HPLC fingerprint of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting period
LIU Ai-xia, ZHOU Ming-yan, LI Xiang-yi, LI Li, ZHANG Yu-xin, ZHENG Xiu-wen,WEN Huan, ZHANG Jun-qing,2?, ZHANG Xu-guang,2?
1.Hainan Province Key Laboratory of R&D on Tropical Herbs, Haikou 571199, China
2.School of Pharmaceutical Sciences Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, China
ABSTRACT Objective: To establish HPLC fingerprint of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting periods, and analyze the effect of harvest time on the quality of the medicinal materials by combining with chemical pattern recognition.Methods: The analysis was performed on Sun Fire -C18(150 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm) column.The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile-0.1% phosphoric acid solution (gradient elution) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min.Results: The HPLC fingerprint of Nauclea officinalis stems was established and 12 common peaks were determined, and 3 chromatographic peaks were identified by comparison with the mixed references.There were some differences in the quality of Nauclea officinalis in different harvesting periods.The OPLS-DA analysis successfully predicted four main markers of quality difference.Conclusion: The established HPLC fingerprint could reflect the composition characteristics of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting period, and the main markers that influence the composition difference of the stems could be used as key indicators for the quality control.
Keywords:
Nauclea officinalis stems
HPLC fingerprint
Chemical pattern recognition
1.Introduction
Nauclea officinalis, also known as ebony, mountain bear bile,bear bile tree, etc., is the dried stems and root of Nauclea officinalis Pierre.ex Pitard, which can be harvested all year round[1].Due to its function of clearing heat and detoxifying, Nauclea officinalis has been used as a folk medicine plant for cold, fever, pharyngitis and acute conjunctivitis[2,3].Currently, the stems is considered to be the main medicinal part of Nauclea officinalis (Pharmacopoeia 1977).In addition, Nauclea officinalis in China is mainly distributed in Hainan,Guangdong, Guangxi and Yunnan, and it is one of the important traditional Li nationality medicine in Hainan[4, 5].The preparations produced from the extract of Nauclea officinalis mainly include Danmu extract syrup and Danmu injection[6, 7, 8], which are used to treat infectious diseases such as acute tonsillitis, acute pharyngitis and upper respiratory tract infection[9, 10, 11].The chemical composition of Nauclea officinalis includes alkaloids, phenolic acids and other compounds, and indole alkaloids strictosamide is the main pharmacodynamic components[12,13], which has antibacterial,antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities[14, 15].In recent years, the chemical composition and pharmacological action of Nauclea officinalis had been reported in munch literatures, but there are few researches on its fingerprint.Literature showed that Lian[16] et al.used HPLC fingerprint to study the similarity of three batches of Nauclea officinalis leaves and Nauclea officinalis.In addition, our research group[17] previously established HPLC fingerprint of Nauclea officinalis in different cultivation areas in Hainan.However, the sample size of previous studies was relatively small, and only similarity analysis was conducted, so the quality evaluation had certain limitations.
Literature search found that there was no report on the fingerprint of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting periods.Therefore, in order to improve the quality analysis model of Nauclea officinalis, this study adopted HPLC method to establish the fingerprint of 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting periods, combined with cluster analysis,principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis to evaluate the quality change of Nauclea officinalis stems and screen the main markers that affect the intrinsic quality difference of Nauclea officinalis stems at different harvest times.It can provide a valuable reference for the quality evaluation of Nauclea officinalis.
2.Instruments, materials and methods
2.1 Instruments and reagents
LC-2010A HT Liquid Chromatograph (Shimadzu); Ultrasonic instrument (KQ-5200DE); Blast drying oven (DI+G-9070A);BS210S electronic balance; XS105 DuaIRange electronic analysis balance.
The cryptochlorogenic acid (lot number PRF8010501, quality score98%), vanillic acid (lot number PRF7120842, quality score≥98%), sweroside (lot number PRF10121921, quality score98%)and vanillin (lot number PRF9052242, quality score98%) were all purchased from Chengdu puruifa technology development Co., Ltd.The chlorogenic acid (lot number MUST-13031401, quality score98%) was gained from Chengdu manster biotechnology Co., Ltd.The Protocatechuic acid (lot number 110809-200503, quality score99%) was obtained from China pharmaceutical and biological products inspection institute.The angustoline, strictosamide,naucleamide B, pumiloside and vincosamide were all extracted by ODS column in our laboratory, and identified by nuclear magnetic and mass spectrometry with a purity of more than 98%.Chromatograde acetonitrile; Analytical grade methanol; Ultra-pure water; Phosphoric acid.
