Preparation Technology and Property Research of Ultra-Concentrated Liquid Detergent
Xiumei Tai, Xiaoying Liu, Guoyong Wang, Xuebin Mao
China Research Institute of Daily Chemical Industry, China
Zhiping Du
Resources and Environment Engineering Research Institute, Shanxi University, China
Introduction
With the development of modern science and technology, environmental protection and green movement received widespread attention in the whole world, the washing products were promoted updated unceasingly. Natural, concentrated, biodegradable,renewable, pollution-free green products become the mainstream of detergent production and consumption.Low energy consumption and low pollution products will be more and more favored by consumers. On the other hand, consumers have changed washing requirement and the cognition of dirt due to changing of living environment and enhancing of cleaning awareness. The consumers need a detergent that can not only tackle a wide range of common stains on the clothes, but also save water and eco-friendly in the course and after washing.Therefore, energy saving, high efficiency, environmental friendly, low carbon liquid detergent will become the development goal of washing products.
The demand of concentrated liquid detergent was increasing due to its higher content of active substances,stronger detergency, less production cost, packaging material,transportation cost and small storage space.[1-5]Ultraconcentrated liquid detergent with surfactant content up to 55% was appeared in 2006, which was a valuable washing product for society and consumers, and these products can reduce energy consumption and decrease packaging waste at the same time.
Ultra-concentrated liquid detergent has great significance in environmental protection, energy saving and carbon emission reduction, which makes it become one of the hot spots in the study of detergent industry.[6-8]In this paper, a series of ultra-concentrated liquid detergents with solid content more than 60% was designed based on the interaction principle of surfactants and previous study.Its stability, foaming power, detergency and water-saving performance were tested.
Experimental Section
Materials
Fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether carboxylate(AE9C, 98wt.%, carbon chain length 12~14); anionic surfactant A, nonionic surfactant B, industrial grade, China Research Institute of Daily Chemical Industry; fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate (AE3S, 70wt.%, carbon chain length 12~14), fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether(AEO9), industrial grade, Zhejiang Jilida Co. Ltd.; the Gul Bert alcohol ether (1307, 1008, 1310 and 1007), industrial grade, Zibo Yunchuan Chemical Co. Ltd.. All products were used without further purification. Deionized water (18.2 MΩ) was used for all experiments.
Apparatus
PHS-3C pH detector, Shanghai precision scientific instrument Co., Leici instrument factory; Terg-O-tometer,Ross-Miles foam meter, China Research Institute of Daily Chemical Industry; WSD-3C whiteness meter, Beijing Kangguang Optical Instrument Co. Ltd.; K12surface tensionmeter, German Krüss company.
Preparation of ultra-concentrated liquid detergent
Ultra-concentrated liquid detergents were prepared using anionic surfactant A, nonionic surfactant B, AE9C, AE3S,AEO9and the Gul Bert ether with different carbon chain length and different EO numbers. First, the formulas were screened by the appearance of product. Liquid detergent formulas were designed (Table 1). It can be seen that the appearance of product from formula II with AEO9and the Gul Bert ether 1008 compound system was clear and transparent, the formula II was selected as the basic formula.
Using formula II as the basic formula, keeping AE9C=5,AEO9=10 and anionic surfactant A=5, the formula is designed through the following experiments. The formulations are shown in Table 2.
The preparation processes of ultra-concentration liquid detergents were as follows: firstly, some deionized water was added into the reactor and heated to 60~70°C;then anionic surfactant A, nonionic surfactant B, AE9C,AE3S, AEO9and Gul Bert ether 1008 with the melting state were added in order with stirring. Stirring wascontinued until the solution became homogeneous. The required amount deionized water was added. When the system temperature decreased to room temperature, pH was adjusted to 7~8 with pH modifier, ultra-concentration liquid detergents with clear and transparent appearance were obtained.
