lndirubin suppresses 4T1 murine breast cancer in vitro and in vivo by induction of ferroptosis
Xiu-Ping Kuang,Ji-Wei Huang,Ying-Nan Jiang,Yong-Zhi Guo,Chang-Yu Yan,Wei-Xi Li*
1 Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Kunming 650500,Yunnan,China.
2 Perfect Life Sciences Research Institute,Zhongshan 528400,Guangdong,China.
3 Department of Pharmacy,The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University,Guangzhou 510630,Guangdong,China.
4 School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Key Laboratory of Structure-Based Drug Design &Discovery of Ministry of Education,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China.
Abstract Objective Indirubin,isolated from Indigo Naturals,has been reported to have the inhibitory activity of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro.However,studies on its anti-breast cancer activity in vivo and the underlying mechanism are insufficient.We explored whether indirubin could trigger ferroptosis of breast cancer cells to exert anti-tumor activity.Methods Bioinformatical analysis was performed to detect the expression of prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2(Ptgs2)in breast cancer tissues and Ptgs2-related prognosis for patients with breast cancer.The inhibitory effects of indirubin on 4T1 cells were assessed using MTT assay and LDH activity detection.The levels of 4-HNE,GPX4,PTGS2 and GSK-3β proteins were detected by Western blotting,and the mRNA of Ptgs2 was tested by qPCR.The contents of GSH and MDA were determined by commercial kits.Molecular docking was employed to study the interaction between indirubin and GSK-3β.A 4T1 murine breast cancer was adopted to evaluate the in vivo antitumor activity of indirubin.Results Indirubin promoted ferroptosis of 4T1 breast cancer cells with depleting of GSH,increased MDA and 4-HNE levels,as well as decreased GPX4 expression.Indirubin suppressed 4T1 breast tumor in vivo.The mechanism study showed indirubin up-regulated Ptgs2 expression by promoting phosphorylation(Ser 9)of GSK-3β.Conclusion Indirubin suppresses 4T1 murine breast cancer in vitro and in vivo by induction of ferroptosis.
Keywords Breast cancer,Indirubin,Ferroptosis,Ptgs2,GSK-3β
Background
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women with increasing incidence year by year.Furthermore,it is also one of the leading causes of death among women with cancer worldwide[1-3].Chemotherapy is one of the important methods for the treatment of breast cancer,but the drug resistance and side effects make it imperative to find new breast cancer treatment drugs[4-6].
Indigo Naturalis,the classical Chinese medicine,has been used in China for many centuries,and modern pharmacological studies have shown that it has anti-inflammatory,antiviral,antibacterial,antitumor and anti-psoriatic activities[7-11].In the study of the pharmacologically active components ofIndigo Naturalis,indirubin has received the most attention[12].Indirubin,the major active component ofIndigo Naturalis,has been widely known for its clinical use for the treatment of chronic myelocytic leukemia(CML)[13,14].Recent studies have shown that indirubin can also be used to treat other types of cancer,like breast cancer[15-17].However,the research on the mechanism of indirubin in the treatment of breast cancer is still insufficient.Ferroptosis,a new type of cell death,is mediated by iron-dependent accumulation of lipid peroxidation.It was found that ferroptosis can be involved in the occurrence,progression and treatment of tumors.Emerging evidences have indicated that triggering ferroptosis of cancer cells is an important means for cancer therapy[18-21].
