Glycoalkaloids and phenolic compounds in three commercial potato cultivars grown in Hebei,China
Cheng-Yu Jin,Hong Liu,Dan Xu,Fan-Kui Zeng,Yu-Ci Zhao,Hai Zhang,Gang Liu
aResearch&Development Center for Eco-material and Eco-Chemistry,Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Lanzhou 730000,China
b University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
c CAS Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources and Key Laboratory for Natural Medicine of Gansu Province,Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Lanzhou 730000,China
d Zhangjiakou Hongji Agriculture Science and Technology Development Co.Ltd,Zhangjiakou 076576,China
ABSTRACT In order to investigate the food nutrition and safety of potato,the objective of the present study is to quantify glycoalkaloids (α-chaconine and α-solanine) and phenolic compounds in three potato cultivars,namely,Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody,grown in Hebei,China,and these two classes of biologically active compounds in commercial dehydrated potato flakes were also investigated.The total glycoalkaloid levels in whole potatoes ranged from 4.72 mg/kg for Shepody potatoes to 34.45 mg/kg for Russet Burbank potatoes.The ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine in whole potatoes ranged from 0.41 for Russet Burbank potatoes to 3.61 for Atlantic potatoes.The removal rate of total glycoalkaloids in Russet Burbank potatoes during dehydrated potato flake processing is 90.0%.Chlorogenic acid is the dominant phenolic compound in Russet Burbank potatoes.By contrast,Atlantic and Shepody potatoes contain considerable caffeic acid.The loss rate of phenolic compounds in Russet Burbank during dehydrated potato flake processing is 50.47%.
Keywords:Glycoalkaloids Phenolic compounds Dehydrated potato flake Potato
1.Introduction
China is the no.1 potato producer in the world,with a total production of 96.14 Mt,which accounted for 24.97%of the total world production in 2014[1].China has a rapidly developing processing industry of potato with at least 8 modern French fries plants,24 potato chips plants,and 34 dehydrated potato plants in 2013.The Chinese consumed approximately 10%of potato in processed form,including potato starch in 2014.
Dehydrated potato flake is made from fresh potato tubers.The processing steps include washing,steam peeling,slicing,washing,blanching,cooling,cooking,mashing,drum drying,flaking,and packaging [2,3].Although the major processed potato products in the world are currently French fries and potato chips,dehydrated potato may be the first global processed potato product[4,5].Dehydrated potato was first introduced in the 20th century wartime (World War I and World War II) in industrialized countries [6,7].Today,dehydrated potato flake is an intermediate material for mashed potato,as well as for potato chips,military vacuum-packaged compressed biscuits,and many other convenience products[8-10].
At the beginning of 2015,the Ministry of Agriculture(MOA)of the People’s Republic of China announced that potato will soon be China’s newest staple food [11].According to the MOA,30% of the annual potato production will be consumed as a staple food by 2020,with potatoes being turned into noodles,steamed bread,and other staple food products.Although limited to the processing performance,dehydrated potato products may be used as replacement of wheat flour for production of staple food because dehydrated potato products can be stored over several years and used when fresh potatoes are scarce[12,13].
Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody are three potato cultivars widely cultivated commercially in Western countries[14,15].In north China,particularly in Inner Mongolia,Gansu,and Heilongjiang,Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody are also the major potato cultivars for French fries and potato chips processing.In Zhangjiakou,Hebei Province,these commercial potato cultivars are grown using modern agricultural irrigation technology and the potato yield reached 60 MT/ha,which is higher than the national average value of 15 MT/ha.Three modern dehydrated potato flake plants can be found in Zhangjiakou.
Steroidal glycoalkaloids are an important class of biologically active compounds in potatoes[16,17].They influence the flavor of fresh and processed potatoes from a bitter taste toward a burning sensation at higher concentrations and are regarded to be toxic to humans in concentrations of more than 200 mg/kg of the fresh weight of potatoes [18-21].α-Chaconine and α-solanine are the major glycoalkaloids in potato tuber[22,23].Previous studies have shown that glycoalkaloids can induce gastrointestinal and systemic effectsin vivoandin vitroby disrupting the cell membranes and inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase activity[24,25].
Potato supplies remarkable portions of phenolic compounds,which are predominantly found in the peel and adjoining tissues[26,27].In nutrition,these components have been the focus of considerable attention as they contain potentially protective factors against cancer and heart diseases basically because of their potent antioxidative properties[28].Furthermore,potato polyphenols are important for the quality and processing of food,in particular with regard to their flavor induction(astringency)and capacity to promote discolorations,such as enzymatic browning reactions[26,27].
