Effect of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on infarction volume in animal models of ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis
Di Luan,Zheng-Yu Wu,Yuan-Xiang Zhang,Li-Li Yuan,Yang Xu,Zhao-Hu Chu,Ling-Song Ma,Ya-Ping Wang,Shou-Cai Zhao
Di Luan,Li-Li Yuan,Yang Xu,Zhao-Hu Chu,Ling-Song Ma,Ya-Ping Wang,Shou-Cai Zhao,Department of Neurology,Yijishan Hospital affiliated to Wannan Medical College,Wuhu 241000,Anhui Province,China
Zheng-Yu Wu,Yuan-Xiang Zhang,Department of Clinical Pharmacy,Yijishan Hospital affiliated to Wannan Medical College,Wuhu 241000,Anhui Province,China
Abstract
Key words: Butylphthalide; Animal model; Ischemic stroke; Meta-analysis
INTRODUCTION
Ischemic stroke is a frequently-occurring disease in the elderly and characterized by high morbidity and mortality[1,2].The current treatment includes drug-based thrombolysis and interventional therapy in acute stage,however there were many inherent limitations of it[3,4].To date,more than 1000 clinical trials of potential neuroprotective drugs have been verified to be failures[5].
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP),a synthetic compound based on natural celery seeds,has potential therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemia,brain trauma,memory impairment,and epilepsy,of which the injectable formulations have been approved for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in China[6].NBP protects the integrity of cerebrovascular structures[7],promotes the formation of collateral circulation,accelerates the proliferation of neonatal capillary[8,9],and increases the cerebral blood perfusion[10]; by targeting mitochondria,it improves neuronal energy metabolism[11],reduces oxidative stress damage and neuronal apoptosis[12].The systematic review of animal research is of great significance in drug development[13].To this end,we conducted a meta-analysis of preclinical studies to evaluate the efficacy and the mechanisms of NBP for experimental ischemic stroke.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search strategies
This meta-analysis was based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement[14].All Chinese and English literatures before August 2018 on the effects of NBP for experimental ischemic stroke were searched in the six databases,which included PubMed,EMBASE,Web of Science,Wanfang database,VIP Chinese Journal Service Platform database and China National Knowledge Infrastructure database.Furthermore,to further confirm the relevant literature,we searched the list of references for potential publications.In the retrieval of the Web of Science,PubMed and EMBASE databases,only one keyword of“butylphthalide” was retrieved.In the searching of other databases,the following search strategy: “butylphthalide” AND “cerebral ischemia OR brain ischemia OR cerebral infarction OR brain infarction OR stroke OR cerebral ischemia/reperfusion OR cerebral I/R” were performed.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria must be met the follows: (1) The experimental ischemic stroke model was established by the adoption of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO);(2) The intervention group used NBP and the control group applied blank or nonfunctional solvent; and (3) The cerebral infarct volume was included in the study results and the unit of infarct volume was “%”,and the calculation formula was(infarction volume / whole brain volume) × 100%.The exclusion criteria were followed: (1) The intervention group was not administered NBP or the intervention group was taken NBP with other medicines concomitantly; (2) The animal models was not adopt for proceeding to MCAO; (3) Without control group; (4) Repeating literature; and (5) The data were not available.
Literature screening and data extraction
By reading the title,abstract and full text according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria,the literature and extracted data were screened independently and crosschecked by the first author and the second author.When there was a disagreement,the point must be reached through the discussion panel which consisted of all authors,and the final conclusion was determined by the corresponding author.
Extracting the following data from the included literature: (1) The year of publication and the name of the first author; (2) The species,age,weight,gender,anesthesia methods,and model types of experimental animals (transient MCAO or permanent MCAO); (3) Therapeutic dose,route of administration,time of onset of treatment,and duration of treatment of the interventions; (4) The mean value and standard deviation of the cerebral infarction volume; and (5) The potential therapeutic mechanism of NBP for ischemic stroke.
Moreover,to study the multiple doses and multiple time points on effects of NBP,the final experimental data using the highest dose was extracted; If the volume of cerebral infarction cannot be obtained directly from the original text,the author of the literature is contacted by e-mail to get complete data,and if not,calculation was performed by using digital scale software.
Quality assessment
The risk of bias tool of the Systematic Review Centre for Laboratory animal Experimentation's was applied to assess the methodological quality of the included studies[15]: (1) Baseline characteristics: The strain,gender,age,weight,anesthesia methods,name and anesthetic dose of the experimental animals were involved; (2)Allocation concealment: The experimental animals were grouped randomly; (3)Sequence generation: The generation of allocation sequence was random; (4) Random housing: The living environment and feeding conditions of each group of animals were in the conformity with those of each group; (5) blindly feeding: The blind method was adopt for the breeder; (6) Random outcome assessment: Evaluate the outcomes stochastically on the premise of random selection of animals; (7) Result evaluator blindly: The blind method adopted by the outcome evaluator; (8) Outcome data completely: All data of animals were included in the final analysis; (9) No selective outcome reporting: No report bias; and (10) No other sources of bias: There were no other factors that contributed to the risk of high bias.
Statistical analysis
The Revman 5.3 software was used to analyze all data,the cerebral infarction volume was considered as continuous data,and the standard mean difference with random effects model were used to assess the combined effect sizes.
RESULTS
Study inclusion
A total of 5149 relevant literatures were retrieved from six databases,in them,there were 4630 duplicates and irrelevant were excluded,resulting in 519 literatures.After reading the titles and abstracts of the enrollment articles,449 were rejected due to review comments,reviews,case reports,clinical trials and editorials literatures.By reading the full text of the remaining 70 articles,49 articles were eliminated as the animal model was not established by the MCAO method and the intervention drug was not NBP monotherapy; there was no control group and the infarct volume calculation formula did not meet the inclusion criteria.Ultimately,21 eligible articles were identified[8,16-35](Figure1).
