tumors, not including HCC[116].If combination therapy involving PT-112 and immunotherapy is safe and effective, the natural properties of phosphaplatins may prevent drug resistance, leading to more durable responses.If these regimens are truly less toxic than other combination regimens due to low levels of intracellular accumulation of phosphaplatins, PT-112-based combination therapy may become an alternative option for HCC patients who cannot tolerate other regimens due to adverse effects if it is proven safe[113].
CONCLUSION
Although immunotherapy remains a promising strategy for HCC patients with unresectable disease, checkpoint inhibitors used as single-agent therapy produce relatively modest overall response rates without significant improvements in survival[18,19].As we have outlined in this review, a combination treatment strategy pairing checkpoint inhibitors with additional pharmacologic agents, locoregional therapy or radiation therapy may produce greater responses than single-agent immunotherapy.Multiple active clinical trials are underway to determine which combination strategies can safely produce durable clinical responses, ideally with significant improvements in overall survival and overall response rates.
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2020年3期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2020年3期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- COVID-19: Off-label therapies based on mechanism of action while waiting for evidence-based medicine recommendations
- Learning and competence development via clinical cases – what elements should be investigated to best train good medical doctors?
- Combined endoscopy/laparoscopy/percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, hybrid techniques in gastrointestinal and biliary diseases
- Thrombopoietin-receptor agonists in perioperative treatment of patients with chronic liver disease
- Role of non-coding RNAs in pathogenesis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- Exclusive cigar smoking in the United States and smoking-related diseases: A systematic review
