Unilateral post-chemotherapy robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in Stage II non-seminomatous germ cell tumor:A tertiary care experience
Drio Frnzs , Antonio Tuno , Alssnro Izzo ,Rl Musrillo , Giovnni Grimli , Giuspp Qurto ,Luigi Cstlo , Sbrin Rosstti , Svio Domnio Pnolo ,Soni Dsito , Pol Dl Prt , Mtto Frro ,Snro Pignt , Sisto Pronà ,*
a Department of Urology, National Cancer Institute, Pascale Foundation, Naples, Italy
b Urology Unit, Department of Maternal-Child and Urological Sciences, “Sapienza” University, Rome,Italy
c Department of Neurosciences,Science of Reproduction and Odontostomatology,University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
d Scientific Directorate, Istituto Nazionale Tumori di Napoli, IRCCS “G.Pascale”, Naples, Italy
e Division of Urology, European Institute of Oncology (IEO), IRCCS, Milan, Italy
f Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Uro-Gynaecological Oncology, Istituto Nazionale per lo Studio e la Cura dei Tumori “Fondazione G.Pascale”, IRCCS, Naples, Italy
KEYWORDS Testis tumor;Robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection;Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection;Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor;Unilateral dissection;Modified template;Post-chemotherapy
Abstract Objective: Post-chemotherapy retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (PC-RPLND)represents an integral component of the management of patients with non-seminomatous germ cell tumor (NSGCT).Modified templates have been proposed to minimize the surgical morbidity of the procedure.Moreover, the implementation of robotic surgery in this setting has been explored.We report our experience with unilateral post-chemotherapy robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection(PC-rRPLND)for clinical Stages IIA and IIB NSGCTs.Methods: A retrospective single institution review was performed including 33 patients undergoing PC-rRPLND for Stages IIA and IIB NSGCTs between January 2015 and February 2019.Following orchiectomy, patients were scheduled for chemotherapy with three cycles of bleomycin-etoposide-cisplatin.Patients with a residual tumor of <5 cm and an ipsilateral metastatic disease on pre-and post-chemotherapy CT scans were eligible for a unilateral template in absence of rising tumor markers.Descriptive statistics were provided for demographics, clinical characteristics, intraoperative and postoperative parameters.Perioperative, oncological, and functional outcomes were recorded.Results: Overall, 7 (21.2%) patients exhibited necrosis or fibrosis; 14 (42.4%) had mature teratoma; and 12 (36.4%) had viable tumor at final histology.The median lymph node size at surgery was 25 (interquartile range [IQR] 21-36) mm.Median operative time was 180 (IQR 165-215)min and no major postoperative complications were observed.Anterograde ejaculation was preserved in 75.8% of patients.Median follow-up was 26 (IQR 19-30) months and a total of three recurrences were recorded.Conclusion: PC-rRPLND is a reliable and technically reproducible procedure with safe oncological outcomes and acceptable postoperative ejaculatory function in well selected patients with NSGCTs.
1.Introduction
Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) for post-chemotherapy residual retroperitoneal masses represents an essential component in the multimodality treatment of non-seminomatous germ cell tumors (NSGCTs) in absence of rising tumor markers [1,2].Open RPLND is associated with high perioperative morbidity and prolonged hospitalization [3,4].For this reason, less invasive surgical techniques have been explored.Specifically, laparoscopic RPLND offers similar oncologic outcomes with better tolerability and shorter hospital stay [5].However, this technique remains challenging with a limited adoption over time.With the tremendous uptake of robotic surgery in urology, robot-assisted RPLND (rRPLND) has gained popularity since its first application in 2006 by Davol et al.[6].
One of the major postoperative complications of RPLND is represented by retrograde ejaculation due to the division of sympathetic plexus.Thus,nerve-sparing techniques and modified templates for RPLND procedure have been investigated over the years [7,8], generating some ongoing controversy.According to current the European Association of Urology guidelines, a unilateral template resection can be adopted for post-chemotherapy residual tumor of<5 cm and with ipsilateral disease, both on pre- and post-chemotherapy computed tomography (CT) scans [9].
The current study aimed to report our experience with unilateral post-chemotherapy robot-assisted retroperitoneal lymph node dissection(PC-rRPLND)for clinical Stage II NSGCTs.
2.Patients and methods
2.1.Study population
We retrospectively queried our testis cancer database to identify patients affected by NSGCTs with clinical stage of ≥IIA, who had undergone PC-rRPLND at “Istituto Nazionale Tumori IRCSS-Fondazione G Pascale” (Naples,Italy) between January 2015 and February 2019.The present study was approved by the Ethical Committee of IRCCS Pascale-A.O.R.N.Santobono-Pausilipon(protocol number 56/22).After orchiectomy, all patients had received chemotherapy.Briefly, three cycles of bleomycin-etoposide-cisplatin were scheduled according to both histological features of the primary tumor and instrumental and biochemical findings.Presence of postchemotherapy residual masses was assessed, by thoracoabdominal CT scan and evaluation of serum tumor markers.
