Development of Alternative to Animal Testing on Cosmetics by Middle-out Strategy
Shujun Cheng, Yu Chen, Yihui Ke
Guangdong Inspection and Quarantine Technology Center, China
Xiaoting Qu, Yao Qin, Jiating Xu
Guangzhou Chn-alt Biotechnology Ltd., China

The popularization of 3Rs principle of Reduction,Refinement and Replacement to animal testing in China has undergone 3 phases. The first phase, so called as enlightenment, was initiated from 1990s when laboratory animal welfare and 3Rs principle has emerged as a promising research direction in laboratory animal science.many scientists have done a vast of propaganda and research work.[1,2]It took around 20 years of continue endeavors that 3Rs was finally adopted in the mOST’s(ministry of Science and Technology of China) guidance,local laboratory animal regulation, national and local lab animal standards and accreditation criteria for laboratory animal related institute.[3]The other landmarks include establishment of Animal Welfare Ethics Committee in Chinese association for laboratory animal science(CALAS) and followed by three times of consecutive Sino-British International Seminar on Laboratory Animal Welfare & Ethics; Accreditation by AAALAC(Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International) was positive accepted as activities.Chinese scientist has reached a consensus that 3Rs principle should act as important guidance for scientific research and bio-pharmacy industry. Albeit the more and more attention has been paid on 2Rs, i.e, “Reduction” and“Refinement”, the 1R represented by Replacement was still lack of in-depth investigation.

The second phase is a rather initial phase that 1R principle based on Alternative to Animal Testing (AAT)and toxicity testing modernization has arouse increasing attention when entered into 21stcentury, especially the great impact to inspection of import and export goods imposed by cosmetic animal testing ban and the important chemical legislation REACH issued by EU. The“technology barrier” has become a predominate problem in international trade due to retarded inspection standards and weak laboratory capability in non-animal testing methodology.[5]Under the background of international legislation reform and the need to synchronize port inspection with international recognized technology,entry and exit inspection and testing institutions have taken the lead to take action and promote the application.The initial phase has been taken around 15 years.Represented by Guangdong CIQ, it has promoted the development and application of alternatives in China in various aspects, such as interpretation of legislation at very beginning, science propaganda, technology tracking, laboratory capability building, validation mode exploration and practice, standardization, transformation& application, education & training, academic seminar,technology development, industrialization acceleration and international cooperation.
The third phase was started since 2015. Alternatives activity has entered into fast track in academic research and cosmetic industries application. multiple industry proactively involvement was seen as an obvious trend.Scholar education, academic communication and training was booming. Retrospect more than 30 years history of the developing way of Chinese 3R principles and alternative testing, it is summarized as a “middle-out” way as experience. From the “middle-out” model, considering the unbalanced and no consensus in whole China, the“middle-up” stand for the standardization, means through the leadership of Chinese important department such as CIQ, CDC, NIFDC and National society, driving up to scientific innovation and regulation changes. The “middledown” stands for the mercerization means through the popularization of in vitro science and technologies to industries including cosmetics companies, official or thirdpart institute, public education and commercial service to promote the development of market.
Middle-up way to drive the development of alternative technology
Standardization and implementation capability building
When EU issued the directive on cosmetic animal testing in 2003, there was a big technology gap of China toward AAT methods, not only knowledge consensus but also application experience. Inspection and Quarantine of China (CIQ) system undertook the responsibility of break through technological barrier. The primary task was to identify pragmatic testing standards and build up the capability. In 2006, General CIQ kicked off a project on standard transform, established Cosmetic Standardization Technical Committee and selected a bunch of methods from OECD test guidelines and EURL-ECVAm (European Union Reference Laboratory for alternatives to animal testing) in vitro method database and then accepted as official standards after confirmation, peer review and authorization. Three more batches of standards were published successively.[5]Especially, the Chinese national testing standards, GBIT 21769-2008 3T3 neutral red uptake phototoxicity test, was built in 2008. These works filled up the gap in alternative methods standard and construct foundation for similar AAT methods standardization. Those standards are still act as important references for application of alternatives in China. After the first official in vitro lab established by Guangdong CIQ in 2005, followed up a number of in vitro labs established in local CIQ, CDC, cosmetic companies and third-party organizations, which laid the foundations to the lab network in the future.