Study characteristics
A total of 21 articles were collected,and among which,5[24,25,32,33,35]were published in Chinese and the remaining were in English.A total of 314 animals were included in 21 studies to investigate the effect of NBP on the volume of cerebral infarction in the experimental ischemic stroke model.A total of 314 animals,including 159 in the experimental group and 155 in the control group were involved in 21 studies to investigate the effect of NBP on the volume of cerebral infarction in the experimental ischemic stroke model.Moreover,in 21 articles,there were 15 studies were performed on SD rats (15/21,71.4%),3[25,29,35]on Wistar rats (3/21,14.3%),one[22]on C57BL6/J mice (1/21,4.8%),one[16]on CD1 mice (1/21,4.8%),one[31]on 129S2/Sv mice (1/21,4.7%); meanwhile,twenty studies of them were applied males (20/21,95.2%),and both males and females (1/21,4.8%) one were adopted in one study[18].As for anesthesia method,intraperitoneal injection of chloral hydrate in animals was used in the study of fourteen(14/21,66.7%),injection of sodium pentobarbital in the abdominal cavity was adopted in one[19]study (1/21,4.8%),ketamine and xylazine injection into the peritonealcavity in anesthesia of experimental animals were employed in one[29]study (1/21,4.7%),isoflurane inhalation anesthesia was accepted in the study of one[22](1/21,4.8%),and only one study[34]was adopted both atropine sulfate to reduce airway secretions,and inhalation anesthesia with isoflurane (1/21,4.7%),in addition,three studies[17,18,33]that were not mentioned the anesthesia methods(3/21,14.3%).Meanwhile,the animal models used in the fifteen studies were transient MCAO (tMCAO) (15/21,71.4%),and a permanent MCAO (pMCAO) were proceeded in six studies (6/21,28.6%)[16,25,29,33,35].To detect infarction volume,there were 19 and 2[8,22]studies adopting the 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride and cresyl violet as the staining agents respectively (Table1).
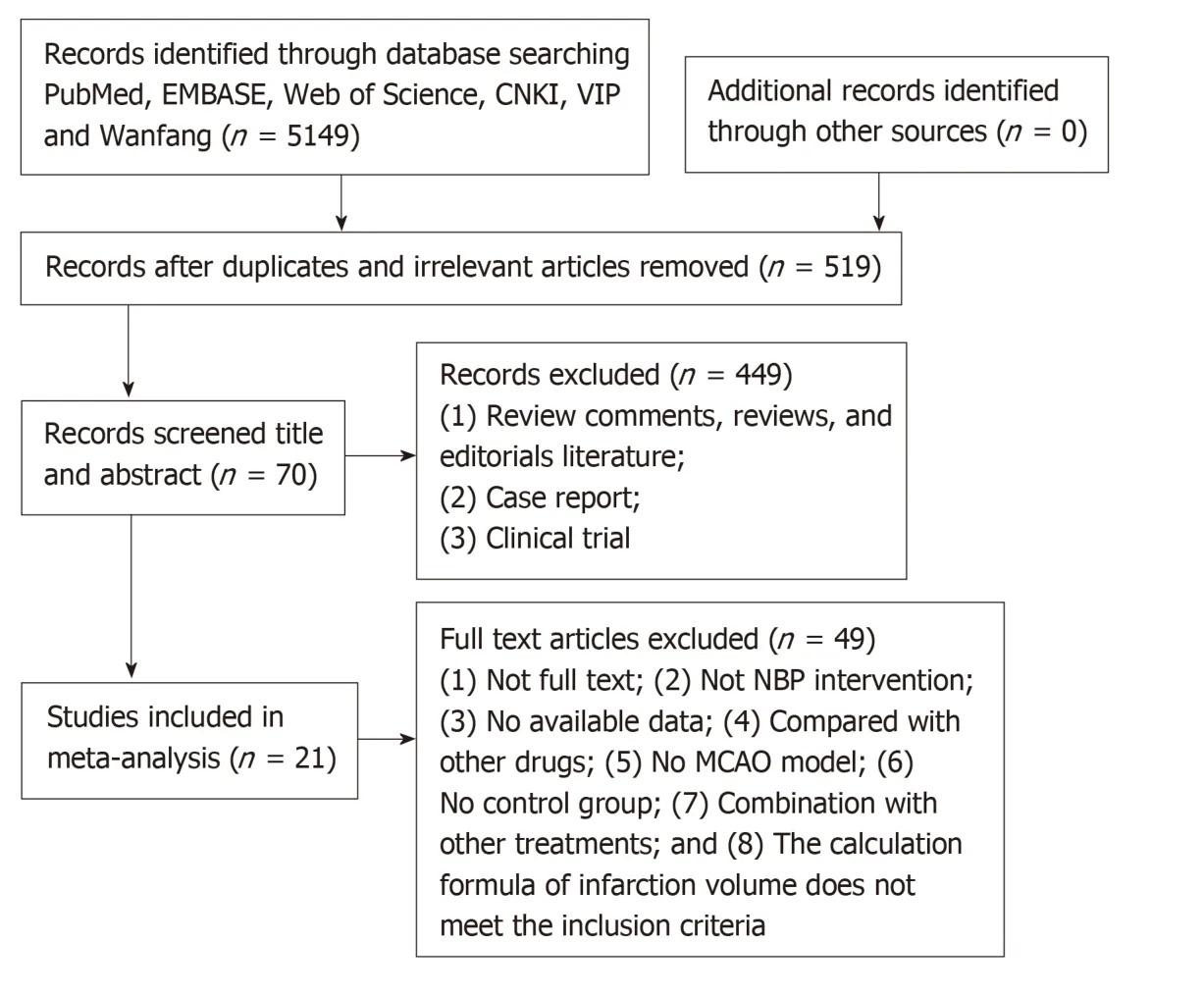
Figure1 Literature inclusion flow chart.NBP: Dl-3-n-butylphthalide; MCAO: Middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Study quality
Of the 21 studies,five studies got 7 points,four studies got 6 points,eight studies got 5 points,two studies got 4 points,and two studies got 3 points.None of the studies described blind feeding and random outcome assessment; the result evaluator blindness was described only in two studies[8,32]; all studies described the data of baseline characteristics; two studies[18,29]have found other sources of bias; no incomplete outcome data,and no selective outcome reporting were described in 11 and 17 studies,respectively (Table2).
Effectiveness
The data of Meta-analysis of the 21 studies had suggested that NBP reduced the cerebral infarction volume of MCAO model animals compared to the control group significantly [SMD: -3.97,95%CI: -4.71 to -3.23,P< 0.01; heterogeneity:χ2= 59.09,df =20 (P< 0.01);I2= 66 %] (Figure2).Moreover,the data of meta-analysis of fifteen studies adopting the tMCAO model also had verified that NBP reduced infarct volume significantly [SMD: -3.67,95%CI: -4.52 to -2.82,P< 0.01; heterogeneity: χ2=42.34,df = 14 (P< 0.01);I2= 67%] (Figure3A).The same is true of studies using the pMCAO model [SMD: -4.70,95%CI: -5.92 to -3.47,P< 0.01; heterogeneity: χ2= 9.26,df= 5 (P= 0.10);I2= 46%] (Figure3B).To analyzed the effects of the NBP on the volume of cerebral infarction with pre- or post-administrated NBP in proceeding the MCAO model,the data had showed that both the pre-administration [SMD: -3.93,95%CI: -5.51 to -2.36,P< 0.01; heterogeneity: χ2= 25.58,df= 6 (P< 0.01);I2= 77%] (Figure4A)and the post-administration [SMD: -3.62,95%CI: -4.32 to -2.92,P< 0.01; heterogeneity:χ2= 17.92,df = 11 (P=0.08);I2= 39%] (Figure4B) all reduced the infarct volume of the model animals.A funnel plot was adopted to evaluate publication bias and a slight bias was found (Figure5A).