M?der et al.[3]determined the influence of the commercial production process for dehydrated potato flakes on the content of glycoalkaloids and phenolic compounds.Tajner-Czopek et al.[29]determined the influence of the thermal process of colored potatoes on the content of glycoalkaloids in potato products.El ˙zbieta[30]determined the effect ofindustrial potato processing on the concentrations of glycoalkaloids and nitrates in potato granules.However,information on the three commercial potato cultivars(i.e.,Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody) grown in China is unavailable.The objective of the present study is to quantify the glycoalkaloids and phenolic compounds in Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody grown in Zhangjiakou,Hebei.The contents of these two classes of biologically active compounds in dehydrated potato flakes were also investigated.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Materials
Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody potatoes and dehydrated potato flake were gifts from Zhangjiakou Hongji Agriculture Science and Technology Development Co.Ltd.in Hebei Province,China.The harvest time is September 15,2015,the growth time for Atlantic is about 90 days,for Shepody is about 110 days,for Russet Burbank is about 130 days,after harvest from the field directly transport into the production line for dehydrated flake processing.α-Chaconine and α-solanine were purchased from ChromaDex (Irvine,CA,USA).Chlorogenic acid (≤95%; catalog no.C3878-250MG,lot no.WXBB6039V),p-coumaric acid (catalog no.C9008-1G,lot no.BCBN8568V),trans-ferulic acid (catalog no.46278-1G-F,lot no.BCBN3037V),trans-cinnamic acid(catalog no.C80857-5G,lot no.MKBT2807V),and caffeic acid (catalog no.C0625-2G,lot no.SLBN1752V)were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich(St.Louis,MO,USA).High-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)grade acetonitrile,tetrahydrofuran,analytical grade potassium dihydrogen phosphate(KH2PO4),and ammonium hydroxide(NH4OH)were obtained from commercial sources.
2.2.Dry matter and total starch content
The total starch content was determined by using the Megazyme Total Starch Assay Kit(AA/AMG).The result was detected by using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer at 510 nm[31].The dry matter content was obtained by freeze-drying[32].Dry matter content was determined from the difference in the weight of potato samples before and after freeze-drying.
2.3.Extraction of glycoalkaloids for HPLC
The cortex layer (approximately 5 mm of peripheral tissue) of tubers was peeled and chopped with a knife.The flesh,peel,and cubes of whole potato were ground in a ceramic mortar with liquid nitrogen.The samples(2 g to 2.5 g)or dehydrated potato flakes(5 g)were extracted with 40 mL of 5%acetic acid accompanied by ultrasonication for 10 min at room temperature.The other treatment steps were the same as that described in the study of Friedman et al.[33].The glycoalkaloids were precipitated with concentrated NH4OH,dissolved in 500-1000 μL of a mixture of tetrahydrofuran/acetonitrile/20 mM KH2PO4,and centrifuged at 18,000×gfor 10 min at 1°C.The supernatant was used for HPLC.
2.4.HPLC analysis of glycoalkaloids
The method used in this study was adapted from the literature [33]and employed an Inertsil NH2column (5 μm,4.0 mm×250 mm; GL Science Inc.,Tokyo,Japan).HPLC was conducted with the aid of a Waters liquid chromatograph model 600-2998 equipped with a model 2998 photodiode array detector set at 208 nm.Chromatogram peak areas were integrated with a Waters Empower 2 chromato-integrator.The mobile phase was acetonitrile/20 mM KH2PO4(80:20,v/v).The flow rate was 1 mL/min at a column temperature of 20°C.The concentrations of α-chaconine and α-solanine in the potato extracts were calculated by comparing with the integrated peak areas of known amounts of the standards by a Waters chromato-integrator.α-chaconine or α-solanine of 20 μg/mL were prepared by dissolving the glycoalkaloids in pyridine,and then dilute with the mobile phase into 10,5 and 1 μg/mL respectively,20 μL of each standard solution were used to make the calibration curves.
2.5.Extraction of phenolic compounds
The method used in this study was adapted from the literature[26]with minor modifications.Potato peel (2-3 mm thick),flesh,and whole potatoes were cut with a knife into slices.After homogenization in a blender,samples of fresh materials(10 g-15 g)from each potato cultivar or dehydrated potato flake(approximately 5 g)were placed in a 250 mL flask with a reflux condenser to which 50 mL of 80% ethanol was added,followed by heating at 80°C for 10 min and centrifugation at 12,000×gfor 15 min at 5°C.The residue was extracted twice with 20 mL of 80% ethanol and centrifuged.The combined extracts were made up to a final volume of 100 mL with 80%ethanol.This solution(10 mL)was evaporated under reduced pressure at 20°C,and the residue was dissolved in 80%ethanol(1 mL)and centrifuged.The supernatant was used for HPLC.
2.6.HPLC analysis of phenolic acids
HPLC analysis was conducted on an Agilent liquid chr omatograph 1200 series equipped with a G1315D DAD UV-Vis detector set at 280 and 340 nm.The column temperature was controlled with an AT-900 thermometer.Chromatogram peak areas were integrated with Agilent ChemStation.An Inertsil ODS-3 V column(5 μm,4.0 mm×250 mm;GL Science Inc.,Tokyo,Japan)was used to analyze phenolic acids.The mobile phase of the (A/B) gradient was(A)acetonitrile and(B)0.5%formic acid.The content of acetonitrile in the solvent was increased as follows:5% (0 min to 5 min),18% (30 min),70% (90 min),and 5% (120 min).The flow rate was 1 mL/min at a column temperature of 30°C.Three separate analyses of each sample were conducted.
Mixture standard solution of chlorogenic acid,caffeic acid,pcoumaric,ferulic acid,andtrans-cinnamic acid were prepared by dissolving 5 mg of each standard phenolic compound in 5 mL 30%methanol,and dilute with the mobile phase into 2.5,5,10,and 20 μg/mL respectively,20 μL of each diluted standard solution were used to make the calibration curves.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Dry matter and starch content
Potato cultivar with a high content of dry mater is preferred for potato flake processing because ofits high yield.The major component of the dry matter in potato tubers is starch(approximately 80%).In this study,the dry matter and starch content of three potato cultivars,namely,Shepody,Russet Burbank,and Atlantic,grown in Hebei,China were quantified.Shepody potato,with 21.11%±0.63 a of dry matter and 16.26%±0.22 of total starch,is the lowest among the three cultivars.By contrast,Russet Burbank and Atlantic potatoes have similar contents of dry matter (Russet Burbank:23.62%±0.57;Atlantic:23.22%±0.71)and total starch(Russet Burbank:18.13%±0.15;Atlantic:17.89%±0.43),with Atlantic potato being slightly lower than Russet Burbank potato on the two indicators.