Generally, the implementation of alternatives in in vitro labs should comply with GLP and it is also keep consistent with requirement of CNAS in China. most of these labs should be followed the accreditation standards and rules by CNAS issued, such as those refer to fundamental elements of in vitro assessment and research: the CL01’criteria for the competence for testing and calibration laboratory accreditation’, Bio-Safety (CL05), medicine (CL02),microorganism (CL09), and “General requirements for quality and ability of experimental animals institutions”(CL55) issued in 2014.[3]The in vitro lab can apply for the CNAS qualification directly, or, just extend qualification scope based on its original one. The lab could enhance its implementation capability on alternatives via reference substance testing, positive control testing, blind sample testing, intra-lab & inter-lab comparison, participating alternative validation and capability validation and etc.With more data accumulated and more problems gradually solved during the practice of alternative application, the enhanced alternative application and innovation capability will be expected in China.
Exploration and activation in validation models
The alternative method validation is a necessary bridge between a new or modified method generated from laboratory and regulatory accept which the process including standardization, internal validation, inter-lab transferability and finally regulatory acceptance. So, it would be vital to establish a validation process that caters to Chinese situation. In 2006, Guangdong CIQ has led to draft a series of official CIQ standards for alternative validation, in vitro laboratory quality control specification and good in vitro methods specifications.[6,7]It was a meaningful pilot for establishing Chinese alternative validation process that comply with international practice.With the instruction of those standards, between 2010 to 2013, General CIQ has organized the multi-center validation on Episkin (Shanghai) model skin irritation. It is the first normal validation activation in China follow the international criterion and implants the scientific conception of validation in attending laboratories.
Technology research and innovation
The development of alternatives is a process of continuous innovation in practice. Optimization appears in every element of an in vitro method, such as the testing system, endpoint, assay method, integrated strategy, predictive model and etc. Based on the current situation, the innovation may be attributed to two ways. One way is to apply the available internationally authorized test guidelines to chemical and cosmetic safety assessment and optimize them step by step. For example,Qin Yao has optimized the CAmVA and BCOP irritation methods and established BCOP-CAmVA-EPISKIN irritation integrated strategy for formula research and ingredients evaluation.[8]moreover, Qin Yao also investigated the application of integrated strategy for assessing the correlation of oral mucosa irritation and vaginal mucosa irritation to testing disinfection products and personal care hygienic products. Chen Yu et al has developed a modified BCOP that combined with histology quantitative scoring which is able to classify the potent of irritation from weak to strong.[9]Yihui Ke et al has set up an integrated method consisting of DRPA and h-CLAT that might be used to screen the skin sensitization of complex compounds such as plant extracts with relative simple combination which would be more efficient.[10]moreover, a co-culture model of skin models and THP-1 were attempted to establish to screen the sensitization of metabolic activation materials and insolubility substance. Therefore, it is benefit for industries to make use of alternative methods and to accumulate abundant data.
In addition, it needs to invest basic research and develop new test method for complex toxicological endpoint, such as developing new 3D skin equivalent models for inspection and establishing new alternative methods under AOP (adverse outcome pathway)framework.[11,12]For example, the AAT method for developmental neurotoxicity and integrated strategy,mitochondrial oxidant stress pathway and refined embryonic stem cell method for assessment of embryonic toxicology.[13-15]
Middle-down strategy of promote the application of alternative methods
Academic communication and continual education
The 1R means absolute Replacement which is often merged with toxicity testing modernization. In recent years, new instruction concepts like TT21C (toxicity testing 21stcentury: vision and strategy), AOP and ITIS have thrown both new challenges and opportunities for in vitro alternatives. In order to build a bridge between academic and industry, Guangdong CIQ has hold several alternatives seminars and training courses since 2010.There are 6 formal academic conferences and handon trainings since 2013. The content of the trainings covered skin irritation, eye irritation, phototoxicity, skin sensitization, genetic toxicity, endocrine toxicity and efficacy evaluation. While the hand-on trainings methods include BCOP, CAmVA, HET-CAm, DPRA, HCLAT,EPISKIN, 3T3 NRU PT, skin micronucleus test and integrated strategy. Apart from testing methods, application of AOP, in vitro lab construction & quality control, round table discussion, GLP in vitro were also held.