DISCUSSION
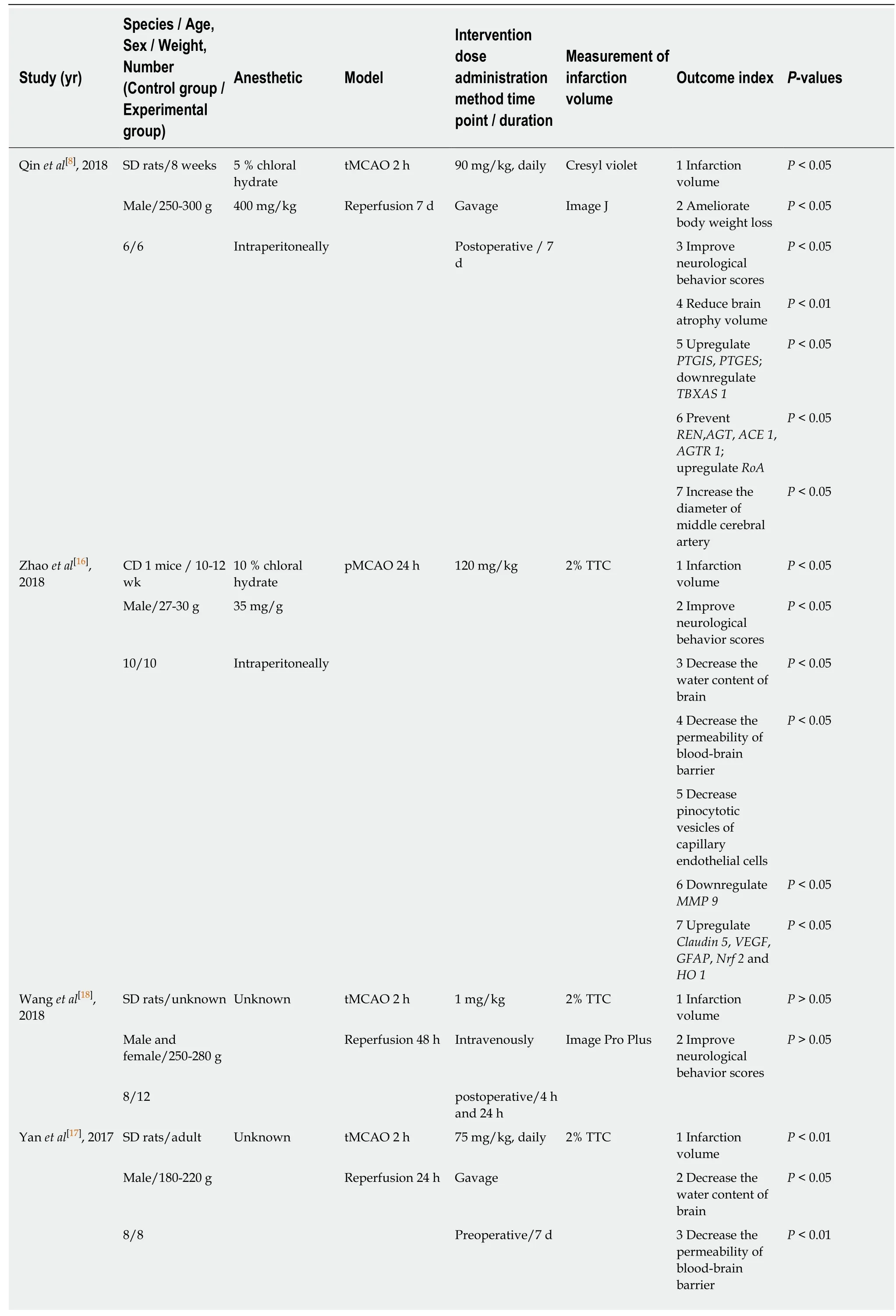
Table1 Characteristics of the included studies
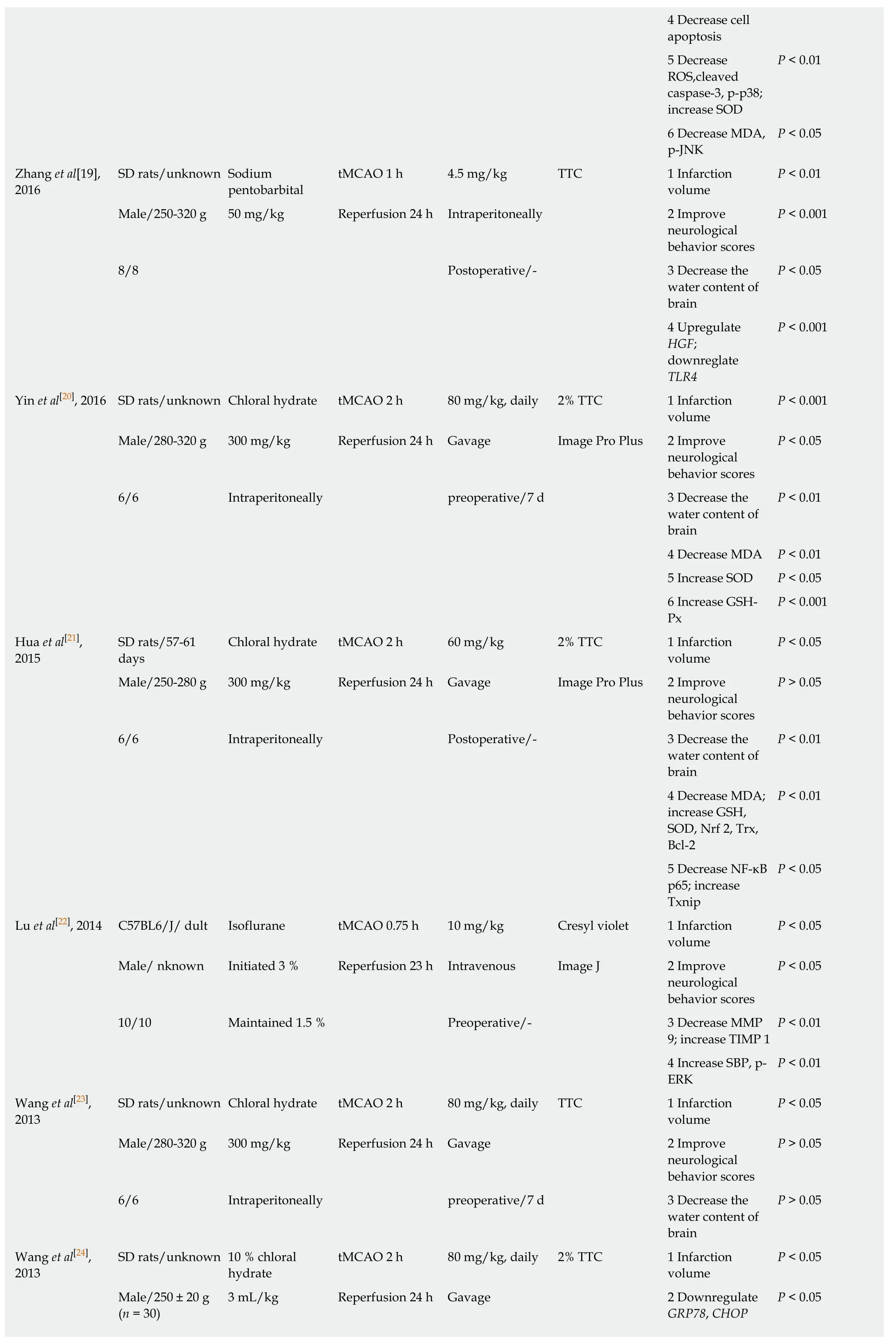
4 Decrease cell apoptosis 5 Decrease ROS,cleaved caspase-3,p-p38;increase SOD P < 0.01 6 Decrease MDA,p-JNK P < 0.05 Zhang et al[19],2016 SD rats/unknown Sodium pentobarbital tMCAO 1 h 4.5 mg/kg TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.01 Male/250-320 g 50 mg/kg Reperfusion 24 h Intraperitoneally 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.001 8/8 Postoperative/- 3 Decrease the water content of brain P < 0.05 4 Upregulate HGF;downreglate TLR4 P < 0.001 Yin et al[20],2016 SD rats/unknown Chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 80 mg/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.001 Male/280-320 g 300 mg/kg Reperfusion 24 h Gavage Image Pro Plus 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.05 6/6 Intraperitoneally preoperative/7 d 3 Decrease the water content of brain P < 0.01 4 Decrease MDA P < 0.01 5 Increase SOD P < 0.05 6 Increase GSHPx P < 0.001 Hua et al[21],2015 SD rats/57-61 days Chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 60 mg/kg 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/250-280 g 300 mg/kg Reperfusion 24 h Gavage Image Pro Plus 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P > 0.05 6/6 Intraperitoneally Postoperative/- 3 Decrease the water content of brain P < 0.01 4 Decrease MDA;increase GSH,SOD,Nrf 2,Trx,Bcl-2 P < 0.01 5 Decrease NF-κB p65; increase Txnip P < 0.05 Lu et al[22],2014 C57BL6/J/ dult Isoflurane tMCAO 0.75 h 10 mg/kg Cresyl violet 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/ nknown Initiated 3 % Reperfusion 23 h Intravenous Image J 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.05 10/10 Maintained 1.5 % Preoperative/- 3 Decrease MMP 9; increase TIMP 1 P < 0.01 4 Increase SBP,p-ERK P < 0.01 Wang et al[23],2013 SD rats/unknown Chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 80 mg/kg,daily TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/280-320 g 300 mg/kg Reperfusion 24 h Gavage 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P > 0.05 6/6 Intraperitoneally preoperative/7 d 3 Decrease the water content of brain P > 0.05 Wang et al[24],2013 SD rats/unknown 10 % chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 80 mg/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/250 ± 20 g(n = 30)3 mL/kg Reperfusion 24 h Gavage 2 Downregulate GRP78,CHOP P < 0.05
