College Basic Development Status Data Management System Based on Data Governance Framework
LIU Linlang(劉琳瑯), LU Linzhen(盧林珍), WU Qinghong(吳清紅), XU Zhongqi(徐中其)
Informatization Office, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
Abstract:In the era of big data, data application based on data governance has become an inevitable trend in the construction of smart campus in higher education. In this paper, a set of data governance system framework covering the whole life cycle of data suitable for higher education is proposed, and based on this, the ideas and methods of data governance are applied to the construction of data management system for the basic development status of faculties by combining the practice of data governance of Donghua University.It forms a closed-loop management of data in all aspects, such as collection, information feedback, and statistical analysis of the basic development status data of the college. While optimizing the management business of higher education, the system provides a scientific and reliable basis for precise decision-making and strategic development of higher education.
Key words:big data; data governance; data quality; smart campus
0 Introduction
As the carrier of information, data is the most important foundation for constructing, using and maintaining various information systems. Under the macro environment of the current era of big data in higher education, high-quality basic data has become more and more valuable for the smooth running of teaching, research, and management in higher education, as well as for leadership decision support and better service for teachers and students.
It has become an inevitable trend that data governance and data application construction in higher education are aimed at improving data quality, standardizing data usage, and supporting teaching and research applications and decision-making. In the construction of smart campuses, the framework of the data governance system is reasonably planned to promote the formation of “One Data, One Source” and an effective working mechanism of data integration and sharing. It scientifically constructs a data resource catalog and data traceability map at the higher education level to maximize the value of the data assets of higher education. All these have become issues that must be addressed in the reform and development of higher education.
In this paper, we discuss the methods and solution ideas for implementing data governance in various fields, and plan a data governance system framework covering the whole life cycle of data for higher education. By monitoring and governing the whole process of data from generation to extinction, this framework can ensure the integrity, accuracy, consistency, and timeliness of business data in the whole process of collection, conversion, storage, and application in higher education. Therefore, it is possible to establish a data asset catalog and data governance system suitable for the characteristics of higher education. Ultimately, it can help higher education achieve global management of their data. At the same time, the ultimate purpose of data governance is to better serve the daily teaching, research, and management improvement needs of higher education. Therefore, by combining the data governance practices at Donghua University and focusing on the data problems faced in actual business management of higher education, we propose to apply the methodology and solution approach of data governance to the construction of a data management platform for basic development status of colleges in higher education.
1 Overview of Data Governance Research
1.1 Domestic and international data governance research developments
By searching the relevant literature, we know that the understanding of data governance in foreign academia started in 2004[1], and the practice of data warehouse governance in enterprises has opened the curtain of data governance. In recent years, under the guidance of governance thinking, foreign academics have conducted a lot of theoretical research and practical exploration of data governance in enterprises, governments, hospitals, and universities. Researchers have developed some data governance frameworks and models and outlined the elements of data governance to guide the construction of governance frameworks[2].
Subsequently, combining with management innovation, domestic scholars have promoted the concept of data governance from various perspectives. However, research on the methodology, technological platforms, and visualization presentation of data governance remains relatively weak. Most studies are still concentrated on theoretical exploration, with a noticeable lack of research on practical applications[3].
1.2 Status of data governance in domestic higher education
After more than ten years of development, although many higher education institutions in China have accumulated a large amount of business data, there are generally problems such as low data quality, large amounts of redundant data, low data availability and difficulty in data sharing among management departments, which have seriously restricted the improvement of the daily management and teaching level of higher education. Therefore, it is imperative to manage the data in higher education and improve the value of data. At present, some scholars in China have done relevant research in the field of data governance in higher education. Lietal.[4]proposed key aspects for data governance, such as grasping top-level design, system and standard preparation, key technology research and security construction. Zhao[5]discussed the path of data integration and its governance framework in higher education from the perspective of data integration. Lietal.[6]proposed the RACI model of data governance (RACI is a matrix model, where R=Responsible; A=Accountable; C=Consulted; I=Informed, which is used to specify the main objectives, relevant roles, governance activities and corresponding responsibilities of data governance) and introduced the implementation process of master data management and data quality assessment approach. Baoetal.[7]discussed the significance of data governance maturity assessment in their design of China Academic LibraryDG Framework (CALib) model for implementation and evaluation. By combining management innovation and technology practice, domestic scholars have introduced data governance ideas for higher education from different aspects.
