A Review of White Granulated Sugar Standard Development in China and Comparative Study on the Chinese White Granulated Sugar Standard with International Standard
DENG Dandan, SHEN Li, LI Mei, LIU Xiao
(Institute of Nanfan & Seed Industry, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510316)
Abstract: The sugar standard implemented under specific historical conditions had played a positive role in standardizing the production of China's sugar industry, promoting the development of sugar industry and strengthening the quality management of sugar products.This paper systematically combs the development of national standard and industrial standard of white granulated sugar, and analyzes the technical requirements such as sensory indicators, physical and chemical indicators and health indicators.From the development of China's white granulated sugar product standard, the sucrose content of the same level of white granulated sugar has not been adjusted, while the standard for indexes other than sucrose content, have been improved to meet the needs of the development of China's sugar industry and the development of domestic and foreign trade.Through comparison with the international standard of white granulated sugar, it is concluded that China’s national standard of white granulated sugar has kept pace with international standard.
Keywords: White granulated sugar; National standard; Industry standard; International standard; Comparison
0 Introduction
China is one of the biggest sugar producing and consuming countries.According to the data of U.S.Department of Agriculture, China's sugar production ranked fourth in the world with 10.6 million tons,accounting for about 5.88% of the world's total in 2020/21 crushing season.China's sugar consumption ranked third in the world with 15.5 million tons,accounting for about 9.06% of the world's total[1].At present, white granulated sugar is still the main product of China's sugar industry, and its market share accounts for more than 95% of the total sugar share.
In order to standardize the production of sugar products, relevant national departments have formulated a series of national standard and industrial standard to ensure sugar quality.National standard is the “most basic requirements” of similar products, and relevant professional departments will also formulate industry standard according to industrial requirements[2].In 2020, there were 96 standard projects in the technical standard system of sugar industry, including 49 currently effective standards, 8 standard plan projects and 39 standard projects to be formulated.By December 2020, 49 sugar standards have been centrally managed by National Technical Committee of Sugar Standardization, including 15 national standards and 34 industrial standards.The existing standards are mainly product standard,method standard and basic general standard.
This paper focuses on the development of national and industrial standard of sugar core category,i.e., white granulated sugar, and compares them with international white granulated sugar standard, so as to provide direction for the production management andquality improvement of sugar enterprises in China.
1 Development of China's white granulated sugar standard
1.1 Early days of the People's Republic of China(before 1957)
Before 1957, there was no unified quality standard for white granulated sugar.All sugar factories generally adopted the quality requirements for plantation white sugar in the technical management documents of Hawaiian sugar factory, and conducted ex-factory inspection on the quality indexes of white granulated sugar, such as sucrose, reducing sugar,color value, conductive ash, loss on drying and so on[3].
1.2 Planned economy period (1957-1990)
On December 1, 1957, the former Ministry of Food Industry formulated and issued the quality standard of white granulated sugar for sugarcane,coded Sugar 0101-57, and implemented nationwide instantly.According to the standard, white granulated sugar was grouped into two categories, i.e, first-grade and second-grade.
In 1964, the former Ministry of Light Industry formulated and issued the national standard for white granulated sugar products to replace Sugar 0101-57,coded GB 317-64.
In 1984, the former Ministry of Light Industry revised GB 317-64.Approved by the National Bureau of Standard, the national standard for white granulated sugar 1984 has been implemented since October 1,1985, coded GB 317-84.The above standard specified the indexes of sucrose content, reducing sugar content,conductive ash content, loss on drying, color value,turbidity, insoluble impurities and so on in different grades of white granulated sugar[3].