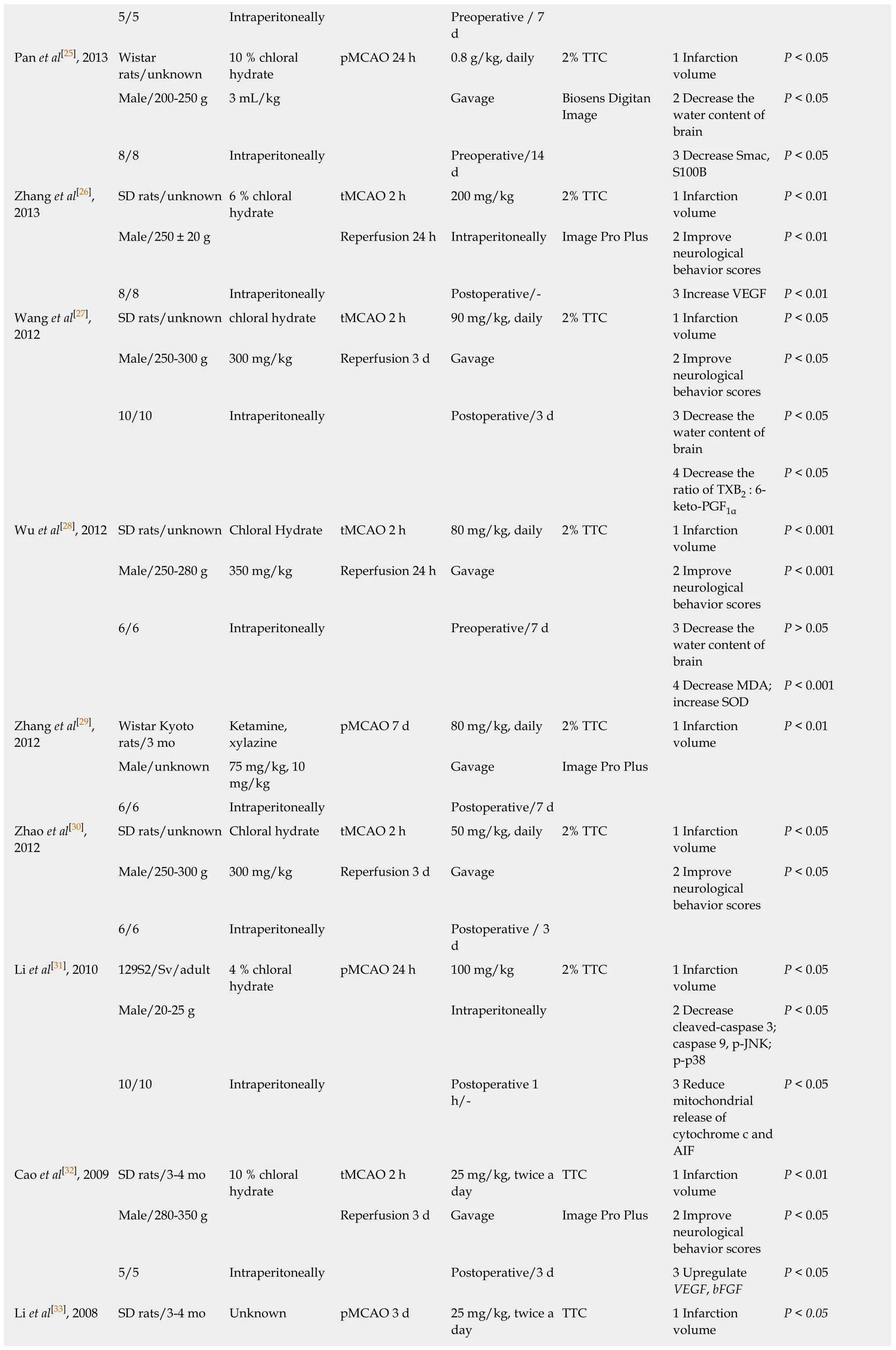
5/5 Intraperitoneally Preoperative / 7 d Pan et al[25],2013 Wistar rats/unknown 10 % chloral hydrate pMCAO 24 h 0.8 g/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/200-250 g 3 mL/kg Gavage Biosens Digitan Image 2 Decrease the water content of brain P < 0.05 8/8 Intraperitoneally Preoperative/14 d 3 Decrease Smac,S100B P < 0.05 Zhang et al[26],2013 SD rats/unknown 6 % chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 200 mg/kg 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.01 Male/250 ± 20 g Reperfusion 24 h Intraperitoneally Image Pro Plus 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.01 8/8 Intraperitoneally Postoperative/- 3 Increase VEGF P < 0.01 Wang et al[27],2012 SD rats/unknown chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 90 mg/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/250-300 g 300 mg/kg Reperfusion 3 d Gavage 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.05 10/10 Intraperitoneally Postoperative/3 d 3 Decrease the water content of brain P < 0.05 4 Decrease the ratio of TXB2 : 6-keto-PGF1α P < 0.05 Wu et al[28],2012 SD rats/unknown Chloral Hydrate tMCAO 2 h 80 mg/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.001 Male/250-280 g 350 mg/kg Reperfusion 24 h Gavage 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.001 6/6 Intraperitoneally Preoperative/7 d 3 Decrease the water content of brain P > 0.05 4 Decrease MDA;increase SOD P < 0.001 Zhang et al[29],2012 Wistar Kyoto rats/3 mo Ketamine,xylazine pMCAO 7 d 80 mg/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.01 Male/unknown 75 mg/kg,10 mg/kg Gavage Image Pro Plus 6/6 Intraperitoneally Postoperative/7 d Zhao et al[30],2012 SD rats/unknown Chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 50 mg/kg,daily 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/250-300 g 300 