At the meeting of In Vitro Sciences Promote the Developing of Interdisciplinary and multi—Industries in this year, the experts from China were in-depth exchange with those from ECVAm, JaCVAm and cosmetics company, regarding adoption of available, validated AAT approaches, current research efforts to establish“adverse outcome pathways” (AOPs) as a next-generation approach to alternatives, and future trends in research and regulatory policy.
Continuous conference provided a technological communication platform of equality and opening for stakeholders, which broadened horizons and promoted technology for regulators, research institutes and daily-use chemical industries. It has become the leading power for alternative technology research and application in China.
In order to meet the increasing needs of prompt information exchange in alternatives in China, an educational website, i.e http://www.vitrotox.com/ was established by Center for Alternative Research and Evaluation(CCARE), a branch of Chn-Alt Institute to promote the awareness of the state-of-the-art alternative technologies and updated global non-animal testing policies. In June 2016, Chn-alt has built a collaboration with Humane Society international (HSI) to co-develop the website as a free information and training hub for non-animal testing in China. The website also built a good collaboration relationship with international organization like OECD, NC3Rs,HIS to share information.
Translation of OECD test guidelines and AOP-related guidance continues to increase their accessibility to Chinese authorities and scientists.
Co-development of the Chinese-language website www.vitrotox.com is a hub for non-animal testing and AOP-related materials in China.
These series of activities have become the leading effort to drive the development and application of Chinese alternative technology. It not only provides an open communication platform for domestic scientists,regulators, research institutes and cosmetic and chemical industries, but also offers an opportunity to leverage the international efforts.
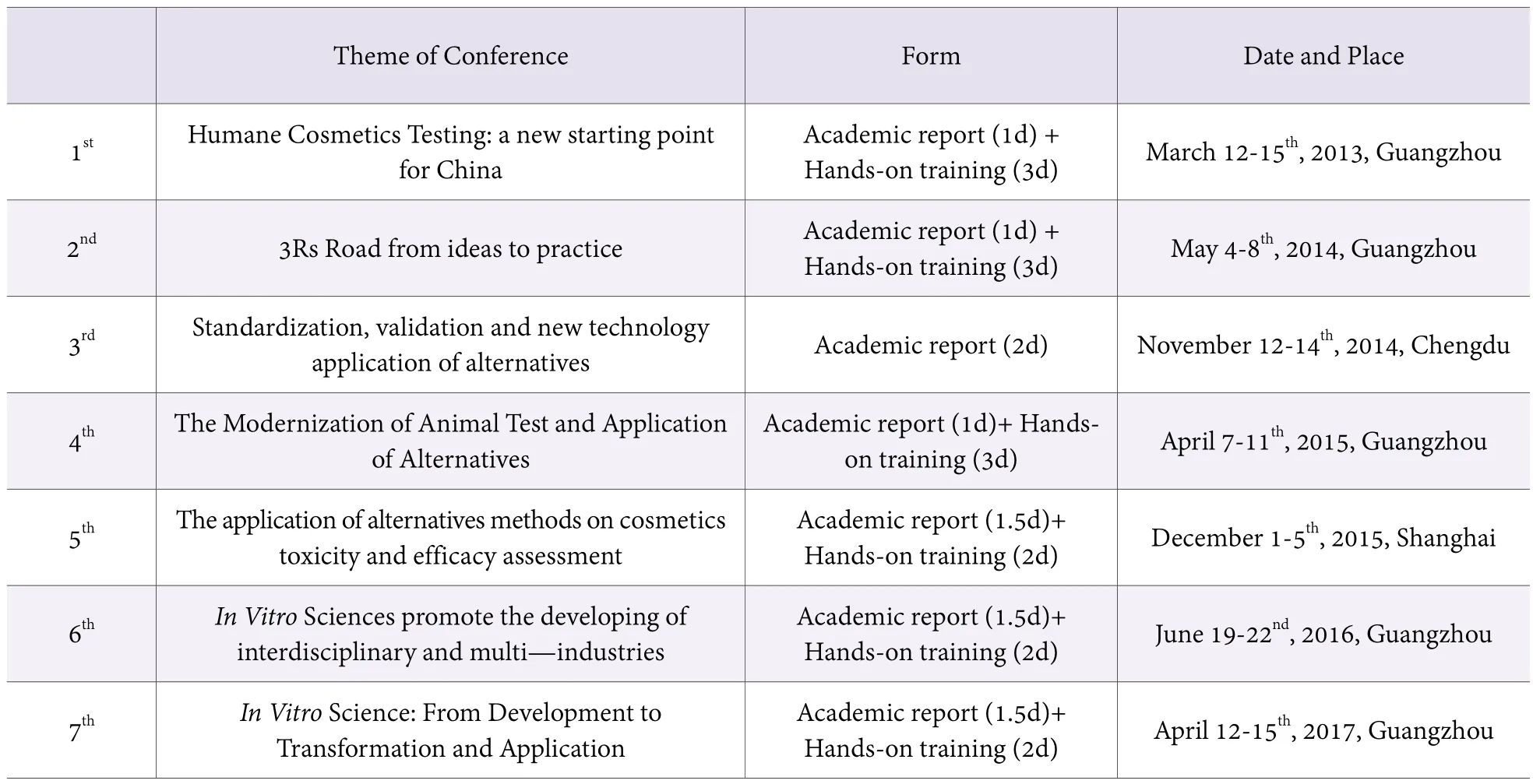
Table 1. All alternative conferences in China
Industry popularization and application