2.2 Materials
The 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems of the same age (5 years old) in different months were collected from Qiongzhong County, Hainan Province, and all of them were identified as the dried stems of Nauclea officinalis Pierre.ex Pitard by professor Tian Jianping from the School of Pharmacy, hainan medical university.The samples were divided into spring-summer and autumn-winter harvesting periods.The specific information of the sample was shown in Table 1.
2.3 Methods
Preparation of reference solution: Accurately weighed the reference of cryptochlorogenic acid, vanillic acid, sweroside, vanillin,chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid, angustoline, strictosamide,naucleamide B, pumiloside and vincosamide into the volumetric bottles and added appropriate amount of methanol to fix the volume,then dissolved by ultrasound and shaken well.All of them were prepared into mother liquor with a concentration of 1 mg·mL-1, and 100 μL mother liquor was mixed for each to obtain mixed reference solution.In addition, appropriate amount of analytical grade methanol solution was filtered by 0.22 μm organic microporous filter membrane to obtain negative control solution.
Preparation of sample solution: About 0.5 g of Nauclea officinalis stems powder was weighed and added with 20 mL methanol,dissolved by ultrasound and then used solvent to make up the lost weight and mixed it evenly.Finally, the solution was filtered with 0.22 μm microporous filter membrane to obtain the sample solution.
Chromatographic conditions: Sun Fire-C18(150 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm) chromatographic column; column temperature: 30 ℃; the flow rate was 1.0 mL·min-1; detection wavelength: 258 nm; injection volume: 10 μL;mobile phase: acetonitrile (A)-0.1% phosphoric acid water (B), gradient elution (0-6 min, 10%~11%A; 6.01~9 min,12.6%~12.9%A; 9~35min, 12.9%~25%A; 35~50 min, 25%~60%A),the elution time of each sample was 50 min.
Specific test: According to chromatographic conditions, the negative control solution, mixed reference solution and sample solution (S6)were respectively injected for determination.Results there were no interfering solvent peak in the 50 min elution procedure, indicating that the method was more specific.
Precision test: According to chromatographic conditions, the sample solution (S6) was continuously injected 6 times for determination, and the chromatogram was recorded.Results with peak 9 as the reference peak, the relative retention time RSD of common peaks was 0.06%-1.19% and the relative peak area RSD was 1.41%~3.05%, indicating that the instrument used had good precision.
Stability test: According to chromatographic conditions, the sample solution (S6) was injected at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16 and 24 h for determination, and the chromatogram was recorded.Results with peak 9 as the reference peak, the relative retention time RSD of common peaks was 0.01%~1.18% and the relative peak area RSD was 0.79%~3.33%, indicating that the sample solution was stable within 24 h.
Repeatability test: The 6 samples solution of Nauclea officinalis stems was prepared, and then samples were injected for determination respectively according to chromatographic conditions,and the chromatogram was recorded.Results with peak 9 as the reference peak, the relative retention time RSD of common peaks was 0.01%~0.13% and the relative peak area RSD was 1.47%~3.32%, indicating that the method had good repeatability.
Sample determination: The 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems powder were taken to prepare samples solution according to the method, and then samples were injected for determination according to chromatographic conditions.The HPLC chromatogram was recorded and the peak area was analyzed according to the external standard method.
