Recent advances in the protective role of hydrogen sulfide in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury:a narrative review
Meng-Ling Zhang,Wei Peng,Jian-Qiang Ni,Gang Chen
1 Department of Neurology,The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University,Suzhou,Jiangsu Province,China
2 Department of Neurosurgery & Brain and Nerve Research Laboratory,The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University,Suzhou,Jiangsu Province,China
Abstract Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is recognized to be a novel mediator after carbon monoxide and nitric oxide in the organism.It can be produced in various mammalian tissues and exert many physiological effects in many systems including the cardiovascular system.A great amount of recent studies have demonstrated that endogenous H2S and exogenous H2S-releasing compounds (such as NaHS,Na2S,and GYY4137) provide protection in many cardiovascular diseases,such as ischemia/reperfusion injury,heart failure,cardiac hypertrophy,and atherosclerosis.In recent years,many mechanisms have been proposed and verified the protective role exhibited by H2S against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury,and this review is to demonstrate the protective role of exogenous and endogenous H2S on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Key words:anti-apoptotic; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; autophagy; hydrogen sulfide; medical gas; mitochondrial preservation; myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
INTRODUCTION
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is traditionally reported to be a toxic gas and environmental pollutant.However,it is now recognized as one of the endogenous gasotransmitters family along with nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide.1The generation of H2S in the mammalian tissues is mainly mediated by three endogenous enzymes:cystathionine γ-lyase,cystathionine β-synthase,and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur-transferase.1Growing evidence has indicated that it plays a vital role in biological events in many organ systems.At cardiovascular level,H2S exerts great influence in maintaining the homeostasis and inducing vasodilation and cardioprotective effects.The maintenance of physiological concentrations of H2S seems to be essential in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases,such as atherosclerosis,hypertrophy,hypertension and myocardial infarction.2-4Numerous studies indicate the distinct role of H2S against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury,its correlative mechanisms involve anti-inflammatory,antioxidation,inhibition of cell apoptosis,and so on.5-7In this review,we retrieved studies by searching the terms of H2S and myocardial I/R injury through literature databases.A search for literature describing animal models was conducted via the conditions:SCI and animal experimentation.Non-SCI experiments and review articles were excluded.We briefly summarized the influence of H2S in myocardial I/R injury and the underlying mechanisms.
GENERATION OF HYDROGEN SULFIDE
The production of endogenous H2S in mammalian tissues is through enzymatic and non-enzymatic pathways.8,9In the non-enzymatic pathway,elemental sulfur is reduced to H2S due to reduction equivalents obtained from the oxidation of glucose.In fact,when every two molecules of glucose are consumed,three molecules of lactic acid and carbon dioxide and six molecules of H2S are produced.H2S is generated enzymatically in mammalian species via the three key enzymes in the cysteine biosynthesis pathway:cystathionine γ-lyase,cystathionine β-synthase,and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfutransferase.10The rate of H2S production in tissue homogenates has been reported to be in the range of 1–10 pmol/s per mg protein,contributing to low micromolar extracellular concentrations.At these low concentrations,H2S has been reported to exert cytoprotective effects in many models of cellular injury,particularly the heart.11
MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA/REPERFUSION INJURY
Myocardial I/R injury is a severe trauma that cells undergo and is associated with cardiomyocyte apoptosis.12The I/R damage is characterized by a first step of hypoxia that causes cell death for necrosis,and a second step of reperfusion that is paradoxically responsible of a further cell damaged caused by apoptosis.In particular,the ischemic event leads to a dramatic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) level decrease,responsible for the inhibition of Na+/K+ATPase pump with the consequent increase of intracellular Na+.13This event causes the inhibition of the Na+/H+antiporter and thus a lowering of the pH,reversing the Na+/Ca2+antiporter and leading to an increase of intracellular Ca2+that is stored in the mitochondria.14ATP depletion,high concentration of Ca2+and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are the main causes of the ischemic event.14During reperfusion,ATP levels are restored,leading to the of the Na+/K+ATPase pump with a consequent reactivation of the Na+/H+and Na+/Ca2+antiporter.15Although the electrolyte levels are restored and the pH returns to the physiological level,the production of ROS and the high intracellular level of Ca2+cause the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore,inducing the apoptotic process.16Studies in the past have unraveled that therapeutic intervention with the purpose of reducing reperfusion-induced injury is beneficial at the time of opening the obstructed vessel.17,18Naturally,it results in the discovery of pre- and post-conditioning.