mg/kg Reperfusion 3 d Gavage 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.05 6/6 Intraperitoneally Postoperative / 3 d Li et al[31],2010 129S2/Sv/adult 4 % chloral hydrate pMCAO 24 h 100 mg/kg 2% TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05 Male/20-25 g Intraperitoneally 2 Decrease cleaved-caspase 3;caspase 9,p-JNK;p-p38 P < 0.05 10/10 Intraperitoneally Postoperative 1 h/-3 Reduce mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and AIF P < 0.05 Cao et al[32],2009 SD rats/3-4 mo 10 % chloral hydrate tMCAO 2 h 25 mg/kg,twice a day TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.01 Male/280-350 g Reperfusion 3 d Gavage Image Pro Plus 2 Improve neurological behavior scores P < 0.05 5/5 Intraperitoneally Postoperative/3 d 3 Upregulate VEGF,bFGF P < 0.05 Li et al[33],2008 SD rats/3-4 mo Unknown pMCAO 3 d 25 mg/kg,twice a day TTC 1 Infarction volume P < 0.05
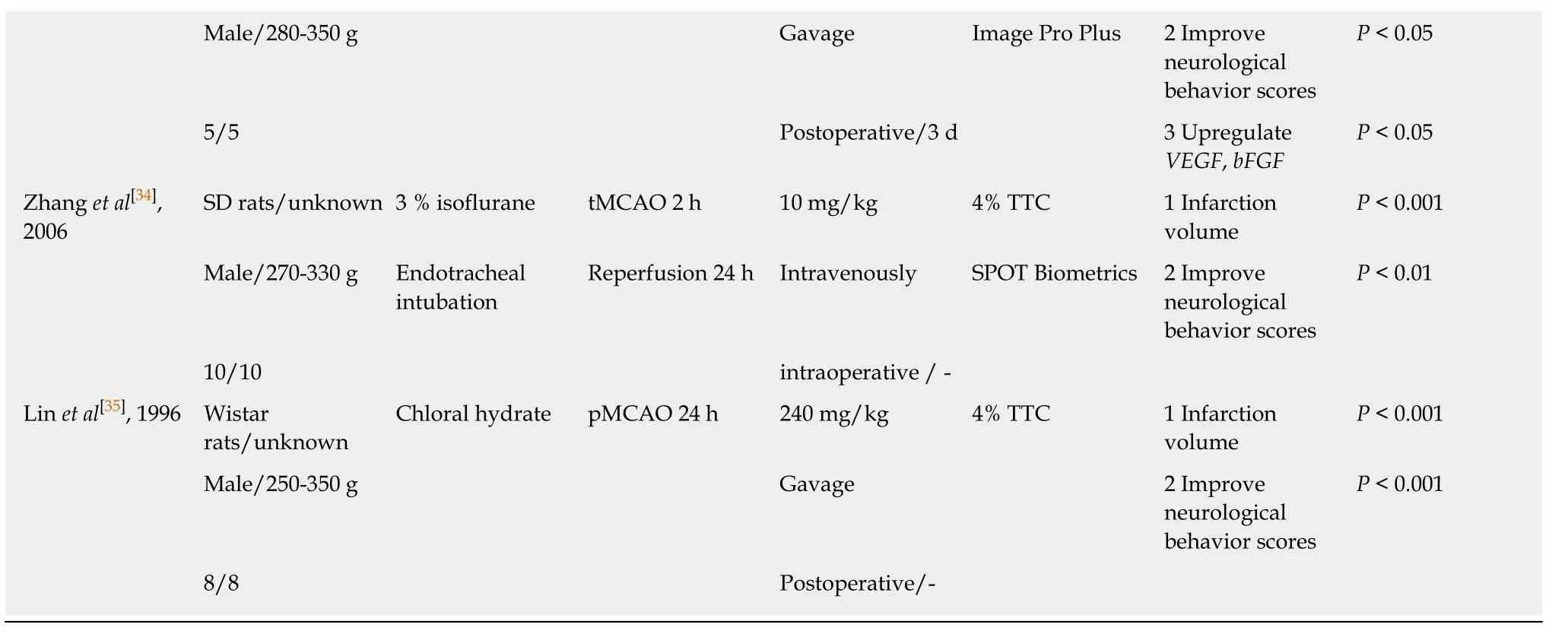
PTGIS: Prostacyclin synthase; PTGES: Prostaglandin E synthase; TBXAS 1: Thromboxane A2 synthase 1; REN: Renin; AGT: Angiotensinogen; ACE 1: Angiotensin converting enzyme 1; AGTR 1: Angiotensin II receptor type 1; tMCAO: Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion; pMCAO: Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion; TTC: 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride; MMP 9: Matrix metallopeptidase 9; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; Nrf 2: NF-E2-related factor 2; HO 1: Heme oxygenase 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malonaldehyde; HGF:Hepatocyte growth factor; TLR4: Toll like receptor 4; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; GSH: Glutathione; Trx: Thioredoxin; Txnip: Thioredoxin-interacting protein; TIMP 1: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; SBP: Spectrin breakdown product; GRP 78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; CHOP: C/EBP-homologous protein; Smac: Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases; S100B: S100 calcium binding protein B; TXB2: Thromboxane B2; 6-keto-PGF1α: 6-ketoprostaglandin F1α; AIF: Apoptosis-inducing factor; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor.