1.3 Current status of data governance applications in higher education
The ultimate purpose of data governance in higher education is to help the construction of higher education’ smart campuses so that data can generate value and better serve all aspects of teaching, research, and management of higher education. At present, data governance results are mainly applied to building personal data centers for teachers and students, comprehensive data query services and other application services. However, when it comes to certain business scenarios in higher education, the application of data governance to meet the needs of rapid response to data application and management decisions is still in the exploratory stage.
2 Data Governance System Architecture for Higher Education
2.1 Ideas for data governance in higher education
Data governance in higher education is the management of data as an asset throughout its life cycle, including strategy, planning, design, construction and application[8]. By monitoring and governing the whole process of data from creation to extinction, it realizes the unified management of data in the whole business domain, the whole data domain, and the whole time domain of higher education.
2.1.1Coregoalofdatagovernanceinhighereducation
Data governance in higher education is not something that can be achieved overnight. It should grasp the core objective of unified management of data assets to achieve “comprehensive collection”, “unified standard” and “interconnection” of data in higher education. It establishes a data asset catalog that meets the business characteristics of higher education, standardizes the definition of data resources, and realizes the sharing of data among organizations to help higher education improve the quality of data and ensure the safety of data, so as to better serve the daily teaching, research, and management of higher education[9].
2.1.2Valueorientationofdatagovernanceinhighereducation
Data governance in higher education can quickly respond to the demand for data applications in higher education and output data service value. It ensures the steady improvement of data output in quantity and quality, thus truly forming a vital and iterative optimized data ecology.
2.2 Main construction content and system architecture of data governance in higher education
Data governance in higher education refers to the process of data construction in the whole business domain (covering all business areas of higher education), the whole data domain (covering all data types), and the whole time domain (covering historical data). According to the business characteristics of higher education, in this paper, the data at the higher education level is divided into eight data subject domains, covering data assets such as “student, staff, finance, assets, teaching, research, administration, and public service”, as shown in Fig.1.
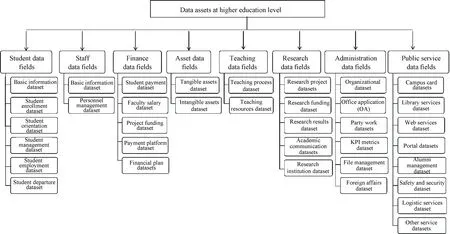
Fig.1 Data subject domain delineation at the higher education level
It completes the collection, storage, management, opening, and application of university-wide data through data governance. The main construction contents include the following parts.
1) Management of information standards
Information standard management includes the development of unified and standardized metadata standards, data exchange technical specifications, data classification and encoding standards, data quality standards,etc[10].
2) Metadata management
Metadata refers to data that describes other data, providing information about the attributes, structure, definition, and usage of the data. In the context of campus data asset management, metadata plays a crucial role. It helps establish a data map and data lineage in higher education and serves as a core driving force for data governance.
3) Management of master data
Master data management refers to the process of integrating and centralizing the most critical and urgently needed shared data (master data) from multiple business systems in higher education. It involves data cleansing, enrichment, and ultimately providing authoritative master data as data services to the required application systems[11].
4) Data quality control
Data quality control refers to the closed-loop management of data quality. It is based on data metrics, quality checks, problem detection and tracking to ensure the authenticity, accuracy, completeness and timeliness of source data.