1.3 Reform and opening up period (since 1991)
1.3.1 National standard
1.3.1.1 GB 317.1-91 “white granulated sugar”[4]
In GB 317.1-91 standard, the sensory indexes,physical and chemical indexes and hygienic indexes of white granulated sugar were specified in detail.Among them, the sensory indicators required that the sugar grains be uniform, dry, loose, white and shiny,the grains or their aqueous solution be sweet without peculiar smell.The particle size was divided into coarse grain, large grain, medium grain and fine grain,which should be no less than 80% in different ranges,i.e., coarse granulated sugar: 0.8-2.5 mm; large granulated sugar: 0.63-1.6 mm; medium granulated sugar: 0.45-1.25 mm; fine granulated sugar: 0.28-0.8 mm.For the physical and chemical indexes, there were requirements on sucrose, reducing sugar, conductive ash, loss on drying, color value, turbidity and insoluble impurities, and they were classified into three grades, i.e., premium, first and second.For health indicators, arsenic ≤ 0.5 mg/kg, lead ≤ 1.0 mg/kg, copper ≤ 2.0 mg/kg were specified, and sulfur dioxide was classified according to different processes,i.e., sulfur dioxide of white granulated sugar in carbonation sugar plant ≤ 20 mg/kg, and sulfur dioxide of white granulated sugar in sulfite sugar plant ≤ 50 mg/kg.
1.3.1.2 GB 317-1998 “white granulated sugar”[5]
GB 317-1998 “white granulated sugar” was revised on May 7, 1998, according to GB 317.1-91“white granulated sugar”, GB/T 317.2-91 “analysis method of white granulated sugar”[6], QB 1213-91“refined white granulated sugar”[7]and its implementation, as well as GB 13104-91 “hygienic standard for white sugar”[8].In terms of technical requirements, CXS 4-1981 “codex standard for white sugar”[9]and “sugar analysis ICUMSA methods”(1982 Chinese version)[10]were adopted unequivalently to meet the needs of the development of sugar industry and domestic and foreign trade under China's market economy.In the technical requirements,one more grade was added up to the current category,which is termed as refining.The purpose was to incorporate the refined white granulated sugar industry standard into the national standard of white granulated sugar, so as to meet the needs of the continuous development of sugar producing technology and the continuous expansion of refined white granulated sugar market in China.For sensory indicators, it wasclearly required to “have no obvious black spots”, but there was no clear detection method or evaluation standard of black spots.For physical and chemical indexes, higher requirements were enforced on all except for sucrose and loss on drying.Moreover, in the hygienic requirements, the sulfur dioxide index was taken as one of the basis for classification for the first time, and the indexes of total bacterial count, coliform group, pathogenic bacteria and mites were also increased.The buffer solution method was used to replace the previous pH adjustment method, and the mite test method was added.
1.3.1.3 GB 317-2006 “white granulated sugar”[11]
With the continuous improvement of sugar producing technology and equipment, combined with higher level of consumption, old white granulated sugar standard could not meet the new market demand.The new sugar standard GB 317-2006 “white granulated sugar” was issued on March 31, 2006.This version of the standard was not equivalent to CXS 212-1999[12].In terms of sensory indexes, fine granulated sugar was added: 0.14-0.45 mm, and the particle size was smaller.For the physical and chemical indexes, the conductivity ash, loss on drying,turbidity and water insoluble impurities of refined white granulated sugar; reducing sugar, conductivity ash, color value, turbidity and water insoluble impurities of premium white granulated sugar; color value, turbidity and water insoluble impurities of first-grade white granulated sugar; the reducing sugar,conductive ash, loss on drying, color value, turbidity and water-insoluble impurities of second-grade white granulated sugar all met the requirements.In terms of hygienic index requirements, yeast and mold items were added and copper items were deleted.Except for sulfur dioxide, all items were required to directly refer to the project indicators in GB 13104-2005 “hygienic indicators for sugar”[13], and sulfur dioxide indicators equal to or stricter than GB 13104-2005 were formulated according to the level.The new standard changed the calculation and expression method of turbidity from “degree” to “milli attenuation unit”(MAU), and added the content of “recommended shelf life” in the label.
