Effects of electroacupuncture at auricular concha area on the circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion in p-chlorophenylalanine-induced insomnia rats
Wen-Ya Huang, Wei-Wei Xu, An-Ning Zhu, Si-Yu Liu, Yang Huang, Peng Li, Zong-Bao Yang, Shu-Qiong Huang, Xian-Jun Meng*Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Medical College, Xiamen University,Xiamen 6005,China. Yangzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yangzhou 5009, China. Longyan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Longyan 64000,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Insomnia,Electroacupuncture of auricular concha area,Plasma melatonin,P-chlorophenylalanine.
Highlights
The mechanism of auricular concha area (EA-ACR) between the melatonin and insomnia has rarely been studied before. The present study observed the effects of EA-ACR on the circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion in p-chlorophenylalanine(PCPA) induced insomnia rats, and demonstrate that EA-ACR can improve the quality of life (weight), ameliorate exploring irritable and anxiety behaviors in PCPA-induced insomnia rats. The underlying effects of EA-ACR may be excited on the circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion in PCPA-induced insomnia rats.These findings may provide a scientific and practical evidence for the EA-ACR treatment in insomnia.
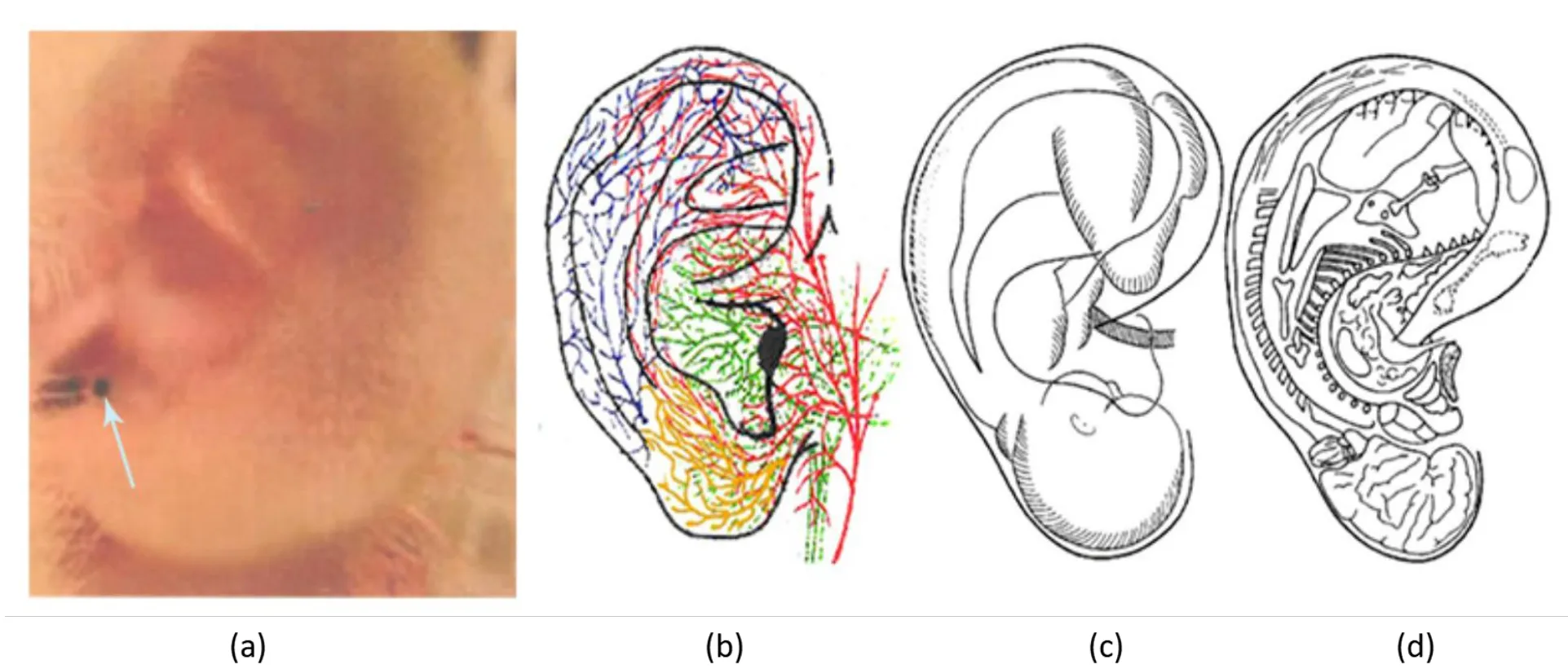
Figure 1 The ER-ACR area is the most concentrated area of vagus nerve in the ear nail area. a, The ear branch is the visceral representative area of the inverted auricle fetus, which is the EA-ACR intervention area. b,Innervation of the outer ear and representative area of auricular point,green lines represents the vagus nerve.c,The distribution of auricular points is like an inverted fetus. b, d, The organs and nerves of the human body have corresponding response areas.EA-ACR,electroacupuncture of auricular concha area.
