Theanine combined with cisplatin inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of TNBC cells through Akt signaling pathway
Xiao-Yu Shi,Xiao Bao,Yao Li,Cheng-Liang Yin
1College of Pharmacy,Yantai University of Pharmacy Molecular,Yantai 264005,China. 2College of Pharmacy,Wenzhou Nursing School,Wenzhou 325000,China.3Department of Pharmacy,The Second Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College,Bengbu 233000,China. 4Faculty of Medicine,Macau University of Science and Technology,Macau 999078,China.
Abstract Background: Theanine, was natural compounds, has been employed in antibacterial,antineoplastic, promotion of hair growth, therapy of poliosis,and removing pattogenic heat from the blood and toxic material from the body for centuries.However,few reports focused on the treatment by theanine combined with chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer.Methods: Our study aimed to evaluate and compare the molecular and cellular effects of theanine in combination with cisplatin in triple negative breast cancer lines MDA-MB-231.The 50% inhibitory concentration and cell viability were determined by the cell counting kit-8 assay.Meanwhile,wound healing and transwell assays were used to evaluate the effect of theanine combination with cisplatin on triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell metastasis. Moreover, the label-free proteomic method was available to explore the molecular mechanism of theanine combination with cisplatin on TNBC cells. What’s more,reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blotting were carried out to evaluate the related protein and mRNA alteration in the Akt signaling pathway. Results:With theanine added, the inhibitory effect of cisplatin on cell proliferation and metastasis was significantly improved. Meanwhile, with the increase of theanine concentration, the anti-tumor effect of the combination group was also significantly improved. Afterward,label-free proteomics analysis showed that theanine combined with cisplatin could significantly activate the Akt signaling pathway, thus improving the anti-tumor effect of cisplatin. Finally, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blotting experiment showed that the combination of cisplatin with theanine induced the greatest down-regulation of phosphorylated Akt expression. Conclusion: All in all, combining theanine with appears to be a promising strategy for the effective treatment of TNBC in the prospective application which merits further clinical investigation.
Keywords: triple negative breast cancer; theanine; cisplatin; combination therapy; Akt pathway
Highlights
1. Theanine can enhance the anti-tumor effect of cisplatin.2. Theanine combined with cisplatin may be a new treatment for triple negative breast cancer.
Medical history of objective
In traditional medicine,the efficacy of tea is very comprehensive and magical.According to the ancient books,it was recorded inTong Yuewritten by Wang Bao in the Western Han Dynasty(202 B.C.E.–8 C.E.).The record of tea later appeared inShen Nong Ben Cao Jing(25–220 C.E.),which said that in order to find plants beneficial to human beings,Shen Nong tasted all kinds of herbs and finally found tea to detoxify,where tea was first used as medicine to detoxify hundreds of poisons.AndCha Jing(780 C.E.)is the earliest,most complete and most comprehensive monograph on tea in China and even in the world,and is known as the"tea encyclopedia".As more and more functions have been found,scientists have also begun to analyze the main components of tea.It was found that theanine,tea polyphenols,alkaloids,and other compounds contained in it have very important effects.This study systematically introduced the role of theanine,the main component of tea,in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer,and provided scientific basis for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer.
Background
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease, which includes hormone receptor positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 positive,and triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Different subtypes of breast cancer have different treatment schemes and prognosis [1]. Among them, TNBC has drawn great public attention with the characteristics of the negative estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor[2].TNBC accounts for about 15%–20%of all breast cancers, owning the highest degree of malignancy [3]. TNBC is characterized by small onset age, strong invasion, high metastatic potential, and poor prognosis [4]. In clinical treatment, surgery and chemotherapy are still the main treatment methods due to the lack of clear treatment targets and insensitivity to endocrine treatment [5].Cisplatin (DDP) is a commonly used chemotherapy drug in clinical practice for TNBC, and is reported to improve pathological complete response rates in TNBC patients, but its use is limited due to chemotherapy resistance and large adverse reactions [6]. Because multiple drugs affect multiple targets and cell subsets, and drug resistance often occurs when utilized alone, leading to reduced efficacy. Then, drug combinations are widely used, and medical researchers have to seek new treatment options[7].
Some natural chemopreventive agents have displayed the potential of enhancing the influences of drugs against cancer [8]. For example,tea has various health benefits and tea polyphenols are regarded as the main anticancer compounds in tea [9]. However, many researchers have indicated that besides tea polyphenols, theanine, a nonproteinic amino acid in the tea also has significant bioactivity against some cancer [10].