1.3.1.4 GB/T 317-2018 “white granulated sugar”[14]
The current national standard GB/T 317-2018“white granulated sugar” was released on February 6,2018, which specified technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, labeling, packaging,transportation and storage requirements of white granulated sugar.The new standard was adjusted as follows: black spots added, and the detection method of black spots “the number of black spots with a length greater than 0.2 mm per square meter of surface area is no more than 15” defined in the sensory indexes,which will help the laboratory personnel to accurately judge whether the sensory indexes are qualified or not.The food safety requirements were revised, the sulfur dioxide indicators were deleted in terms of health indicators, and the sulfur dioxide indicators should be implemented in accordance with GB 2760-2014“standard of using food additives”[15].The requirements on raw materials were added, that is,sugarcane as raw material should comply with the provisions of GB/T 10498[16], sugar beet as raw material should comply with the provisions of GB/T 10496[17], raw sugar as raw material should comply with the provisions of GB/T 15108[18], and the net content of quantitative packaging should comply with the provisions of “measures for metrological supervision and administration of quantitatively packed commodities”.The test methods for sensory items and physical and chemical items were modified.The color, taste, smell, state and food safety requirements were determined according to the methods specified in GB 13104.The particle size,black spot, sucrose, reducing sugar, conductive ash,loss on drying, color value, turbidity and water-insoluble impurities were determined according to the methods specified in GB/T 35887[19].The net content should be determined according to the method specified in JJF 1070[20].The inspection rules were modified, including relevant contents of type inspection, delivery inspection and judgment rules.
Table 1 shows the comparison of physical and chemical indexes of previous versions of national standard for white granulated sugar.From the development of domestic white granulated sugar product standard, sucrose content of same level of white granulated sugar has not been adjusted, while the standard for indicators other than sucrose content,reducing sugar, conductive ash, color value and water-insoluble impurities have been improved to meet the needs of development of China's sugar industry, domestic and foreign trade.
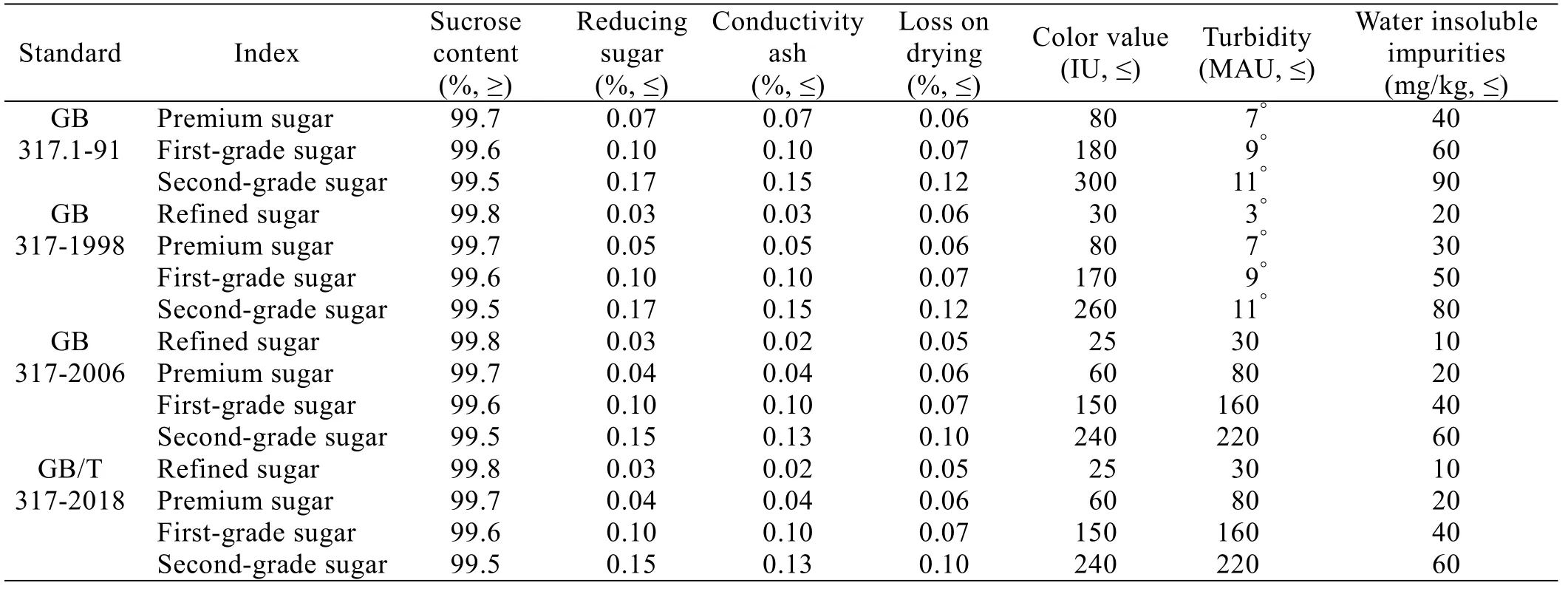
Table 1 Comparison of physical and chemical indexes of previous versions of national standard for white granulated sug ar
1.3.2 Industry standard
1.3.2.1 QB 1213-91 “refined white granulated sugar”