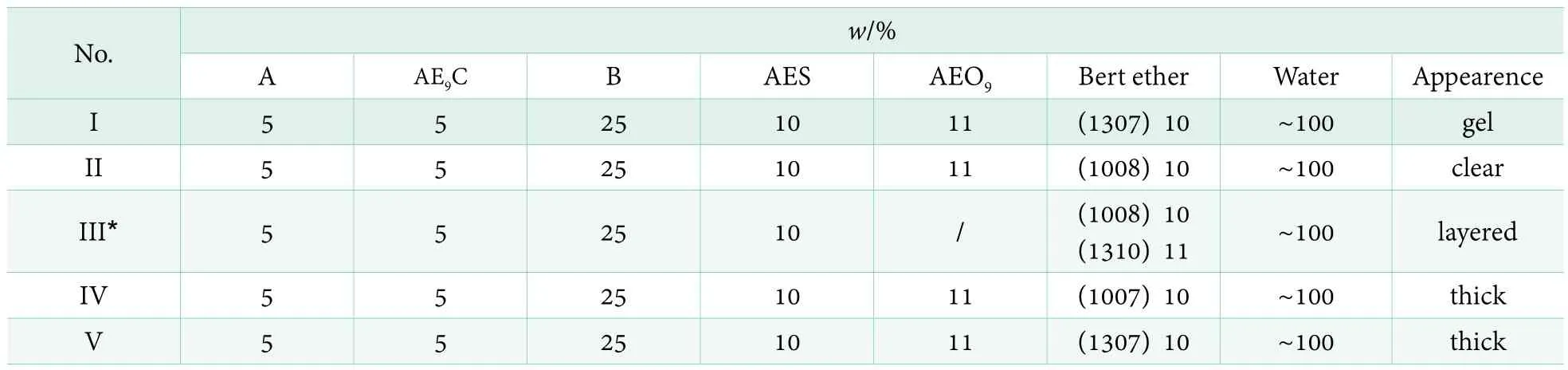
Table 1. Formulations of ultra-concentrated liquid detergent
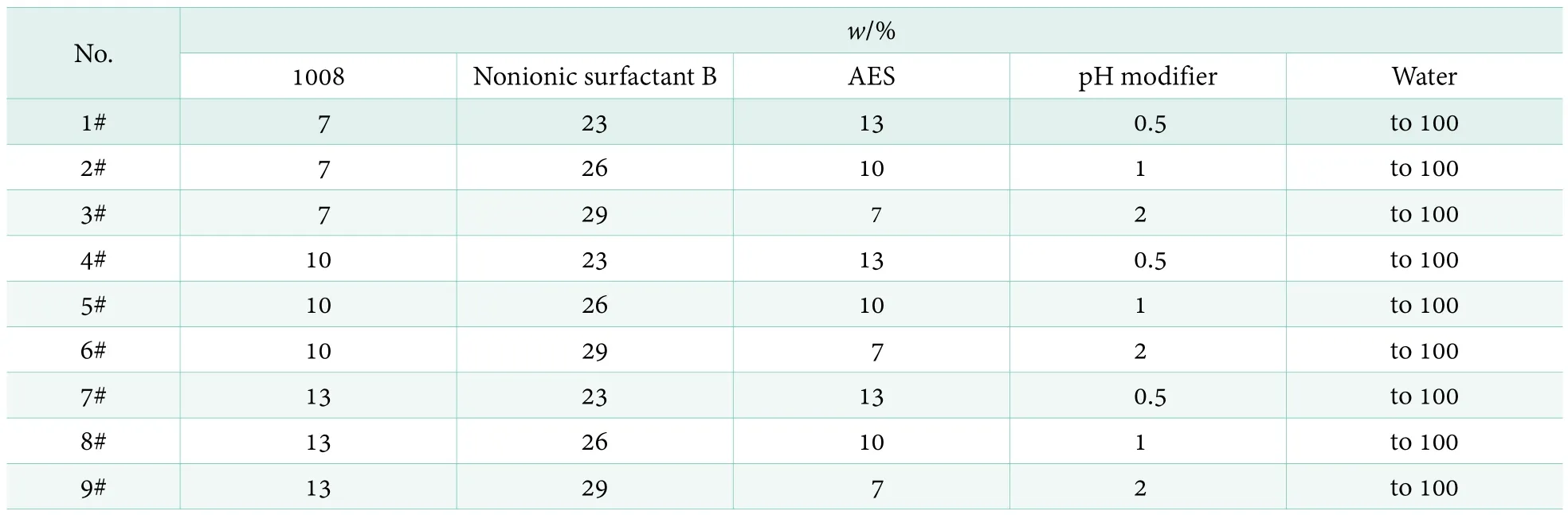
Table 2. Formulations of ultra-concentration liquid detergent
Performance testing of ultra-concentrated liquid detergent
Storage stability.Thermal storage stability: the sample was placed in (40±2) °C oven for 24 h, then the sample was taken out to return to room temperature, and the difference between the original sample and the treated sample was observed whether stratification phenomenon was occurred.