3.2.Glycoalkaloids
Potato peels usually contain more glycoalkaloids than the pulp.In China,traditional household processing methods of potatoes without peeling involve boiling and baking.This investigation determined the contents of α-chaconine and α-solanine of three different cultivars on their peel,pulp,and whole potato and calculated the total amount of glycoalkaloids and the ratio of two glycoalkaloids.
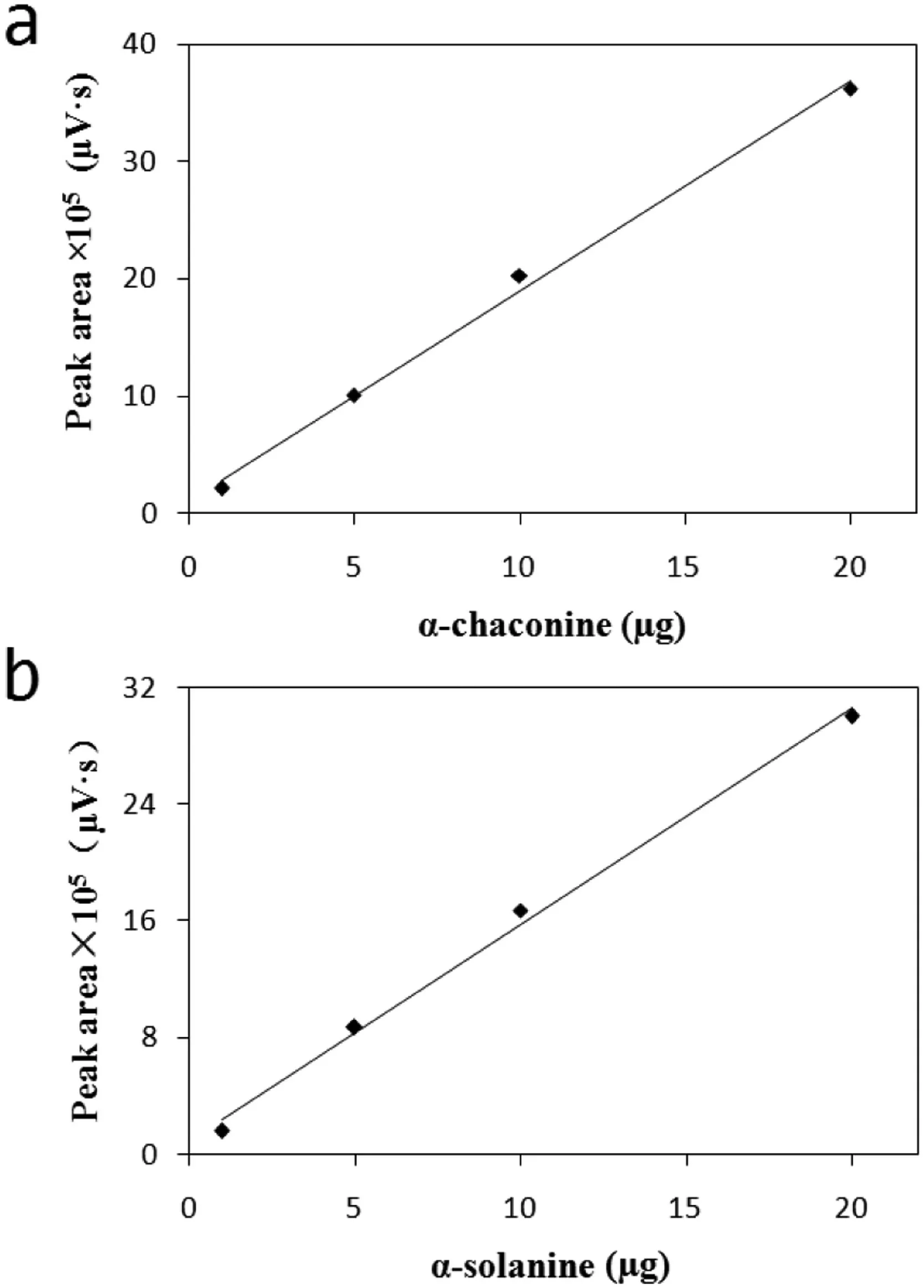
Fig.1.Calibration curves of α-chaconine (a) and α-solanine (b) determination obtained using HPLC.
The both calibration curves of α-chaconine and α-solanine are presented in Fig.1.The calibration cures for α-chaconine andα-solanine determination arey=1.789x+1.075,R2=0.996,andy=1.482x+0.953,R2=0.995.As one can see from the results presented in Fig.1,the calibration curve obtained from HPLC method has good linearity,and betterR2factor.
Fig.2 shows the HPLC chromatograms of α-chaconine and αsolanine from the peels of three potato cultivars.The retention times of the two glycoalkaloids on the HPLC column at 208 nm ranged as follows:α-chaconine,13.5 min; α-solanine,23.5 min.The corresponding limits of detection(LOD values in μg)from multiple determinations were 0.31,0.48.Notably,the peel of Russet Burbank possesses the highest content of glycoalkaloids,whereas that of Shepody contains the lowest amount of glycoalkaloids.However,the α-chaconine to α-solanine ratio of Russet Burbank was the lowest,whereas that of Shepody was the highest(Table1).Several studies have shown that the toxicity of the two compounds in mixture can act synergistically rather than additively[34,35].