Introduction
Insomnia is the most common sleep disorder in clinical practice. It is manifested in the changes of sleep time,sleep quality, sleep maintenance state, and even the next day's mental state [1]. Furthermore, severe patients may be accompanied by mental illnesses in serious cases, such as depression and mania.Nowadays, more and more young people suffer from the influence of working environment and so on,which are accompanied by different degrees of insomnia. At present, most research on insomnia is focused on clinical study, while the basic mechanism of insomnia is rarely studied,which needs to be further explored.
Acupuncture, especially electroacupuncture, have increasingly become an effective and safe alternative therapy for insomnia [2]. In modern medicine, the mechanism of acupuncture treatment of insomnia is mainly by regulating the nervous immune system.Some researchers have found that electroacupuncture of auricular concha area (EA-ACR) has a good regulatory effect on hypertension,diabetes,depression,epilepsy and other diseases [3-6]. Meanwhile, the researchers also put forward the theory of “ear-vagus nerve connection”[7].
The ER-ACR area is the most concentrated area of vagus nerve in the ear nail area.As shown in Figure 1,the only branch of the vagus nerve distributed on the body surface is in the ear nail area (green represents the vagus nerve).It has been found that acupuncture in the nail cavity can directly stimulate vagal afferent fibers from the surface of the skin [8]. Through the electrical stimulation of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve in the ear nail area, the nerve impulse fibers are transmitted to the lower receptor through the afferent fibers to the nucleus of the solitary tract of the central nervous system, and then to the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve through the nucleus of the solitary tract. The nerve fibers from the dorsal vagus nucleus are transmitted to the tissues related to melatonin secretion, such as pineal gland, gastrointestinal tract,hypothalamus, amygdala, kidney,etc., through a series of biochemical actions to promote melatonin secretion.
Melatonin is one of the important hormones that the human body participates in many physiological activities [9]. The release of melatonin is independent of the alternation of day and night. The mechanism is extremely complex and has not yet been fully understood. Studies have shown that sleep involves many nuclei, such as the nucleus tractus solitarius,raphe nucleus, suprachiasmatic nucleus and advanced central nervous system, as well as many neurotransmitters, such as monoamines, amino acids and peptides. Melatonin plays an important role in regulating circadian rhythm and sleep cycle, and its release is most closely related to sleep.In recent years,Melatonin has gradually been widely studied in depression, anxiety disorders, insomnia and other diseases [10]. However, there is little research to demonstrate the mechanism of EA-ACR between the melatonin and insomnia.
Therefore, the objective of present study is to discuss the mechanism of EA-ACR adjusted the insomnia rats and observe the effects of EA-ACR on the circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion in p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA)-induced insomnia rats,so as to provide a scientific and practical evidence for the EA-ACR treatment in insomnia.
Materials and methods
Experimental animals and grouping
Seven-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats(260-300g)were purchased from the Laboratory of the Animal Center of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Academy of Military Medical Sciences (Certificate Number: SCK-(Army) 2007-004). In this study, the care and experimental procedures for all rats were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Xiamen University (Permit Number:XMULAC20170376) and performed in accordance with National Institutes of Health: “Guide for the Care and Use of LaboratoryAnimals”.
Thirty-six healthy rats were randomly divided into three groups: control group (12 rats), model group (12 rats), and EA-ACR group (12 rats). All animals (1 rat/cage (25 × 20 × 18 cm)) were housed in a room with controlled temperature (22-25 oC) and humidity(50%), under a 12h light-dark cycle. All rats were regularly replaced padding, cleaned the mouse cages and provided unlimited water and food. Feed was maintained by ordinary pellet rats. The control group was blank group without any handing; rats in model group (insomnia model) received PCPA intraperitoneal injection for 2 days; rats in EA-ACR group used EA-ACR intervesion for 28 days after the insomnia model established. We observed rats weight and behavioral changes during the whole experiment.