Theanine has been widely used as a functional ingredient without toxic effects on human health. In order to determine the potential of theanine as an adjuvant therapeutic agent against TNBC, our present study was focused on the effects of theanine combination with traditional cytotoxic anticancer DDP on human TNBC cells (Figure 1).
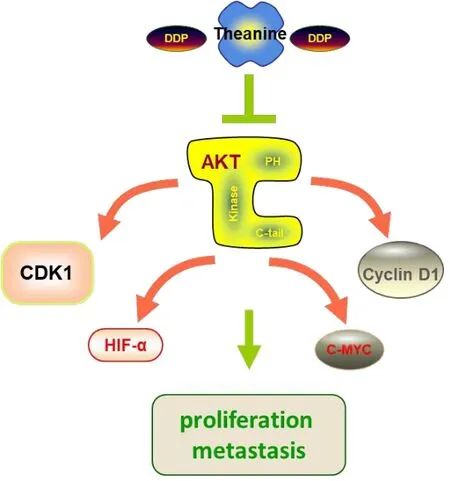
Figure 1 Mechanism of theanine combined with cisplatin on TNBC cells. TNBC, triple negative breast cancer; DDP, cisplatin; PH,pleckstrin homolgy domain; CDK1, cyclin dependent kinase 1; HIF-α,hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; C-MYC, V-Myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog; AKT, protein kinase B.
Materials and methods
Materials
Primary antibodies and secondary antibodies for western blotting were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology Inc. (Shanghai,China), Santa Cruz Biotech Inc. (Shanghai, China), and R &D Systems(Shanghai, China). 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EDU) detection kit,fibronectin, and transwell chambers were obtained from BD Inc.(Shanghai, China). All materials for cell culture and other chemicals including theanine, trypsin, dithiothreitol, alkylatingagents and DDP was acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (Shanghai,China).
Cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay
The MDA-MB-231 cell line was obtained from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing, China). The cells grew in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, glutamine (200 μM), streptomycin (0.1 mg/mL) & penicillin (100 U/mL) at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 95% air and 5% CO2atmosphere. The colorimetric CCK8 metabolic activity assay was used to identify the relative rate of cell growth, according to previously published methods[11].Cells(2×103/mL)were seeded into a 96-well plate and incubated overnight to allow attachment. After treatment with theanine at 5 to 20 μM, or in the combination with anticancer drug DDP (5 μM), the absorbance values in each test sample and relative cell growth(%) were analyzed using CCK8 assay.
EDU assays
Cell proliferation ability was tested by EDU assay. Cells were treated for 48 h with different concentrations of theanine (T/5-20 μM),cisplatin (DDP/5 μM), theanine + DDP. After dyed, the cells were taken photos under the fluorescent microscope(Nikon,Tokyo, Japan).Proliferation ability was further detected by counting EDU positive cell ratio.
Wound healing assay
The wound healing assay for cell migration was evaluated according to the published method. Cells grew in a 6-well plate with completed medium until confluent. The wounds were scratched with a 100 μL pipette tip. After the cell debris were washed three times with serum free media and treated with different concentrations of theanine,DDP,and the combination of theanine with DDP for 24 h.The wounds were photographed with a light microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) at the same field of view at 0 and 24 h, respectively. The relative distance of the scratches was recorded under the microscope and evaluated using the ImageJ software.
Transwell assay
The invasion cells were measured by transwell chambers coated with matrigel on polycarbonate filters. The cells (1 × 105) were plated on the upper surface of a filter with theanine, DDP, and the combination of theanine with DDP. The medium was added into lower chamber in the absence or presence of 10% of fetal bovine serum. The cells that invaded (12 h later) through the filter were stained with crystal violet and then counted under a fluorescent microscope (Nikon, Tokyo,Japan).
Western blot analysis
MDA-MB-231 cells were incubated for 48 h with different concentrations of cisplatin(DDP/5μM),T+DDP(T/20μM+DDP/5μM).The protein expressions were analyzed by Western Blotting using the previously reported. The lysates were extracted as directed by the kit’s manufacturer (Beyotime, Haimen, China). Proteins in cell lysates were electrophoretically separated on SDS-PAGE gels and then identified using primary and secondary antibodies to the specific proteins. With the use of improved chemiluminescence reagents,signals were detected (Beyotime, Haimen, China).
