Total spinal involvement due to delayed diagnosis and treatment of noncontiguous brucellar spondylitis
Jie He, Qiang Zhang
Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, 100015, China
ABSTRACT
KEYWORDS:Brucella; Spondylitis; Tuberculosis; Polymerase chain reaction; Radiology
1.Introduction
Brucellosis is common in Brucella spp.endemic regions.In 2015,the number of reported brucellosis cases in China was approximately 59 000, and the incidence of brucellosis has increased even more in recent years[1].The disease can affect any organ or system.Patients with brucellosis are mainly characterized by non-specific symptoms.The disease was transmitted to humans via direct contact with infected animals, inhalation of contaminated aerosols, or by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or dairy products[2].The lumbar segment is by far the most commonly affected structure in patients with spondylitis, followed by the thoracic and cervical segments[3].The involvement of multiple systems and its non-specific symptoms makes early diagnosis difficult which results in clinical misdiagnosis and mistreatment[4].Currently, brucellosis is mainly diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and blood culture.Here we report a case of total spinal involvement due to delays in diagnosis and treatment of noncontiguous brucellar spondylitis in a 62-year-old woman.The oral consent to report the case has been obtained from the patient, and the Ethics Committee of Beijing Ditan Hospital has approved the report (approval No.201904801).
2.Case report
A 62-year-old woman was admitted to our department due to lower back pain and pain in the right lower extremity for six months in July 2018.She experienced intermittent sweating (during the night)and fatigue in April 2018 and received anti-tuberculosis treatment(doxycycline, rifampicin, isoniazid, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide)for three months at another hospital but symptoms did not significantly relived.Further surgical treatment was considered.During the past six months, her lower back pain had gradually aggravated, and walking activities were limited.On admission,the patient’s erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein concentration were 64 mm/h (Normal value <15 mm/h) and 31 mg/L (Normal value<5 mg/L), respectively.Brucella agglutination test results were positive (1:320; Normal value <1:80), but the bacterial culture was negative.A PCR test indicated the diagnosis of brucellosis.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the patient showed that low to intermediate signal intensities on T1-weighted images of the C5-T1 (a, b, c), T5-T6 (d, e, f), and L4-L5 (g, h, i) intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies (Figure 1).The signals in these areas are hyperintense on T2-weighted MRI sequences[5].The patient was diagnosed with multi-segment noncontiguous brucellar spondylitis.A combination of doxycycline 200 mg/d, rifampicin 900 mg/d, levofloxacin 0.5 g/QD,and ceftriaxone 2 g/QD was administered for one week.The L4-S1 vertebral body was fixed by posterior lumbar debridement surgery and antibacterial treatment was continued for six months following her discharge.Six months later, the follow-up radiographic images showed that the vertebral height was stable and lumbar stability was good (J, K).She complained no discomfort.
3.Discussion
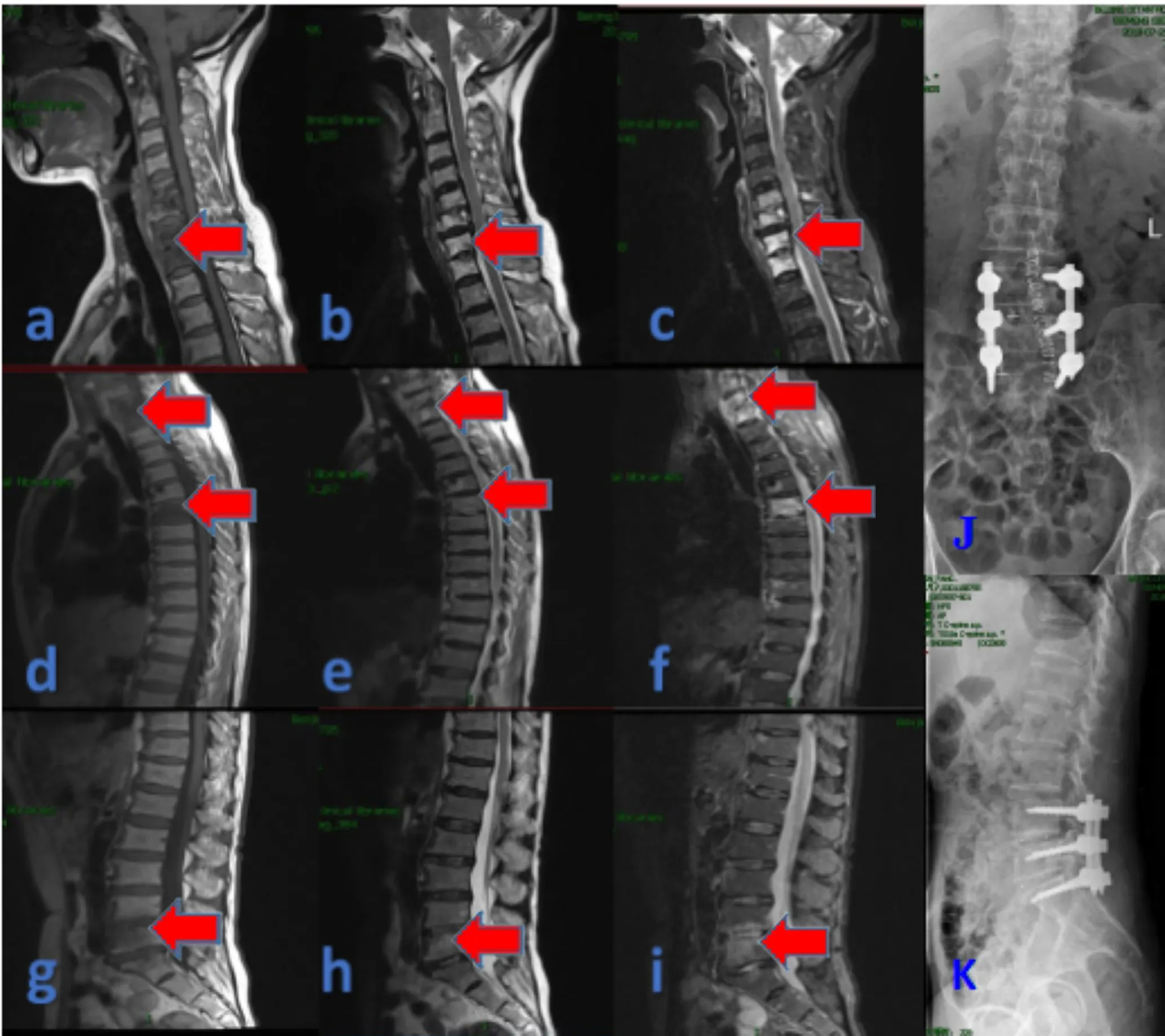
Figure 1.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a 62-year-old woman with brucellar spondylitis showed that the C5-T1 (a, b, c), T5-T6 (d, e, f), and L4-L5 (g, h, i) intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies were hypointense on T1-weighted images (T1WI) and heterogeneous on T2-weighted images (T2WI)and short-T1 inversion recovery (STIR).Follow up images show that the L4-S1vertebral body is fixed by the nail rod, and the position is stable without looseness 6 months after discharge (J, K).