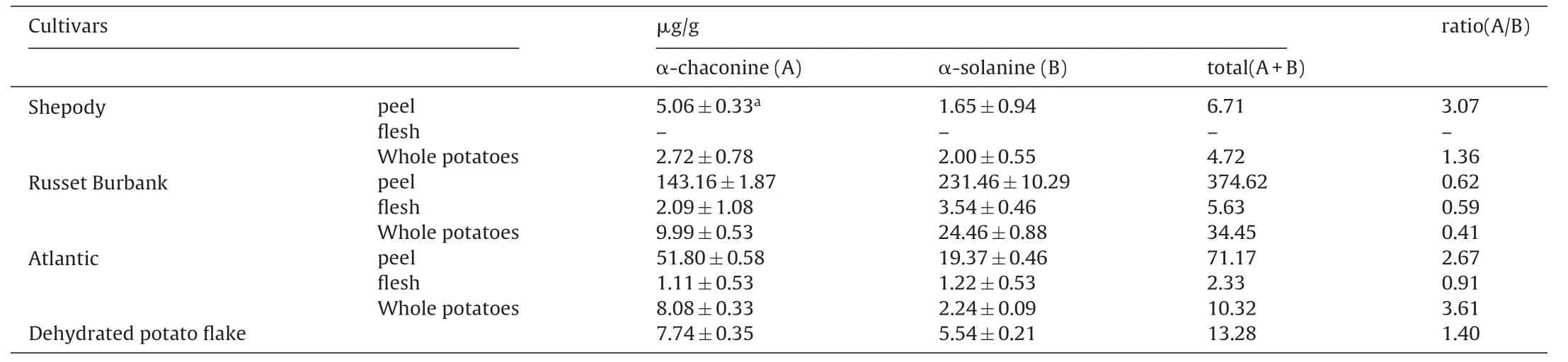
Table1 Glycoalkaloid Content of Potato Flesh,Peel,and Whole Potatoes of Three Potato Cultivars.
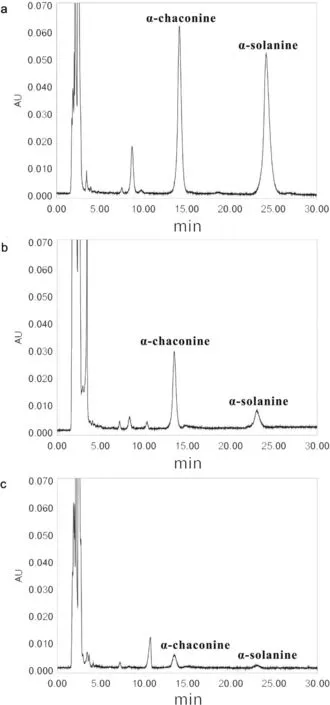
Fig.2.HPLC chromatograms of α-chaconine and α-solanine from the peels of three potato cultivars:(a)Russet Burbank,(b)Atlantic,and(c)Shepody.
The extraction of glycoalkaloids is a crucial step for analysis,however,it is really very difficult to extract all glycoalkaloids in the sample,especially those bound glycoalkaloids.In order to extract the glycoalkaloids as many as possible,various critical control factors have been considered:Firstly,high ratio of extraction solution(40 mL) to material (2-2.5 g) was used at the extraction step,the fresh potato tuber contains about 85% water,~0.4 g of material was used in fact.Though 5 g dehydrated potato flakes were used as material,the glycoalkaloids content is very low compared to the potato tuber.Secondly,glycoalkaloids are easier to dissolve in acid extract solution,so 5%acetic acid was used,in addition,weak acid is beneficial to avoid hydrolysis of glycoalkaloids.Thirdly,ultrasonication at long time was used(10 min).Fourthly,multiple extraction was used,3 times were used in this investigate.
Table1 shows the distribution of the two glycoalkaloids in the flesh,peel,and whole potatoes of the three cultivars grown in Hebei,China.α-Chaconine levels in peel (in mg/kg fresh weight)ranged from 5.06 for Shepody to 143.16 for Russet Burbank.α-Solanine levels in peel ranged from 1.65 for Shepody to 231.46 for Russet Burbank.The total glycoalkaloid (A+B) levels in peel ranged from 6.71 for Shepody to 374.62 for Russet Burbank.The ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine in peel ranged from 0.62 for Russet Burbank to 3.07 for Shepody.
As for glycoalkaloid levels in flesh,the Russet Burbank potatoes also have high contents of α-chaconine,α-solanine,and total glycoalkaloids(A+B)at 2.09,3.54,and 5.63,respectively.The corresponding ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine is 0.59.The Atlantic potatoes have lower glycoalkaloid contents in flesh of 1.11,1.22,and 2.33 for α-chaconine,α-solanine,and total glycoalkaloids(A+B),respectively,than the Russet Burbank potatoes.The corresponding ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine is 0.91.The Shepody potatoes have the lowest glycoalkaloid content in flesh,which is lower than the limit of detection.