QB 1213-91 “refined white granulated sugar”was a light industry standard approved and implemented by the Ministry of Light Industry, which specifies the technical requirements, test methods,inspection rules, marking, packaging, transportation and storage requirements of refined white granulated sugar.The sensory indexes of refined white granulated sugar in this standard are consistent with those in GB 317.1-91, and for physical and chemical indexes,sucrose content ≥ 99.8%, reducing sugar content ≤0.03%, conductive ash content ≤ 0.03%, loss on drying≤ 0.06%, color value ≤ 30 IU, turbidity ≤ 4 degrees,insoluble impurities ≤ 20 mg/kg.That is, the requirements for physical and chemical indexes are significantly stricter than those in GB 317.1-91,indicating that refined sugar enjoys higher purity and higher quality.Compared with GB 317.1-91, the health indicators are supplemented with items and indicators of total bacteria, coliform and pathogenic bacteria, stipulating that the residual amount of sulfur dioxide be ≤ 20 mg/kg.
1.3.2.2 NY/T 422-2000 “green food- white granulated sugar”[21]
NY/T 422-2000 “green food-white granulated sugar” was an agricultural industry standard issued by the Ministry of Agriculture to determine the quality and safety of green food-white granulated sugar,which stipulates the definition, requirements, test methods, inspection rules, marks, labels, packaging,transportation and storage of green food-white granulated sugar.It is applicable to green food-white granulated sugar Class A produced from sugarcane.The sensory indexes of white granulated sugar are consistent with those in GB 317.1-91, the environmental requirements of sugarcane producing area shall comply with the provisions of NY/T 391[22],and the processing water shall comply with the provisions of GB 5749[23].All the physical and chemical indexes except for sucrose, are stricter than the requirements of GB 317.1-91.Compared with GB 317.1-91, the hygienic index increases the indexrequirements of carbendazim, i.e., the content of carbendazim ≤ 0.1 mg /kg.In terms of biological indicators, it is stipulated that the total number of colonies be ≤ 200 cfu/g, coliform group ≤ 30 MPN/100g, pathogenic bacteria not to be detected, and mites not to be detected in 300 g white granulated sugar.
1.3.2.3 NY/T 422-2006 “green food-edible sugar”[24]
NY/T 422-2000 “green food-white granulated sugar” is the single standard for green food-white granulated sugar, while NY/T 422-2006 “green food-edible sugar” is applicable to green food: white granulated sugar, white soft sugar, monocrystal rock sugar, multi-crystal rock sugar and cube sugar produced directly or indirectly from sugarcane or sugar beet.The standard requires that the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers in the production of raw materials should comply with the provisions of NY/T 393[25]and NY/T 394[26].The physical and chemical indexes of white granulated sugar are lower than those of NY/T 422-2000, which is consistent with the physical and chemical indexes of first-grade products in GB 317-2006 “white granulated sugar”.In terms of health indicators, the requirements on sulfur dioxide whether in carbonic acid method or sulfite method are all the same.And, the indicator of carbendazim is deleted, the indicators of yeast and mold added.
