Cupping therapy adverse events: A protocol of a comprehensive systemic review
Tamer S.Aboushanab, Monear Qoqandi, and Saad Baslom
Abstract—Cupping therapy is one of the most ancient traditional and complementary medicine practices that using globally by many civilizations.This protocol is setting the methods for conducting a new comprehensive systematic review to evaluate and set recommendations regarding safety of cupping therapy practice.Randomized clinical trials, case series, and case studies will be selected to be included in this study.PubMed, Trip medical database, and Cochrane Library be searched Since inception to 1 December 2021.The main outcomes of the systematic review will be: details of adverse events, casualty of identified adverse events (WHOUMC causality scale) and severity of adverse events(Common Terminology Criteria (CTCAE) scale).Assessment of quality of reporting of safety in randomized clinical trials will be done.Classification of adverse events related to cupping therapy, recommendations regarding safety and suggestions regarding future cupping therapy research will be provided in the full-text of the systematic review.
INTRODUCTION
Adverse event was defined by Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 as: “any unfavorable and unintended sign (including an abnormal laboratory finding), symptom, or disease temporally associated with the use of a medical treatment or procedure that may or may not be considered related to the medical treatment or procedure” [1].Cupping therapy is one of ancient complementary medicine practices which was used by most of the ancient civilization [2].Safety of cupping therapy and evaluation of adverse events related to cupping therapy were assessed in very few systematic reviews [3-5].The previous systematic reviews were limited by certain boundaries.Kim et al.reviewed the adverse events related to cupping therapy in trials conducted in Korea, while Albedah et al.reviewed the adverse events related to cupping therapy in trials conducted from year 2000 and after.Assessment of safety of cupping therapy is very important to improve the quality of cupping therapy practice, and to help in developing policies and clinical guidelines.
This systematic review aims to provide comprehensive systematic review of all adverse events related to cupping therapy without location or time boundaries.It also will give descriptive details about cupping therapy related adverse events.This systematic review will also aim to classify adverse events related to cupping therapy according to various elements such as: adverse event location, severity, and cupping type.This systematic review tries to answer these questions: 1) Is cupping therapy a safe practice? 2) What is the rate of adverse events related to cupping therapy in published research? 3)What are recommendations for prevention of cupping therapy adverse events? This review is very important to ensure safe practice of cupping therapy and to assess its safety.The results of this systematic review can be used to ensure safety and to enhance the quality of reporting of adverse events in the future cupping therapy research.
METHODS AND ANALYSIS
Criteria for including studies
Types of studiesClinical trials, case studies, and case series will be included in this study.Other research types will be excluded.English literature only will be included.
Types of ParticipantsAll patients receiving any type of cupping therapy regardless of age, race, age, gender, or condition will be included in this review.
Types of interventionsAny type of cupping therapy according to classification of cupping therapy types will be included [2].
Types of outcome measures1.Adverse events.2.Casualty of identified adverse events (WHO-UMC causality scale) [6].3.Severity of adverse events (Common Terminology Criteria (CTCAE) scale) [1].
Search strategy
Electronic searchesThree Medical databases will be searched from their inception to December 1, 2021, which will be: PubMed, Trip medical database, Cochrane.The following search terms will be used: Cupping, cupping therapy, dry cupping, wet cupping, adverse event, adverse effect, side effect.Examples of search strategy are:“cupping” AND “adverse event” OR cupping AND“adverse effect” OR “cupping” AND “side effect” OR“cupping” AND “complication”.The search strategy will be modified according to the searched database.
Searching other resourcesThe reference lists of included studies will be hand searched for potential inclusion of other studies.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studiesTwo authors independently will review and screen titles, and abstracts for all retrieved articles to select eligible studies. Full-text articles will be obtained for further assessment.The research flowchart will be reported on PRISMA on the same format as Figure 1.Any disagreement will be resolved by discussion.

Figure 1 PRISMA chart for the flow of systematic review
Data extraction and management
Two reviewers will independently extract data according to a predesigned data extraction form.The following information will be extracted: First author, year of publication, adverse events cases (gender/age), condition,cupping type, cupping region or point, cupping session details (number of cups, number of sessions, duration of cup retention, course of treatment, and pressure inside the cup), practitioner type, adverse event type, sequalae of adverse events.
Any disagreement will be resolved by discussion or judged by the third author.If there is a need for more details for any included article, there are two options to solve this: by contacting the corresponding author of included article or by analyzing, and discussing the available data.
Assessment of adverse events causality in included observational studiesWHO-UMC causality scale (Table 1)[6] will be used to assess cupping therapy adverse events in the observational studies.Scoring of adverse events in included observational studies will be as follows: “certain”,“probable”, “possible”, “unlikely”, “conditional” or“unclassifiable”.

Table 1 WHO-UMC causality scale (in case of cupping therapy)
Assessment of adverse events severityAdverse events severity will be assessed according to the Common Terminology Criteria (CTCAE) scale (Table 2) [1].