Cold storage stability.The sample was placed in (5±2) °C refrigerator for 7 d, then the sample was taken out to return to room temperature, and it was observed whether flocculation phenomenon was occurred.
Freeze thaw stability.The sample was placed in (-18±2) °C refrigerating chamber for 24 h, then the sample was taken out to return to room temperature, and the difference between the original sample and the treated sample was observed whether stratification phenomenon was occurred.
pH testing.pH measurements were performed at(25±1) °C with using a PHS-3C pH detector. 1 g sample was dissolved in 100 g deionized water with new boiling and cooling. The pH value was recorded after 30 s when the pH electrode was placed in the sample solution under the electromagnetic stirring. The pH measurement was repeated three times in each case.
Foaming measurement.Foaming power was measured by Ross-Mile method. Hard water was prepared according to GB/T 6367-1997. The foaming power and foam stability of the sample were determined by measuring the foam height at 0, 5, 10 min.
Detergency testing.The detergency was tested by Terg-O-Tometer, and the whiteness value of the test cloth was read out before and after washing by the full automatic whiteness meter WSD-3C, compared with the standard liquid detergent. Then, calculating the detergency index I. If I >1, it means that the detergency is stronger than standard liquid detergent. Three kinds of China national standard stained clothes, carbon stained cloth JB-01, protein stained cloth JB-02 and sebum stained cloth JB-03 were used. 9 pieces of clothes (3 pieces of each kind of stained clothes) at a time were agitated for 20 min at 120 rpm in the wash liquor (washing concentration was 0.2% for standard liquid detergent and was 0.05% for ultra-concentration liquid detergent) at 30 °C. The clothes were rinsed two times and dried at room temperature. The measurement of detergence test was repeated two times in each case.
Water saving performance.Water saving performance was evaluated by surface tension of rinsing solution in washing process. Surface tension was measured by William Plate Method using a Krüss K12 surface tensiometer at (25±0.1) °C. Before the measurements, the instrument was calibrated with deionized water ( (72.0± 0.2) mN/m). The surface tension of detergent solution after washing, the first rinsing solution and the second rinsing solution were measured by single point method.According to the surface tension result, the corresponding detergent concentration and the corresponding surfactant concentration of solution was calculated. According to the residual surfactant concentration in the second rinsing solution, the water saving performance of the detergent was determined. The lower residual surfactant concentration, the better the water saving performance.
Results and discussion
Stability
Stability was an important indicator of product performance, and good stability meant long shelf life for goods. After preparation of ultra–concetrated liquid detergent, 4#, 7#, 8# and 9# products showed cloudy appearance. Table 3 shows the stability of different formulas(1#, 2#, 3#, 5# and 6#). It can be seen that 5 samples exhibited good thermal, cold, and freeze thaw stability. It is proved that the prepared ultra-concentrated liquid detergent products had good stability.
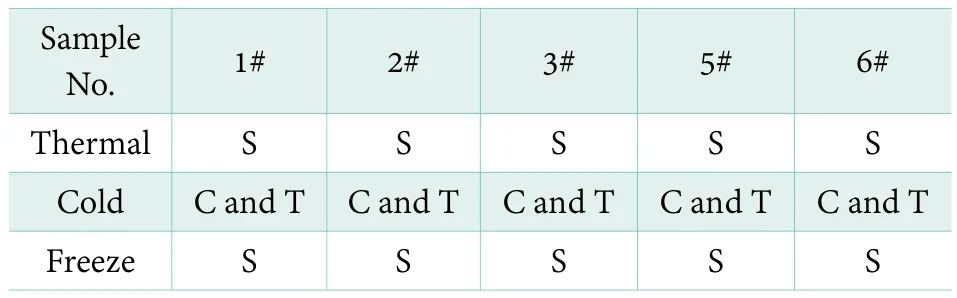
Table 3. Stability of ultra-concentrated liquid detergents
pH value
The pH values of the 5 ultra-concentrated liquid detergents were tested. The testing results are shown in Table 4. It can be seen that all the pH value of 5 samples are less than 9, and less than the national standard 10.5, which showed that these products were slightly irritating to skin.