STUDIES OF THE PROTECTIVE ROLE OF HYDROGEN SULFIDE IN MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA/REPERFUSION INJURY
H2S is an endogenously produced gaseous mediator that is crucial for the maintenance of cardiovascular homeostasis.19Several labs have studied the therapeutic potential of H2S in the last years.These studies have shown that both exogenous and endogenous H2S exert protective effects on myocardium ,particularly against myocardial I/R injury.20-22For example,Elrod et al.20declared that an increase of the generation of endogenous H2S could distinctly lessen the severity of myocardial infarction in mice by using a myocardial I/R model.Besides,Bliks?en et al.23reported that the use of propargylglycine to inhibit cystathionine γ-lyase and the subsequent deficiency of H2S production,caused the increase of infarct size in rat isolated hearts submitted to I/R damage.Furthermore,I/R injury was attenuated by exogenous L-cysteine administration through a mechanism that may involve H2S production,since the effect was reduced by inhibiting cystathionine γ-lyase.24One report suggested that both the administration of exogenous H2S and the increase of endogenous H2S production were possible to be a therapeutic strategy in the treatment of heart failure following I/R injury.25Together,these studies have shown the potential role of both exogenous and endogenous H2S as a cytoprotective agent,especially against myocardial I/R injury.
MECHANISMS OF HYDROGEN SULFIDE IN MYOCARDIAL PROTECTION AGAINST MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA/REPERFUSION INJURY
Antioxidant properties of H2S
A quantity of researches demonstrated that the production of ROS following ischemia-reperfusion is an original cause of damage to the myocardium.26-28A high amount of ROS produced during oxidative stress are capable of oxidizing membrane lipids,oxidizing proteins to inactive states,and causing DNA strand breaks,all leading to the damage to normal cellular function.26H2S can regulate the production of ROS.The signaling pathways which are involved in ROS generation,including activator of transcription 3 pathways,Janus kinase-2-signal transducer and nuclear factor-kappa B,have been studied intensively.29Li et al.29in 2016 shows that exogenous H2S could reduce ROS production via downregulating the Janus kinase-2-signal transducer and nuclear factor-kappa B and activator of transcription 3 pathways,contributing to the restoration of the aging cardiomyocytes.Furthermore,H2S can reduce oxidative stress through upregulating antioxidant defenses.Kimura and colleagues30in 2004 stated that H2S can protect cells against damage by increasing the antioxidant,glutathione via a model of oxidative stress induced by glutamate.They discovered that H2S increased the level of glutathione by upregulation of cystine transport and enhancing the activity of glutamylcysteine synthetase.A recent study demonstrated that H2S could increase endogenous antioxidants in a nuclear-factor-E2-related factor-2 dependent signaling pathway.31Nuclear-factor-E2-related factor-2 is a potent antioxidant transcription factor which is normally located in the cytosol,but after oxidative stimuli it is transferred into the nucleus,where it increases the transcription of antioxidant proteins through its bound with the antioxidant response elements,leading to reduced apoptosis and to an increase of mitochondrial biogenesis.32
Anti-apoptotic properties of H2S
Several investigations demonstrated the anti-apoptotic effect of H2S in cardiomyocytes in I/R injury experimental models.33,34Endoplasmic reticulum stress increases after I/R (or hypoxia/reoxygenation) injury and then induces apoptosis.35It was reported that H2S reduced endoplasmic reticulum stress to limit I/R induced-myocardial injury.35One study states that exogenous H2S decreased the level of endoplasmic reticulum stress through down-regulating protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α-activating transcription factor 4,inositol-requiring enzyme 1α-X-box binding protein1 and activating transcription factor 6 pathways,contributing to the myocardium preservation.36In addition,a research has demonstrated that NaHS affected the cross-talk between apoptogenic factors and mitogenactivated protein kinases associated with mitochondria and nuclear factor-kappa B,thus reducing apoptosis.37Calvert et al.31found that H2S could regulate the expression of many apoptosis-related genes,including heat shock protein-90,Bcl-2,and heat shock protein-70.H2S was capable of regulating multiple genes which are aberrantly expressed in I/R cardiac tissue.31Members of the Bcl-2 protein family play vital roles in the process of apoptosis.38Kang et al.34in 2014 found that H2S attenuated cardiomyocyte apoptosis via down-regulating I/R-induced miR-1 expression and up-regulating Bcl-2 mRNA and protein expressions.Furthermore,a recent study states that H2S protects cardiomyocytes from myocardial ischemiareperfusion injury by enhancing phosphorylation of apoptosis repressor.Apoptosis repressor has been shown to block apoptotic cascades in hearts.39