5) Comprehensive data link monitoring
Data chain monitoring refers to the comprehensive management and automatic tracking of the life cycle and usage traces of data, in order to achieve chain data management and improve the overall level of data governance[12].
6) Data security management
Data security management provides centralized security governance for shared data by providing functions such as data desensitization, data classification, data authorization, data encryption, and data security watermarking to ensure the security of data[13].
Based on the research on data governance in higher education, we have formulated a comprehensive data governance architecture suitable for the business characteristics of higher education, as shown in Fig.2.
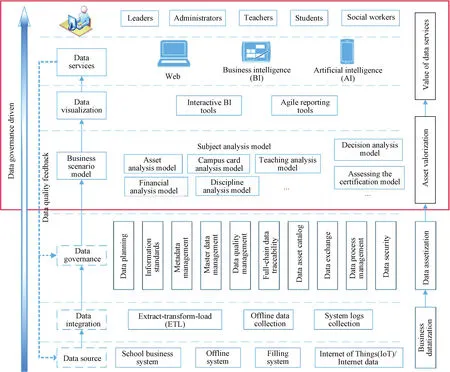
Fig.2 Data governance system architecture for higher education
2.3 Implementation principles and methods of data governance in higher education
Effective top-level planning and design are essential for data governance in higher education. Following the principles of “one data, one source” and “one source, multiple uses”, data governance should be purposefully conducted by aligning with the specific business scenarios of higher education. Here are several key points to follow for implementing data governance in higher education.
1) Data governance in higher education should start from top-level design and establish a data governance office in order to guarantee the smooth implementation of various management rules, authority and responsibility relationships.
2) The implementation of data governance in higher education requires the formulation of data management measures and relevant technical specifications to ensure the effective implementation of data governance.
3) Data governance in higher education requires sufficient research in core departments, based on which thematic data assets are sorted out according to school business, and higher education-level code standards are built to create a “common language” for school data.
4) Data governance in higher education requires building a data governance platform and integrating various sources and types of scattered data into a unified data governance platform in accordance with higher education-level data standards, quality rules, and security indicators.
5) Data governance in higher education uses the data governance platform to sort out data lineage, draw a panoramic map of school data, and provide open data services with hierarchical authorization.
6) Data governance in higher education improves the quality of source data through feedback from data applications while in turn promoting data governance, forming a closed loop of data governance.
3 Construction of College Basic Development Status Data Management System Based on Data Governance Framework
3.1 Current management situation of college basic development status data
The relevant management departments of the university regularly collect the basic development status data of the college from all functional departments of the university every year, and the data involves personnel, academic affairs, research, finance, assets and other related data. The collection of this data involves many departments and takes a long time to collect completely. At the same time, the collection and management of college basic development status data is often carried out by administrative personnel. They are busy with operational tasks and tend to rely on traditional manual or spreadsheet methods for data collection and analysis. Due to the wide scope of college basic development status data, the complexity of the data, and the lack of uniform data standards, the use of traditional offline data collection methods and simple data analysis methods not only brings a huge workload to administrators but also makes it difficult for them to comprehensively and objectively analyze the implied business logic relationships behind each data. It also tends to cause problems such as repeated data collation work, low efficiency, and inaccurate information mastery. Meanwhile, the insufficient use of data feedback by administrators can also result in the use of basic development status data not being fully utilized. Therefore, there is an urgent need to build an information system to assist the management to view the progress of data filling in real time and improve the efficiency of data collection, as well as to further improve the accuracy of data filling with the help of campus-level data assets[14].
Based on the above research on the data governance systems of higher education and the analysis of the current situation of the basic development status data management of colleges, we believe that the college basic development status data management system should be built on the basis of the data governance framework system. That is, the concepts and methods in the data governance system such as data collection, data standard management, master data model, data quality management, data full chain feedback and data analysis should be applied to all aspects of the basic development status data management of colleges[12]. This can be of great help to form the closed-loop management of the basic development status data and improve the level of data information management. and at the same time, help to provide the most real and effective scientific basis for the optimization and strategic development of the teaching management business of the college.