In this study,we aimed to explore whether indirubin could play an anti-breast cancer role by inducing the occurrence of ferroptosis.We analyzed the clinical data provided by the NCBI database and found that breast cancer was related to the low level of prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2(Ptgs2),a molecular marker of ferroptosis.In vivoandin vitrostudies suggested that indirubin could exert the anti-breast cancer effect by inducing ferroptosis,which mechanically was related to up-regulation of Ptgs2 by the binding of indirubin with GSK-3β.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
Indirubin(wkq-01742,purity ≥ 97.0%,HPLC)was purchased from Sichuan Weikeqi Biological Technology Co.,Ltd(Chengdu,China).The primary antibody to PTGS2(GB11077-2)was purchased from Servicebio Co.,Ltd(Wuhan,China).Primary antibodies,anti-GSK-3β(D5C5Z,#12456)and anti-phospho-GSK-3β(Ser 9,5B3)(#9323),were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology(CST)(Boston,MA,USA).Primary antibodies to 4-HNE(ab46545)and GPX4(ab125066)were purchased from Abcam(Cambridge,MA,USA).Adriamycin(A183027,purity ≥ 97.0%)was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co.,LTD(Shanghai,China).Antiglyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH)antibody(FD0063)was from Fude Biological Technology(Hangzhou,China).Other chemicals were purchased from standard commercial suppliers.
Bioinformatical analysis of breast cancer-related genes
The gene expression profile of GSE20713,GSE42568 and GSE 54002 in breast cancer and normal breast tissues were obtained from the free public database,NCBI-GEO database.Differentially expressed genes(DEGs)between breast cancer specimen and normal breast specimen were identifiedviaGEO2R online tools with log FC < -2 and adjustPvalue < 0.05[22].Then,the raw data in TXT format were checked in Venn software online to detect the commonly DEGs among the three datasets.The prognostic relationships between selected genes and breast cancer were analyzed by Kaplan-Meier plotter and GEPIA online tools[23,24].
Cell culture
4T1 mouse breast cancer cells were purchased from the Cell Bank of the China Academy of Sciences and cultured in DMEM medium(C11995500BT,Gibco,Carlsbad,CA,USA)supplemented with 10% FBS(ST40-39500,PANSeratech,Aidenbach,Germany)and 1% penicillinstreptomycin(C0222,Beyotime,Shanghai,China)at 37°C under a humidified 5% CO2atmosphere.
Cell viability analysis
4T1 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS overnight.After 24 h of drug treatment,3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide(MTT)solution was added into each well and incubated at 37°C for 4 h.The medium was removed and formazan crystals were later dissolved in DMSO.The absorbance was measured at 570 nm.
LDH(lactate dehydrogenase)activity detection
4T1 cells were seeded and cultured in a 96-well plate overnight.After 24 h of indirubin treatment,the supernatants were collected for detection of LDH release with Cytotoxicity Detection Kit(LDH)according to the manufacturer’s instructions(Promega Corporation,Madison,WI).The absorbance was measured at 492 nm.
Animal experiment
BALB/c mice(6-8 weeks old,female)were purchased from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center(Guangzhou,China)with permission No.SCXK 2017-0174.Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Jinan University and conducted in accordance with National Institute of Health’s Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals(7th edition,United States).All mice were kept in a non-pathogenic animal chamber with a temperature of 23± 1°C and a dark period of 12 h,and fed with a standard laboratory diet and water.The animals were allowed to acclimatize for a week before the experiment.
Mice received a subcutaneous injection with 4T1 cells(2 ×106cells)into the mammary fat pad.When the tumor diameter reached about 5 mm,the mice were randomly divided into 5 groups.The mice were treated with saline,indirubin(low dose,10 mg/kg;high dose,20 mg/kg)and adriamycin(1 mg/kg,clinically used in the treatment of breast cancer,as a positive control drug)every day.The tumor sizes were measured every 2 days using calipers,and the tumor volume was calculated by the following formula:volume(mm3)= 0.5 ×[length(mm)]×[width(mm)]2.The tumor weight at the 21st-day post-injection was used as the endpoint reading.Mice were sacrificed with diethyl ether anesthesia.
Histological analysis
Breast tumors were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 h at room temperature.Then,they were dehydrated,transparent,paraffin-embedded and cut into 5 μm thick slices.Hematoxylin and eosin(H&E)were used for staining tumor tissues.The histological changes were observed and imaged under an automatic scanning microscope(PreciPoint M8,Freising,Germany).