1.3.2.4 QB/T 4564-2013 “refined fine sugar”[27]
According to the classification principle of GB/T 35886-2018 “classify of sugar”[28], sugar is mainly grouped into nine categories, and white granulated sugar category includes white granulated sugar and refined fine sugar.Refined fine sugar has the advantages of being highly pure, white, fine grain and instantly soluble.It is a relatively high end edible sugar in the market, which is used for drinks and coffee.It is also the main raw material for cube sugar production.QB/T 4564-2013 “refined fine sugar” is a light industry standard issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, which specifies the terms, definitions, requirements, test methods,inspection rules and marks, packaging, transportation and storage of refined fine sugar.In terms of sensory indexes, refined fine sugar is divided into small particles (0.28 - 0.80 mm) and fine particles (0.14 -0.45 mm).The smaller the particle size is, the more quickly the refined fine sugar can be dissolved.And also, the number of black spots with a length greater than 0.2 mm per square meter of surface area shall not be more than 12.In terms of physical and chemical indexes, the sucrose content, loss on drying, turbidity and water-insoluble impurities of refined fine sugar are equivalent to the corresponding indexes of refined white granulated sugar in the current national standard GB/T 317-2018 “white granulated sugar”, but the indexes of reducing sugar, conductive ash and color value are lower than those of refined white granulated sugar.In terms of health indicators, it is stipulated that sulfur dioxide residue ≤ 6 mg/kg, total bacterial count≤ 100 cfu/g, coliform group ≤30 MPN/100g, mold ≤25 cfu/g, yeast ≤10 cfu/g, pathogenic bacteria shall not be detected, and mites, total arsenic and lead shall meet the requirements of GB 13104.
1.3.2.5 NY/T 422-2016 “green food-edible sugar”[29]NY/T 422-2016 “green food-edible sugar” is applicable not only to white granulated sugar, but also to raw sugar, refined fine sugar, brown granulated sugar, brown sugar, golden slab sugar, demerara sugar,liquid sugar and icing sugar.The standard is mainly adjusted as follows: 1.terms and definitions are added,in which liquid sugar is defined as “edible liquid sugar produced from white granulated sugar, white soft sugar, refined molasses or intermediate products through processing or conversing”.2.The sensory requirements are modified, that is, the product shall have proper color and shape, sweet taste, no peculiar smell, no foreign matter visible to normal vision, and the use of food additives shall comply with the provisions of NY/T 392[30].Physical and chemical index items such as turbidity and water insoluble impurities and their index values are added.The turbidity and water insoluble impurities of white granulated sugar are consistent with those offirst-grade products of GB 317-2006 “white granulated sugar”, and the turbidity and water insoluble impurities of refined fine sugar are consistent with those of QB/T 4564-2013 “refined fine sugar”.The copper index and its limit value in the hygienic requirements are deleted.
1.3.2.6 NY/T 422-2021 “green food-edible sugar”[31]Referring to the provisions of GB/T 1.1-2020“directives for standardization-Part 1: rules for the structure and drafting of standardization documents”[32], the current agricultural industry standard NY/T 422-2021 “green food-edible sugar”was issued by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs on June 1, 2021 and implemented on November 1, 2021.There are only a very few changes on the indicators of white granulated sugar and refined fine sugar products in the standard, except for the sucrose content of refined fine sugar, i.e., t ≥ 99.8 g/100g.The limit value of sulfur dioxide residue in white granulated sugar in the food additive limit is changed, i.e., ≤ 15 mg/kg.
Table 2 shows the comparison of physical and chemical indexes of previous versions of industry standard for white granulated sugar.The agricultural industry standard NY/T 422-2000 has strict requirements on indexes of white granulated sugar,which is equivalent to premium sugar indexes in national standard GB/T 317-2018.The physical and chemical indexes of white granulated sugar amended in 2006, 2016 and 2021 have decreased, which is equivalent to first-grade sugar index in national standard GB/T 317-2018.The reducing sugar,conductivity ash, drying on loss, color value, turbidity,water insoluble impurities of refined fine sugar are much better than white granulated sugar, and the overall quality is higher than white granulated sugar.