Sample preparation
Two sets of MDA-MB-231 cells were available,and one group received 5 μM DDP, while the other received 5 μM DDP and 20 μM theanine.After a 24-hour incubation period, the standard procedures were used to extract the total protein of the cells. After measuring the 50 μg of protein with bicinchoninic acid, 4 times the volume of acetone was added to extract the sample. The mixture was then centrifuged for 15 minutes at 14,000 g at 20 °C. Remove the supernatant, add dithiothreitol, and incubation at 55 °C for 1.5 hours before incubation with alkylatingagents for 30 minutes.Trypsin was added for digestion,and the sample was kept at 37 °C overnight. Then take 2 μg protein from each sample for liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry detection.
MaxQuant and Perseus
MaxQuant was used as a peptide search engine. In a nutshell, just two missed cleavages were permitted. For peptide and protein, the maximum false discovery rate was set at 0.01, and label-free quantitation (LFQ) was enabled with an LFQ minimum ratio count[12]. The tolerances for the parent ion (the main search) and the peptide (the daughter) searches were 20 and 4.5 ppm, respectively.Methionine oxidation and acetylation were employed as the variable modifications, whereas cysteine was carbamidomethylated as the fixed modification. The output for the protein group was then processed using the Perseus computer software for the study of proteomics data. In a nutshell, the probable contaminants were eliminated, the reverse peptide was added, the LFQ was log2transformed, and proteins were identified by site. Following the identification of the proteins with at least two peptides and their presence in at least 70% of the samples, the missing values were imputed using values from the normal distribution to replace those that were missing.
Bioinformatics analysis
Annotations in the protein analysis through Database for Annotation,Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) database(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) were used to categorize proteins based on biological processes, cellular components, and molecular function, in accordance with Gene Ontology (GO) standards [13]. Signaling pathway analysis was carried out using the tools available in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database(http://www.genome.jp/kegg/pathway.html) [14].
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed on the data from independent experiments using the SPSS 16.0 program. Data (mean ± standard deviation,n ≥3)represented independent experiments.P<0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Theanine displayed synergistic effects with DDP on repression of TNBC cell growth
To study the function of theanine in TNBC, DDP was added to the MDA-MB-231 cells in combination with theanine of different concentrations, and the changes in cell functions were observed.CCK-8 assay was used to measure cell growth ability. Compare the cells in the DDP group alone, the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50)of combination group were significantly decreased. After 24 h treatment,the IC50of DDP alone treatment group was 8.485 μM,while the IC50of DDP combined with 5 μM theanine group decreased to 7.66 μM, and the IC50decreased to 2.25 μM after increasing the concentration of theanine to 20 μM,P<0.05.After 72 h,IC50value of DDP in MDA-MB-231 cells were 6.02 