Latest Research Progress of Alkyl Polyglycosides
Yang Liu
Shanghai Fine Chemical Co., Ltd., China
Introduction of alkyl polyglycosides
In 1893, German scientist Emil Fisher first reported the synthesis of alkyl glycosides,[1]his early work focused mainly on the short carbon chain glycosides using hydrophilic alcohol to react with glucose. After that,scientists had successfully synthesized the long carbon chain glycosides, which is now well known as APG (alkyl polyglycoside), with the hydrophobic C8-16 fatty alcohol as the raw material.
Forty years after APG was reported, the first patent application describing the use of alkyl polyglycosides in detergents was filed in Germany.[2-5]Rohm & Haas was the first to market a C8-10 APGs in commercial quantities in the late 1970s, followed by BASF and Seppic.However, due to the unsatisfactory performance of this short chain version as a surfactant and the poor color quality, applications were limited to few market segments,for example industrial cleaning. The product quality had been improved a lot in the following years and new types of alkyl polyglycosides were comprehensively used in many applications. At the beginning of the 1980s, several companies started programs to develop alkyl polyglycosides in the long alkyl chain for applications in the cosmetics and household industries, and at the same time, patents were applied.[6]The following companies made the major efforts:Proster & Gamble, Horizon (acquired later by Henkel),Henkel, Hüls, Kao and Seppic.[7]
In 1988 and 1989, Henkel built a pilot plant to manufacture APGs in Crosby, USA, with a capacity of 5,000 MT per year. Between 1990 to 1992, other companies announced their intention to build up industrial plants of APGs, among them are Hüls, ICI, Kao and Seppic. The final breakthrough in the commercial exploitation of alkyl polyglycosides was reached in 1992 with the inauguration of a production plant with annual capacity of 25,000 MT by Henkel in Cincinnati, USA and in 1995 with the opening of a second plant of equal capacity by Henkel in Dusseldorf,Germany.[5,7]
The product APGs were further developed in the 21stcentury. LG healthcare from Korea also built a production line. After acquiring Cognis, BASF has become the biggest APG manufacturer in the world. The industrialization of alkyl polyglycosides in China started only in recent years,but the development is rather fast and pleasant. Shenzhen Changyuan and Yangzhou Chenhua have built their APG production lines respectively. It has to be highlighted that China Research Institute of Daily Chemical Industry has transformed its technical advantage into industrial advantage by establishing Shanghai Fine Chemical Co.,Ltd. in 2006, whose focus is green surfactants, with the APG capacity of 15,000 MT.
Alkyl polyglycosides is a type of mild nonionic surfactant,which also has the good characteristics of anionic surfactant.With many superior properties such as rich foam, low irritancy, non-toxicity, 100% biodegradability (Figure 1), APG can be used in different applications accordingly. Currently,APG is comprehensively applied to cosmetics, detergent and industrial cleaning, in which most of the papers and reports introduced a lot. However, this review mainly demonstrated the latest research progress of synthesis technology and applications in environmental waste disposal, medicine and stockbreeding for APG, and based on this, the future development of APG was also prospected.
Synthesis of alkyl polyglycosides
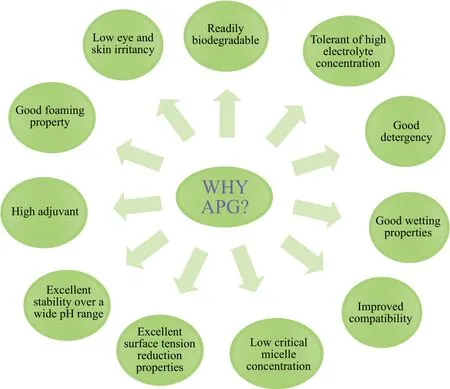
Figure 1. Properties of Alkyl Polyglycosides
Until now, the methods of Koenings-Khorr, mold catalytic synthesis, acetylation alcoholization, suger’s ketone alcoholization, one-step and two steps process are the main synthesis technologies to produce APGs,[8]in which two-step process domains the industrial manufacturing.For two-step process, glucoside reacts with butyl alcohol first to synthesize butyl glucoside and then butyl glucoside makes the glycosidation reaction with long carbon chain alcohol to manufacture alkyl polyglycosides. However, butyl glucoside will exist as by-product in the final version. With the improvement of modern technology, several companies in the world such as BASF, Shanghai Fine Chemical, etc.,hold the more advanced one-step method, which is easy,energy and cost saving and so on.[9]The manufacturing scheme of one-step process is as below.