Summary of evidence
The preclinical meta-analysis study evaluated the effects of NBP on infarct volume in experimental ischemic stroke,which was based on experimental data from 314 animals in five Chinese literatures and sixteen English literatures.The evidence obtained from present study suggest that NBP might play potential neuroprotective roles for ischemic stroke by increasing cerebral blood flow,enhancing mitochondrial function,protecting integrity of the structure and function of blood-brain barrier,and developing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant stress.
Limitations
First,the absence of relevant literatures in other languages other than Chinese and English,may lead to selective bias.Second,none of study provides sample size calculations,blind feeding,and random outcome assessment.Third,the lack of negative research may result in an overestimation of the efficacy of NBP.Fourth,cerebral infarction is usually accompanied by other conditions,such as old age,hypertension,hyperlipidemia,diabetes,heart disease and so on[36-39].We did not analyze the effects of NBP on cerebral infarction when the accompanying situation occurred.Fifth,one study[18]using female animals does not rule out estrogen neuroprotection,that has been reported[40].One study[29]of anesthetic drugs containing ketamine did not eliminate its neuroprotection,that has been reported in preclinical and clinical studies[41,42].
Potential neuroprotective mechanisms
Summarizing the included literatures,we have found that NBP plays a neuroprotective role in experimental ischemic stroke by acting on multiple targets(Figure5B).We have drawn a conclusion of the underlying mechanisms as follows:(1) Increase blood supply to brain tissue in the ischemic area: Dilate the middle cerebral artery[8]; regulate the expression ofREN,AGT,ACE 1,AGTR 1,RoA,PTGIS,PTGESandTBXAS 1in ischemic brain tissue[8],decrease TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1α ratio[27],and reduce thrombosis; (2) Promote angiogenesis: Increase VEGF and bFGF in ischemic brain tissue[16,26,32,33]; (3) Anti-inflammatory: Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[19,21]; decrease the expression of S100B in ischemic brain tissue[25].(4)Protect the structure and function of the blood-brain barrier: Modulate the expression ofMMP-9andclaudin-5in ischemic brain tissue[16,22]; up-regulate the expression ofGFAPin ischemic brain tissue,stabilize astrocytes[16]; increase the expression of TIMP1 and decrease the expression of SBP in ischemic brain tissue[22]; (5) Antioxidative stress:Enhance Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway[16]; reduce the expression of ROS and MDA in ischemic brain tissue; increase the expression of SOD,GSH-px,GSH,Trx and Txnip in ischemic brain tissue[17,20,21,28]; (6) Protect the structure and function of mitochondria:Increase the expression of Bcl-2 in ischemic brain tissue[21]; reduce the expression ofSmac in ischemic brain tissue[25]; reduce mitochondrial release of cytochrome C and AIF[31]; and (7) Anti-apoptosis: Reduce the expression of cleaved caspase-3,p-p38 and p-JNK in ischemic brain tissue[17,31]; increase the expression of HGF and p-ERK in ischemic brain tissue[19,22]; decrease the expression of GRP78 and CHOP in ischemic brain tissue,and inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis[24].