Western blotting
The cells and tumor tissues were lysed using RIPA(P0013C,Beyotime)lysis buffer containing 1 mM PMSF(P1005,Beyotime)on ice for 30 min.After centrifugation at 12,000 ×gat 4°C for 10 min,the supernatants were collected and total protein concentrations were determined using a BCA protein assay kit(Pierce,Rockford,IL,USA).The protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to PVDF membranes(Millipore Corporation,Billerica,MA,USA).The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk dissolved in TBST buffer at room temperature for 1 h and probed with the indicated primary antibodies at 4°C overnight and then incubated with HRP-labeled secondary antibodies at room temperature for 2 h.Target proteins were detected using ECL Western blotting Detection Reagent(20190120,Fude Biological Technology)and visualized by Tanon 5200 imaging system(Tanon,Shanghai,China).GAPDH is used as an internal control.
Reverse transcription and quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA of cells was extracted using TRIzol reagent(Invitrogen,Carlsbad,CA,USA)according to the manufacturer’s instructions.RNA concentrations were determined by optical density measurement at 260 nm on a spectrophotometer(NanoDrop 2000,Thermo Scientific;Wilmington,DE,USA).cDNA was synthesized from the purified RNA by both random and oligo(dT)priming by a TransScript One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix kit(AT311,TransGen Biotech,Beijing,China)and amplified in real-time quantitative PCR by a TransStart Top Green qPCR SuperMix kit(AQ131,TransGen Biotech).The following primer sequences were used:Ptgs2,5’-CCACTTCAAGGGAGTCTGGA-3’(Forward),Ptgs2,5’-AGTCATCTGCTACGGGAGGA-3’(Reverse);Gapdh,5’-AACTTTGGCATTGTGGAAGG-3’(Forward),Gapdh,5’-GGATGCAGGGATGATGTTCT-3’(Reverse).Using the comparative threshold cycle(Ct),relative expression was calculated using the 2-△△Ctmethod and normalized by the expressions ofGapdhfrom the same samples.
Determination of glutathione(GSH)and malondialdehyde(MDA)
The cells and tumor tissues were lysed using RIPA lysis buffer containing 1 mM PMSF on ice for 30 min and then centrifuged at 12,000 ×gat 4°C for 10 min.Then,the resulting cell lysates were utilized to assess GSH and MDA content,using commercially test kits(GSH,A061-1-1,Nanjing Jiancheng BioTechnology,Nanjing,China;MDA,S0131,Beyotime),respectively,according to the manufacturer's protocols.
Molecular docking
The molecular docking method was used for the analysis of indirubin binding with GSK-3β.The discovery Studio 3.0 docking program was adopted[25].The structure of GSK-3β was downloaded from PDB database(PDB ID:2O5K).The preparation of protein structure included adding hydrogen atoms,removing water molecules,and assigning Charmm forcefield.All parameters were set as default.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software(San Diego,CA,USA).The statistical significance of differences between the two groups was determined with an unpaired Student'st-test and multiple comparisons were analyzed with one-way ANOVA.All data presented as mean ± standard deviation.Differences were considered statistically significant atP< 0.05.
Results
Low expression of Ptgs2 in breast cancer
There were 587,343 and 564 DEGs between breast tumors and normal breast tissues from GSE20713,GSE154002 and GSE42568,respectively,viaGEO2R online tools.Then,we used Venn diagram software to identify the commonly down-regulated genes in the three datasets.Results showed that a total of 16 down-regulated genes(log FC < -2,p< 0.05)was identified in the breast cancer tissues(Figure 1A-B).Noticeably,Ptgs2,a ferroptosis marker,was down-regulated in breast cancer patients,which indicated that ferroptosis may be related to breast cancer[26,27].Furthermore,the prognostic information of Ptgs2 was analyzed employing the Kaplan-Meier plotter.The result showed that the low mRNA expression of Ptgs2(HR,0.82;CI,0.7-0.96)was associated with the poorer overall survival for patients with breast cancer(Figure 1C).In addition,we also performed GEPIA and found that Ptgs2 mRNA was significantly lower in breast cancer tissues than that in normal tissues(P< 0.05)(Figure 1D).Results above showed the low expression of Ptgs2 in breast cancer.