But the one-step process suffers from some serious drawbacks such as the use of corrosive or toxic acid catalyst, the requirement for N2atmosphere and the high-level management.[10]Camille and his team[10]have committing their effort to the new method for synthesis of APGs and recently successfully produced decyl glucoside by an ion-liquids (ILs) method using sulfoxides and sulfones as solvents in the absence of catalyst.The advantages of this method are: 1) relatively low requirement for management and facility as the process is under constant pressure; 2) catalyst is not needed in the process avoiding the use of corrosive and toxic catalyst;3) the reaction time is short. The yield was only 47 % and the reaction time was as long as 9 hours when dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2) was used as the solvent. Changing to dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), diphenylsulfoxide (DPSO)and ditolysulfoxide (DTSO), the yield was increased to around 68% with the reaction time 0.5—1 hour. However,the yield significantly reached 83% when sulfolane was used in the process and the reaction time was only 0.25 hour which is shortened a lot.
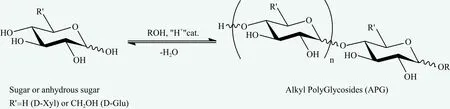
Figure 2. Scheme of one-step process to produce APG
The manufacturing scheme was provided by Camille that decyl glucoside was directly synthesized by glucose,decyl alcohol and sulfolane under certain temperature,and sulfolane and decyl alcohol were recycled in the process of liquid-liquid separation and distillation respectively in order to save the raw materials. Camille believed that the caramelization of the glucoside in the process would generate low amount of weak organic acids that would catalyse the glycosidation. He also noticed that a reduced coloration of the glycoside was obtained,meaning a possible simplification of the purification step on the industrial scale.
Although the methodology of Camille takes a short time for reaction and requires only constant pressure and no catalyst, but some problems must be solved in front of the industrialization, such as if the cost for sulfoxides and sulfones would be lower, if sulfoxides and sulfones would be more environment-friendly and if the long chain APG1214 could be achieved by this method. Anyway,this method provides more theories for the further development on synthesis of APGs.
Applications of alkyl polyglycosides
Application in waste disposal
At present, the Chinese economy is under re-construction that the transformation of industrial structure requires pepole to take more consideration of the environment in daily life. The amount of organic waste generated annually in China is rather huge. In 2006, only the food waste was about 90 million tons.[11]Incineration and landfill are the most common ways for waste disposal,nevertheless, these two methods would have irreversibly negative impact to the environment. Some researches show that converting the organic waste into the useful resource, such as compost, is a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to disposal. Short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) is considered as a critical substrate for higher performance of biological nutrient removal (BNR).[12]Usually, 1.07~1.82 mg and 1.87~3.00 mg SCFA is required to remove 1mg N and 1 mg P.[13]However, conventional SCFA is insufficient,[14,15]fermentative SCFA as the additional carbon source could result in superior BNR performance.[16,17]Compared with the expensive synthetic volatile fatty acid (VFA), SCFA derived from anaerobic fermentation is more cost-effective and environment-friendly.[12]In general, anaerobic digestion for disposal of waste active sludge (WAS) includes three steps,[18]namely solubilization and hydrolysis, acidification and methanogenesis, among which solubilization and hydrolysis are considered as the rate-limited step,[19]which need to be accelerated. Reports from Chen et al[19]and Jiang et al[20]revealed that surfactant could improve greatly the solubilization of WAS due to its soluble and synergistic properties. Based on this, Kanga et al[21]did the research using Tween 20, Tween 80, Triton X-100,SDS and SDBS, but these surfactants have the potential harm to the human’s health and the environment.Thus, alkyl polyglycoside, as a non-toxic, biodegradable,highly commercial surfactant, is a new option for this application.[12,18,22-24]
Zhao et al[12]added APG into anaerobic fermentation system to enhance SCFA production and found that APG would not only improve the production, but also shorten the production time for maximum SCFA accumulation.The maximum amount of SCFA reached 21.4, 30.0, 37.2,39.0 and 40.3 g/L respectively when 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4 g/g APG were added, while the amount was only 12.0 g/L without APG assistance. Compared to the production time 14 days, it took merely 6 days to get maximum amount of SCFA in the presence of APG, which showed that APG saved a lot of time and cost by shortening the time. Additionally, the compositions of SCFA kept the same with or without APG. The results proved that APG could be used in the anaerobic process to disposal municipal solid waste which might be applied comprehensively.