μM. After combination with 5–20 μM theanine, the IC50value decreased to 4.33, 2.67 and 1.09 μM, respectively (Figure 2A). Subsequent EDU assays also confirmed that incubation with theanine increased the sensitivity of cells to DDP.After theanine was added, the proportion of EDU positive cells decreased significantly, and with the increase of theanine concentration, the proportion of proliferating cells decreased gradually (Figures 2B, 2C). The results indicated that incubation with theanine could decrease the proliferation of TNBC cells and increase the cells’ sensitivity to DDP treatment.
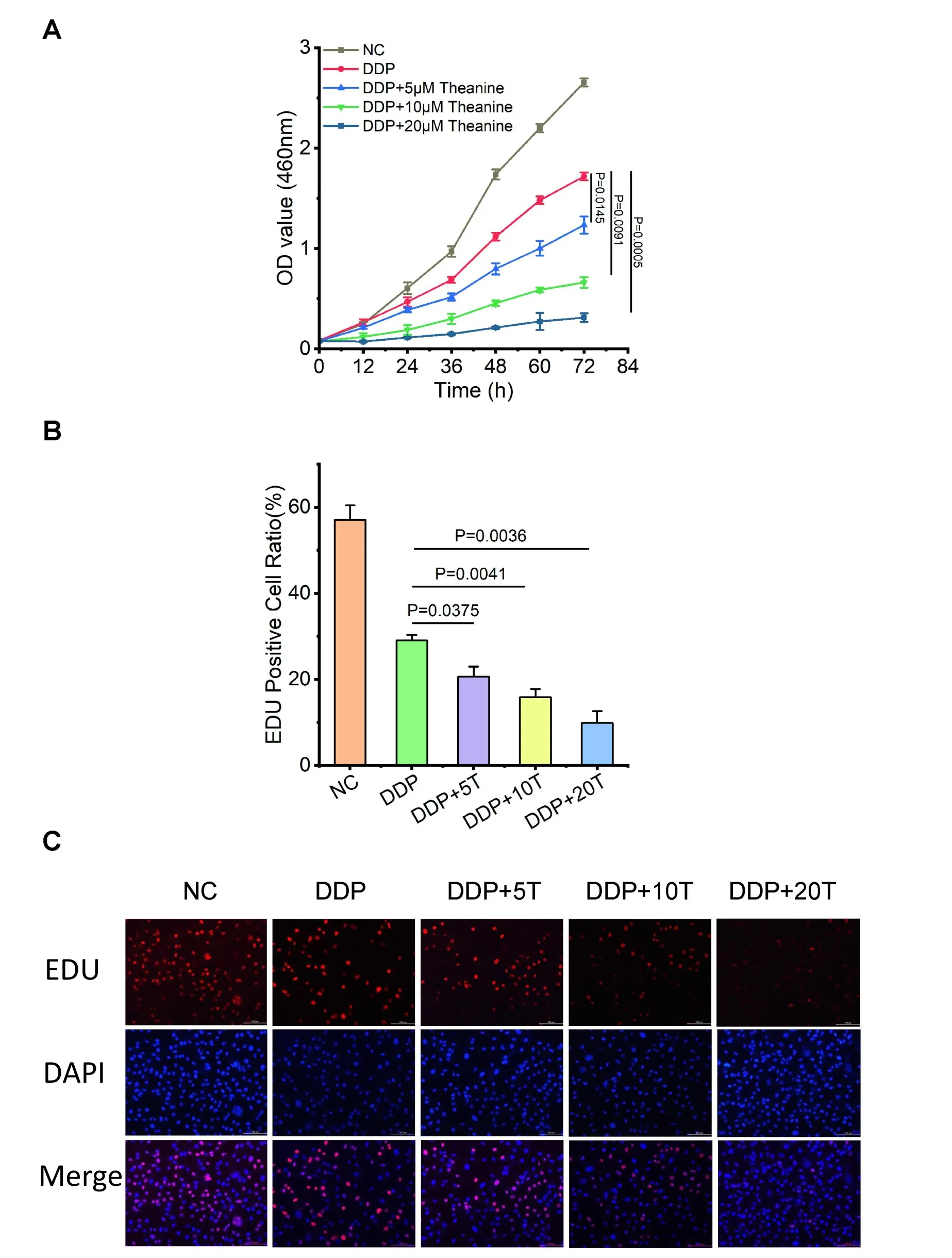
Figure 2 Influence of theanine and cisplatin on the growth of TNBC cells.Cells in triplicate culture were incubated with cisplatin,and different dosage of theanine, single or in combinations. In the combination group, cells were pretreated with a single dose of 5 μM cisplatin for 24 h before incubation with 5–20 μM theanine. Cell viability was determined by CCK8 assay(A) and EDU assays(B, C), scale bar, yellow, 100 μM. Comparing to cisplatin-treated control, P < 0.05 was statistically significant. TNBC, triple negative breast cancer. DDP, cisplatin; OD, optical density; NC,numerical control; EDU, 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine; DAPI,2-(4-Amidinophenyl)-6-indolecarbamidine dihydrochloride.
Theanine showed synergistic effects with DDP on inhibition of TNBC cell migration and invasion
TNBC cell migration is the key step for further progression &metastasis.Thus,we investigated the impacts of theanine combination with DDP on TNBC cell migration and invasion. The wound healing assay demonstrated that DDP (5 μM) significantly suppressed the TNBC cell migration. After theanine treatment, theanine combination with DDP significantly decreased cells migration ability compared with the single DPP group. Meanwhile, with the increase of theanine concentration, the metastatic potential of TNBC cells were significantly repressed in a dose-dependent way(Figures 3A, 3B). The cell rate of migration inhibition by 1.50-fold (5 μM) to 2.54-fold (20μM) (in the case of theanine + DDP) compared to the single DDP group. Similarly, we used the transwell experiment to explore the effect of theanine combination with DDP on the invasion of TNBC cells. The experimental results showed that theanine combination with DDP could significantly inhibit the invasion of TNBC cells compared with the single DDP group (Figures 3C, 3D). It should be noted that with the increase of theanine concentration,the invasion of TNBC cells in the combined group was significantly reduced compared with the DDP group. These results indicated that theanine combined with DDP could significantly reduce the migration and invasion ability of TNBC cells.

Figure 3 Influence of theanine and DDP on the migration and invasion of TNBC cells.Cells in triplicate culture were incubated with cisplatin,and different dosages of theanine,single or in combinations.In the combination group,cells were pretreated with a single dose of 5 μM cisplatin for 24 h before incubation with 5–20 μM theanine.Cell migration was determined by wound healing assay(A,B),scale bar,black,50 μM.Cell invasion was determined by transwell assays (C, D), scale bar, yellow, 100 μM. Statistically significant compared to cisplatin-treated control (P < 0.05).TNBC, triple negative breast cancer. DDP, cisplatin; NC, numerical control.