Figure 1.Low Expression of Ptgs2 in Breast Cancer.(AB)Authentication of 16 down-regulated genes(log FC < -2)in breast tumor compared to normal breast tissues from the three datasets(GSE20713,GSE54002 and GSE42568)by Venn diagrams.(C)The prognostic information of Ptgs2 was shown by Kaplan-Meier plotter.(D)Gene Expression Profiling Interaction Analysis(GEPIA)for the expression of Ptgs2 in tumor tissues(red box)and normal tissues(gray box).T,tumor tissues;N,normal tissues.*P< 0.05 vs. normal tissues.
Indirubin induces ferroptosis of 4T1 breast cancer cells
In order to investigate whether indirubin(Figure 2A)has an inhibitory effect on breast cancer,we firstly performed an MTT assay to study the effect of indirubin on the viability of 4T1 cellsin vitro.The result showed that the viability of 4T1 cells was significantly inhibited in a dosedependent manner after incubation with indirubin(Figure 2B).We evaluated the cytotoxic effect of indirubin on 4T1 cells by detecting LDH activity in cell culture supernatants.As shown in Figure 2C,indirubin significantly promoted the LDH release of 4T1 cells(P< 0.001).Next,we explored whether ferroptosis was involved in the antibreast cancer effect of indirubin.The pre-treatment of Fer-1(ferrostatin-1,ferroptosis-specific inhibitor,25 μM)significantly reversed indirubin-induced inhibition of 4T1 cells viability(P< 0.05).However,Nec-1(necrosis inhibitor,50 μM)and z-VAD(apoptosis inhibitor,50 μM)didn’t protect 4T1 cells from indirubin-induced inhibition of viability(Figure 2D).These results indicated indirubininduced ferroptosis of breast cancer cellsin vitro.The occurrence of ferroptosis is characterized by the depletion of GSH and the accumulation of lipid peroxides.Meanwhile,the result showed that indirubin(40 μM and 80 μM)reduced the GSH content of 4T1 cells(P< 0.05,P< 0.05)(Figure 2E).MDA and 4-hydroxynonenal(4-HNE)are major end products derived from lipid peroxides.As shown in Figure 2F-H,indirubin(80 μM)significantly increased the level of MDA(P< 0.05)and 4-HNE(P<0.05).In addition,glutathione peroxidase 4(GPX4)plays a key role in reducing lipid peroxides.The expression level of GPX4 significantly decreased by indirubin(40 μM and 80 μM)(P< 0.05,P< 0.05)(Figure 2G and I).These results indicated that indirubin induced ferroptosis of breast cancer cellsin vitro.
Indirubin up-regulates the expression of PTGS2 in 4T1 breast cancer cells
Given that low expression of Ptgs2 in breast cancer was found by bioinformatics analysis in Figure 1,We sought to explore whether indirubin-induced ferroptosis was related to PTGS2.We firstly detected the effects of indirubin on the expression of PTGS2 by qPCR and Western blotting.As shown in Figure 3A,indirubin(40 μM and 80 μM)significantly elevated the mRNA level of Ptgs2 in 4T1 cells(P< 0.01,P< 0.001).Moreover,indirubin(80 μM)significantly increased the expression level of PTGS2 protein(P< 0.05)(Figure 3B-C).Indirubin was reported as the potent inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta(GSK-3β)[28].We found that indirubin could form hydrogen bonds with Arg141,Gln185 and Val135 of GSK-3β protein by molecular docking(Figure 3D).We further analyzed the effect of indirubin on phosphorylation(Ser 9)of GSK-3β in 4T1 cells by Western blotting.Indirubin could promote phosphorylation(Ser 9)of GSK-3β(Figure 3E).Indeed,it has been reported that GSK-3β participates in regulating the expression of PTGS2[29,30].Hence,we speculated that indirubin may regulate the activity of GSK-3β to promote the expression of PTGS2 and then trigger the ferroptosis of tumor cells.