Zhang et al[22]made the research of APG in composting. The results suggested that APG addition increased the total nitrogen and nitrate concentration by 0.05%and 80% and promoted the matter degradation and GI by 6% and 29%without affecting the pH and EC throughout the process, which showed that APG could also be used in industrial composting.
In addition, Zhao et al[23]studied APG in the waste-water treatment application. The MBR market has been expanded at an average annual growth rate of approximately 10.9%, much faster than other advanced waste-water treatment technologies. However, the low biodegradability of conventional MBR limits its further application. As a result, Zhao et al embraced fully biodegradable and eco-friendly APG into MBR to remove N and P in waste-water, in which way the enhancement of biodegradability can be achieved. The results showed that the yield of SCFA reached 282.9 mg chemical oxygen demand (COD)/g volatile suspended solids (VSS) with the optimum APG dosage of 0.2 g/g dry sludge (DS), yields were 4.8 times higher than that no added APG. At the same time, the production of SCFA got to the highest point when the initial pH of MBR system was 11. It has to be pointed out that the pH value of commercial APGs in the market is around 11.5~12.5 which is very suitable for MBR system.

Application in medicin e
Microemulsions seem to be ideal liquid vehicles for drug delivery because of their several advantages such as thermodynamic stability, very small droplet size(5~100 nm), low viscosity (with Newtonian behavior) and high surface area.[25]Microemulsions consist of oil phase,water phase, surfactant and co-surfactant.[26,27]Unlike the case of ethoxylates surfactants, APGs are less influenced by temperature with non-toxicity and biodegradability.So many researchers developed microemulsions with APG[28-30]and applied the colloidal structure as a delivery vehicle to medicine.[31,32]
Based on the physicochemical properties of some formulations with APG, Savic et al[32]studied the in vitro and in vivo bioavailability of hydrocortisone (HC). In vivo results suggested that the APG formulation with non-polar oil phase would enhance the permeation and absorption of HC. Meanwhile, Savic highlighted that no adverse effects could be found which proved that APG is safe to be used in medicine.
Ascorbic acid (AA) is a major protector from reactive oxygen skin damage, but the application is limited due to its un-stability and weak skin penetration. Pakpayat et al[33]developed an APG-microemulsion system to study its effect towards AA. The results confirmed that the system not only resisted the degradation of AA, but also enhanced the penetration of AA into skin. Pakpayat believed that microemulsions with APG could be considered as a suitable carrier system for application of ascorbic acid as whitening and anti-oxidation agent.
Besides, with anti-baterial activities against gramnegative, gram-positive bacterium and funguses, C8-12 APG can be used as sanitizing compounds.[34]Also, APG could be mixed with the traditional Chinese herbs to make anti-itching medicines.[35]
Application in stockbreeding
Food toxicity tests reveals that APG can be used as emulsifier, preservative, foaming agent, dispersing agent,wetting agent, thickening agent and defoaming agent, and could improve the taste of food.[36]Apart from this, APG would also improve the utilization of roughage.
Cong et al[37]studied the in vitro fermentative effect of APG to corn and wheat straws and got the positive feedbacks. Yuan et al[38]made the research to study the effects of different dietary alkyl polyglycoside (APG)levels on ruminal fermentation characteristic in order to observe the potential use value of APG in feed additive area. The results showed APG had no effect on rumen pH and significantly improved the fuminal concentrations of ammonia nitrogen, total VFA, acetic acid concentration and the ratio of acetic and propionic acid content. It was concluded that the addition of APG enhanced the fuminal fermentation characteristics of the goats.
Expectations
Several APG productions have been built recently which signals that the production capacity will be saturated soon. As the increase of capacity and competition, the price of APG in the market will be lower and lower gradually. So the development of new domestic and oversea markets and the exploitation of new applications have become the key direction of APG in the future.
APGs have been comprehensively applied to cosmetic,household and industrial cleaning, thus the exploitation of APGs in petrochemical, medicine, environmental waste disposal and stockbreeding should be taken into consideration. Furthermore, with the superior synergistic characteristic, APG can be mixed with other surfactants to form new types of functional materials. Also, new markets can be explored for the functional APG derivatives as specialties.