Brucellosis is a globally prevalent zoonotic disease.The reported frequency of osteoarticular involvement in the disease varies between 10% and 85%[6].The spectrum of musculoskeletal manifestations of brucellosis includes spondylitis, sacroiliitis, arthritis, osteomyelitis,tenosynovitis, and bursitis.Rarely, multifocal involvement of the skeleton may be observed.Brucellar spondylitis represents 6% to 58% of osteoarticular localizations.It typically occurs in men elder than 40 years.The most commonly affected area is the lumbar spine(60%), followed by the thoracic (19%) and cervical spine (12%).More than one level of the lumbar spine is affected in 3% to 14% of cases[7].Multi-level involvement is an unusual form of brucellar spondylitis, and only few similar cases have been reported[8].MRI is the best imaging tool for the early diagnosis and follow-up of brucellar spondylitis[9], and it provides high sensitivity as well as excellent definition of paravertebral and epidural extension.MRI also allows the detection of otherwise unsuspected additional noncontiguous spinal foci.In acute brucellar infections, MRI shows low to intermediate signal intensities on T1-weighted images of the intervertebral discs and low signal intensity in the adjacent vertebral bodies.The signals in these areas are hyperintense on T2-weighted MRI sequences, with either a homogeneous or a heterogeneous pattern.However, the disc signal may remain low on T2-weighted images in brucellosis cases.These features are best shown when fatsuppression techniques are applied to contrast enhanced images.Paravertebral abscesses are observed in approximately 30% of brucellosis cases and are typically characterized by well-defined margins.During the chronic stages, the MRI patterns of the discs and vertebral bodies may vary.However, vertebral bodies usually show heterogeneous signal intensity.MRI offers a better specificity than bone scintigraphy for diagnosis of the disease and has the advantage of allowing the assessment of disco-vertebral, soft tissue,and epidural involvement.
However, it is difficult to differentiate multilevel spinal brucellosis from tuberculous spondylitis.If clinical and radiographic presentations are typical, the distinction between tuberculous and brucellar spondylitis is clare.Brucellar spondylitis most commonly affects the lower lumbar spine, while tuberculous spondylitis affects the thoracic spine more[10].The combination of severe vertebral collapse, large paraspinal abscesses extending beyond the area of vertebral disc involvement, and gibbus deformity are typical symptoms of tuberculosis But presence of osteophyte formation at the anterior vertebral endplate (parrot’s beak) is typical in brucellosis.One more mimicking tuberculosis symptom of brucellosis in our case was the multilevel non-contiguous spinal involvement.Our patient was initially diagnosed with tuberculous spondylitis and received long-term anti-tuberculosis treatment, which caused the patient’s condition aggravated.Actually, when brucellosis is suspected, a Brucella agglutination test should be applied.It provides evidence for early diagnosis of the disease.PCR test and bacterial culture is then required for confirmation of the diagnosis.
In clucions,multi-level involvement is an exceptional form of brucellar spondylitis.To the best of our knowledge, only few similar cases have been reported.PCR test and bacterial culture is necessary for confirmed diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study was funded by science foundation of Beijing Ditan Hospital Capital Medical University (No.DTQL201803).
Authors’contributions
Both QZ and JH contributed to the final version of the manuscript.QZ supervised the project.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2021年1期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2021年1期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Gender disparity in COVID-19:Role of sex steroid hormones
- Association between Guillain-Barré syndrome and hepatitis E infection:A datadriven ecological study in Hong Kong
- Gracilaria changii (Rhodophyta) alleviates bisphenol A-induced adverse reproductive abnormalities in mice
- Anopheles gambiae larvicidal and adulticidal potential of Phyllanthus amarus(Schumach and Thonn, 1827) obtained from different localities of Nigeria
- Intestinal parasitic infections and risk factors among Myanmar migrant workers in northeast Thailand
- Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Mazandaran province, Iran