3.Results
3.1 Establishment of fingerprint and identification of common peaks
The HPLC chromatogram was imported into the “TCM Chromatographic Fingerprint Similarity Evaluation System (2012 edition)”in AIA format.The median method was used for multipoint correction, and then HPLC fingerprint chromatographic overlay of 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems was established.Total of 12 common peaks were determined in fingerprint, and 3 chromatographic peaks were identified by comparing the chromatogram of mixed reference substance, which were peak 2 Protocatechuic acid, peak 9 strictosamide and peak 11 vincosamide.Chromatographic overlay and reference substance chromatogram were shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Calculation of relative retention time and relative peak area
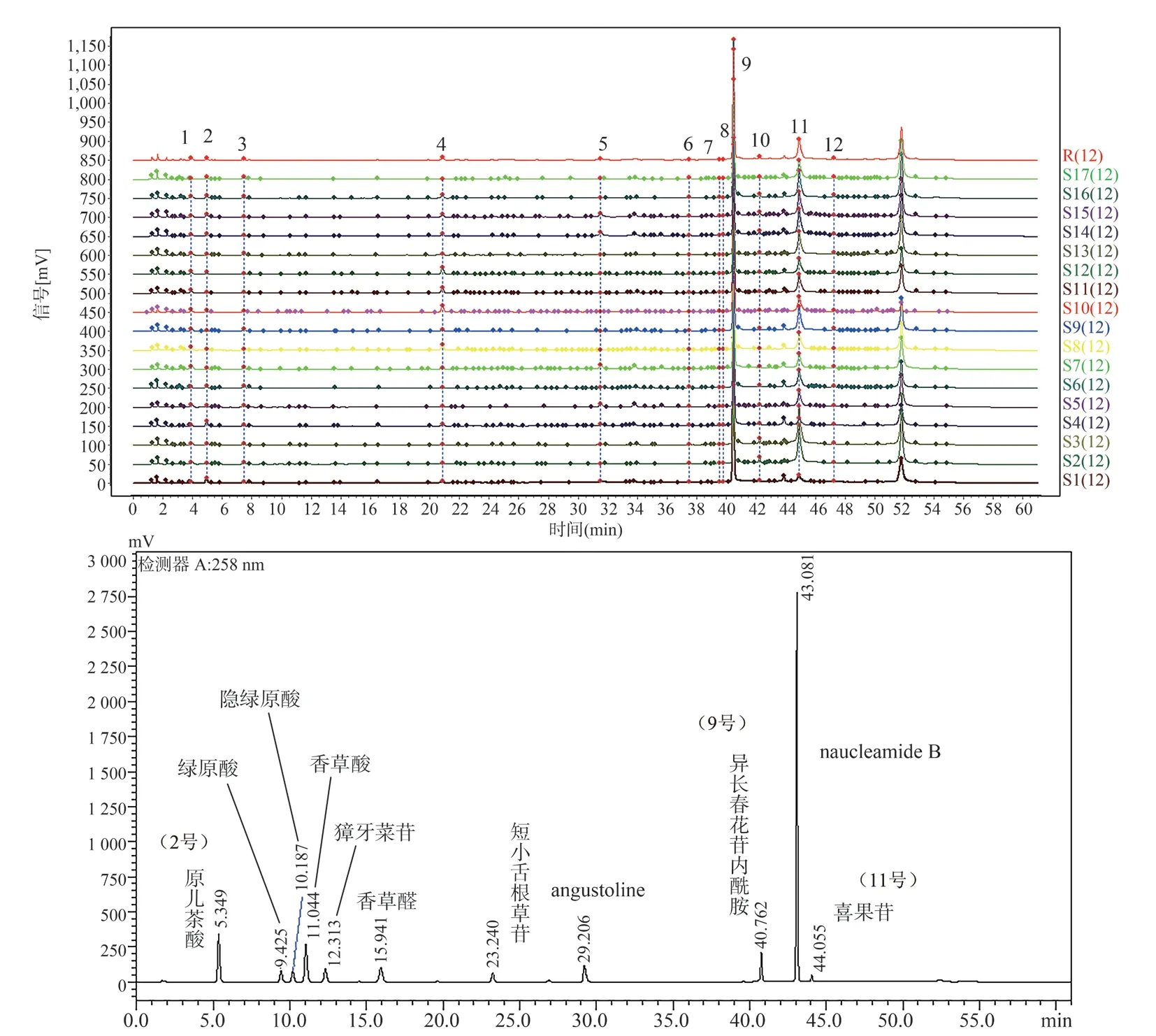
Fig 1 HPLC superimposed fingerprints of 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems and mixed reference substance chromatogram
Because strictosamide (peak 9) was the main active component of Nauclea officinalis and the peak area was large, the peak time and peak shape were stable, this peak was used as the reference peak to calculate the relative retention time and relative peak area of common peaks of 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems.Results the relative retention time RSD of 12 common peaks were all less than 0.89%, indicating that the established characteristic fingerprints were accurate and feasible.The relative peak area RSD value fluctuated greatly, ranging from 39.72% to 124.89% except for the reference peak 9 (S), which showed a big difference in peak area, indicating that the chemical composition of Nauclea officinalis stems was similar at different harvesting time, but there were some differences in content.The results were shown in Table 2 and 3.