In the current study, only unilateral PC-rRPLND for ipsilateral residual masses of<5 cm in the diameter and either normalized or plateauing serum tumor markers patients were included.Secondary RPLND, desperation RPLND (rising serum tumor markers during or after chemotherapy),and RPLND for late relapse(disease recurrence of>2 years after last treatment) were excluded.
2.2.Surgical technique
All procedures were performed by a single surgeon (Perdonà S) with extensive experience in robotic surgery.In all cases, a transperitoneal approach was used.Surgery was performed either with the da Vinci SI or Xi surgical system(Intuitive Surgical Inc., CA, USA).
Briefly,with the Vinci SI robotic system,patients were in the flank position,with a 12-mm camera port and two 8-mm robotic ports in pararectal linear configuration.Moreover,two additional assistant 5-mm and 12-mm ports were placed.With the da Vinci XI robotic system, patients were positioned on the operating table in supine position, with the camera port 1 cm below the navel, and three more ports on the pararectal line (right or left based on the tumor side) and the mid-clavicular right and left lines.
The surgeons followed the RPLND modified template as described by Heidenreich et al.[10].This included on the left side the preaortic nodes to the level of the inferior mesenteric artery, the para-aortic, and retro-aortic nodes with the ureteral crossing of the iliac artery representing the caudal and lateral boundaries of the dissection; right sided template resection included the paracaval,precaval,retrocaval, interaortocaval nodes and the area lateral to the common iliac vessels with the crossing of the ureter as caudal boundary and the ureter serving as lateral boundary of dissection.
2.3.Data analysis
The collected data were analyzed using SPSS v.26.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).Descriptive statistics were provided for demographics, clinical characteristics, intraoperative and postoperative parameters.Quantitative variables were described using median and interquartile range(IQR)or mean and standard deviation(SD),while the discrete or qualitative variables were described using frequency and proportion.
3.Results
3.1.Patient and primary tumor characteristics
Baseline characteristics of the 33 patients included are summarized in Table 1.Thirteen (39.4%) underwent right-sided rRPLND and 20 (60.6%) underwent left-sided rRPLND.Median age was 31 (IQR 25-38) years with a median body mass index of 26 (IQR 24-27) kg/m2.Overall,9 (27.3%), 19 (57.6%), and 5 (15.2%) patients exhibited clinical Stages IIA, IIB, and IIC, respectively, prior tochemotherapy treatment.The median tumor size at rRPLND was 25 (IQR 21-36) mm.Primary tumor histology revealed rete testis invasion and lymphovascular invasion(LVI) in 11 (33.3%) and 20 (60.6%) patients, respectively.