Figure 2.Indirubin induces ferroptosis of 4T1 breast cancer cells.(A)Chemical structure of indirubin.(B)The viability of 4T1 cells with indirubin at indicated concentrations for 24 h.(C)The LDH activity in culture supernatants of 4T1 cells.(D)The viability of 4T1 cells pretreated with Fer-1(25 μM),Nec-1(50 μM)or z-VAD(50 μM)and then with indirubin(80 μM).(E)The GSH content of 4T1 cells.(F)The MDA level of 4T1 cells.(G-I)Western blotting detection for 4-HNE and GPX4 and quantitative analysis.*P< 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001 vs. Control group;ns(not significant),#P< 0.05 vs. Indirubin group.
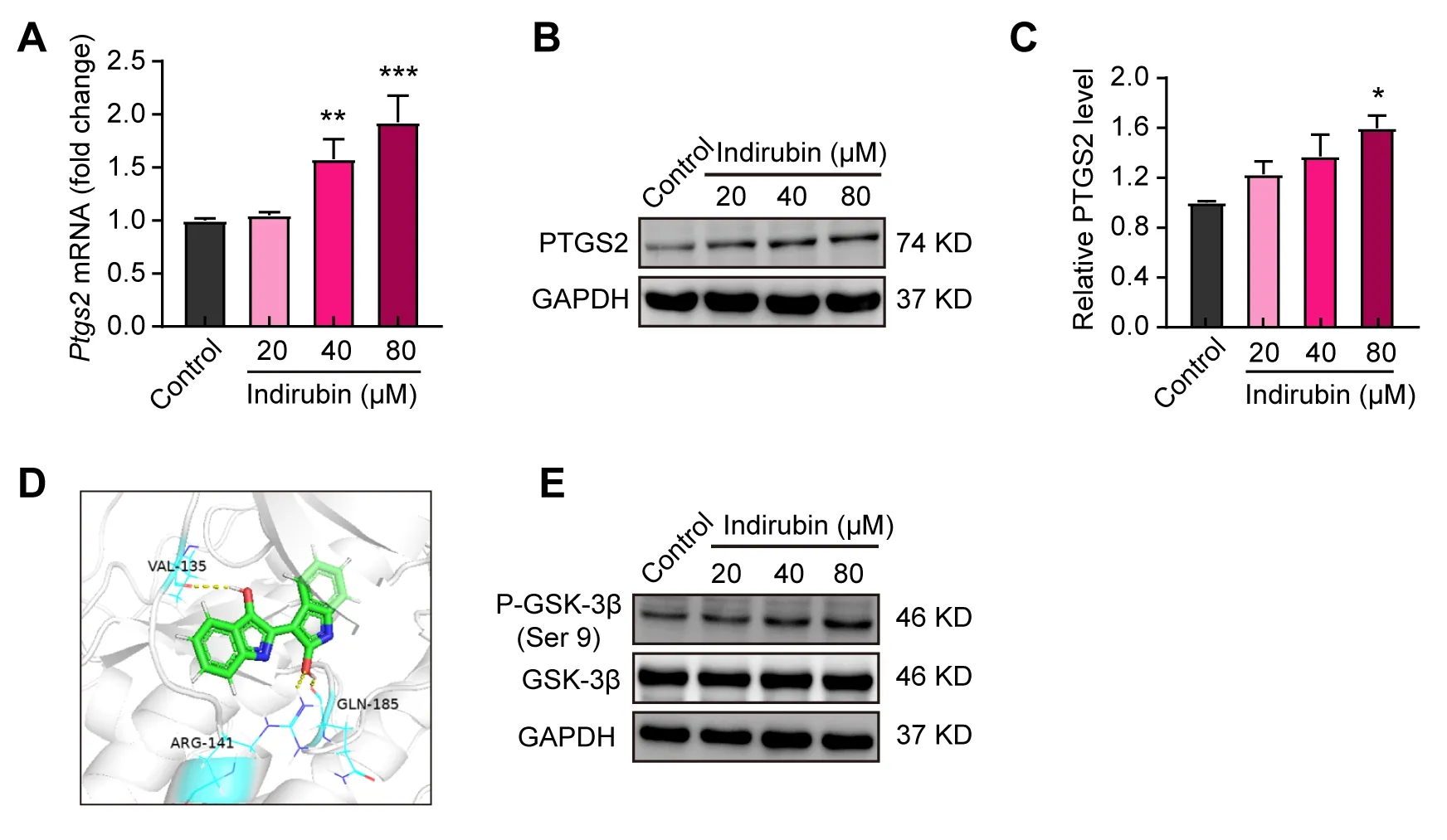
Figure 3.Indirubin up-regulates the expression of PTGS2 in 4T1 breast cancer cells.(A)The mRNA level of Ptgs2 in 4T1 cells with indirubin.(B-C)Western blotting for PTGS2 in 4T1 cells with indirubin and quantitative analysis.(D)Molecular docking of indirubin with GSK-3β.The yellow dot line indicated the interaction of the hydrogen bond.(E)Western blotting for P-GSK-3β(Ser 9)and GSK-3β in 4T1 cells with indirubin.*P< 0.05,**P< 0.01 and ***P< 0.001 vs.Control group.

Figure 4.Indirubin suppresses 4T1 breast cancer in vivo.(A)The tumor weight of mice in each group was determined at the end of treatment.(B)Tumor growth curves of different groups of mice.(C)Histological images of tumors sections stained by H&E.Scale bar:25 μm.(D)The GSH content of tumor tissues.(E)The MDA level in tumor tissues.(F-G)The protein expressions of 4-HNE,GPX4,PTGS2,GSK-3β,and P-GSK-3β(Ser9)were detected by Western blotting in tumor tissues.GAPDH was used as an internal control.*P< 0.05,**P< 0.01 and ***P< 0.001 vs. Control group.ADR,Adriamycin.