To promote non-animal testing concept in China, we need to both popularize 3Rs and alternative principles and update toxicity testing framework like AOP and TT21C. CCARE contributes to the Chinese blueprint with distribution propaganda brochures and issuing Chinese version of classic 3R publications[16]to public and technicists for free. CCARE also expands alternatives to a more broaden in vitro science area such as cosmetic efficacy evaluation. For example, 3D re-constructed skin model has been developed to repair skin injury and research of antiirritation for active raw materials. Optimized HET-CAm is to provide the data for claiming the efficiency of promoting blood circulation and improving black eyes. After long terms of incubation, nowadays, Chinese in vitro testing market is prospering with more and more third party assessment organizations emerged like Guangzhou Chnalt Biotech. A great many of companies invests in training professional people and developing system of assessment.It’s cheerful to see that the alternative technology in China has entered into a promising era.
Outlook
In the past 30 yesrs, great progress has been achieved in alternatives research in China. A highlight event is that the Society of Toxicological Alternatives & Translational Toxicology under Chinese Society of Toxicology and Society of Toxicity Testing and Alternative methods under Chinese Environment mutagen Society have been established in 2014. Up till now, two national wide academic conferences have been held, and attracted over 500 attendees each time. The Chinese in vitro and alternative society is now under construction. Excitedly,the OECD test guild line 432 3T3 neutral red uptake phototoxicity test was transformed in China and will be updated in‘Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics’by CFDA as well as the data of AAT will be accepted step by step. With more and more dedication to alternatives,Chinese scientists frequently took role in the World Alternative Conference, Intercontinental Alternative Conference (European Alternative Conference and Asian Alternative Conference) and professional international conference. Enthusiasm from academic and industry is the very important impetus for alternative development.It’s estimated that in the following 20 years, with the efforts of middle-out strategy, a breakthrough could be achieved in method development and regulation authorization.