3.2 Building college basic development status data management system based on data governance framework
The ultimate goal of data governance is to make data reflect value. Therefore, based on the study of data governance system, we built a college basic development status data management system, which includes modules for data filling, review process, information feedback, analysis and statistics, forming a closed-loop management of the basic development status data of the college. Based on the research outcomes of data governance, we have constructed a service-oriented and data-centric college basic development status data visualization dashboard. The aim is to integrate data analysis support into the management processes of the college, enabling school leaders and administrators to have a comprehensive understanding of the basic development status of the college. It also helps administrators to accurately grasp the problems in the development of the college and introduce corresponding improvement initiatives.
3.2.1Systemconstructionprinciples
During the design of the system, we followed several key principles.
1) Data filling
The system makes full use of the results of data governance to assist in the filling of basic development status data. When filling in the basic status data of the college, it is required to follow the principle of consistent data authority and responsibility to avoid multiple maintenance, redundancy, conflict, and loss of data filling. Using the governed data, the system realizes automatic data filling as much as possible.
2) Filling progress
Through the system, managers can view the progress of data filling by each department in real time and supervise to improve the efficiency of data collection.
3) Permission control
The system has set up filling authority, submitting authority, and reviewing authority for departmental personnel to meet the authority and responsibility requirements of data filling.
4) Process control
The system controls the entire process of data filling through various steps such as filler, submitter, functional department review, and school management review.
5) Feedback on data
The system can trace various problematic data in data filling with the help of data lineage in data governance and realize the guideline of “one authoritative data source”.
6) Statistical analysis of data
The system has a statistical summary function of the filled data, which can show the filled data to the manager visually from different dimensions.
3.2.2Systemarchitecture
The structure of the college basic development status data management system based on the data governance framework is shown in Fig.3.

Fig.3 System architecture of college basic development status data management
3.2.3Mainservicesofsystem
1) Filling out basic development status data of college
The collection of the basic development status data of the college involves various functional departments and colleges at all levels, and the data sources are of various calibers and types. Data collection and statistics based on different calibers are prone to problems such as poor data consistency, difficult identification of effective data, and difficulties in data sharing and docking. For the data traditionally collected offline, we use the data governance platform to collect the basic development status data of the college online and share the data in a graded and classified manner. For the data with an information system, the results of data governance can be used to automatically fill in the data with clear data responsibility subjects and report them after confirmation by users, which greatly reduces the workload of data filling. The content of the college basic development status data collection involves the college’s staff size, financial investment, talent team construction, student situation, scientific research awards, etc. The construction idea of the college basic development status data filling service is shown in Fig.4.
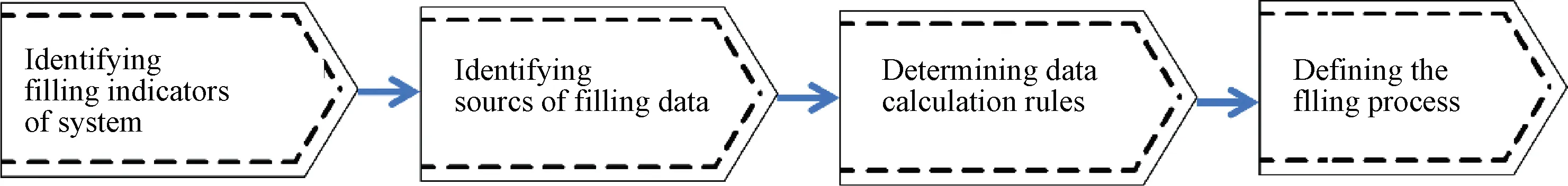
Fig.4 Construction idea of filling service
2) College basic development status data audit
As shown in Fig.5, managers logging into the filling system are able to view the filling progress of each functional department and their respective filling status (unfilled, in the process of filling, under review, completed).