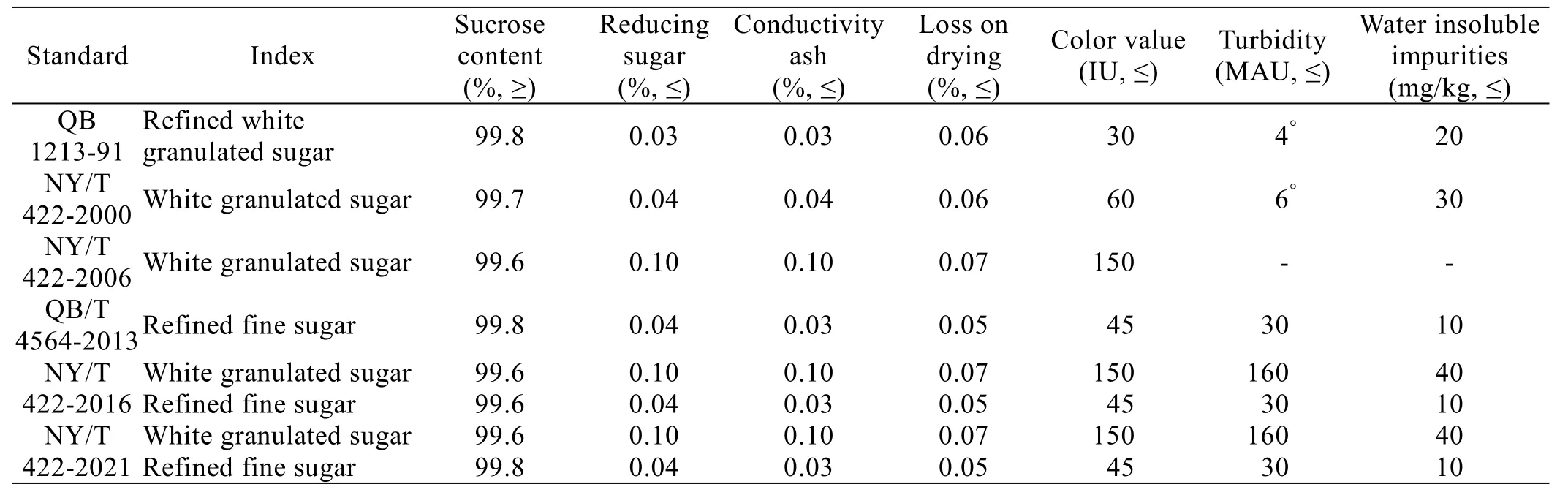
Table 2 Comparison of physical and chemical indexes of previous versions of industry standard for white granulated sugar
Table 3 shows the comparison of health indicators of previous versions of industry standard for white granulated sugar.From the development process of health indicators of domestic white granulated sugar industry standard, the indicators of coliform group,pathogenic bacteria and mites have not been adjusted.Carbendazim only appeared in NY/T 422-2000, and other health indicators have changed, among which the indicator of sulfur dioxide has changed greatly.
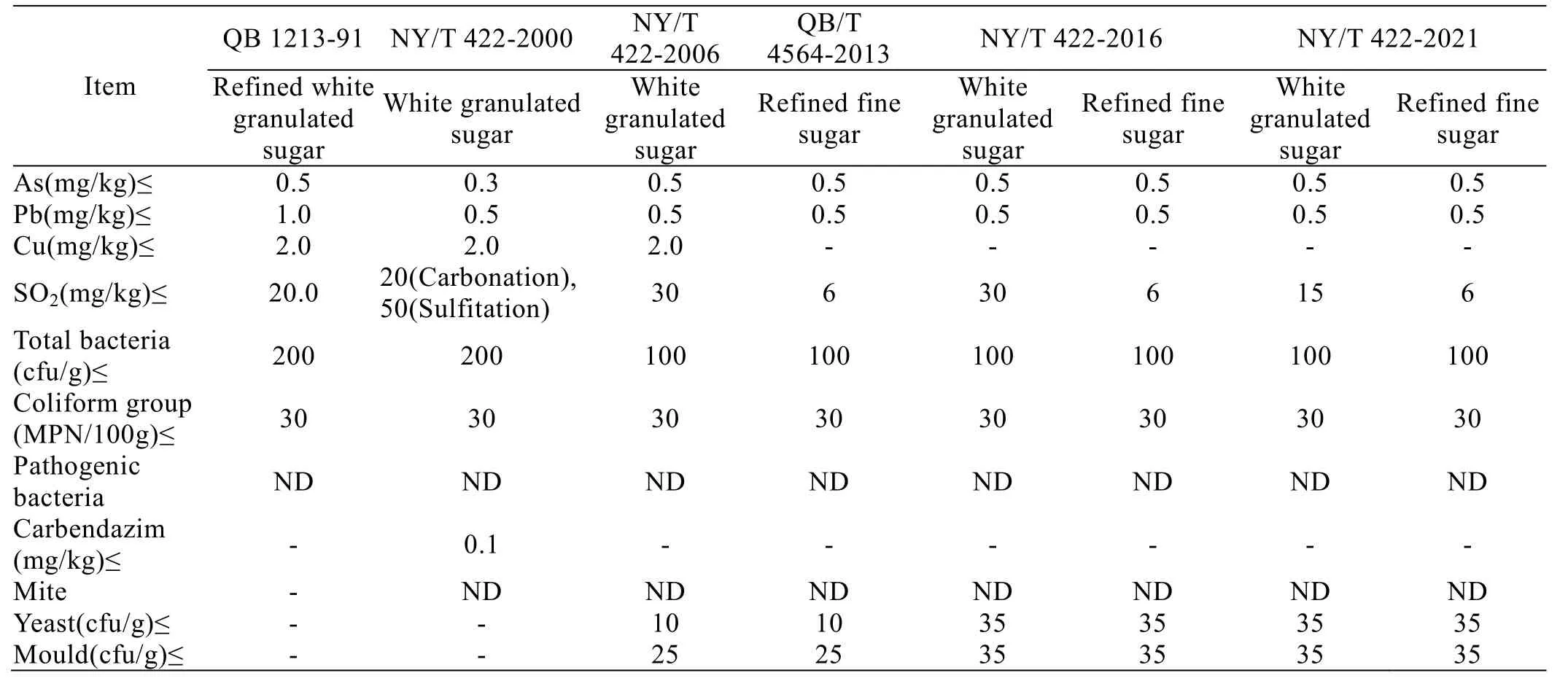
Table 3 Comparison of health indicators of previous versions of industry standard for white granulated sugar
2 Comparison between the current national standard of white granulated sugar and the international standard of white granulated sugar
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) is an intergovernmental organization jointly established by Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO)for the purpose of formulating international food standard, in a way to ensure food safety and the fairness of food trade.The international sugar standard was formulated by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC).CXS 4-1981 was issued in 1981.CXS 212-2019 was issued in 1999, and was revised twice later in 2001 and 2019 respectively.
Table 4 shows the comparison of physical and chemical indexes between the current national standard of white granulated sugar and the international standard of white granulated sugar.It can be concluded that the physical and chemical indexes of the international standard of white granulated sugar include sucrose content, reducing sugar, conductive ash, loss on drying and color value, while GB/T 317-2018 has two more items as turbidity and insoluble impurities in water.Therefore, the index setting is more rigorous and more in line with China's national conditions.Insoluble impurities and turbidity are also important indicators of the quality of white granulated sugar, and the increase of water insoluble impurities means of low filtration efficiency or crud pollution in the sugar tank in the sugar making process.Turbidity is an important index of the clarification effect in the sugar producing process[33].
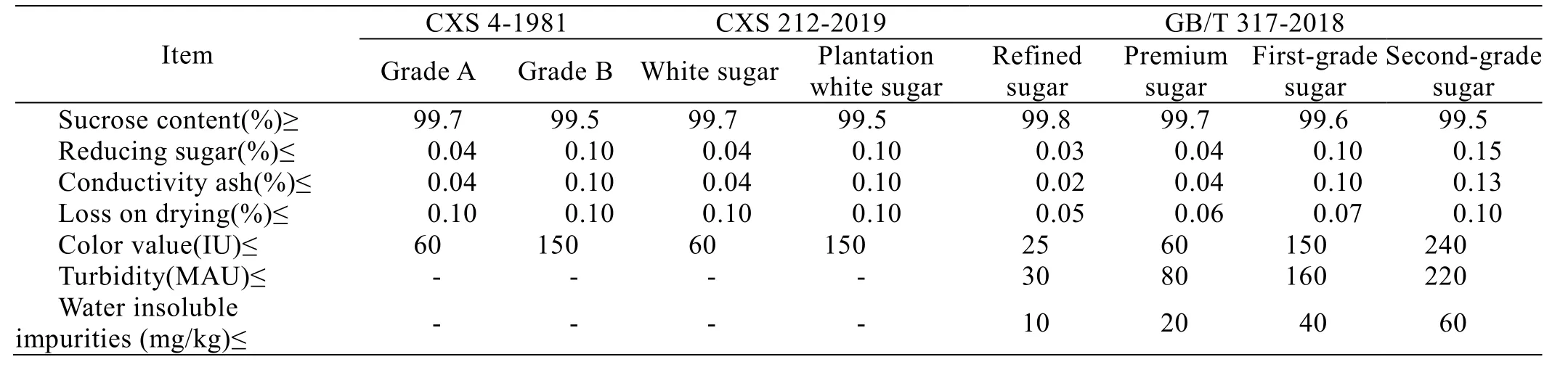
Table 4 Comparison of physical and chemical indexes between current national standard of white granulated sugar and international standard of white granulated sugar