MS-based LFQ quantification reveals molecular effects of theanine combination with DDP
Next, we reviewed and considered the molecular mechanism related to the effect of theanine combined with DDP on the growth and migration of TNBC cells through label-free proteomics. Firstly, we treated MDA-MB-231 cells with DDP, cisplatin and theanine respectively, and each group contained three biological repeats. After 24 h incubation, cells were collected. Then, the total cell protein was extracted, in order to detect the protein, and the sample was precipitated to reach the optimal concentration for digestion.Afterward, the protein was analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The raw data were identified by MaxQuant software and corrected by Perseus software.Finally, we identified 3648 proteins (Figure 4A). Then, to gain insight into the functions of the identified proteins, we calculated the different protein expressions according to the intensity of the two groups of proteins. Under the threshold of fold change (FC),differentially expressed proteins were screened. According to the results of FC andPvalues, we obtained 100 significantly different proteins. For DDP + theanine/theanine, 24 proteins were up-regulated (Log2FC > 0.6 andP< 0.05) and 76 proteins were down-regulated (Log2FC < ?0.6 andP< 0.05) in the combination group.The expression of these 100 different proteins was shown in the heatmap (Figure 4B). To assess the quality of our data sets, we performed Pearson analysis on the three biological replicates of these two groups of samples, and the results showed that the data shown good repeatability (Figure 4C), and the histogram also showed that the sample protein shown normal distribution (Figure 4D).
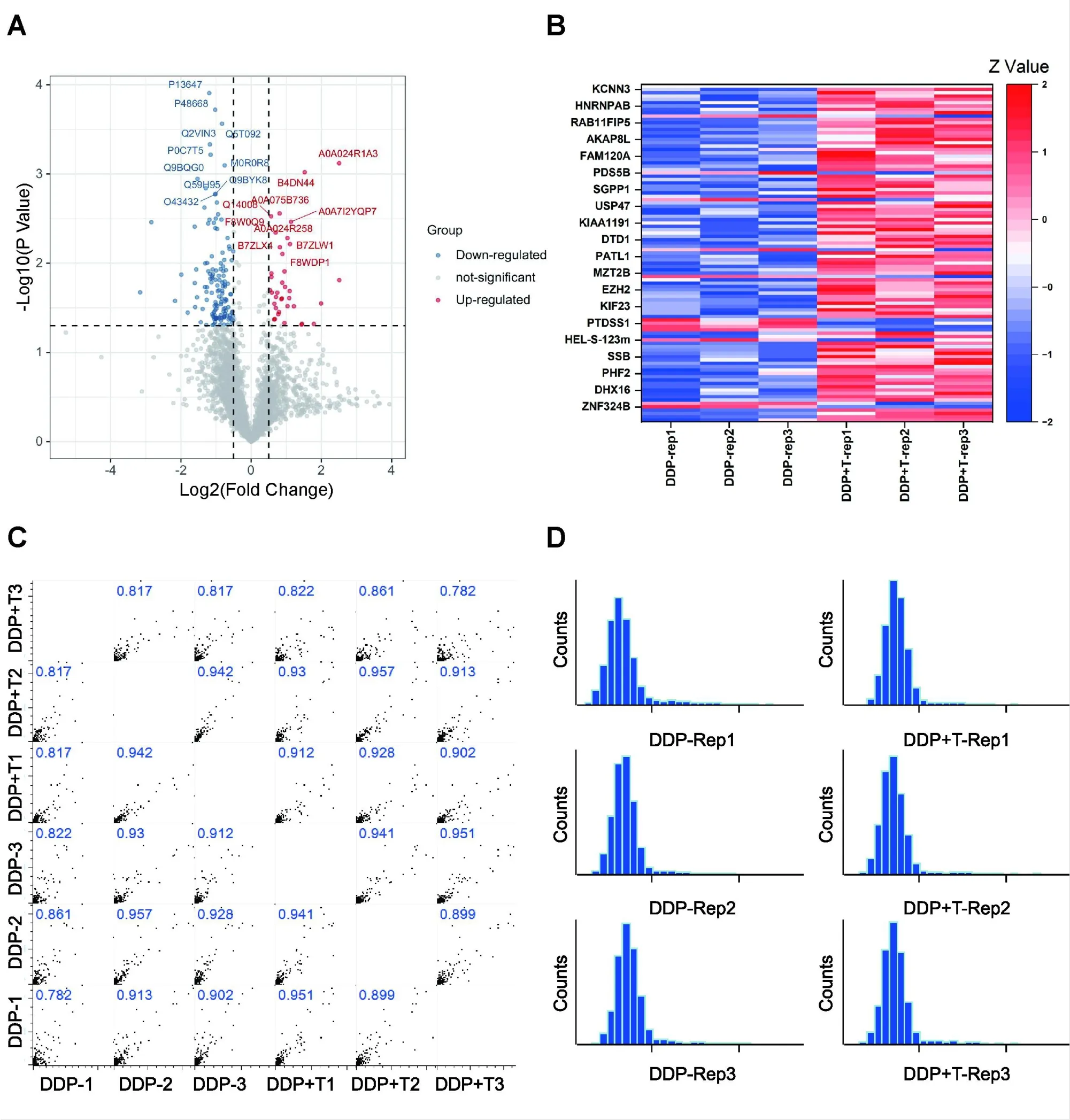
Figure 4 Expression of total protein and differential protein in two groups of cells detected by LC-MS.(A)Volcano plot of identified proteins.The blue dot represents the down-regulated protein,the red dot represents the up-regulated protein,and the gray dot represents the protein with no significant difference. Student’s t-test (P value ≤0.05).(B) Heatmap of the differentially expressed proteins in two groups. (C) Pearson correlation show clustering of samples replicate reproducibility. (D) The distribution of peptide number. LC-MS, liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry;DDP, cisplatin.
Functional analysis of differentially abundant proteins
Subsequently, for a deeper analysis of our dataset and to confirm obtained results, we performed a GO enrichment analysis through the DAVID database (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) [15]. DAVID is a system for hierarchically classifying genes or proteins in a graph structure,retrieving,in a ranked list,both the set of terms used to describe these proteins and the correspondingPvalues [16]. GO was carried out for the biological process, cellular components, and molecular functions associated with the differentially abundant proteins [17]. Compared to DDP single group, the 100 differently