3) Feedback service for basic development status data of college
For the data with problems in filling in the basic development status of the college, we can rely on the data lineage in the data governance system to trace the source of the problem, and use the full data link management in the data governance system to provide convenient, fast, and accurate information feedback on the problematic data. This not only improves the accuracy of data filling but also forms a closed-loop management of the quality of the basic data filled, as shown in Fig.6.
4) Statistical analysis of college basic development status data
After the basic development status data of the college was filled in, we constructed data analysis models for the relevant topics. Using intelligent data analysis tools and agile report development tools, we performed multidimensional and multilevel analysis and presentation on the filled-in data. We present dynamic data on different topics such as discipline and major construction, talent cultivation, international cooperation and exchange, faculty construction, teaching conditions and investment, and scientific research to decision makers and managers at the college level in the form of a big screen for intelligent data analysis. The system also provides graphical and textual data analysis result reports on relevant topics. The system supports flexible expansion and configuration of Key Performance Indicators (KPI)-related data statistics according to the leadership’s concerns and changes in stage work priorities. The big screen of intelligent data analysis also supports drill-down and detailed query functions of key indicators.
Since the data management system based on data governance was put online at Donghua University, it has assisted 15 colleges and departments in completing online data filing for 21 statements, 28 detailed tables, and 61 observation indicators. The system automatically generates the annual basic development status report of the college after the filled-in data has passed the audit. With the support of the system, the collection and summarization of the basic development status data of colleges has been greatly shortened from two months to two weeks, which has greatly improved the efficiency of filling, reviewing and summarizing the basic development status data of colleges.
4 Conclusions
Under the data governance framework based on the business characteristics of higher education, we divide the data generated in daily teaching, scientific research, and management into different thematic data domains, and apply data governance methods and concepts to manage the entire process and lifecycle of school business data, thereby precipitating loose business data into scientific and effective school data assets. On this basis, we have built a college basic development status data management system. In the construction of smart campus, the framework and practical methods proposed in this paper have certain reference value in rapidly transforming school data assets into data services and quickly responding to school data application needs.
1) Under the framework of data governance in higher education, we have achieved unified management of data by monitoring and governing the entire lifecycle of data from creation to extinction. This ensures the integrity, accuracy, consistency, and timeliness of the school’s business data throughout the processes of collection, transformation, storage, and application. It also helps establish the formation of “one data, one source” and ensures the authority and consistency of core master data in higher education.
2) Based on the data governance framework of higher education, the college basic development status data management platform can make full use of the results of data governance, integrate data of existing business systems on campus and offline form data, and provide data support for college basic development status data filling. It alleviates the pain point of repeated filling and greatly reduces the work intensity of data filling.
3) For the collection of college basic development status data, our system has implemented a complete process of data entry, auditing, display, and analysis. We have innovated a new model for transitioning the collection of college basic development status data from offline manual methods to online data filling. This enables intelligent data collection, management, and application throughout the entire value chain, achieving the goal of “more running with data, less running with teachers and students”.
4) Through online data filling and analysis, our system has helped schools sort out core data on college basic development status, enabling management departments to comprehensively grasp school-level data assets related to filling data. This has also improved the scientific accuracy of school decision-making.
5) The college basic development status data management system makes full use of the results of data governance. It also verifies the accuracy, standardization, and consistency of the data through the filling and application of basic development status data. In turn, it also tests the effectiveness and reasonableness of the master plan for data governance in higher education.
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2023年4期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2023年4期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Image Retrieval with Text Manipulation by Local Feature Modification
- Multi-style Chord Music Generation Based on Artificial Neural Network
- Polypyrrole-Coated Zein/Epoxy Ultrafine Fiber Mats for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding
- Design of Rehabilitation Training Device for Finger-Tapping Movement Based on Trajectory Extraction Experiment
- High-Efficiency Rectifier for Wireless Energy Harvesting Based on Double Branch Structure
- Review on Development of Pressure Injury Prevention Fabric