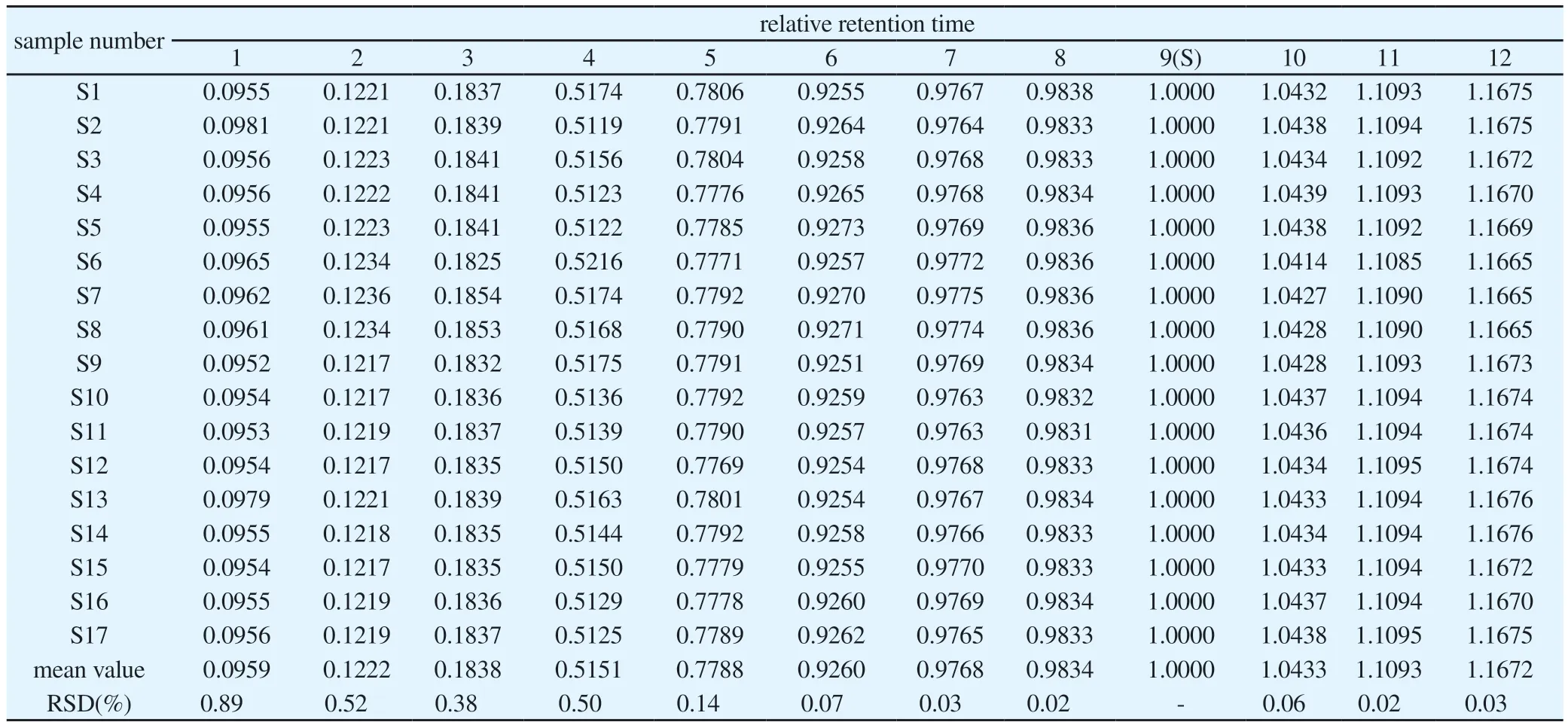
Tab 2 Relative retention time results of common peaks
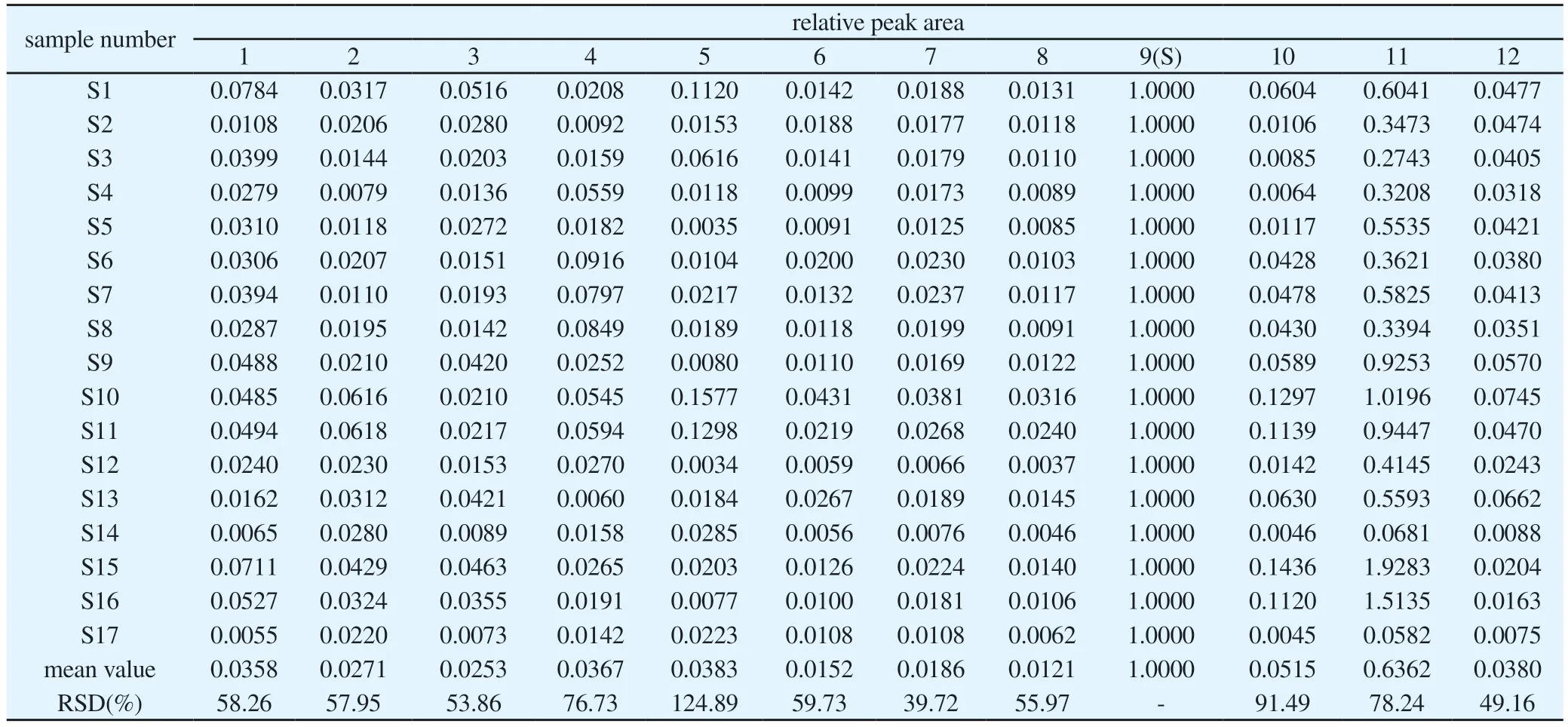
Tab 3 Relative peak area results of common peaks
3.3 Evaluation of similarity
The HPLC chromatogram was imported into the “TCM Chromatographic Fingerprint Similarity Evaluation System (2012 edition)”in AIA format, and control chromatogram was generated according to the method under 2.1.Then, the similarity of Nauclea officinalis stems in 17 batches was calculated using common pattern(R) as control.The results showed that except for the two batches of samples collected in autumn-winter with low similarity (S15 and S16), the similarity of samples from different batches was higher than 0.9, indicating that the quality of Nauclea officinalis collected in spring-summer was more stable than that in autumn-winter.The similarity results were shown in Table 4.

Tab 4 Similarity results of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting periods
3.4 Chemical pattern recognition
3.4.1 Cluster analysis (HCA)
The peak area of common peaks was imported through SPSS 22.0 software.The peak area was set as a variable, and then the intergroup connection method and square Euclidean distance were selected as the classification methods.Finally, the system clustering was performed and the pedigree map was drawn.The results were classified by distance 10, and 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems were divided into 2 classes, of which S14 and S17 were clustered into one class and the other batches were clustered into the second class.It was observed that the samples harvested in spring-summer were all grouped into one category, and those harvested in autumnwinter were divided into two categories, indicating that the overall quality of Nauclea officinalis herbs harvested in spring-summer was more stable compared to autumn-winter, which was basically consistent with the similarity results.The clustering pedigree diagram was shown in Figure 2.