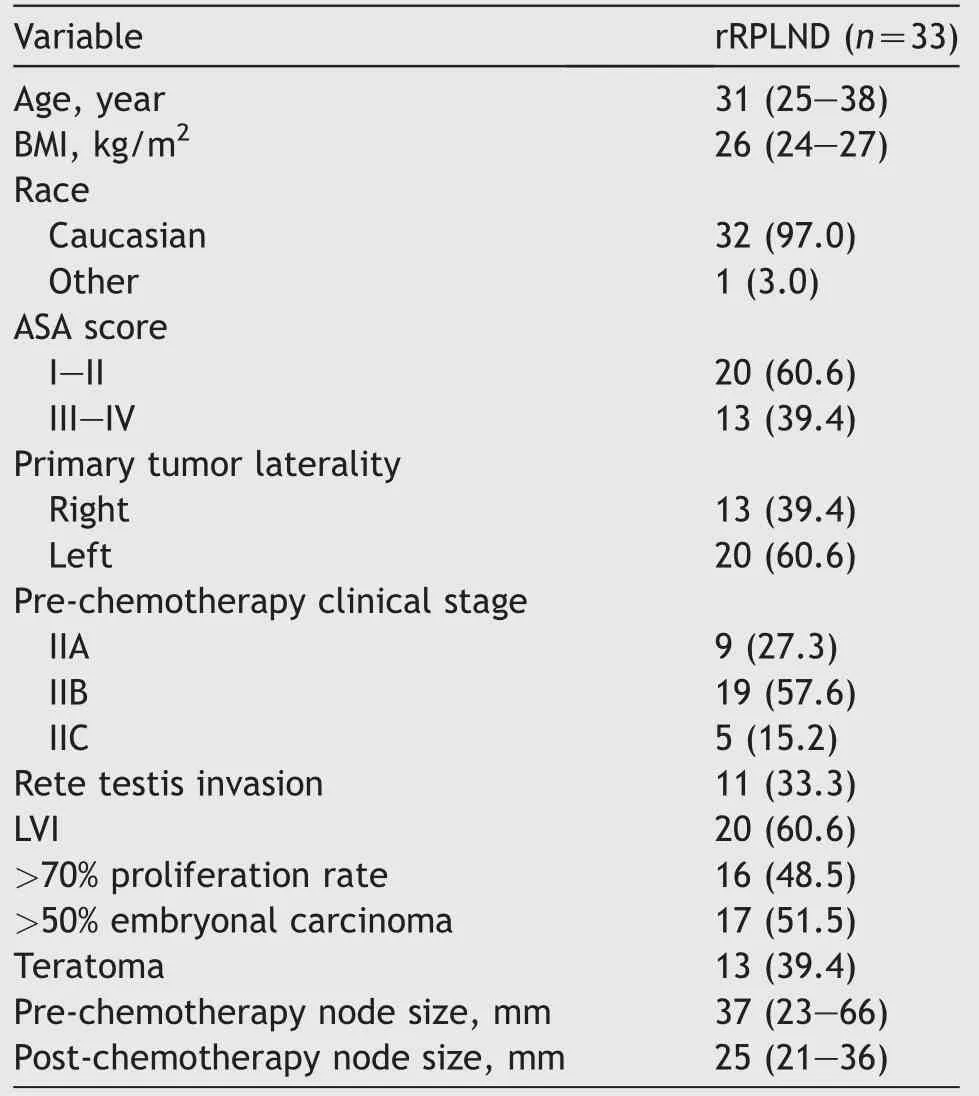
Table 1 Baseline characteristics.
3.2.Surgical outcomes
The median operative time was 180(IQR 165-215)min with a median intraoperative estimated blood loss of 150 (IQR 100-200)mL and a median length of hospital stay of 3(IQR 2-4) days.
An intraoperative complication (vena cava injury managed without open conversion) occurred in two cases.No perioperative transfusions were needed.In the postoperative period, only two early complications (within 30 days from surgery) occurred, while no late complications were recorded.Both early complications were classified as Clavien-Dindo Grade I.Specifically, one postoperative ileus occurred that did not required any management, and one small lymphocele was treated conservatively (Table 2).
3.3.Oncological and functional outcomes
Following rRPLND,the median retroperitoneal lymph node yield was 20(IQR 16-23).Final histology revealed necrosis or fibrosis in 7 (21.2%) patients, mature teratoma in 14 (42.4%) patients, and viable tumor in 12 (36.4%)patients.
The median postoperative follow-up time was 26 (IQR 19-30) months.All the recurrences occurred outside the boundaries of a full bilateral RPLND template.Two patients reported single lung relapses, which were revealed as teratoma after surgical excision; currently, these patients are disease-free.Only one patient received additional(adjuvant)chemotherapy treatment because of progressive disease with multiple metastatic sites during follow-up and died during systemic salvage treatment.Lastly, mean time to recurrence was 11.5 (SD 3.5) months.
Anterograde ejaculation was achieved in 75.8% of our cohort.In one patient, ejaculatory status could not be assessed due to erectile dysfunction.Notably, retrograde ejaculation was present in four patients after left-sided rRPLND and in three right-sided rRPLND.
4.Discussion
RPLND plays a crucial role in the treatment of NSGCTs.However, the anatomical boundaries of dissection have been controversially discussed for decades.To date, patients are more frequently diagnosed with a low-volume metastatic disease and bilateral templates may represent an overtreatment[11,12].Nevertheless,bilateral RPLND is related to glaring functional drawbacks such as sexual satisfaction, erectile and orgasmic function, and fertility[13].
Therefore, an increasing body of evidence is supporting a unilateral approach for patients with a residual tumor of<5 cm and an ipsilateral metastatic disease on pre- and post-chemotherapy scans in absence of rising tumor markers [14,15].
Additionally, there are only a few studies reporting the experience of unilateral rRPLND for post-chemotherapy residual masses [16-18].In our study, we aimed to externally validate the unilateral PC-rRPLND applying the Heidenreich criteria to our NSGCT clinical Stages IIA and IIB robotic cohort.