Anti-inflammatory effects of H2S
Inflammation response is programmed to reduce cell injury and facilitate tissue repair,but on the other hand can lead to a further injury due to cell debris and proinflammatory cytokines.Indeed,inflammation reduction during the myocardial I/R injury has been shown to be a useful strategy to limit the infarct size and to promote the recovery of heart function.One of the proposed mechanisms of H2S-mediated cardioprotection involves its ability to reduce inflammatory processes.40,41Zanardo et al.42demonstrated that several H2S donors are capable of suppressing leukocyte adherence to the vascular endothelium and can reduce leukocyte infiltration.Leukocyte infiltration represents an early phase in the inflammatory process leading to the production of free radicals and proteases which can injury the myocardium.41Furthermore,H2S administration before and during the reperfusion was able to prevent nuclear factor-kappa B translocation,leading to a reduction of the amount of proinflammatory mediators.Among them,the authors reported a significant decrease of interleukin-1β and interleukin-6,which is detrimental for the myocardial function,43,44and interleukin-8 is physiologically involved in neutrophil adhesion and tumor necrosis factor-α which can exacerbate several inflammatory effects.45A recent study stated that exogenous H2S may protect cardiac cells against inflammation with the involvement of the coldinducible RNA-binding protein-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.7H2S displayed a dual ability to attenuate inflammation by inhibiting neutrophil and leukocyte extravasation and reducing inflammatory cytokines which are responsible to produce free radicals.Both the mechanisms may promote the recovery of the myocardial function after the I/R injury.
H2S and autophagy
Autophagy is upregulated in response to energy crisis and oxidative stress under the condition of cardiac I/R injury.6Luo et al.46demonstrated that autophagy exhibited protective effects against ischemia,but it turned to be detrimental during reperfusion with subsequent heart failure.The potential mechanism about how H2S works on autophagy has not fully investigated.One study demonstrated that H2S administration after ischemia could suppress autophagy as they found that the mRNA level of genes (Atg9,Atg5,andBeclin1) and the protein level of LC3II/I a and Beclin1 which are the most widely used markers of autophagy significantly decreased.47Besides,H2S can interfere with autophagic flux and exhibiting cardioprotection against injuries in rat cardiomyocytes exposed to hypoxia/reoxygenation by modulating phosphoinositide 3-kinase/serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1/glycogen synthase kinase 3β signaling pathway,which is emerging and similar to phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway.48Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) plays a critical role in the autophagic process.18Increasing the activity of mTOR would inhibit autophagy.A recent study suggested that H2S might minimize the extent of myocardial I/R injury by activating the Akt/mTOR way to decrease autophagic activity.49
H2S and mitochondrial preservation
Mitochondria are critical for energy production and cell survival.Mitochondrial damage will impair energy generation and cell function,causing damage to cardiomyocytes.50A recent study revealed that exogenously administered H2S reduce the production of mitochondrial malondialdehyde and activating superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in the ischemic myocardial mitochondria,resulting in limiting the severity of myocardial infarction.51In addition,the hypothesis that H2S strengthened the function of mitochondria was supported by the increased efficiency of complexes I and II of the oxidation respiratory chain at the time of reperfusion.52Furthermore,suppressing the respiratory system has been reported to reduce myocardial I/R injury by mitigating the equivalent of ROS.20
Other mechanisms
The previous researchers demonstrated that H2S was cytoprotective during the process of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion because of its involvement in the dilation and hyperpolarization of rat cerebral arteries including the basilar artery and the middle cerebral artery.53,54Besides,many studies have reported a positive cross-talk against I/R injury between two endogenous gas transmitters:H2S and NO.H2S avoided the nitrosation on Cys443 leading to a higher endogenous NO production.55Moreover,H2S selectively inhibited cardiac phosphodiesterase-5 isoform,increasing NO half-life.55
The experimental data for H2S-induced protection against myocardial I/R injury are summarized in Table 1.