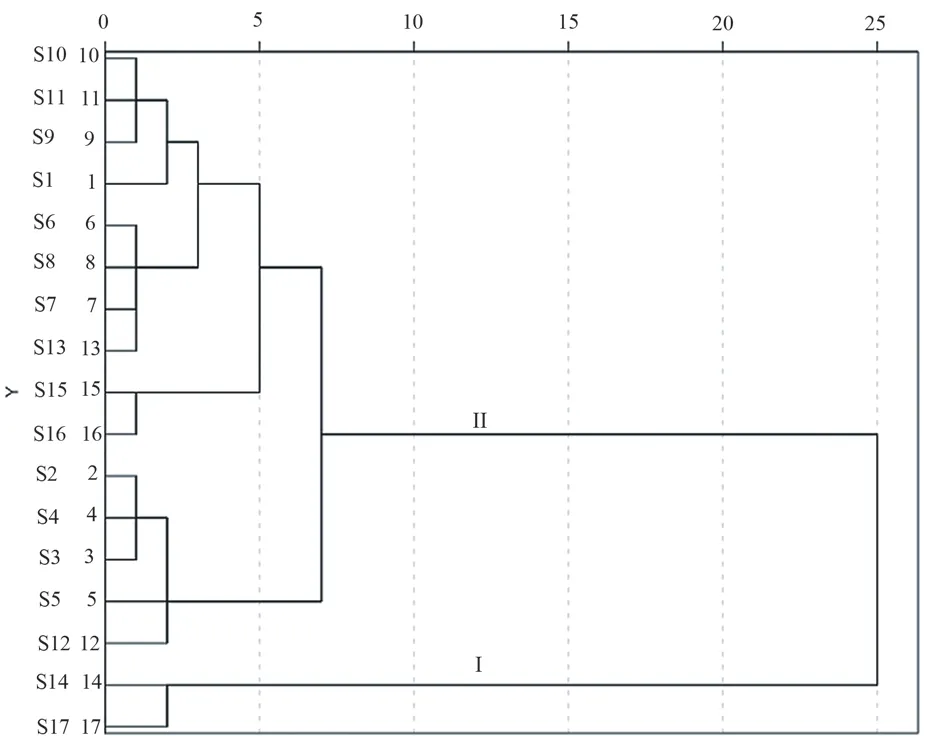
Fig 2 Dendrogram of cluster analysis of Nauclea officinalis stems in different harvesting periods
3.4.2 Principal component analysis (PCA)
The peak area of common peaks was marked as a variable, and the peak dimension was reduced by SPSS 22.0 software to achieve the purpose of principal component analysis.After data standardization,the SIMCA 14.0 software was used to automatically fit and solve, and the first 4 principal components were extracted to draw PCA score map, which visually examined the quality difference characteristics of Nauclea officinalis in different harvesting periods.The results obtained four principal components with eigenvalues greater than 1 as the criterion, and the cumulative total variance contribution reached 84.88%, indicating that the first four principal components could reflect all the original data characteristics,which was sufficient to illustrate the level of quality differences of 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems at different harvesting periods.Among them, common peaks 6 and 7 accounted for the highest percentage in principal component 1; common peaks 9 and 10 had the highest score coefficients in principal component 2,and peak 9 was negatively correlated with principal component 2;those contributing more to principal component 3 were common peaks 2, 3 and 12, and the peak 2 was negatively correlated with principal component 3; the common peak 4 accounted for the largest percentage in principal component 4, and was negative.The variance contribution rate and score coefficient matrices were shown in Tables 5 and 6.In addition, the PCA score plot showed that the samples did not obtain a clear distinction between the spring-summer and autumn-winter groups, but the distribution of samples harvested in spring-autumn was found to be relatively concentrated, while the distribution of samples harvested in autumn-winter was sporadically distributed within the interval, indicating that the quality of Nauclea officinalis collected in spring-summer was relatively stable, which might be related to the influence of factors such as stable sunlight and rainfall.The PCA score plot was shown in Figure 3.