Indirubin suppresses 4T1 breast cancer in vivo
Indirubin has been shownin vitroto induce ferroptosis of breast cancer cells,which may concern the up-regulation of Ptgs2.Therefore,we next sought to investigate whether indirubin could suppress breast cancerin vivo.Firstly,we evaluated the anti-tumor activity of indirubin using the mouse model of breast cancer by injection of 4T1 cells subcutaneously.Results showed that indirubin(20 mg/kg)significantly inhibited breast cancer with reduced tumor weight(P< 0.05)and volume(P< 0.01)compared with the control group(Figure 4A-B).Histopathological observation of tumor tissue showed that indirubin resulted in breast tumor necrosis(Figure 4C).Meanwhile,the positive drug ADR suppressed breast cancer(Figure 4AC).After indirubin(20 mg/kg)treatment,the GSH content of tumor tissues significantly decreased(P< 0.05)(Figure 4D).Indirubin(10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg)significantly increased the MDA level of tumor tissues(P< 0.01,P<0.01)(Figure 4E).In addition,we also detected the levels of 4-HNE and GPX4 in tumor tissues by Western blotting.As shown in Figure 4F,indirubin promoted the expression of 4-HNE,while down-regulated the level of GPX4,suggesting induction of ferroptosis in tumor tissues.Consistent with thein vitroresults,indirubin also promoted GSK-3β phosphorylation(Ser9)and PTGS2 expressionin vivo(Figure 4G).The results showed that indirubin promoted lipid peroxidation of tumors and suppressed breast cancerinvivo.