[1] Fisher E. über die Glucoside der Alkohole. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges 1893(26), 2400-2412.
[2] H TH B?hme AG. Verwendung von Hochmolekularen Synthetischen Glucosiden als Saponinersatz, als Emulgierungs-,Reinigungs- und Netzmittel: DRP, 593422, 1931.
[3] H TH B?hme AG. Verfahren zur Herstellung von Glucosiden Hoherer Aliphatischer Alkohole: DRP, 611055, 1933.
[4] Heinrich B.; Gertrud R. (H. Th. B?hme AG). Process for the Production of Glucosides of Higher Aliphatic Alcohols: USA,2049758, 1933.
[5] Knaut J., Kreienfeld G. Alkyl Polyglycosides. A New Surfactant Class Based on Renewable Raw Materials. Chimica Oggi 1993, 41- 46.
[6] Hill K.; Von Rybinski W.; Stoll G. Alkyl Polyglycosides:Technology, Properties and Applications. Weinheim: VCH,1997.
[7] Von Rybinski W.; Hill K. Alkyl Polyglycosides–properties and Applications of a New Class of Surfactants. Angew Chem Int Ed 1998, 37, 1328-1348.
[8] H.L.Sun. A Wide Prospect of Development and Application of Alkyl Polyglycosides. Chemical Intermediate 2000, 3(4),12-14.
[9] Y.Zheng; X.L.Pu; X.D.Bai. Current Situation and New Development of Alkyl Polyglycosides. Detergent & Cosmetics 2006, 29(5), 4-7.
[10] Ludot C.; Estrine B.; Bras J. L.; et al. Sulfoxides and Sulfones as Solvents for the Manufacture of Alkyl Polyglycosides without Added Catalyst. Green Chem 2013, 15, 3027-3030.
[11] D.Q.Zhang; S.K.Tan; Gersberg R. M.. Municipal Solid Waste Management in China: Status, Problems and Challenges. J Enviro. Manage 2010, 91, 1623–1633.
[12] J.W.Zhao; Q.Yang; X.M.Li; et al. Enhanced Production of Short-chain Fatty Acid from Food Wastestimulated by Alkyl Polyglycosides and Its Mechanism. Waste Management 2015,46, 133–139.
[13] Elefsiniotis P.; D.Li. The Effect of Temperature and Carbon Source on Denitrification Using Volatile Fatty Acids. Biochem Eng J 2006, 28, 148–155.
[14] R.Tan; Miyanaga K.; Uy D.; et al. Effect of Heat-alkaline Treatment as a Pretreatment Method on Volatile Fatty Acid Production and Protein Degradation in Excess Sludge, Pure Proteins and Pure Cultures. Bioresour. Technol 2012, 118,390–398.
[15] J.Zhao; D.Wang; X.Li; et al. An Efficient Process for Wastewater Treatment to Mitigate Free Nitrous Acid Generation and Its Inhibition on Biological Phosphorus Removal. Sci Rep 2015 (5), 8602.
[16] J.Tong; Y.Chen. Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Driven by Shortchain Fatty Acids Produced from Waste Activated Sludge Alkaline Fermentation. Environ. Sci.Technol 2007, 41, 7126–7130.
[17] Moser-Engeler R; Udert K. M.; Wild D.; et al. Products from Primary Sludge Fermentation and Their Suitability for Nutrient Removal. Water Sci. Technol 1998, 38, 265–273.
[18] J.Luo; L.Feng; Y.Chen; et al. Alkyl Polyglucose Enhancing Propionic Acid Enriched Short-chain Fatty Acids Production during Anaerobic Treatment of Waste Activated Sludge and Mechanisms. Water Res 2015, 73, 332-341.
[19] Y.Chen; K.Liu; Y.Su; et al. Continuous Bioproduction of Short-chain Fatty Acids from Sludge Enhanced by the Combined Use of Surfactant and Alkaline pH. Bioresour Technol 2013a, 140, 97–102.
[20] S.Jiang; Y.Chen; Q.Zhou; et al. Biological Short-chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Production from Waste-activated Sludge Affected by Surfactant. Water Res 2007a, 41, 3112–3120.
[21] Kanga S. A.; Bonner J. S.; Page C. A.; et al. Solubilization of Naphthalene and Methyl-substituted Naphthalenes from Crude Oil Using Biosurfactants. Environ Sci Technol 1997,31, 556–561.