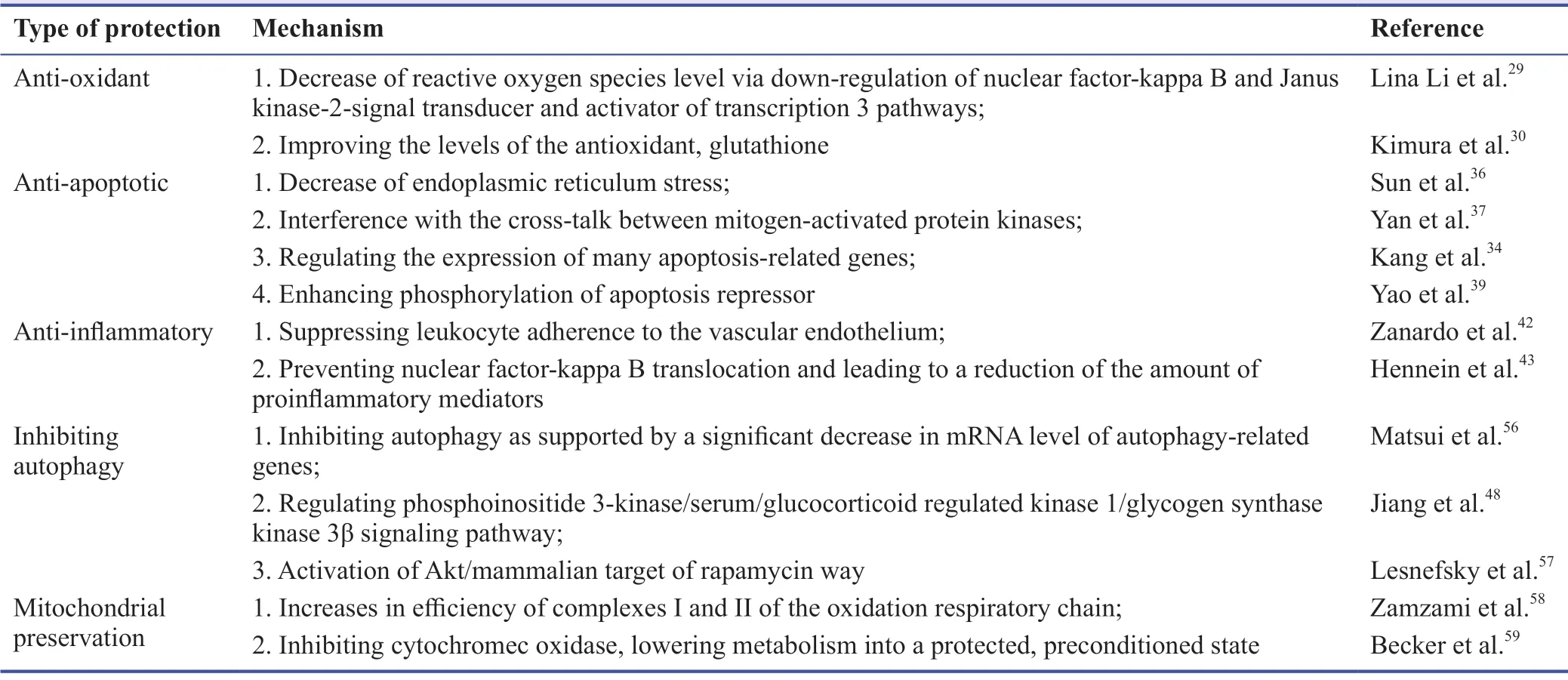
Table 1:Summary of mechanisms of H2S-induced protection against myocardial I/R injury
CONCLUSION
Through the above introduction,it is believed that H2S protects against myocardial I/R injury.The underlying mechanism of H2S administration may involve the reduction of ROS generation,the process of autophagy and the inflammatory system.A larger regulatory network will be discovered and explored.Although we have not fully understood its mechanism,we will continue to do a lot of research in the future.H2S is expected to be used in the clinic,providing a more convenient and less side-effect treatment for myocardial I/R injury.
Author contributions
Manuscript drafting:JQN,GC; manuscript writing:MLZ; manuscript revision:WP,JQN,GC.All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Financial support
None.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by all authors before publication.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
- Medical Gas Research的其它文章
- A review on the neuroprotective effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in inflammatory bowel disease:a narrative review
- Effects of adding dexmedetomidine,fentanyl,and verapamil to 0.5% ropivacaine on onset and duration of sensory and motor block in forearm surgeries:a randomized controlled trial
- Electrolytic hydrogen-generating bottle supplies drinking water with free/combined chlorine and ozone repressed within safety standard under hydrogen-rich conditions
- Tuberculosis incidence in area with sulfur dioxide pollution:an observation
- Sevoflurane versus halothane for induction of anesthesia in pediatric and adult patients