abundant proteins in DDP +theanine comprised including 24 up-regulated proteins and 76 down-regulated proteins which participated in 35 biologicalprocesses, 25 cellular components, and 23 molecular functions.Biological process analysis indicated that these differential proteins were mainly related to negative regulation of transcription from negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of transcription, chromatin remodeling,negative regulation of apoptotic process, and protein deubiquitination(Figure 5A).Cellular component analysis of DDP+theanine/theanine revealed that most of the differentially abundant proteins belonged to the nucleoplasm, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytosol and ribonucleoprotein complex (Figure 5B). Molecular function analysis revealed that most differentially abundant proteins were related to RNA binding,poly(U)RNA binding, protein binding, ATPase activity, and microtubule binding (Figure 5C). KEGG is the public database used to retrieve the pathway [18]. Pathway analysis can identify the most important biochemical pathways and signal transduction pathways in which proteins participate [13]. Then, we put the differently identified proteins on David website to perform KEGG function annotation analysis. A total of 100 different proteins were annotated to 30 KEGG pathways. According to the functions of these pathways, we found that these differential proteins mainly affected the Akt signaling pathway(Figure 5D).

Figure 5 Main functional classification with the most significant enrichment of the differentially expressed proteins. (A) Gene Ontology analysis of biological process. (B) Gene Ontology analysis of cellular component. (C) Gene Ontology analysis of molecular function. (D) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of differentially abundant proteins. GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP,biological process; CC, cellular component; MF, molecular function.
Validation through western blotting and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis
In the above analysis, we found that the addition of theanine would inhibit the Akt signaling pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells, so we used PCR and WB experiments to further verify the above results. Here we used two TNBC cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-453) for verification. Using c-myc, CDK1, HIF-1α, Akt and its phosphorylated Akt primary antibody to verify proteomic analysis by immunoblotting and RT-PCR, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as the load standardization substance. As shown in Figures 6A–6D,it was verified that after theanine was added,the expression of c-myc, CDK1, and HIF-1α in MDA-MB-231 cells which treated with theanine and DDP decreased significantly, and the phosphorylation level of Akt also decreased significantly. Combined with proteomics and Western blotting experimental results, the results showed that theanine can enhance the sensitivity of DDP to TNBC cells by activating Akt signaling pathway.