Table1 also shows the difference in the whole potato glycoalkaloid contents of these three potato cultivars.The α-chaconine levels in whole potatoes ranged from 2.72 for Shepody to 9.99 for Russet Burbank.The α-solanine levels in whole potatoes ranged from 2.00 for Shepody to 24.46 for Russet Burbank.The total glycoalkaloid(A+B) levels in whole potatoes ranged from 4.72 for Shepody to 34.45 for Russet Burbank.The ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine in flesh ranged from 0.41 for Russet Burbank to 3.61 for Atlantic.
We also quantified the glycoalkaloid content of commercial potato flake provided by Zhangjiakou Hongji Agriculture Science and Technology Development Co.Ltd.Its content of α-chaconine and α-solanine(in mg/kg wet weight)is 7.74 and 5.54,respectively.The total glycoalkaloids(A+B)is 13.28,the ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine is 1.40,and the removal rate of total glycoalkaloids in Russet Burbank during dehydrated potato flake processing is 90.0%.According to M?der et al.(3),peeling and blanching are predominantly responsible for the loss of glycoalkaloids.Steam peeling reduces 77.21% of the glycoalkaloid content,blanching reduces 11.22%,and the subsequent cooking,mashing,and drying have no significant effect on the glycoalkaloid concentration.Elzbieta [30]also reported that the highest decrease in glycoalkaloids during industrial processing was caused by peeling (50%) and blanching(63%).
As we known,the residual 10% of glycoalkaloids in the dehydrated potato flakes are very difficult to be removed,but the value is lower than the maximum level 200 mg/kg for safety.In the industrial production of dehydrated potato flakes,the main problem-solving method for control the glycoalkaloids is by control the raw material:sprouted,green potato tubers,and the potato varieties with high glycoalkaloids content will not be used to produce the dehydrated potato flakes.Also,strict post-harvest storage conditions will be used to prevent the increase of glycoalkaloids.
Fig.2 and Table1 show that the glycoalkaloids in these three potato cultivars varied significantly,particularly in the peel,and the content in the peel is several times to a dozen times higher than that in the flesh.Friedman et al.[33]also reported that the content of glycoalkaloids can vary significantly in different potato cultivars and is enhanced postharvest by environmental factors,such as light,mechanical injury,and storage.In this investigation,the total glycoalkaloid content of Russet Burbank in the peel is as high as 374.62 mg/kg,which is higher than the maximum level(200 mg/kg) for safety.Thus,peeling during processing is essential for food safety reasons.Considering several Chinese household processing methods of potatoes without peeling,we do not sug-gest using Russet Burbank potatoes as raw material for cooking;Shepody potatoes are more suitable.
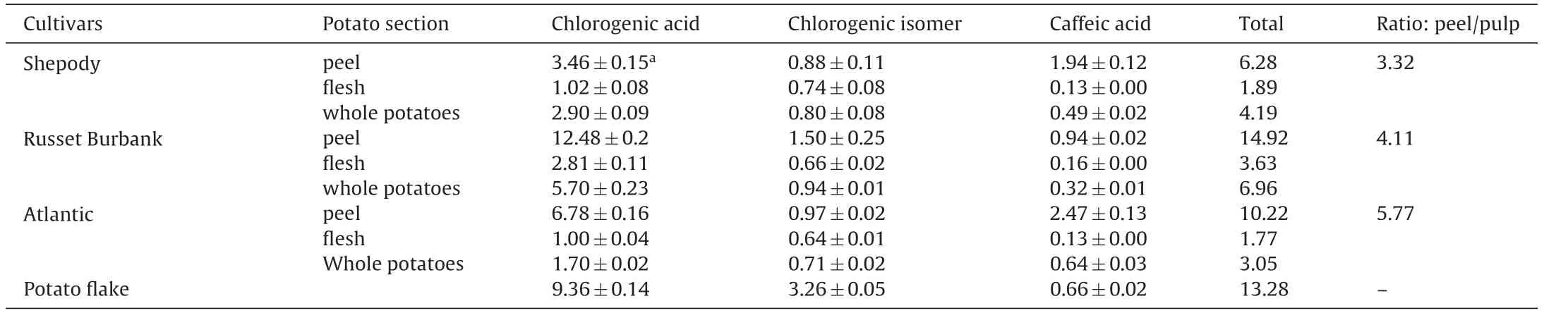
Table2 Content of Phenolic Compounds in the Peel,Flesh and Whole Potatoes of Three Potato Varieties and Potato Flake.