According to CXS 4-1981 standard, white granulated sugar is categorized into grade A and grade B.According to CXS 212-2019 standard, white granulated sugar is grouped into white sugar and plantation white sugar, the physical and chemical indexes of grade A and white sugar are more or less similar, and the physical and chemical indexes of grade B and plantation white sugar are more or less similar.Comparison between CXS 212-2019 and GB/T 317-2018 indicated that all indexes of refinedfine sugar in GB/T 317-2018 are better than those of international white sugar standard.The indexes of premium white granulated sugar are much better than the international plantation white sugar, among which loss on drying is better than the international white sugar index, while other indexes are equivalent to the international white sugar.The reducing sugar content,conductance ash content and color value of first-grade white granulated sugar are equivalent to those of international plantation white sugar, and the sucrose content and loss on drying are better than those of international plantation white sugar.The sucrose content and loss on drying index of second-grade white granulated sugar are equivalent to those of international plantation white sugar, while other indexes are lower than those of international plantation white sugar.
3 Conclusions
With the improvement of people's living standard,sugar enterprises and consumers have higher and higher requirements on product quality.This paper systematically combs the development of national and industrial standard of white granulated sugar, and analyzes the technical requirements such as sensory indicators, physical and chemical indicators and health indicators.From the development of domestic white granulated sugar product standard, the sucrose content of the same level of white granulated sugar has not been adjusted, while the standard for indicators other than sucrose content, reducing sugar, conductive ash,color value and water-insoluble impurities have been improved to meet the needs of the development of China's sugar industry and the development of domestic and foreign trade.Through comparison with the international standard of white granulated sugar, it is concluded that indexes of refined fine sugar in the current national standard GB/T 317-2018 “white granulated sugar” are superior to those of white sugar