Establishment of PCPA insomnia model
According to previous study [11], insomnia rat models were established by using PCPA intraperitoneal injection for 2 days. The PCPA powder (Sigma, USA)was disposed into suspension with weakly alkaline saline and injected intraperitoneally according to the mass fraction of 300 mg/kg, once a day for 2 days. In addition to the blank control group, the other two groups (model group and EA-ACR group) rats were injected with PCPA suspension intraperitoneally at 8:00 AM every day, continuous injection for 2 days, and observed for 2 days. After the first intraperitoneal injection of PCPA 28-30 hours, the circadian rhythm disappeared in model rats, while the blank control group was normal, indicating that the insomnia model was successfully replicated.
Figure 1 The ER-ACR area is the most concentrated area of vagus nerve in the ear nail area. a, The ear branch is the visceral representative area of the inverted auricle fetus, which is the EA-ACR intervention area. b,Innervation of the outer ear and representative area of auricular point,green lines represents the vagus nerve.c,The distribution of auricular points is like an inverted fetus. b, d, The organs and nerves of the human body have corresponding response areas.EA-ACR,electroacupuncture of auricular concha area.
Electroacupuncture method for ear nail region
The HANS-100A electroacupuncture (Nanjing Jisheng Medical Technology Co., Ltd, China) was applied to the EA-ACR group in the ear region, and a self-made conductive iron rod was attached to the bilateral auricular cavity of rats (Figure 1). The intensity of stimulation was 2 mA and the frequency was 2/15 Hz,sustained 30 minutes each time, for 28 consecutive days. The electroacupuncture intervention was conducted under isoflurane gas anesthesia. Isoflurane combined with medical high concentration oxygen(99.5%) was used to perfuse the rats for short-term inhalation general anesthesia. Anesthesia was induced by isoflurane at 4% concentration for 3 min, and the concentration was decreased to 1.5-30% to maintain anesthesia. After electroacupuncture stimulation, the anesthesia was stopped and the rats were perfused with oxygen to wake up as soon as possible.
Open field test
The open-field test was conducted from 8:00 to12:00 AM in 5th day(2 days after modeling observation)and 33rd day(after 28 consecutive days treatment finished).The open-field test was conducted in a self-made square black opaque open box with an average length of 80 cm and a height of 40 cm and its bottom was divided into 25 lattices. After the experiment, all the rats were counted through the video. The two minutes recorded by the tail of the camera were removed and the three minutes in the middle were counted. The counting was based on the horizontal movement score which was the number of crossing the bottom grid(four paws entering the same grid at the same time)and vertical movement score which was the number of upright times of hind limbs (two front paws flying or climbing the wall).
Experimental sampling and blood collection
The blood was collected from the tail vein at different times of the week(0 min,30 min,60 min,90 min,120 min, 150 min) and from the heart at the end of the experiment(33rd day).
Blood collection from rat tail vein
In order to observe the rhythmic effect of electrical stimulation of auricular region on melatonin secretion of insomnia rats induced by PCPA, we only collected blood from tail vein of EA-ACR stimulation group rats in different time periods. The tail vein blood in the EA-ACR stimulation group was collected under gas anesthesia by isoflurane (Brand Lev, Hebei Jiupai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, China). During 8:00 to12:00 AM every week, the time points of each blood collection were 0 min, 30 min, 60 min, 90 min, 120 min,150 min,and 1 mL of blood was collected at each time point. The blood was quickly injected into the biochemical tube and centrifuged after 1-2 hours.The blood was stored in the refrigerator at -80℃.
Although the blood was collected many times in a short time,the blood volume was only 1 mL each time,and during the blood collection period, we placed a indwelling needle in the tail vein of the rat, only a small amount of blood was taken at the point, which minimized the pain of the rat. After the completion of blood collection, we would strengthen the care and observation of these rats. The blood collection process did not affect the survival status of the rats, nor led to the death of the rats.
Blood collection from rat heart
At the end of the experiment (33rd day), the stage of experimental sampling, after euthanasia, blood was collected from the heart of the rats.After pentobarbital sodium (Brand Merck, German Merck Co., Ltd,Germany) anesthesia in rats, the rat's left and right costal arch was cut off quickly to expose the heart.One head of the needle was punctured into the apex of the heart, and the other head was punctured into the blood vessel of vacuum heparin sodium. The blood was collected for about 3 mL and shaken gently so that the blood was in full contact with heparin sodium, then wait for further detection.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis
The level of melatonin was determined by double antibody sandwich kit (Shanghai Dingjie Biotechnology Co., Ltd, China). The steps are as follows:(1)standard dilution,take the standard mother liquor and explain it according to the dilution standard;(2) sampling, blank holes and sample holes are set respectively, the porous microplate coating samples were diluted before adding 40 uL, and 10 uL was added to the sample (the final dilution of the sample was 5 times); (3) temperature incubation and liquid mixing, after sealing the plate with thin film, it is kept at 37 for 30 minutes, the detergent was diluted 30 times with distilled water and stored; (4) washing and enzyme addition, remove the sealing film, discard the liquid, shake off, fill each hole with washing liquid,stand for 30 minutes, drain, repeat 5 times, dry, in addition to the blank pore enzyme reagent, 50 uL sample was added to each pore; (5) colour development and termination,add reagent A(50 uL)to each pore, then reagent B (50 uL), gently shake and mix, shade at 37℃for 15 minutes, the reaction was terminated (blue to yellow) by adding 50 uL terminating solution to each pore; (6) measurement,the absorption of each hole was measured in turn by zero-setting the blank hole and 450 nm wavelength,the determination should be carried out within 15 minutes after adding termination solution.