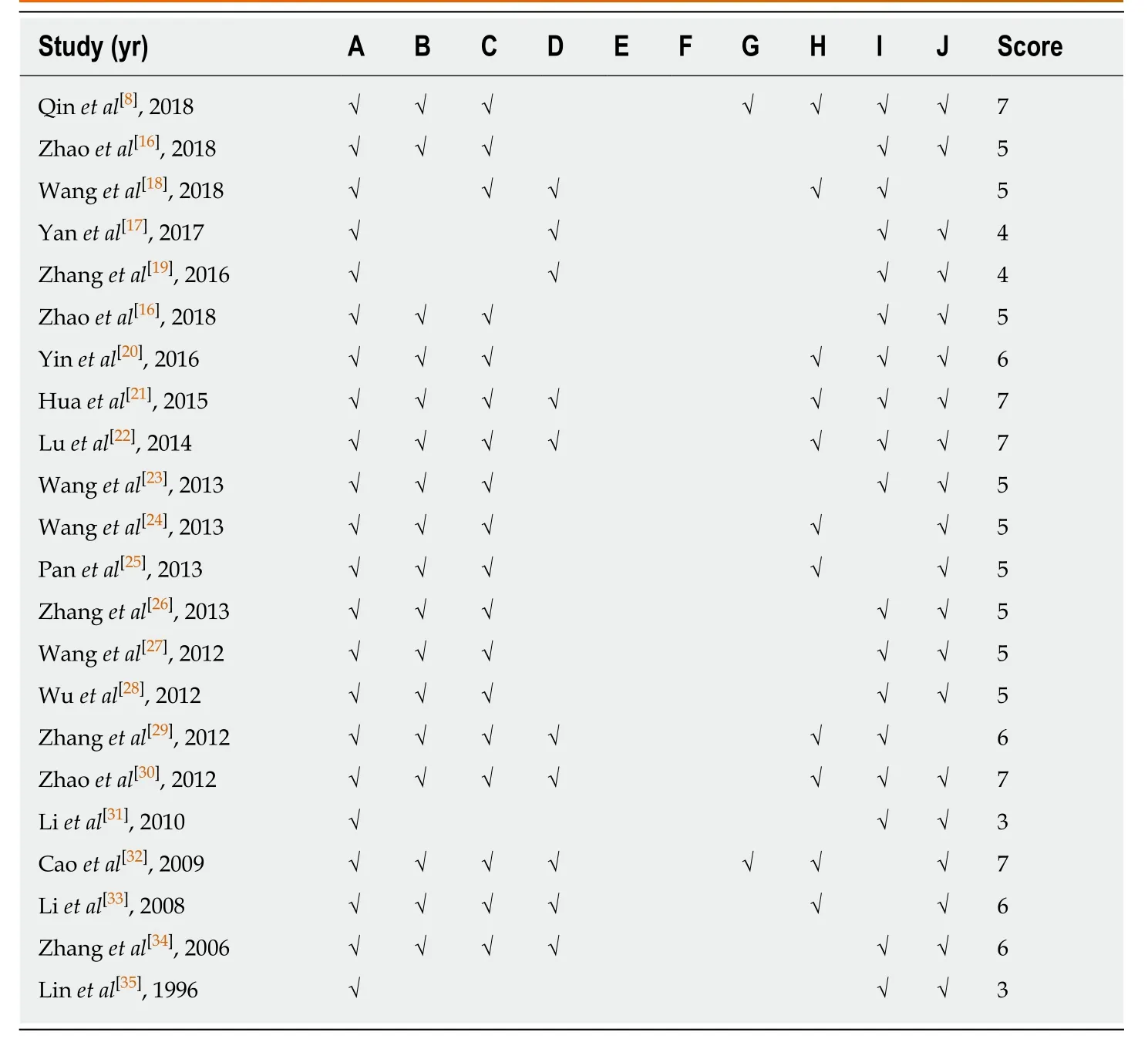
Table2 Risk of bias of the included studies
Implications
Animal experiments are an important link between basic research and clinical experiments.The results have reference value for the next step in designing and implementing clinical research.Compared with clinical research,the principles of randomization and blindness are theoretically easier to be implemented in animal experiments.Animal research is important for comprehending disease mechanisms,and high-quality preclinical research is also critical for translational medicine[43,44].Therefore,to obtain more accurate and less biased experimental data,designing animal programs should follow the guidelines all the time[15,45],calculate sample size in the beginning,apply applicable animals,use appropriate anesthetic drugs,adopt random feeding,and blind models during the experiment,and employ random outcome measurements at the time of evaluation.
Similar to artemisinin,NBP is also a plant-derived drug approved for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in China.We envision that NBP promote to treat more patients in the world,like artemisinin,and it requires a large number of randomized,double-blind,and multi-center clinical trials in terms of safety and efficacy.
In conclusion,we conducted the first preclinical systematic review and metaanalysis of the effects of NBP on experimental ischemic stroke,and found that NBP was effective in experimental ischemic stroke.
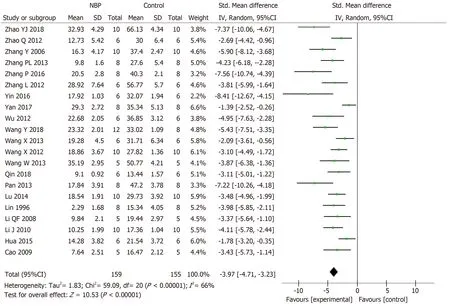
Figure2 The forest plot: Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide for decreasing the cerebral infarction volume compared with control group.

Figure3 The forest plot: Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide for decreasing the cerebral infarction volume compared with control group in transient (A) and permanent (B) middle cerebral artery occlusion model,respectively.
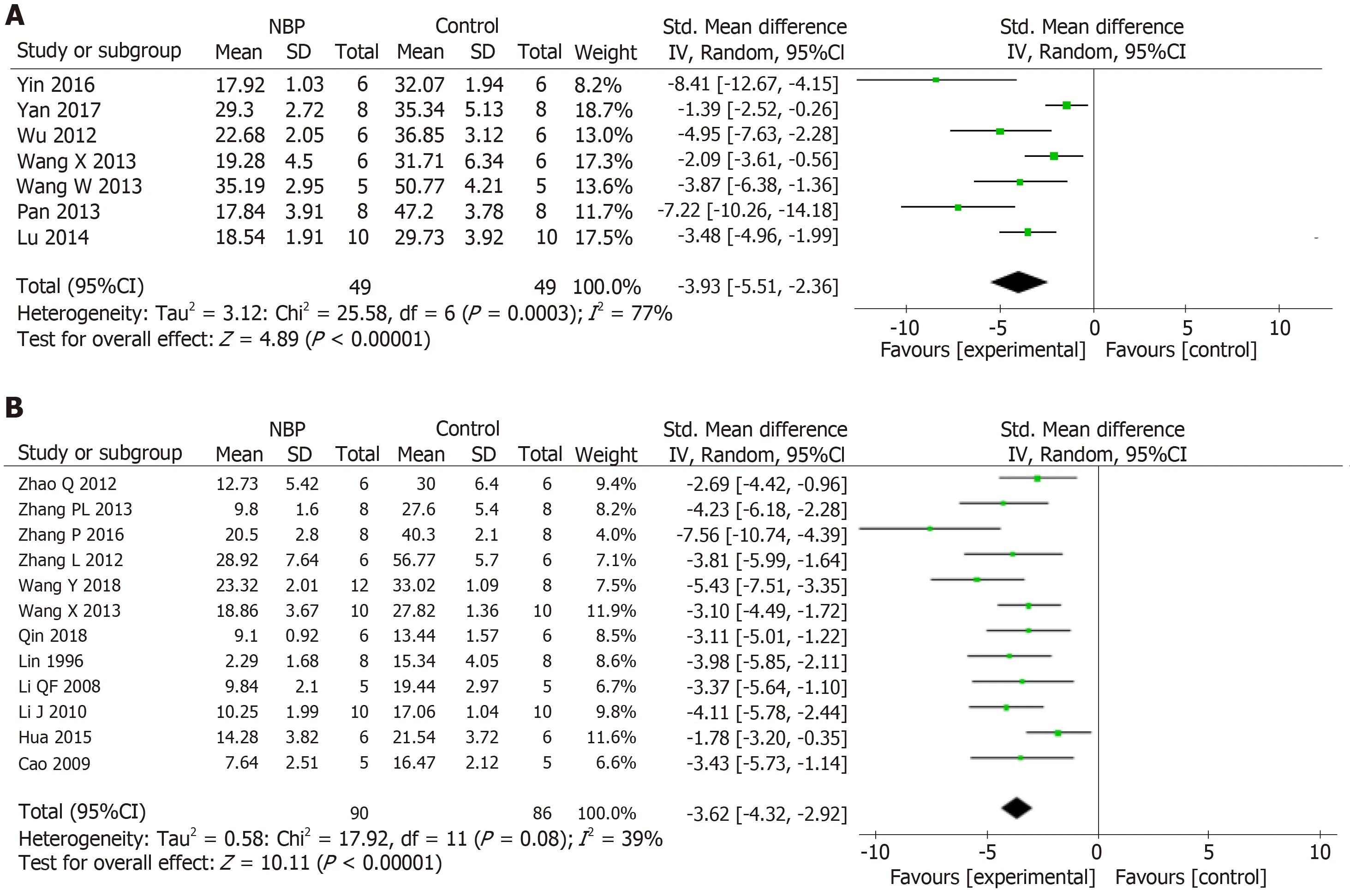
Figure4 The forest plot: Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide for decreasing the cerebral infarction volume compared with control group in pre (A) and postadministration (B) model,respectively.