in Codex Standard for Sugars, and the indexes of superior-grade white granulated sugar meet or exceed the indexes of white sugar in Codex Standard for Sugars.The indexes of first-grade white granulated sugar are equivalent or superior to the indexes of plantation white sugar in Codex Standard for Sugars,indicating that China's national standard of white granulated sugar has gradually kept pace with international standard.
In general, sugar enterprises should strengthen the improvement of process technology, continuously reduce impurity content and product color value, and improve product purity.Relevant measures from source control, process monitoring and follow-up prevention should be taken to control foreign matters in products and improve sensory indicators of products.Tackle key technologies such as raw material quality control, crystallization refinement control, multi-stage screening and caking control to meet the customized particle size requirements of customers.Although the current standard relax the requirements for sulfur dioxide and microorganisms, sugar enterprises still need to formulate a strict health management system to strengthen the tracking and detection of sulfur dioxide and microorganisms.
4 Prospect
According to the purpose, sugar products are generally divided into two categories.One is directly edible sugar, that is, civil sugar, including white granulated sugar, soft white sugar, rock sugar, brown sugar, etc.This kind of sugar products have become increasingly diversified and functional.The other one is industrial sugar as food additives, mainly white granulated sugar, which has higher and higher quality requirements[34].The quality requirements of industrial sugar as food additive are usually much higher than those of household sugar or direct edible sugar.It is suggested to adjust and improve the standardization system of sugar products in China, and formulate the standard of direct edible sugar and industrial sugar according to the use of sugar products.Direct edible sugar should mainly pursue safety and nature, while industrial sugar as food additive should formulate different indicators according to its specific uses to maximize resource savings.The production of sugar for corresponding purposes in proportion toconsumption can not only meet the needs of industrial sugar and civil sugar, but also achieve the purpose of energy conservation, consumption reduction and environmental protection.