Data analysis
The experimental data processing using SPSS Version 19.0 statistical software, all data were expressed by mean value ± standard error (± S). One-way ANOVA analysis was used after data were tested for normality and homogeneity of variance. Taking P <0.05 as statistical significance, P < 0.01 as the significant difference standard, P > 0.05 as no difference.
Results
Effect of electrical stimulation of auricular region on body weight in PCPAinduced insomnia rats.
At the beginning, the groups didn't show any difference in the body weight of mice. From the 5th day, the body weight of mice in both the model group and the treatment group was lower than that of control group (P = 0.012). The growth trend of the treatment group was faster than that of the model group, and the model group gradually increased rapidly after the 13th day(Figure 2a).But until the 33rd day,there was still a difference in the body weight between the model group and the treatment group. The mean weight of the rats in model group was lower than the blank group (P <0.001), but the mean weight of the rats in EA-ACR group was higher than the model group (P = 0.010).These indicate that EA-ACR can increase the body weight of insomnia rats induced by PCPA(Figure 2b).
Effect of electrical stimulation of auricular region on open field test
At the 5th day, compared with the blank group, PCPA intraperitoneal injection significantly decreased the score of crossings (P= 0.014), the score of rearings (P= 0.019) in the model group; and there was no significant difference between model group and EA-ACR group (P = 0.060). At the 33rd day,compared with the model group, the score of crossings (P = 0.015), rearings of the EA-ACR group were significantly improved (P = 0.004) after 28 consecutive days electrical stimulation of auricular region treatment.
Inter-group analysis of crossing and rearing scores in open field test: there was a significant difference in the score of crossing and rearing between the 33rd day and 5th day in the EA-ACR group (P <0.001; P <0.001),as shown in Figure 3.
Effect of electrical stimulation of auricular region on plasma melatonin secretion
After 28 days of electrical stimulation on auricular region, the plasma melatonin level in EA-ACR group was higher than that in model group (P = 0.020), and the blank group's level of the plasma melatonin was significantly higher than model group (P = 0.005)(Figure 4).
Effect of electrical stimulation of auricular region on the rhythmic effect of melatonin secretion in PCPA induced insomnia rats
Melatonin secretion at 6 different time points of 0, 30,60,90,120 and 150 minutes after EA-ACR stimulation showed an upward trend at the end of 30 minutes of EA-ACR stimulation, and at the end of 60 minutes of treatment, the level of melatonin secretion remained elevated.The level of melatonin secretion decreased at 60-120 min and increased at 120-150 min (Table 1,Figure 5).