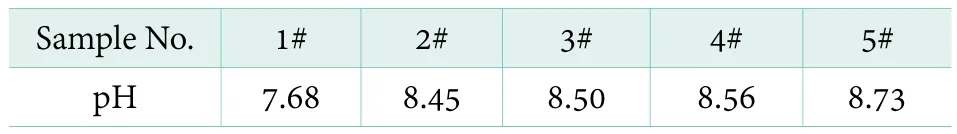
Table 4. pH value of ultra-concentrated liquid detergents

Foam performance
The foam performance is an important property for the detergent. It can be found in the ancient that it is not easy to generate bubbles or easy to disappear when oil was too much in washing. The detergency was generally measured by foam height. Too much foam in the washing machine can lead to prevent the clothes from getting properly clean. Excessive suds can also stop the washing machine from pumping out the water. Therefore, research on the foaming performance of detergent will help to guide the development of new products.
Figure 1 is the results of ultra-concentrated liquid detergent and standard liquid detergent’s foaming performance (0# is standard liquid detergent). It can be seen that sample 1# had the highest foam, and was almost equal to the standard detergent. Other samples foam height had little difference, was slightly lower than the standard detergent. The foam of the samples had good stability, and foams were almost unchanged after 5 min and 10 min.
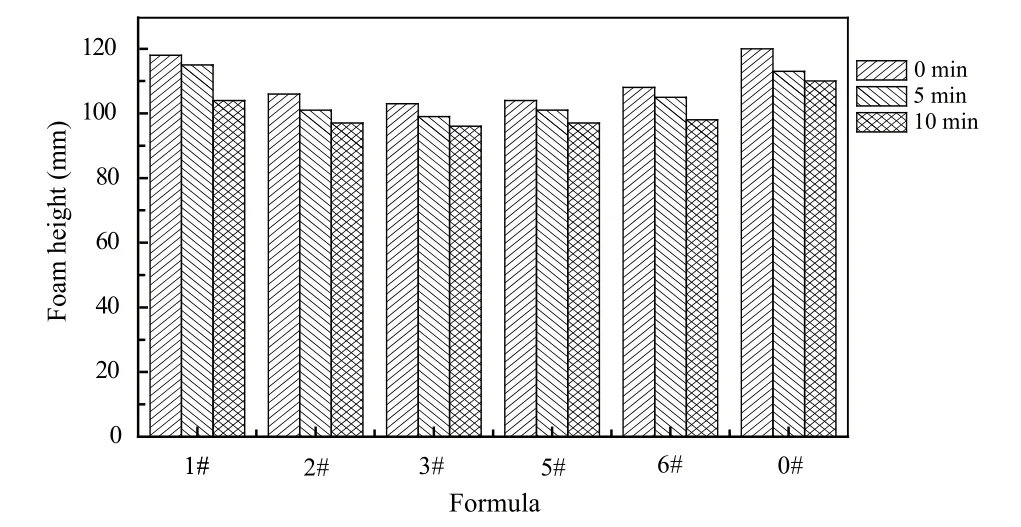
Figure 1. Foam performance of ultra-concentrated liquid detergents and standard liquid detergent (measurement condition: ultra-concentrated liquid detergent: 0.05%,standard liquid detergent: 0.2%, 150 mg/L hard water,(40±0.5) °C)
Detergency
Detergency is defined as the removal of unwanted substances from a solid surface brought into contact with a liquid.[9]The removal of these soils from textiles depends on some factors, such as substrate and detergent.Detergency is tested by measuring the whiteness value of the test clothes prior to washing in detergent under specified conditions.[10]This is followed by measuring the whiteness value of the test clothes after washing, rinsing,and drying cycles.