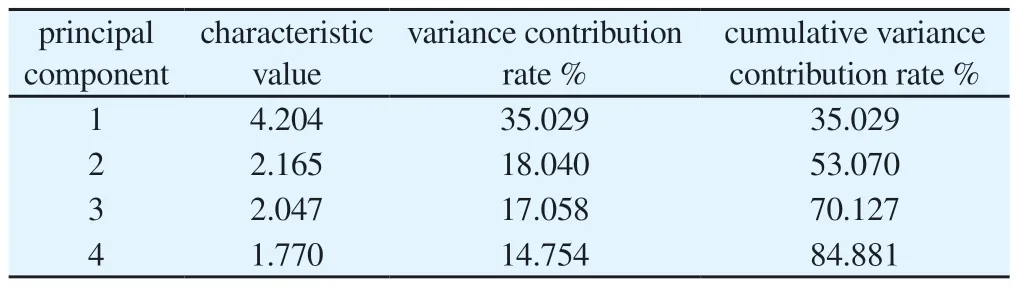
Tab 5 Principal component eigenvalues and variance contribution rate
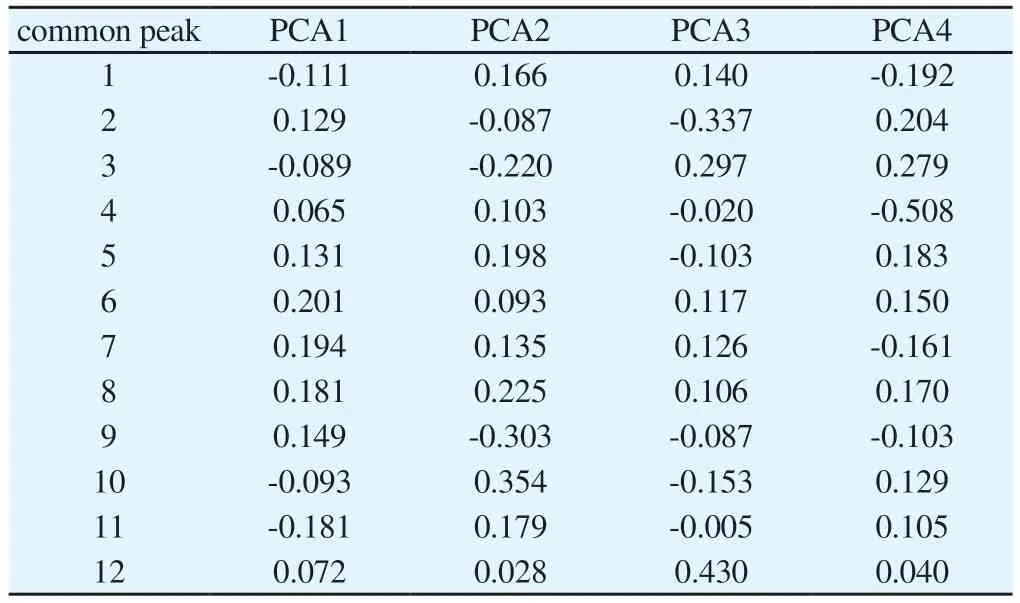
Tab 6 Score coefficient matrix of principal components

Fig 3 PCA score chart
3.4.3 Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA)
Set the common peaks of normalized processing as variables.With the results of cluster analysis as the classification basis, OPLSDA discriminant analysis of samples was carried out by SIMCA 14.1 software to draw the projection map of important variables.The results showed that all data points in the analysis model were within the 95% confidence interval with no outliers and model regression coefficients greater than 0.5, namely Q2=0.826, matrix R2X=0.715, and discriminating parameter R2Y=0.941, indicating that the established projection data model of important variables was stable and reliable.With VIP value greater than 1 as the tradeoff criterion, peaks 9 (strictosamide), 2 (protocatechuic acid), 11(vincosamide) and 1 were identified as important marker compounds affecting the difference in quality of Nauclea officinalis stems at different harvesting periods, which could be used as key component indicators for the investigation of optimal harvesting period and the quality control, in descending order of influence: strictosamide,protocatechuic acid, vincosamide and peak 1.The projection diagram of important variables (VIP values) was shown in Figure 4.
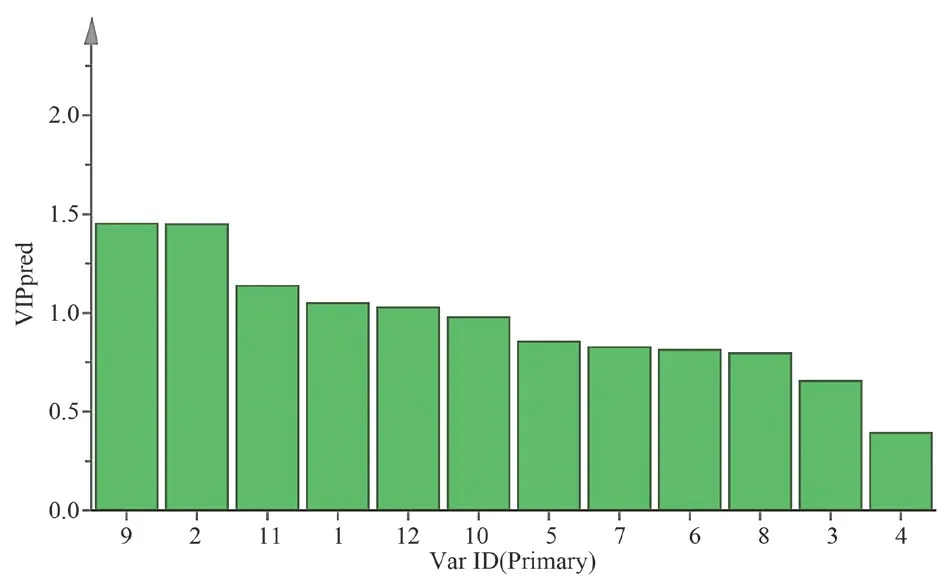
Fig 4 OPLS-DA VIP value plot
4.Discussion
In this experiment, the mobile phase conditions of methanol-water,acetonitrile-0.1% water and acetonitrile-0.2 phosphoric acid water were investigated.The results showed that the number of peaks was higher, the response value was larger and the peak shape was better when acetonitrile-0.1% phosphoric acid water was used as the elution condition.In addition, the gradient elution procedure of acetonitrile-0.1% phosphate water was repeatedly explored.When the initial elution volume ratio of acetonitrile-0.1% phosphoric acid water was 15:85, the peaks started to appear around 4 min, and the peaks were concentrated in 4-30 min, but the analysis time of this condition was long (70 min).After several adjustments, the above optimal elution procedure was finally determined, and the required separation time was 50 min, which was 20 min shorter than the former analytical method[17].The method was able to effectively separate the two pairs of isomers (strictosamide and vincosamide,chlorogenic acid and cryptochlorogenic acid) from Nauclea officinalis without using a chiral column with good reproducibility.
Nauclea officinalis is Hainan characteristic Li medicine.Because of the superior clinical efficacy, medicinal and economic value of significant lead to its overdevelopment, the existing wild Nauclea officinalis resources has been seriously scarce.At present, it mainly relies on the cultivation of producing area to meet the market demand.Additionally, only four years or more old Nauclea officinalis plants can meet the drug application standard, and its artificial cultivation in Hainan is mostly found in Qiongzhong, Wuzhishan and Baoting[18], while the ecological environment is especially best in Qiongzhong County[19].The Nauclea officinalis stems medicinal materials studied in this paper were all from Qiongzhong County,Hainan Province, with a growth period of 5 years.The collection of herbs was time-specific and regionally representative.