Discussion
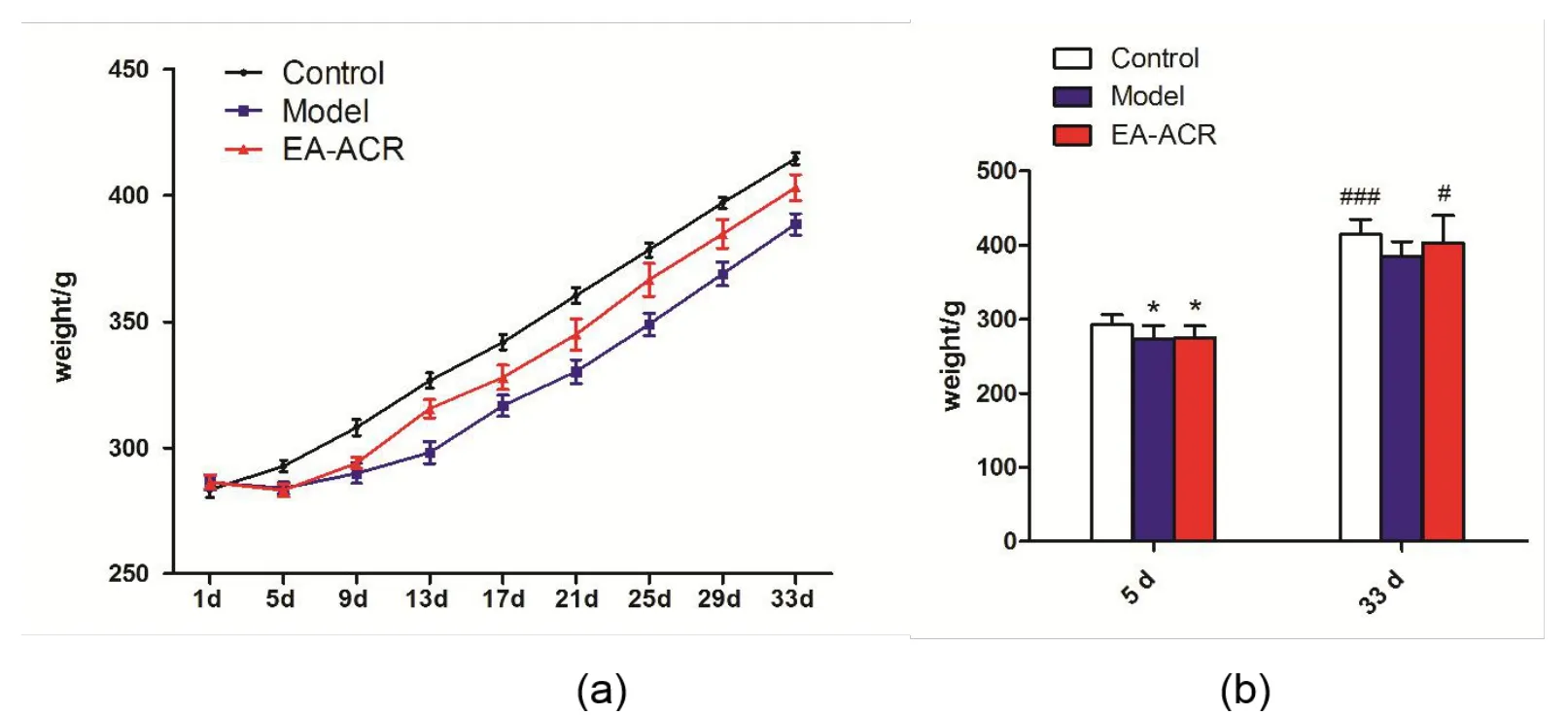
Figure 2 The change of weight in all groups. a, The growth trend of weight in all group after the electrical stimulation of auricular region within 33 days. b,The change of weight in all groups after the electrical stimulation of auricular region in 5th day and 33rd day. *P <0.05,compared with the blank group on the 5th day; #P <0.05, ###P <0.01,compared with the model group on the 33rd day.EA-ACR,electroacupuncture of auricular concha area.
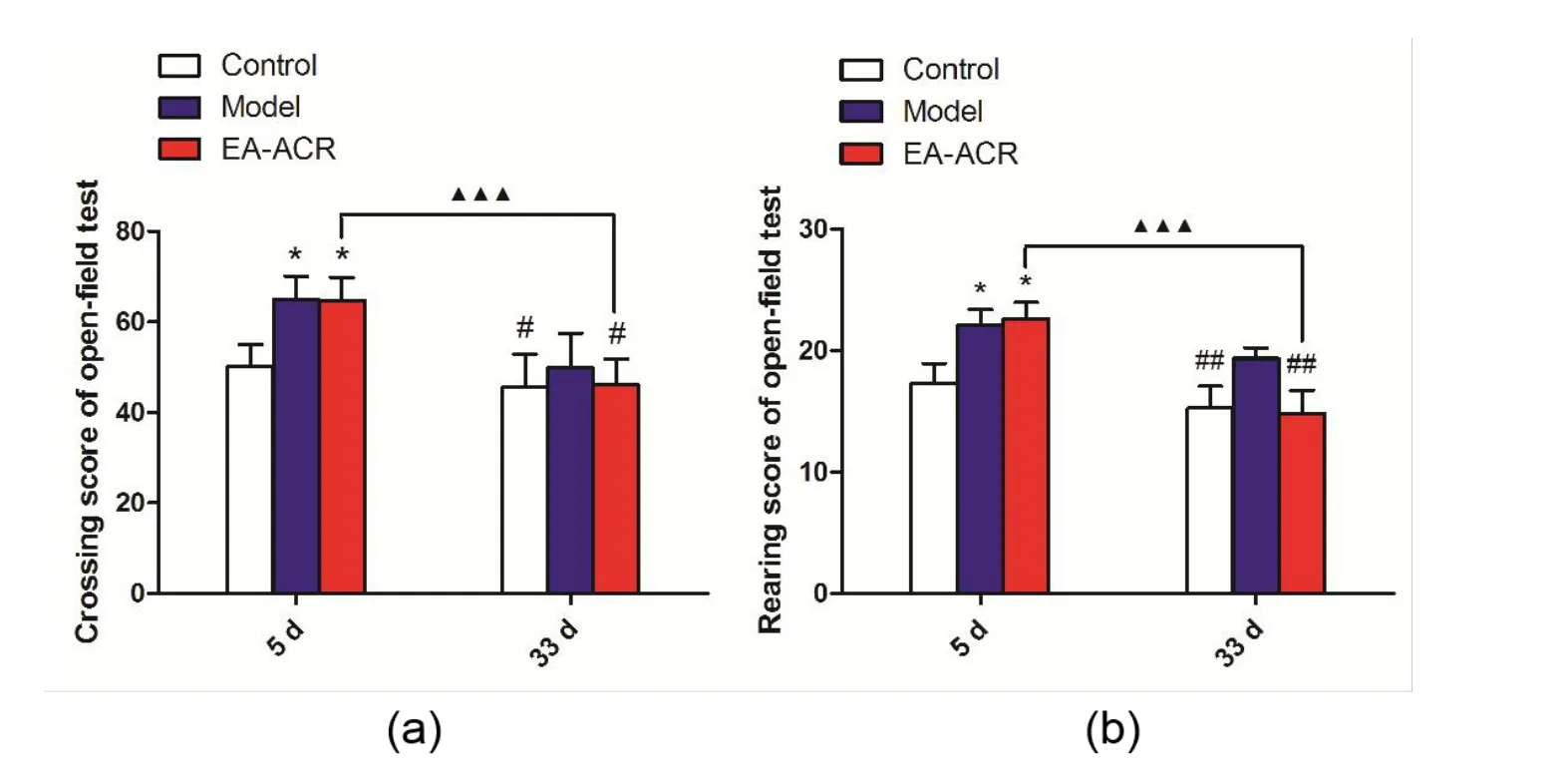
Figure 3 The crossing and rearing score of open field test in all groups.a,The crossing score of open field test in all groups.b,The rearing score