The detergency results of 5 samples are shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that the detergency of 5 samples(0.05%) was better than the standard liquid detergent(0.2%), because the detergency index I was bigger than 1,which indicated that the 5 samples had good detergency.

Figure 2. Detergency of ultra-concentrated liquid detergents
Water saving performance
Water saving performance is a very important property for detergent. Figure 3 is the surface tension curve of 5 ultra-concentrated liquid detergents and stand liquid detergent. Table 5 is the surface tension, corresponding concentration of detergent and surfactant. It can be seen from Table 5 that 1# concentration was the lowest of surfactant for the second rinsed solution, followed by 2#,3# and standard solution, the concentration of 5# and 6#were the highest. The residual surfactant concentration of standard liquid detergent were 5.3 times, 3.8 times and 1.2 times of 1#, 2# and 3#, respectively. It was proved that 1#and 2# samples had better water saving performance than standard liquid detergent.
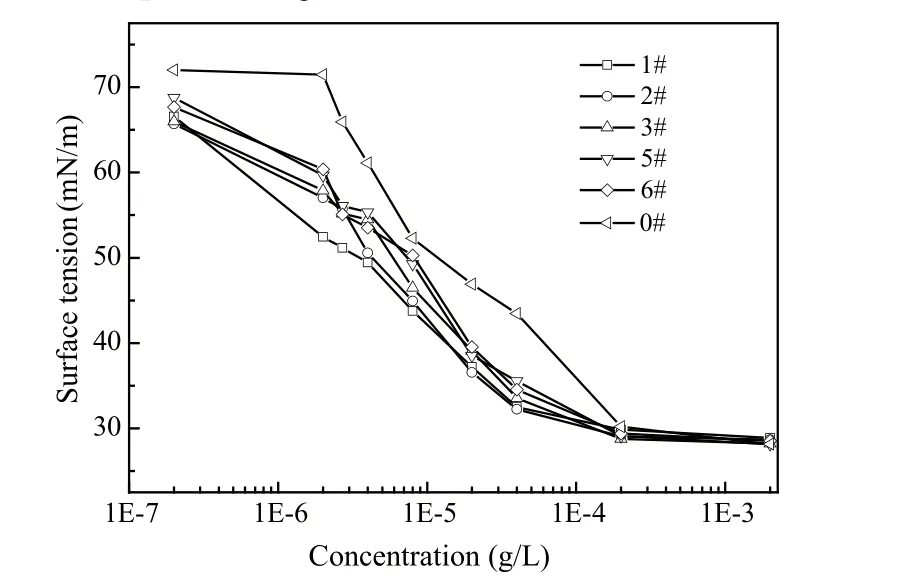
Figure 3. Surface tension of ultra-concentrated and standard liquid detergents as a function of concentration
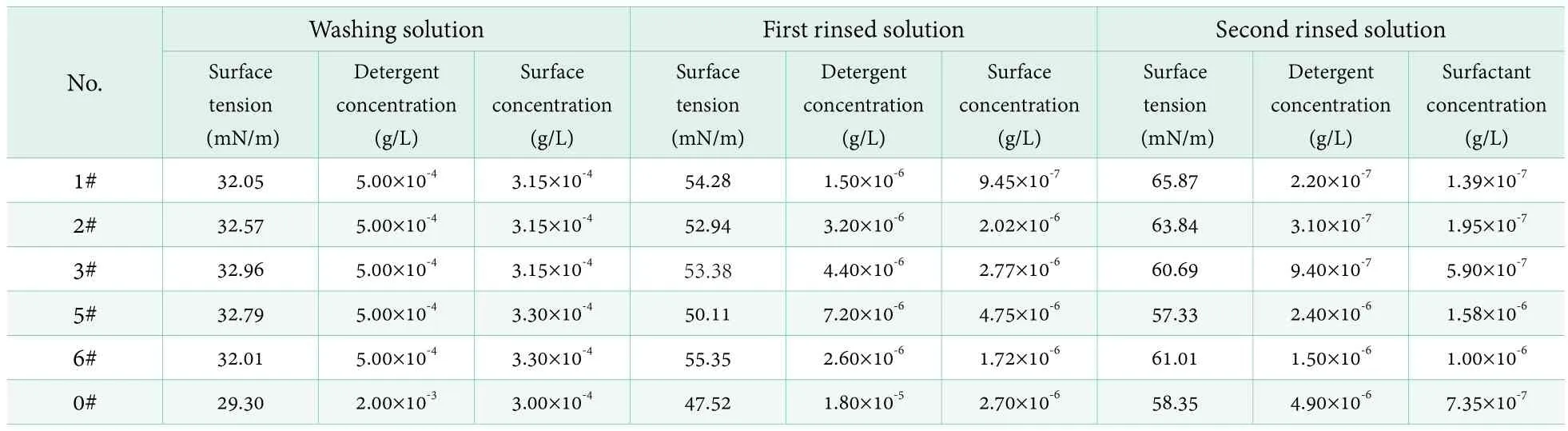
Table 5. Water-saving properties of ultra-concentrated and standard liquid detergents
Conclusions
1) The ultra-concentrated liquid detergent samples screened (solid content > 60%) have good compatibility,thermal, cold and freeze-thaw stability to ensure long enough shelf life.