Table 2 Grading of Severity of adverse events according to CTCAE
Assessment of reporting of safety in randomized clinical trialsQuality of reporting of RCTs will be evaluated according to the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) recommendation for harm data (Table 3) [7, 8].
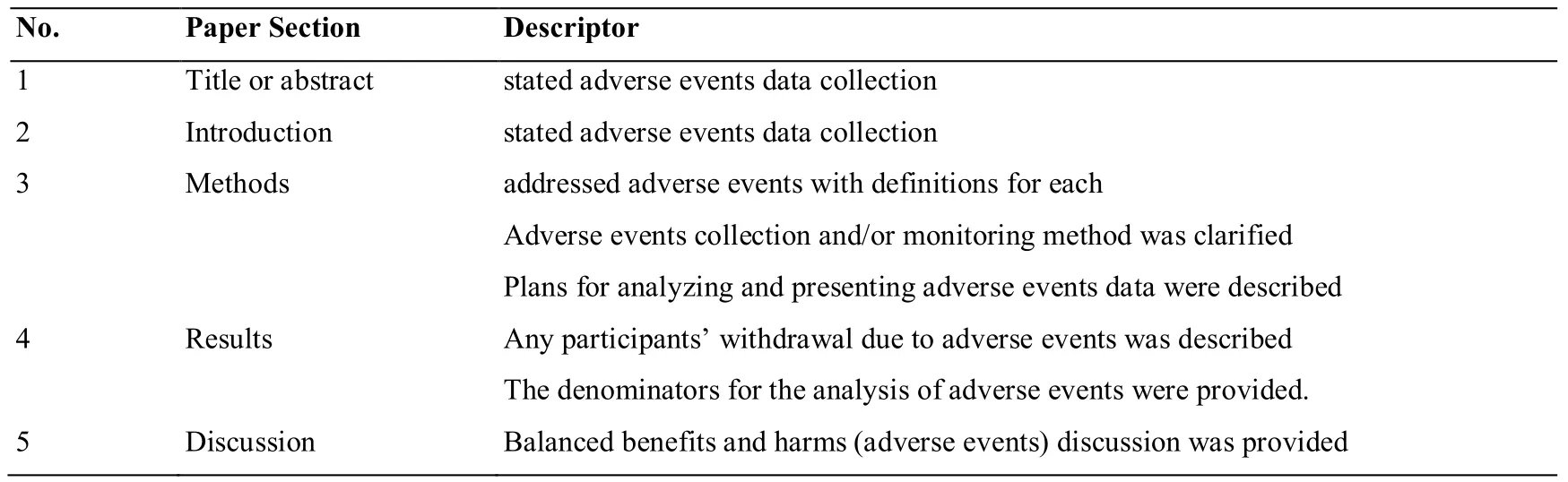
Table 3 CONSORT For harms data recommendations checklist
Qualitative parameters of reporting of RCTs will be as follows; 1) Adequate, 2) Partially adequate, 3) Inadequate,4) Not reported.
Classifying reported adverse eventsWe will try to classify cupping therapy adverse events according to various elements which will include adverse event location,cupping therapy types, and severity.
Data AnalysisThis systematic review will descriptively report the prevalence of adverse events related to cupping therapy in the selected studies.Descriptive approach will be also used to report key features, characteristics, and quality assessment of adverse events in the selected trials.
Subgroup analysis will be conducted according to types of cupping therapy, using sham cupping methods, cupping therapists training, cups types, duration of session and so on.
DISCUSSION
The demonstration of complementary medicine adverse events and harm are inadequate in a large scale [7].The adverse events of cupping therapy are infrequently reported but they are not rare [4].The expected results of applying this protocol are giving profiles of cupping therapy types and related adverse events, commenting generally on cupping therapy safety, and giving recommendations and suggestions.
Furthermore, cupping therapy adverse events were classified three times [2, 4, 9].The recent published classification classified cupping therapy adverse events into preventable and non-preventable adverse events and each category was further classified into local and systemic adverse events. This systematic review will evaluate the previously published classification and represent a new comprehensive classification of cupping therapy adverse events.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors did not receive any funding for this study.
Competing interests:The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Citation:Aboushanab TS, Qoqandi M, Baslom S.Cupping therapy adverse events: A protocol of a comprehensive systemic review.2021;4(4):19.doi: 10.53388/TMRND 20211101001.
Executive editor:Jin-Feng Liu.
Submitted:01 November 2021,Accepted:16 November 2021,Online:19 November 2021
? 2021 By Authors.Published by TMR Publishing Group Limited.This is an open access article under the CC-BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/BY/4.0/)
- TMR Non-Drug Therapy的其它文章
- Application effect of safety hazard selfexamination mode in nursing risk management in hepatobiliary surgery
- Randomized controlled study of Tuina in the treatment of insomnia: A Meta-analysis
- The efficacy of Baduanjin combined rehabilitation therapy on stroke patients: A Meta-analysis
- Flavonoids: Anti-cancer effects of nutritional management