Our study led to several noteworthy findings.First, the distribution of histological specimen for necrosis, teratoma, and viable tumor were 21.2%, 42.4%, and 36.4%,respectively.Notably,teratoma is present in approximately 40% of patients undergoing RPLND for NSGCTs in previously published series [14,19].Despite the histological benign nature of teratoma, there are potential risks of transformation to malignant elements such as sarcoma and carcinoma, with incidence ranging approximately from 3%to 8% in patients undergoing PC-rRPLND and as previously demonstrated by Carver et al.[20].Moreover, growing teratoma syndrome represents a rare condition related to NSGCTs, characterized by a bulky metastatic mass caused by mature teratoma [21].Etiology of growing teratoma syndrome is still unclear;however,chemotherapy has been theorized to stimulate the cell kinetics toward transformation from a totipotent malignant germ cell toward a benign mature teratoma[22].Interestingly,teratoma in the orchiectomy specimen has been shown to significantly predict teratoma in the retroperitoneum [23,24].Conversely, in our cohort, teratoma was found at RPLND in only 40% of patients with teratoma in the orchiectomy specimen.Consequently,multiple clinical variables such as nodal size before and after chemotherapy and yolk sac in the primary tumor could independently predict patients at risk for teratoma in the retroperitoneum for NSGCTs [25].
Second,the main issue with unliteral RPLND is the risk in missing contralateral viable tumor due to undetected cross spreading [26].In our cohort, we recorded 9.1% (3/33)recurrence rate on a median follow-up of 26 months.Specifically, two relapses were outside the boundaries of a bilateral template (lung) and one patient presented at follow-up with multiple metastatic sites and died from progressive disease.Heidenreich et al.[7] reported that among 98 patients undergoing unilateral dissection,3.1%of the relapses were observed outside the full bilateral template dissection.Moreover, relying on RETROP study results,0%and 4%recurrence rates were found for right-and left-sided templates, respectively [14].Hence, our results corroborate present literature investigating the use of modified templates.
Third, in our cohort, we detected a median of 20 (IQR 16-23) lymph nodes.These data are comparable to open unilateral RPLND series, confirming that rRPLND is a feasible and effective procedure in experienced centers,although there are still conflicting data on the impact of the total number of lymph nodes removed on recurrence-free survival after RPLND [27,28].Moreover, it should be underlined that total lymph node counts are influenced by the anatomic boundaries of surgical template, patient variability, anatomic surgical labeling of the specimens,and pathologic processing [29,30].
Fourth, aside from oncologic outcomes, we reported 75.8% anterograde ejaculation preservation.In this regard,our rates are slightly lower than the results presented by Kordan et al.[16] where patients undergoing unilateral template,presenting an 87%ejaculation preservation rate.However, multiple variables may affect functional outcomes, such as location of tumor, disease stage, and nerve-sparing approach [31].In our series, nerve-sparing approach was performed whenever technically feasible and oncologically safe.Finally,when focusing on the frequency of retrograde ejaculation events among the left- and right-side unilateral PC-rRPLND, the rates were similar (4 cases vs.3 cases), confirming previously published reports[14,32].
Taken together, standardization of templates and homogeneous clinical stage populations in PC-rRPLND for NSGCTs are of upmost importance to create similar study populations and make direct comparison of recurrences rates.We confirm the potential benefits of a unilateral template such as less operative time, fewer complication rates, and successful preservation of ejaculatory function that should encourage the application of this procedure in well-selected group of patients.
The single-center retrospective design and the low sample size represent the main limitations of this study.Moreover, this cohort did not include open RPLND for comparison outcomes.All in all, the single-surgeon experience may affect the reported oncological and functional outcomes.
5.Conclusion
In appropriately selected patients, unilateral PC-rRPLND for NSGCTs is a feasible surgical procedure that demonstrates low perioperative morbidity and provides safe oncological outcomes,while maintaining adequate ejaculatory function.
Author contributions
Study concept and design: Dario Franzese, Antonio Tufano.Data acquisition: Paola Del Prete, Sonia Desicato, Alessandro Izzo, Raffaele Muscariello, Luigi Castaldo.
Data analysis:Savio Domenico Pandolfo,Giovanni Grimaldi.Drafting of manuscript: Antonio Tufano, Giuseppe Quarto.Critical revision of the manuscript: Matteo Ferro, Sabrina Rossetti, Sandro Pignata, Sisto Perdonà.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Asian Journal of Urology2023年4期
Asian Journal of Urology2023年4期
- Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- Arterioureteral fistula: An unusual cause of haematuria 10 years after the implantation of a synthetic iliac-femoral stent
- Utility of three-dimensional virtual reconstruction for robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy using the IRIS?
- Robotic surgery in urology: Recent advances
- Right versus left fully robotic live donor nephrectomy and open kidney transplantation: Does the laterality of the donor kidney really matter?
- Contemporary outcomes of patients undergoing robotic-assisted radical cystectomy:A comparative analysis between intracorporeal ileal conduit and neobladder urinary diversions
- Intermediate-term oncological and functional outcomes in prostate cancer patients treated with perineal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: A single center analysis