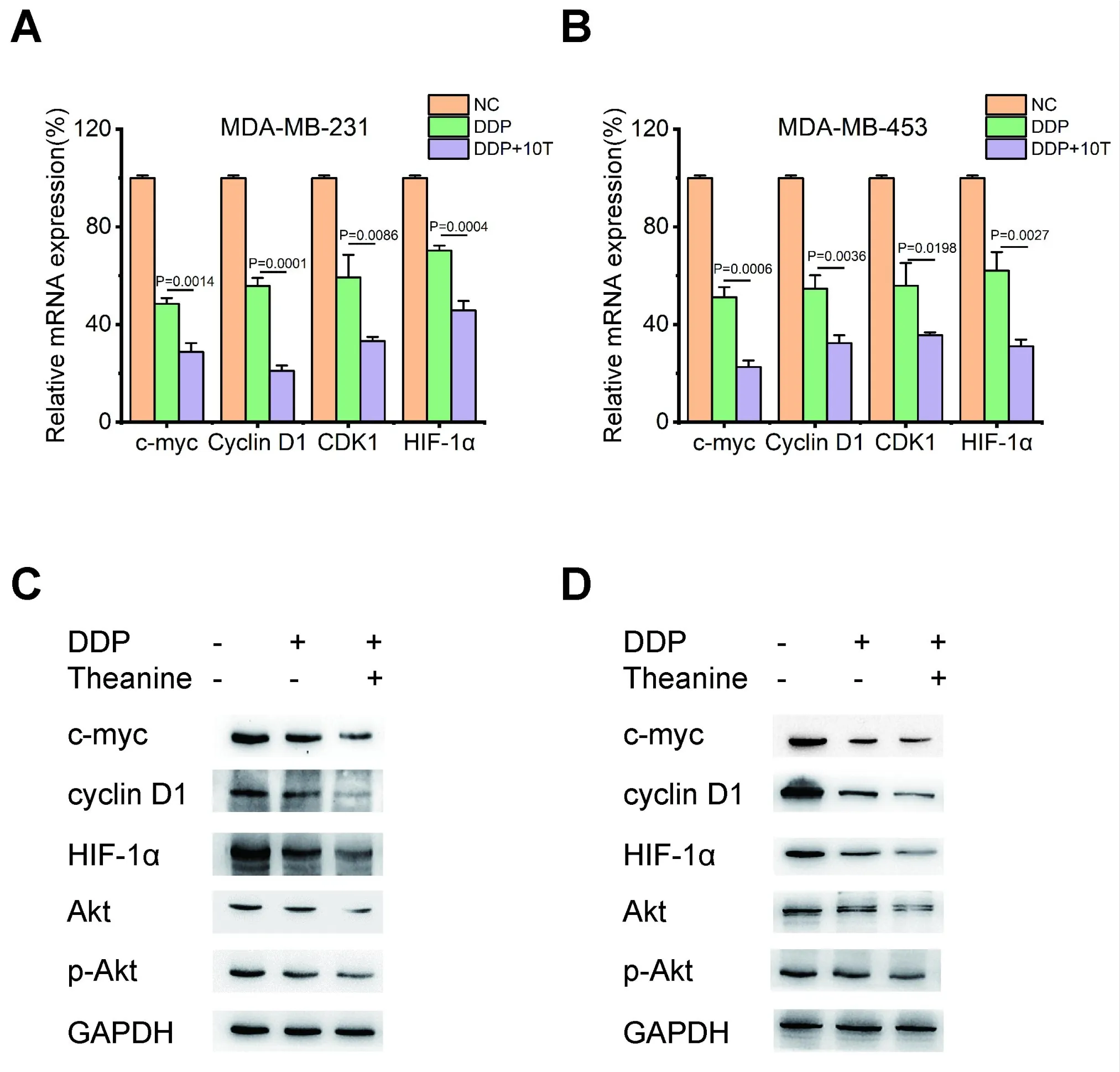
Figure 6 Protein alteration in Akt signaling pathway after combination treatment of theanine and cisplatin. (A, B) The mRNA level determined by RT-PCR demonstrated that treatment of both MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-453 cells with theanine and cisplatin could dramatically reduce the mRNA expression of genes related to the Akt signaling pathway compared with single cisplatin chemotherapy in both two cell lines. (C,D) The protein level determined by immunoblotting demonstrated that treatment of both MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-453 cells with theanine and cisplatin could dramatically reduce the protein expression of genes related to the Akt signaling pathway compared with single cisplatin chemotherapy in both two cell lines. RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; DDP, cisplatin; Akt, protein kinase B; p-Akt,phosphorylation-protein kinase B; mRNA, messenger RNA; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor-1; CDK1, cyclin dependent kinase 1; NC, numerical control.