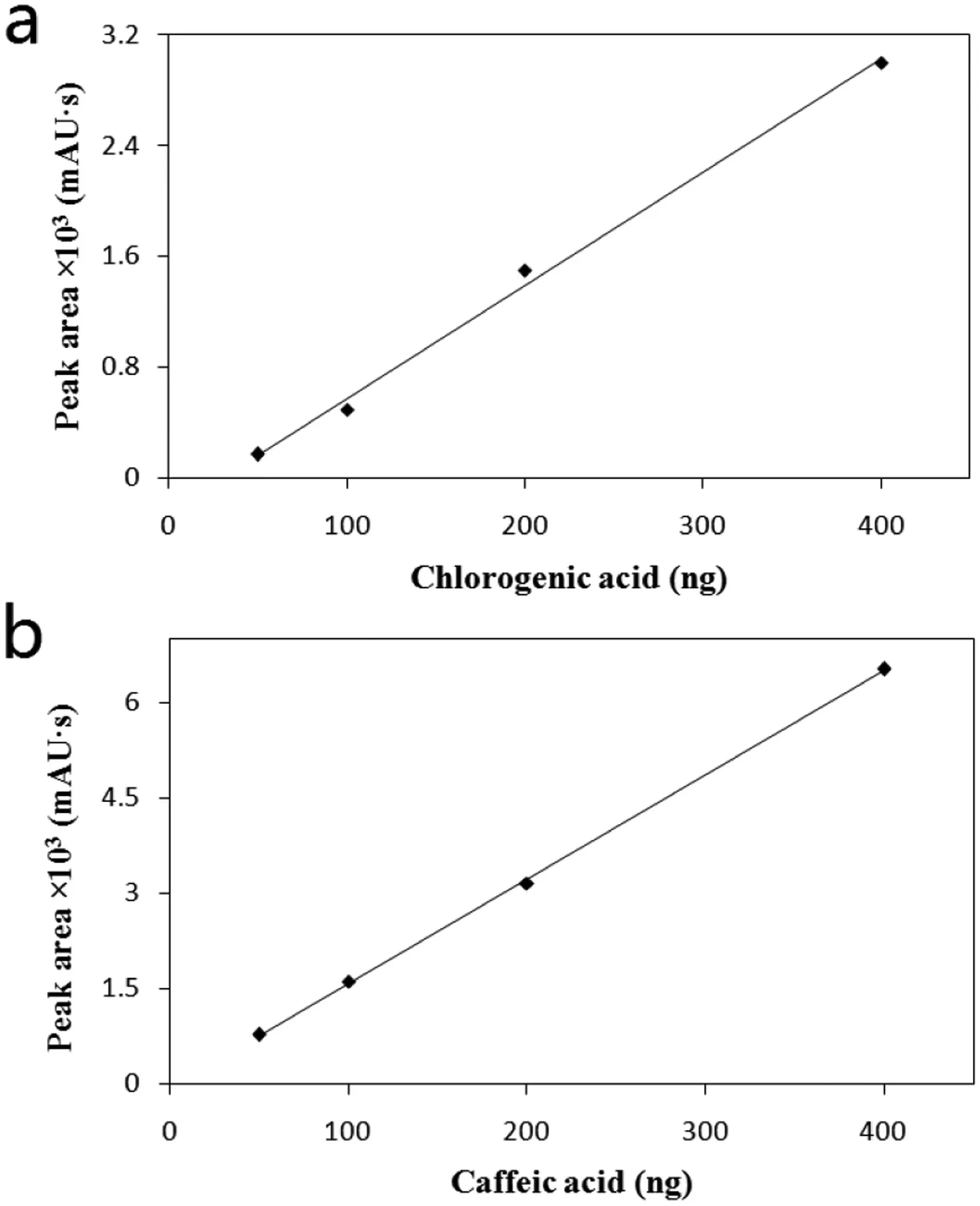
Fig.3.Calibration curves of chlorogenic acid (a),caffeic acid (b) determination obtained using HPLC.
Langkilde et al.[36]reported that changing the ratio of αsolanine to α-chaconine does have an effect,i.e.,a relative decrease in α-solanine resulted in less pronounced toxicological effects.Therefore,the ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine might have an important effect on food safety.Russet Burbank potatoes possess a low ratio of α-chaconine to α-solanine,such that they might be more toxic when the total glycoalkaloid amount is at the same level.Thus,Shepody and Atlantic potatoes may be safer.
3.3.Phenolic compounds
Phenolic compounds are secondary plant metabolites found in potatoes and other plants [37,38].Phenolic compounds not only participate in enzyme-catalyzed browning reactions that may adversely affect the color,flavor,and nutritional quality of potatoes and products but also exhibit beneficial antimutagenic,anticarcinogenic,antiglycemic,cholesterol-lowering,and antimicrobial properties [26].Therefore,processing conditions that minimize their degradation should be adopted during household and industrial processing.
The both calibration curves of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid are presented in Fig.3.The calibration cures for chlorogenic acid ahd caffeic acid determination arey=0.008x-0.249,R2=0.996,andy=0.016x-0.060,R2=0.999.As one can see from the results presented in Fig.3,the calibration curve obtained from HPLC method has good linearity,and betterR2factor.