2) Foam height of Ultra-concentrated liquid detergent(0.05%) was slightly lower than standard liquid detergent(0.2%); pH was less than 9 and the product’s performance was mild with less skin irritation; ultra-concentrated liquid detergent has very better detergency.
3) Sample 1# and sample 2# had better water saving performance than standard liquid detergent. The residual surfactant concentration of standard liquid detergent were 5.3 times and 3.8 times of 1# and 2#, respectively.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Science &Technology Pillar Program during the 12thFive-year Plan Period (No. 2014BAE03B03) and Natural Science Found of Shanxi Province (No. 2014011014-1).

[1] Huatao Zhang. Development Trend of Domestic and Foreign Washing products. China Cleaning Industry 2014(2), 29-36.
[2] Frank Meier. Powders and Pouches-Detergent Innovations,Trends and Challenges. The 9thWorld Surfactant Congress 2013.
[3] Jamie Rosenberg. The Future of Household Products. The 9thWorld Surfactant Congress 2013.
[3] Xiao Yue. Green Trend of Global Detergents. China Cleaning Industry 2012, 25(6), 83-84.
[4] Zeyun Wang; Hailan Chen. Latest Progress of Green Surfactants in Detergent Industry in China. Detergent & Cosmetics 2011,34(7), 21-23.
[5] Yongqiang Sun; Wanxu Wang; Qiuxiao Li; Tao Geng. Green Surfactant Turned into Main Direction of Future Detergent Development. Detergent & Cosmetics 2010, 33(11), 12-14.
[6] Junhua Guo. Development of High Efficiency Concentrated Laundry Detergent with Low Foam. China Cleaning Industry 2015(2), 47-50.
[7] Ying Liu; Lianlian Sun; Weilin Teng. Discussion on the Concentrated Detergent. China Cleaning Industry 2014(2), 37-40.
[8] Hui Zhang; Xiujie Feng. Surfactant for Low Foam and High Concentrated Liquid Laundry Detergent. Detergent & Cosmetics 2013, 36(01), 15-18.
[9] P. Goon; R.G. Bhirud; V.V. Kumar. Detergency and Foam Studies on Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonate and Secondary Alkyl Sulfonate. J. Surfactant Deterg. 1999, 2, 489-493.
[10] K. L. Matheson; M. F. Cox; D. L. Smith. Interactions between Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates and Water Hardness Ions. I.Effect of Calcium Ion On Surfactant Solubility and Implications for Detergency Performance. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1985, 62,1391-1396.
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2016年4期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2016年4期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Biodegradation of Nonylphenol Ethoxylates in the Continuous Flow Activated Sludge Simulation Test
- Relative Content of Phenoxyethanol and p-Hydroxyacetophenone in Water Phase of Oil-water Systems and Teir Relevant Control Parameters
- Alkoxylation for Surfactant Productions:towards the Continuous Reactors
- Development of Alternative to Animal Testing on Cosmetics by Middle-out Strategy
- Introduction on the Standardization and Future Work of Surfactant and Detergent in China
- National Standard of Laundry Powders (Phosphate Free)