Discussion
Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer death in women.Chemotherapy is one of the effective but risky ways to treat breast cancer.Naturally,derived compounds have the potential to develop new drugs because of their safety and efficacy.Indirubin and derivatives have an inhibitory effect on tumors[15-17].In our study,the effectiveness and pharmacological mechanism of indirubin were explored,which may contribute to the development of an anti-breast cancer drug.
Ferroptosis is a unique way of cell death,and it has been shown that ferroptosis plays an important role in the occurrence and development of tumors[31].By inducing ferroptosis of tumor cells,it can be used for tumor therapy[32,33].Ptgs2,also known as cyclooxygenase-2(Cox-2),is the key enzyme in prostaglandin biosynthesis.As a matter of fact,cyclooxygenases can catalyze lipid oxidation[34,35].Studies have shown that Ptgs2 is involved in the process of ferroptosis,and Ptgs2 is significantly up-regulated in the ferroptosis induced by RSL3 and erastin[36].Meanwhile,suppression of Ptgs2 can inhibit the ferroptosis of cells and play a protective role[26,27].In our study,results of the bioinformatical analysis showed that ferroptosis-related gene Ptgs2 was expressed lower in breast cancer,which indicated an efficient strategy for treating breast cancer.It is possible to induce ferroptosis of breast cancer cells by upregulation of Ptgs2.Then,in vivoandin vitroanalysis results showed that indirubin could play an anti-breast cancer role by upregulation of Ptgs2 to induce ferroptosis.
GSK-3β is a protein-related to the regulation of Ptgs2,which can increase the expression of Ptgs2 by inhibiting GSK-3β activity[30].The activity of GSK-3β is regulated by phosphorylation at Ser 9 and Tyr 216 in opposing directions,with phosphorylation of Ser 9 decreasing GSK-3β activity and phosphorylation of Tyr 216 increasing GSK-3β activity[37].However,previous studies have shown that indirubin is an inhibitor of GSK-3β[28].Our results showed that indirubin promoted phosphorylation of GSK-3β at Ser 9 and then inhibited the activity of GSK-3β.Molecular docking further proved that indirubin with two carbonyl groups could form hydrogen bonds with Gln185 and Val135 of GSK-3β indicating the special role of indirubin in regulating GSK-3β.
Conclusion
In conclusion,indirubin suppresses 4T1 breast cancer by induction of ferroptosisin vitroandin vivoin a 4T1 murine breast cancer model,which may be related to up-regulation of Ptgs2 and binding of indirubin with GSK-3β and then promoting its phosphorylation at Ser 9.
Data availability
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to liweixi1001@163.com(Wei-Xi Li).
Abbreviations
HNE,4-hydroxynonenal;CML,chronic myelocytic leukemia;Cox-2,cyclooxygenase-2;DEGs,differentially expressed genes;GPX4,glutathione peroxidase 4;GSH,glutathione;GSK-3β,glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta;LDH,lactate dehydrogenase;MDA,malondialdehyde;MTT,3-(4,5-dimethyl-2- thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-Htetrazolium bromide;Ptgs2,prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department-Applied Basic Research Joint Special Funds of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine(2019FF002(-007),2017FF116(-015));National Natural Science Foundation of China(81560661,81960780).
Author contributions
Xiu-Ping Kuang and Chang-Yu Yan performed the experiments and analyzed the data.Ying-Nan Jiang and Ji-Wei Huang drafted the manuscript.Wei-Xi Li and Yong-Zhi Guo designed the research and revised the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2022年1期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2022年1期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Speed-resolved blood perfusion and oxygen saturation in human skin response to thermal stimulation
- Clinical practice guidelines for traditional Chinese medicine and integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine:a cross-sectional study of data analysis from 2010 to 2020
- Guizhi Fuling capsule can induce apoptosis of myeloma cells through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway
- Efficacy and safety of Phillyrin (KD-1)capsule in the treatment of moderate COVlD-19:protocol for a randomized controlled trial