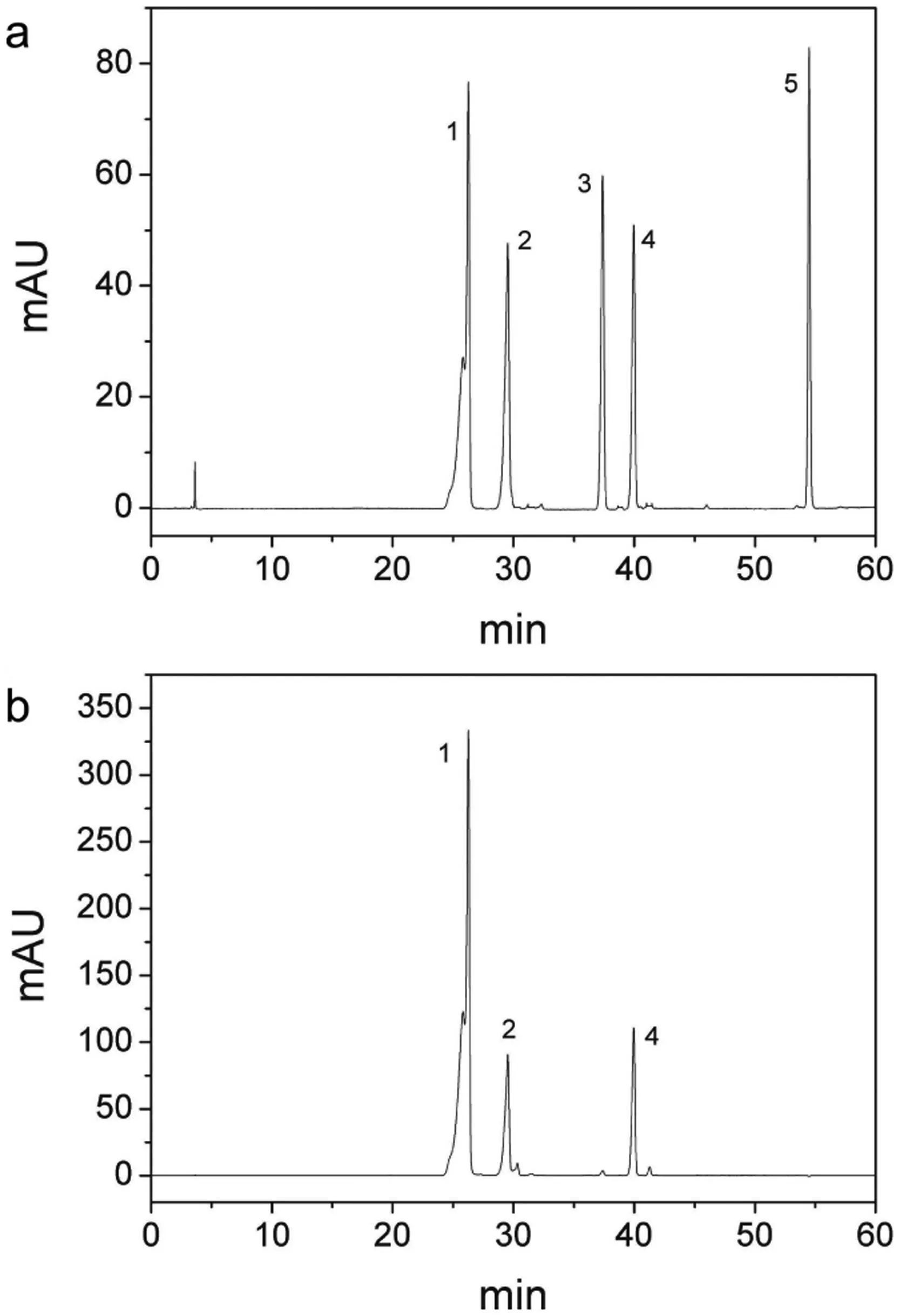
Fig.4.HPLC chromatograms of standard chlorogenic acid(peak 1),caffeic acid(peak 2),p-coumaric(peak 3),ferulic acid(peak 4),and trans-cinnamic acid(peak 5).Column:Inertsil ODS-3 V (5 μm,4.0 mm×250 mm); flow rate,1.0 mL/min; column temperature,20°C; mobile phase,acetonitrile/0.5% formic acid (gradient mode);and detector,UV at 280 nm(a)and 340 nm(b).
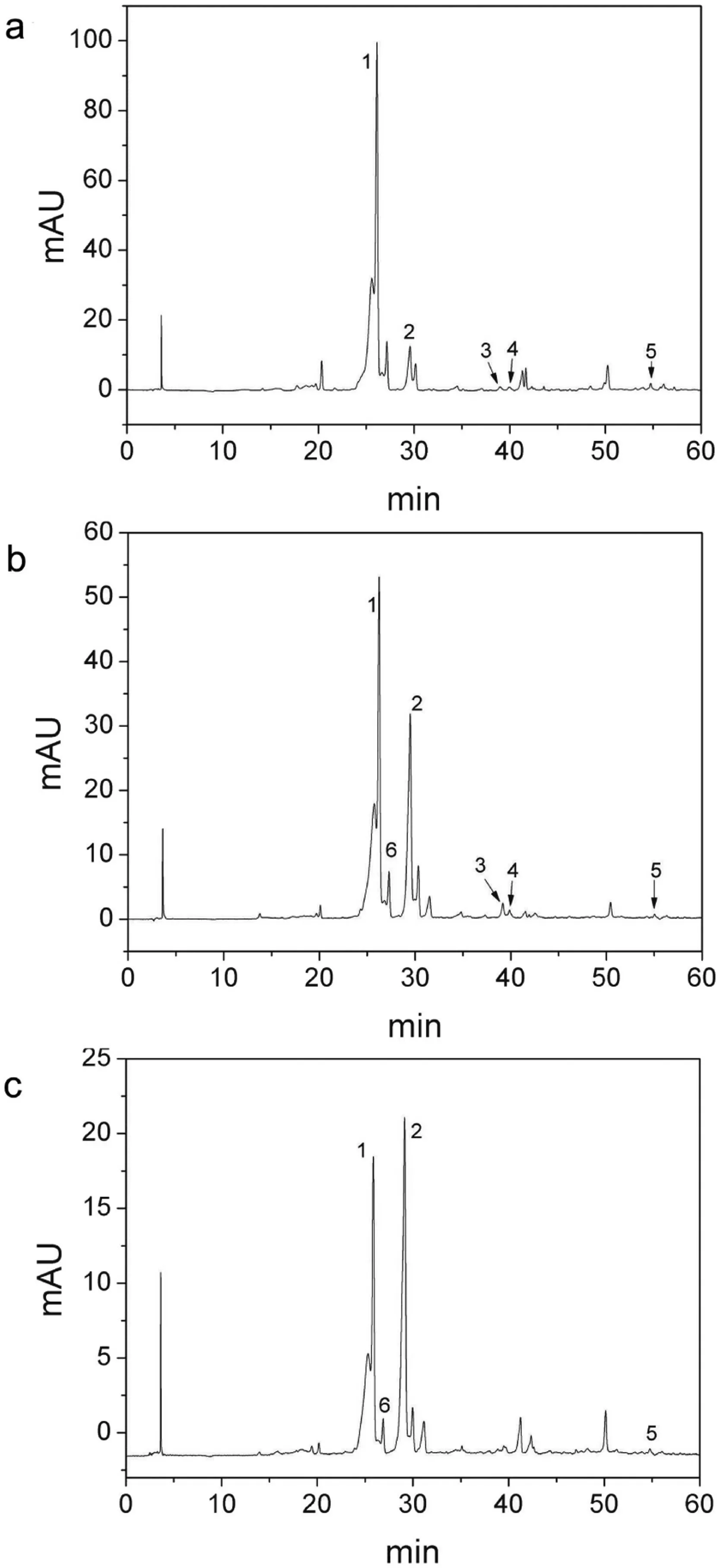
Fig.5.HPLC chromatograms of phenolic compounds in the peel of three potato cultivars:(a) Russet Burbank,(b) Atlantic,and (c) Shepody.Identification; p.1,chlorogenic acid; p.2,caffeic acid; p.3,p-coumaric; p.4,ferulic acid; p.5, transcinnamic acid; and p.6,chlorogenic acid isomer.Chromatographic conditions are the same as that in Fig.4.