of open field test in all groups. *P <0.05,compared with the blank group on the 5th day; #P <0.05, ##P <0.01, compared with the model group on the 33rd day; ▲▲▲P <0.01, compared with the same group on the 5th day.EA-ACR,electroacupuncture of auricular concha area.
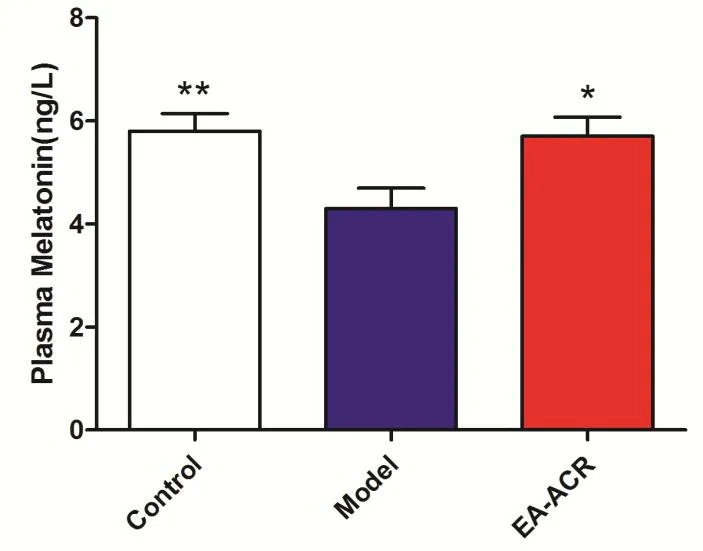
Figure 4 The comparison of plasma melatonin in all groups. **P <0.01, *P <0.05, compare with model group.EA-ACR,electroacupuncture of auricular concha area.

Table 1 Rhythmic change of melatonin secretion during four weeks in EA-ACR group(ng/L)

Figure 5 Rhythmic change of melatonin secretion during four weeks in EA-ACR group. EA-ACR,electroacupuncture of auricular concha area.