The results of similarity, CA and PCA analysis all proved that the quality of Nauclea officinalis harvested in spring-summer was better than that in autumn-winter, but the quality difference between the two seasonal was not obvious, so the OPLS-DA was pre-classified according to the results of CA.The most critical quality marker identified by the results was strictosamide, the main pharmacological component of Nauclea officinalis.The data were accurate and reliable.
5.Conclusion
In this study, HPLC fingerprints of 17 batches of Nauclea officinalis stems at different harvesting periods were established,and 12 common peaks were marked.At the same time, the CA,PCA and OPLS-DA were used to objectively evaluate the quality characteristics of Nauclea officinalis stems at different harvesting periods, and four different markers were selected, among which strictosamide was the most important marker component affecting the quality difference, which could be used as the key index to determine the best harvest date and the quality control.The analytical method established in this paper was accurate, reliable and stable, and could provide scientific reference for further quality analysis of Nauclea officinalis.
6.Innovation
With the characteristics of overall, comprehensive and comprehensive fingerprint technology, the HPLC fingerprint was established for the first time on the Nauclea officinalis stems at different harvesting periods, and the influence of harvesting period on the quality of Nauclea officinalis was analyzed by chemical pattern recognition.The established fingerprint analysis method was simple and feasible, which improved the fingerprint research of Nauclea officinalis.
Statement of Interest
All authors declared that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Author contribution
Liu Aixia and Zhou Mingyan designed the experimental plan,conducted the experiments and wrote the paper; Li Xiangyi and Li Li analyzed the data; Zhang Yuxin and Zheng Xiuwen were responsible for image processing; Wen Huan revised the format of the paper;Zhang Junqing and Zhang Xuguang provided research ideas, guided the writing of the paper and corrected the manuscript.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年7期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年7期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- The research status of Asprosin and its application prospect in the protection of myocardial injury
- Research progress on effective chemical constituents of Sijunzi Decoction and mechanism of prevention and treatment of digestive system diseases
- A Meta-analysis of the spirit turtle eight method Acupuncture Therapy for Insomnia
- Network Meta-analysis of nerve block combined with Chinese medicine for lumbar disc herniation
- Bone palsy eliminates granules to regulate Wnt/PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and intervene in hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits
- Electroacupuncture on hippocampal CREB/BDNF/TrkB in depressive rats effects of signaling pathways