The main phenolic substances in potato tuber include chlorogenic acid and its isomers,namely,coumaric acid,ferulic acid,cinnamic acid,and caffeic acid [26].The retention times of the five standards on the HPLC column at 280 nm ranged as follows:chlorogenic acid,26.27 min; caffeic acid,29.53 min;p-coumaric acid,37.39 min; ferulic acid,39.96 min; andtrans-cinnamic acid,54.49 min(Fig.4a).The corresponding limits of detection from multiple determinations were 24.2,7.3,5.2,6.8,and 3.2,the results are concurring with the results reported by Im et al.[26],while the same sample treatment method and HPLC conditions were used.At 340 nm,chlorogenic acid,caffeic acid,and ferulic acid show strong response values; however,p-coumaric andtrans-cinnamic acid cannot be found(Fig.4b).These results are consistent with the previous study of Im et al.[26].
Fig.5 shows the HPLC chromatograms of phenolic compounds in the peel of the three potato cultivars.The detailed contents of phenolic compounds in the peel,flesh,and whole potatoes of the three potato varieties and potato flake are shown in Table2.The peel contains more phenolic compounds than the pulp,with the ratio ranging from 3.32 for Shepody to 5.77 for Atlantic.Among the three cultivars,Russet Burbank contains more phenolic compounds in the peel and flesh than the other two cultivars(Table2).
Chlorogenic acid is the dominant phenolic compound in Russet Burbank peel; meanwhile,the peels of Atlantic and Shepody contain considerable caffeic acid (Fig.5).Potato flake contains 14.59 mg/100 g (dry basis) of phenolic compounds.The loss rate of phenolic compounds in Russet Burbank whole potato is 50.47%.Table2 also shows that dehydrated potato flake contains more chlorogenic acid isomers compared with the raw materials because the chlorogenic acid content decreased during processing,whereas the concentration of neochlorogenic acid increased because ofisomerization[3].
Although the three varieties are used for potato flake processing in Zhangjiakou Hongji Agriculture Science and Technology Development Co.Ltd.,raw material is brought in batches into the production line with only one variety at a certain period of time.M?der et al.[3]also reported that the retention rate of phenolic compounds is 49.43%during commercial potato flake processing,and the loss of phenolic compounds mainly occur during steam peeling(37.88%),blanching(3.51%),and subsequent cooking(9.05%).
4.Conclusions
Glycoalkaloids and phenolic compounds are two kinds of biologically active compounds in potato tuber,which are predominantly found in the peel and adjoining tissues.The content of these two biologically active compounds in three commercial potato cultivars (i.e.,Russet Burbank,Atlantic,and Shepody) grown in Hebei,China are quantified.The total glycoalkaloid levels in whole potatoes ranged from 4.72 mg/kg for Shepody potatoes to 34.45 mg/kg for Russet Burbank potatoes.The removal rate of total glycoalkaloids in Russet Burbank during dehydrated potato flake process is 90.0%.Chlorogenic acid is the dominant phenolic compound in Russet Burbank.The loss rate of phenolic compounds in Russet Burbank during dehydrated potato flake processing is 50.47%.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-10),the National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFD0401302-02),the Science and Technology Major Project of Gansu Province (1602NKDJ022-1),the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province(1501RJZA004)and the Science and Technology Planing Project of Lanzhou(2016-3-123).
- 食品科學(xué)與人類健康(英文)的其它文章
- Protein quality of four indigenous edible insect species in Nigeria
- Identification of sea snake meat adulteration in meat products using PCR-RFLP of mitochondrial DNA
- Development of a reversed dispersive based graphene functionalized with multiwalled carbon nanotubes for detection of β2-agonists in pork by high-performance liquid chromatography
- Volatile components,total phenolic compounds,and antioxidant capacities of worm-infected Gomphidius rutilus
- Chicken collagen hydrolysates differentially mediate anti-inflammatory activity and type I collagen synthesis on human dermal fibroblasts
- Anticancer effect of curcumin on breast cancer and stem cells