Discussion
One of the challenging issues that need to be solved globally is TNBC.Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are presently the main approaches for treating tumors, along with radiotherapy and chemotherapy [13]. Even if some outcomes have been obtained,effective treatment, prevention, and even cure for malignant tumors are still required. For centuries, tea has been a very well-liked beverage throughout the world. Theanine,an amino acid found in tea,has been shown to have beneficial effects on a variety of conditions,including cancer, cardiovascular disease, obesity, the common cold,and sleep quality[19].D-theanine and theanine are two chiral isomers of theanine, which is a derivative of glutamate[20].
However, theanine is a naturally occurring substance with a very high level of biological activity in vivo.After being absorbed,theanine will swiftly enter the blood as well as several tissues and organs [21].Theanine and its synthetic derivatives have been proven to decrease tumor cell growth, invasion, and metastasis as well as trigger tumor cell apoptosis, which can prevent and treat tumors (including lung cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, and cervical cancer) [22].Additionally, research has shown that theanine can reduce the side effects of anti-tumor medications while simultaneously enhancing the activity of some anti-cancer medications. These findings were crucial in the development of cancer chemotherapy. DDP is commonly used in clinical TNBC chemotherapy,but its application is limited due to its significant side effects[22, 23].
In our study, we firstly verified that the combination of theanine and DDP could improve the anti-tumor effect of DDP through cell proliferation and metastasis experiments, and with the increase of theanine concentration, the combined anti-tumor effect was also significantly enhanced. Then, in order to further explore the mechanism of theanine’s synergistic anti-tumor effect, we performed quantitative proteomics to detect the protein changes of MDA-MB-231 cells before and after combination with the theanine. In detail, the total protein of MDA-MB-231 cells were detected when DDP was used alone, and DDP was combined with theanine to determine and quantify its protein content. In fact, in the era of atomic science,quantitative methods based on mass spectrometry can help reveal which proteins are changed by specific therapies, and thus which pathways are changed [24, 25].We submitted the MS-based results to enrichment the up-regulated and down-regulated proteins and verified the discrete number of changed proteins through western blot analysis, thus strengthening the proteomics method. Proteomic data analysis showed that theanine enhanced the anti-tumor effect of DDP by inhibiting Akt signaling pathway.
As a natural compound, theanine’s specific mechanism in anti-tumor has not been deeply studied.We found that it enhances the anti-tumor efficacy of DDP by inhibiting Akt signal pathway. This result is consistent with the report of Zhang, showing that theanine treatment downregulated the levels of p-Akt protein expression [26].Akt is overactivated in many tumors and is an important signal molecule in PI3K-Akt-mTOR signal pathway [27]. Akt is crucial for proliferation,invasion and metastasis of tumor cells,and ensuring that tumor cells are resistant to chemotherapy and radiation therapy [28].In addition to the key role of Akt in normal cell physiology, many studies have also demonstrated the activation of the Akt cascade in various types of human cancers, which usually leads to tumor invasiveness and drug resistance [29]. Several pathways of Akt regulation are linked to cancer-related phenotypes [30].Some reports showed that PI3K inhibiting could inhibit the function of Akt, and the inhibition of AKT function is often accompanied by the decrease of p-Akt(Ser473) expression.
To the best of our knowledge, no study has investigated whether theanine combination with DDP treatment inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of TNBC cells. These results also confirmed that theanine was closely related to Akt pathway, suggesting that a deeper exploration of theanine may be a potential treatment of TNBC.Unfortunately, due to the problem of experimental conditions, we have not been able to verify it in animal experiments,which is also the direction of further research in the future.
Conclusion
In this study, theanine can significantly improve the anti-tumor effect of DDP, and with the increase of theanine concentration, the anti-tumor effect of DDP is also significantly improved. Through proteomics research, we found that theanine may play a synergistic anti-tumor role by activating the Akt signal pathway.To sum up,these data suggest that using theanine and traditional cytotoxic drugs, a promising new strategy for cancer chemotherapy, should improve the anti-tumor effect of chemotherapy drugs.
 Traditional Medicine Research2023年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2023年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Exploring the compatibility theory of traditional Chinese medicine formulae: the disassembled prescriptions study
- Research progress of artesunate in diabetes and its complications
- Comparison of polysaccharides from 10 species of genera Paris,Trillium,Aspidistra,and Polygonatum
- Mechanism of Baihu Renshen decoction on T2DM rats based on mitochondrial autophagy mediated by PINK1/Parkin
- Network pharmacology and verification experiment-based prediction of active components and potential targets of Alpiniae Oxyphyllae Fructus-Saposhnikoviae Radix(Yizhiren-Fangfeng)for treatment of diabetic kidney disease