[1] Zhengming He; Guanmin Li. Introduction to Alternative methods of Animal Experiment. Beijing: Academy Press,2003.
[2] The Guides of Opinions about the Ethical Treatment of Animals.State Scientific and Technological Commission, 2006.
[3] GB/T 27416. Laboratory Animal Institutions-General Requirements for Quality and Competence. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China.
[4] Shujun Cheng; Zhifei Zou; Ren Huang. Progress of Bulwark Replacement Technology on Cosmetic Toxicity Testing. Chinese Journal of Comparative medicine 2006, 16 (6), 379-382.
[5] SN /T 2329. Cosmetics Ocular Irritant and Corrosive HETCAm Test. Certification and Accreditation Supervision management Committee, 2009.
[6] SN/T 3899. Guidance on Good Cell Culture Practice and Sample Preparation for Cosmetics Alternative Testing in vitro.Certification and Accreditation Supervision management Committee, 2013.
[7] SN/T3898. Guidance on the Validation and Acceptance of Cosmetics Alternative Testing methods in vitro, 2013.
[8] Yao Qin; Shujun Cheng; Jiancong Huang; et al. Integrated CAmVA and BCOP methods to Predict Eye Irritation Caused by Cosmetics. Chinese Journal of Comparative medicine 2014,24(6), 78-82.
[9] Yu Chen; Huan Yu; Shujun Cheng; et al. Research on Bovine Corneal Opacity and Permeability Test Integrating with Histopathological Evaluation. Detergent & Cosmetics 2016,46(2), 106-110.
[10] Yihui Ke ; Yu Chen ; Shujun Cheng; et al. Preliminary Study for Integrating DPRA with H-CLAT to Predict Skin Sensitizers. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica 2016, 24 (6), 613-619.
[11] Shujun Cheng; Hong Jiao; Yao Qin. The Preliminary Study of in vitro Constructing New Skin model Inspectskin I for Cosmetics Inspection. J Toxicol 2008, 22(6), 428-431.
[12] Yu Chen; Huan Yu; Shujun Cheng;et al. Development of Alternative Test Strategy for the AOP-based Skin Sensitization.Detergent & Cosmetics 2016, 39 (4), 4-9.
[13] Jiabin Guo; Hui Peng; Yimei Wang; et al. Significance of mitochondrial Toxicity Testing in the Safety Evaluation of Innovative Drugs. Chinese Journal of New Drugs 2012,21(16), 1867-1871.
[14] Jiancong Huang; Shujun Cheng; Weijun Tan. Development and Validation in Neural Developmental Toxicity of Stem Cells by in vitro Testing. military medical Journal of South China 2014, 28(4), 396-399.
[15] Shujun Cheng; Yao Qin; Huan Yu; et al. Progress for Alternatives methods Predict the Embrytoxicity by Embryonic Stem Cell Test. Chinese Journal of Comparative medicine 2016, 26(1), 81-85.
[16] Shujun Cheng. The Three Rs and the Humanity Criterion.Beijing: Science Press, 2014.
[17] Shujun Cheng; Jiao Hong. Alternative Laboratory Animal methods Principles and Applications. Beijing: Science Press, 2010.
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2016年4期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2016年4期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Preparation Technology and Property Research of Ultra-Concentrated Liquid Detergent
- Biodegradation of Nonylphenol Ethoxylates in the Continuous Flow Activated Sludge Simulation Test
- Relative Content of Phenoxyethanol and p-Hydroxyacetophenone in Water Phase of Oil-water Systems and Teir Relevant Control Parameters
- Alkoxylation for Surfactant Productions:towards the Continuous Reactors
- Introduction on the Standardization and Future Work of Surfactant and Detergent in China
- National Standard of Laundry Powders (Phosphate Free)