During 28-30 hours after the first intraperitoneal injection of PCPA suspension, the circadian rhythm of the model rats changed.Their activities during the day and night increased, and the total sleep time was reduced. We also found that the model rats were alert and aggressive to the outside world, and they fought with normal rats on their own initiative. At the same time, they were irritable and easy to climb on the edge of the cage. The rats in the model group also showed dark fur and lost luster. Compared with the model group,the rats in the blank group were quiet and curled up with little walking and glossy fur. It was observed that the rats after modeling moved more frequently and sensitively than the blank group when placed in a quiet open box, and their exploratory activities increased.After watching the video count, we found that the scores of horizontal and vertical movement in the model rats were higher than those in the blank group,while the scores of horizontal and vertical movement in the open field test in the blank group were lower than those in the model rats. The above results show that the model is successful and consistent with the reported paper [12]. In this study, we found that the body weight of insomnia rats induced by PCPA decreased after modeling, and increased afterwards,but the model group was slower than the EA-ACR group. After 4 days of the electric stimulation of the auricular region, the body weight of rats in EA-ACR group increased faster than model group. While the model 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) group recovered growth trend after 13 days, but in general, it did not exceed the body weight of the EA-ACR group. This may be due to the fact that PCPA acts in the body for a period of 1-2 weeks, after which the inhibition of can be relieved.
After the experiment, we found that the level of melatonin secretion in the EA-ACR group was higher than that in the model group, and the melatonin secretion rhythm in the treatment group was found to have a certain rhythm. The levels of melatonin secretion in plasma at 6 different time points of 0, 30,60,90,120 and 150 minutes after EA-ACR stimulation showed an upward trend at the end of 30 minutes after the treatment, and at the end of 60 minutes after treatment, the levels of melatonin secretion in plasma remained unchanged. The level of plasma melatonin secretion showed a downward trend at 60-120 minutes and an upward trend at 120-150 minutes, indicating that the melatonin has rhythmic characteristics of secretion itself, and further explains that the electric stimulation of the auricular region promotes the secretion of melatonin.
Studies have shown that the antidepressant effect of melatonin is similar to other antidepressant medicines[13]. A reduction in melatonin levels can increase the risk of depression [14]. It can be seen from the open-field test that electrical stimulation in the concha area could reduce the autonomous and exploratory behavior of the rats and alleviate their anxiety symptoms in the treatment group.
Neuroanatomy considers that the auricular branch of the vagus nerve innervating the external auditory canal and concha region is a kind of somatic afferent mixed the branch, which is mainly composed of facial nerve,glossopharyngeal nerve and vagus nerve. The only distribution of vagus nerve on the body surface is in the area of the concha area [15]. Researchers used electrophysiological methods to observe the electro-discharge of nucleus tractus solitarius and dorsal vagus nucleus after acupuncture of auricular concha and somatic acupoints.The results showed that acupuncture at the auricular region could activate the electro-discharge of neurons in the nucleus tractus soliton and dorsal neurons of the vagus nerve more effectively. Therefore, the researchers also proved that the effect of the auditory vagus effector pathway is consistent with somatic visceral reflex [16]. Among various of nerve factors, melatonin plays an important role in regulating circadian rhythm and sleep cycle,and its release is most closely related to sleep[17].It is generally believed that the main place for the biosynthesis of melatonin in vertebrates is its pineal cell. Melatonin mainly secretes at night [18]. It has been proved by evidence that light can enhance sympathetic nervous system activity and inhibit vagal parasympathetic activity [19, 20]. Previous studies showed that intraperitoneal injection of exogenous melatonin every afternoon or electroacupuncture stimulation of the concha area of the anesthetized rats for 30 minutes a day would lead to a significant increase in melatonin expression in the hypothalamus of Zucker glycosuria obese rats, which further indicating that electroacupuncture can promote the secretion of melatonin[21].