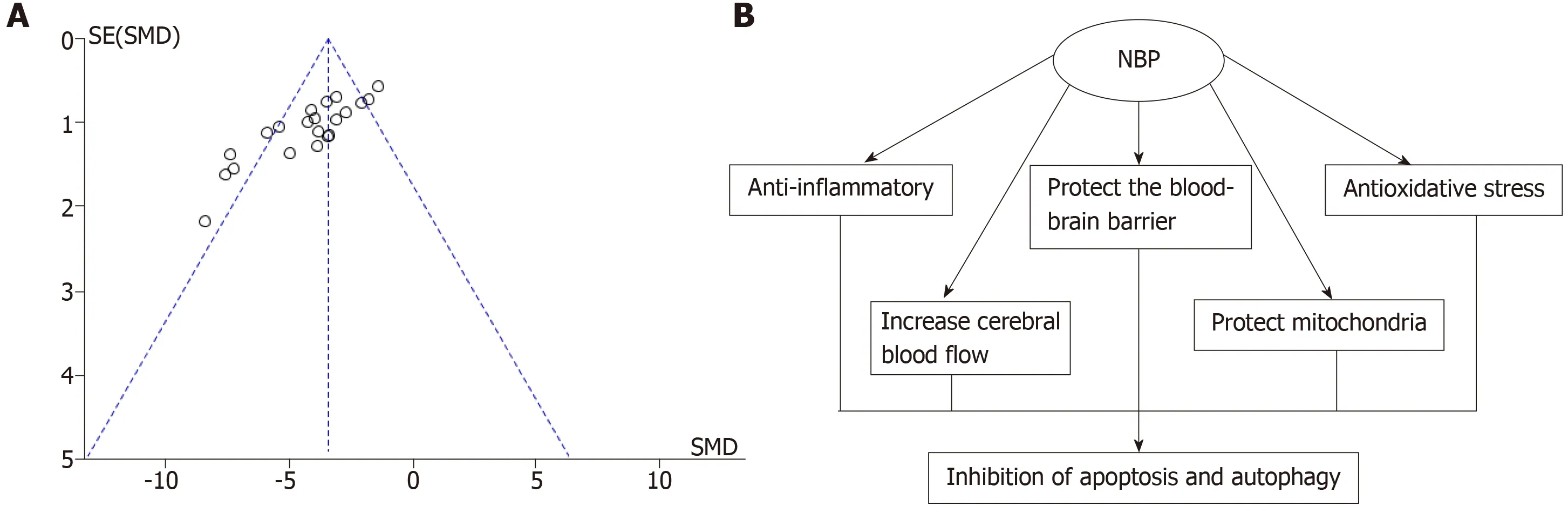
Figure5 The funnel plot evaluation publication bias and underlying mechanism of dl-3-n-butylphthalide in neuroprotection.A: The funnel plot evaluation publication bias for the dl-3-n-butylphthalide on infarction volume; B: The underlying mechanism of dl-3-n-butylphthalide in neuroprotection.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Ischemic stroke is a frequently-occurring disease in the elderly and characterized by high morbidity and mortality.Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP),a synthetic compound based on natural celery seeds,has potential therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemia,brain trauma,memory impairment,and epilepsy.The systematic review of animal research is of great significance in drug development.
Research motivation
There are many studies on the therapeutic effects of NBP in the middle cerebral artery occlusion model,and there is controversy about whether NBP reduces the volume of cerebral infarction.
Research objectives
To evaluated effect of NBP on infarct volume in experimental ischemic stroke.
Research methods
We searched Chinese and English databases to screen NBP-related literature.Data such as cerebral infarction volume and potential therapeutic mechanisms were extracted.The risk of bias tool of the Systematic Review Centre for Laboratory animal Experimentation's was applied to assess the methodological quality of the included studies.Data analysis was performed by Revman 5.3 software.
Research results
The data of meta-analysis of the 21 studies had suggested that NBP reduced the cerebral infarction volume of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model animals compared to the control group significantly.Moreover,the data of meta-analysis of fifteen studies adopting the tMCAO model also had verified that NBP reduced infarct volume significantly.The same is true of studies using the pMCAO model.To analyze the effects of the NBP on the volume of cerebral infarction with pre- or post-administrated NBP in proceeding the MCAO model,the data had showed that both the pre-administration and the post-administration all reduced the infarct volume of the model animals.
Research conclusions
NBP was effective in experimental ischemic stroke.
Research perspectives
Animal experiments are an important link between basic research and clinical experiments.The results have reference value for the next step in designing and implementing clinical research.Compared with clinical research,the principles of randomization and blindness are theoretically easier to be implemented in animal experiments.Animal research is important for comprehending disease mechanisms,and high-quality preclinical research is also critical for translational medicine.Therefore,to obtain more accurate and less biased experimental data,designing animal programs should follow the guidelines all the time,calculate sample size in the beginning,apply applicable animals,use appropriate anesthetic drugs,adopt random feeding,and blind models during the experiment,and employ random outcome measurements at the time of evaluation.
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2019年7期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2019年7期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- Phantom of the inflammasome in the gut: Cytomegalovirus
- Artificial intelligence for endoscopy
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria among hospitalized diabetic patients:Should they be treated?
- Pediatric recurrent Clostridium difficile infections in immunocompetent children: Lessons learned from case reports of the first twelve consecutive patients