[22] F.Zhang; W.Gu; P.Xu; et al. Effects of Alkyl Polyglycoside(APG) on Composting of Agricultural Wastes. Waste Manage 2011, 31, 1333–1338.
[23] J.Zhao; Q.Yang Q.; X.Li; et al. Effect of Initial pH on Short Chain Fatty Acid Production during the Anaerobic Fermentation of Membrane Bioreactor Sludge Enhanced by Alkyl Polyglucoside. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 2015, 104,283–289.
[24] Smu?ek W.; Kaczorek E.; Zgo?a-Grzeskowiak A.; et al. Impact of Alkyl Polyglucosides Surfactant Lutensol GD 70 on Modification of Bacterial Cell Surface Properties. Water Air Soil Pollut 2015, 226, 45.
[25] Kogan A.; Garti N. Microemulsions as Transdermal Drug Delivery Vehicles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 2006, 123, 369–385.
[26] Ceglie A.; Das K. P.; Lindman B. Microemulsion Structure in Four-component Systems for Different Surfactants. Colloids Surf 1987, 28, 29–40.
[27] Kreilgaard M. Influence of Microemulsions on Cutaneous Drug Delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2002, 54, S77–S98.
[28] Kahlweit M.; Busse G.; Faulhaber B.. Preparing Microemulsions with Alkyl Monoglucosides and the Role of N-alkanols.Langmuir 1995, 11, 3382–3387.
[29] Von Rybinski W.; Guchkenbiehl B; Tesmann H. Influence of Co-surfactants on Microemulsions with Alkyl Polyglycosides.Colloids Surf 1998, A 142, 333–342.
[30] Forster T.; Guchkenbiehl B.; Hensen H.; et al. Physicochemical Basics of Microemulsions with Alkyl Polyglycosides.Prog Colloid Polym Sci 1996, 101, 105–112.
[31] Savic S. D.; Miroslav M. M.; Vesic S. A.; et al. Vehicles Based on Sugar Surfactant: Colloidal Structure and Its Impact on in vitro Hydrocortisone Permeation. Int J Pharm 2006, 320, 86–95.
[32] Savic S. D.; Savic M. M.; Tamburic S.; et al. An Alkyl Polyglucoside Surfactant as a Prospective Pharmaceutical Excipient for Topical Formulations: the Influence of Oil Polarity on the Colloidal Structure and Hydrocortisone in vitro/in vivo Permeation. Eur J Pharm Sc 2007, 30, 441–450.
[33] Pakpayat N.; Nielloud F.; Fortuné R.; et al. Formulation of Ascorbic Acid Microemulsions with Alkyl Polyglycosides.European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2009, 72, 444–452.
[34] D.F.Peng; W.Y.Xu. Alkyl polyglycoside—A New Type Green Surfactant. Jiangxi Chemical Industry 2004, 27(1), 31-34.
[35] L.Y.Liang; R.H.Lan; H.Q.Chen. Research on the Application and Complex in Cosmetic of APG and China Herbal Medicine. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics 2002,32(2), 36-39.
[36] W.Xiong; Y.Li; J.S.Zhang; et al. A Study on the Synthesis,Performance and Application of a New Type Surfactant—Alkyl polyglycoside. Jiangxi Chemical Industry 1998, 2, 23-26.
[37] Z.H.Cong; S.X.Tang; Z.L.Tan; et al. Effects of Different Nonionic Surfactants on in vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Cereal Straw. Journal of Animal Science 2009, 87, 1085-1096.
[38] Z.Q.Yuan; Z.L.Tan; C.C.Shen. Effects of Supplementation Levels of Alkyl Polyglycoside on Ruminal Fermentation Characteristic of Goats. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition 2009, 21(6), 872-877.
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2016年3期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2016年3期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Impact of Air Pollution on Skin
- Recent Development on Zero-Phosphate Spray Dried Detergent Powders Incorporated with Palm C16 Methyl Ester Sulfonates
- An Introduction to the Standardization of China Oral Care Products (Toothpaste) Industry
- Comparative Study on the Domestic and Abroad Patent Application about Liquid Laundry
- Standards on the Biodegradability of Surfactants in China
- Qualitative Identification of Propylene Tetramer Alkylbenzene Sulfonate and Alkylphenol Polyoxyethylene in Laundry Powders