After treatment, melatonin level in EA-ACR group was higher than that in model group (P <0.05). This indicates that EA-ACR can increase the level of plasma melatonin. Based on the above studies, the conduction pathway of electrical stimulation in concha region is consistent with visceral vagus nerve. On the other hand, insomnia is associated with 5-HT neurons.Studies have shown that 5-HT mainly exists in the nucleus raphe dorsalis and nucleus raphe magnus [22].Studies have shown that the synthesis of melatonin is transformed from 5-HT.Melatonin is synthesized from 5-HT, a precursor substance, in the presence of tryptophan as a raw material by enzyme. It is also considered that there is interaction between melatonin and 5-HT 2A receptor [23]. This may also be one of the reasons for regulating sleep. When the concha stimulation signal enters the nucleus tractus solitarius via vagus nerve conduction, it can further promote the release of 5-HT in raphe nucleus, increase the content of 5-HT in the central nervous system, and then regulate sleep-wake state [24]. The auricular concha electroacupuncture stimulates the auricular branches of the vagus nerve and activates the excitability of the vagus nerve, thus antagonizing the tension of the sympathetic nerve. Subsequently, through the integration of the brain, the excitability of sympathetic nerve can be inhibited [25]. The afferent fibers release norepinephrine through stimulation of sympathetic nerve terminals via the dorsal vagal nucleus.Norepinephrine activates the beta-adrenergic receptor in the pineal gland, thereby activating adenylate cyclase to promote the synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and further activating serotonin-N-acetyltransferase (SNAT)to catalyze 5-HT synthesis the melatonin. SNAT is a speed limiting enzyme to promote 5-HT synthesis into melatonin.Therefore, electrical stimulation of the concha region can stimulate the 5-HT neuronal system through the auricular branches of the vagus nerve, which directly increases the release of 5-HT in the dorsal raphe nucleus. When the content of 5-HT in the central nervous system increases, 5-HT forms N-acetyl-5-HT catalyzed by SNAT enzyme, and finally synthesizes melatonin. Melatonin secretion is promoted through these pathways directly and indirectly. At the same time, a part of the synapses in the dorsal vagal nucleus are connected to the gastrointestinal tract, kidney and ovary through the vagal trunk.Studies have shown that auricular vagal nerve stimulation can cause melatonin to release rhythmically in tissues outside the pineal gland,such as gastrointestinal tract and skeletal muscle.This further promotes the release of melatonin,providing strong evidence that concha stimulation directly or indirectly affects the occurrence and maintenance of sleep-wakefulness.
From above discussion, we have achieved practical results: (1)insomnia rats model by PCPA is successful,strong repeatability, which is consistent with literature reports; (2) EA-ACR can reduce the independent,exploratory behavior,anxiety status in insomnia rats by PCPA, and increase the weight of insomnia rats; (3)EA-ACR can increase the plasma levels of melatonin in the insomnia rats caused by PCPA.The secretion of melatonin is in rhythmic regularity which can treat insomnia; (4) the mechanism of EA-ACR may be excited ear branch of the vagus nerve so as to promote the secretion of melatonin to achieve therapeutic effect on insomnia. Although this study hypothesizes that electrical stimulation of the concha may stimulate the vagal pathway and promote melatonin release.However, the vagus nerve has a variety of nerve endings distribution, electrical stimulation of the auricular vagus nerve may also be through a variety of pathways to work together. Meanwhile, as a noninvasive vagus nerve stimulation, the electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve is still worth exploring,the effects of EA-ACR remains to be further explored.
Acorrding to previous study [11], PCPA insomnia rat model is recognized at present research, and is widely used in the study of the relationship between 5-HT and other transmitters. And there maybe some better animal models, like the monkey models, which are closer to human physiology and pathology.However, it is much expensive and less convenient than rats, so we choose the rat models. Maybe the monkey models will be considered in our future experiments. Acorrding to previous studies [7], the electroacupuncture get from human subjects can also effect for rats, and our research results also demonstrate the issue. However, there are some limitations need to be improved in our study. Firstly,anesthesia may affect experimental results. But if not anesthetized, rats struggled strongly, leading to the shedding of the needle. Therefore, combined with various factors,we choose to inhale anesthesia through respiratory inhalation, with the advantages of fast metabolism, quick awakening, and the chronic injury and effect on experimental animals being reduced lowest. Secondly, the open field test is only conducted in 5th day and 33rd day. However, whether there are differences in other times and whether there are relationships between pen field test and rats weight?These questions still need to be further studied.Finally,the rats in the EA-ACR group were anesthetized with isoflurane every week to collect blood from the tail vein. Whether the weekly anesthesia can affect the physiological rhythm of rats or not? Whether there is difference between day and night? These questions should also be considered. These limitations will be further improved in our later experiments.
ConclusionIn conclusion,EA-ACR can improve the quality of life,ameliorate exploring irritable and anxiety behaviors in PCPA-induced insomnia rats.The underlying effects of EA-ACR may be excited on the circadian rhythm of melatonin secretion in PCPA-induced insomnia rats.
- TMR Non-Drug Therapy的其它文章
- Neurophysiological basis of auricular acupuncture for the the treatment of p-chlorophenylalanine-induced insomnia
- The effects of Chinese herbal fumigation on the prevention of peripheral neurotoxicity caused by chemotherapy:a meta-analysis
- Research progress on the effect of the combination of Jing acupoints bloodletting therapy and Sangzhi (Mori Ramulus) on shoulder-hand syndrome after stroke
- Effectiveness of complex decongestive therapy in management of breast cancer associated lymphedema
- Core acupoints of acupuncture for hyperplasia of mammary gland:a network analysis

