Monoclonal antibody-based cancer therapies
Yingnan Si,Arin L.Melkonian,Keegan C.Curry,Yuanxin Xu,Maranda Tidwell,Mingming Liu,Ahmed F.Zaky,Xiaoguang (Margaret) Liu,*
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB),1825 University Blvd,Birmingham,AL 35294,USA
2 Department of Medicine,UAB,1720 2nd Ave S.,Birmingham,AL 35294,USA
3 Chinese Medicine Hospital,98 Shengcheng Street,Shouguang 262700,China
4 Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine,UAB,625 19th Street South,Birmingham,AL 35294,USA
ABSTRACT Targeted therapy has been widely demonstrated as an effective strategy to treat cancers,the leading cause of death in the world.This minireview summarizes the technical platforms and methodologies utilized to develop and engineer therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates.First,the USA FDA approved monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based targeted therapies are reviewed.Then the representative innovative chimeric,humanized and fully human anti-cancer antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates are described.Finally,the past and predictive market trend of therapeutic antibodies is discussed.
Keywords:Monoclonal antibody Antibody-drug conjugate Anti-cancer therapy Market
1.Introduction
Despite the advances in research,diagnosis,and treatment,cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide,with an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2018 [1]and an expected rise to 29.5 million new cases and 16.4 million deaths by 2040 (International Agency for Research on cancer).The major obstacles involved in preventing the success and efficacy of standard chemotherapies include limited clinical efficacy,development of drug resistance,severe off-target side effects,and recurrence post primary treatment.With the intensive efforts for discovering the cancer-specific antigens or signaling pathways such as HER2,EGFR,CD20,CD22,CD30,CD33,CD38,CD52,CTLA-4,PD-L1,and others[2–6],numerous targeted anti-cancer strategies that overcome these barriers,such as monoclonal antibody(mAb)-based biologics[7,8],have been developed or are being evaluated in clinical trials.The mAbs have been demonstrated as effective biopharmaceuticals that can improve the overall survival of cancer patientsviamultiple anti-cancer mechanisms,including inhibition of cell proliferation,induction of apoptosis,antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity(ADCC)[9–12]and complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) [13,14](Fig.1).
To develop therapeutic mAbs,hybridoma technology,which fuses the antibody producing mouse immunized B spleen cells and reproducing myeloma(an immortal cancer B cells),was established by K?hler and Milstein in 1975 [15–17].The advantages of hybridoma-based mAbs are the high antigen binding and low aggregationin vivo[18–22];however,the generated murine mAbs have short half-lives,low biological activity,and reduced initiation of effector function [23,24].In 1985,Smithet al.developed phage display technology to develop mAb by screening a preestablished library of mouse or human antibodies [25,26].Phage display screening is fast but the developed mAbs have low antigen targeting specificity,sensitivity,and affinity.
Antibody engineering is a powerful tool to develop novel therapeutic mAbs for clinical application.For example,after sequencing and cloning,murine mAbs can be further engineered to generate either chimeric,humanized,full human,or bispecific antibodies [7,27–31].The first humanized mAb (anti-IL2 daclizumab) was developed by grafting the complementary-determining region(CDR)of murine antibody with the human mAb framework sequence and was approved in 1997 by the US FDA[32].The transgenic animal technology [33]and phage display [34]enabled the development of fully human mAb.The first human antibody,panitumumab generated from XenoMouse transgenic mice,treats epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) positive metastatic colorectal cancer and was approved by the US FDA in 2006 [35].Compared to murine mAb,the constant region in humanized and human mAbs reduces immunogenicity,improves effector functions,and significantly extends the serum half-life[36].Moreover,the affinity maturation,effector function modification,and pharmacokinetic modulation technologies have been developed to improve the stability and function of mAbs [27,37].
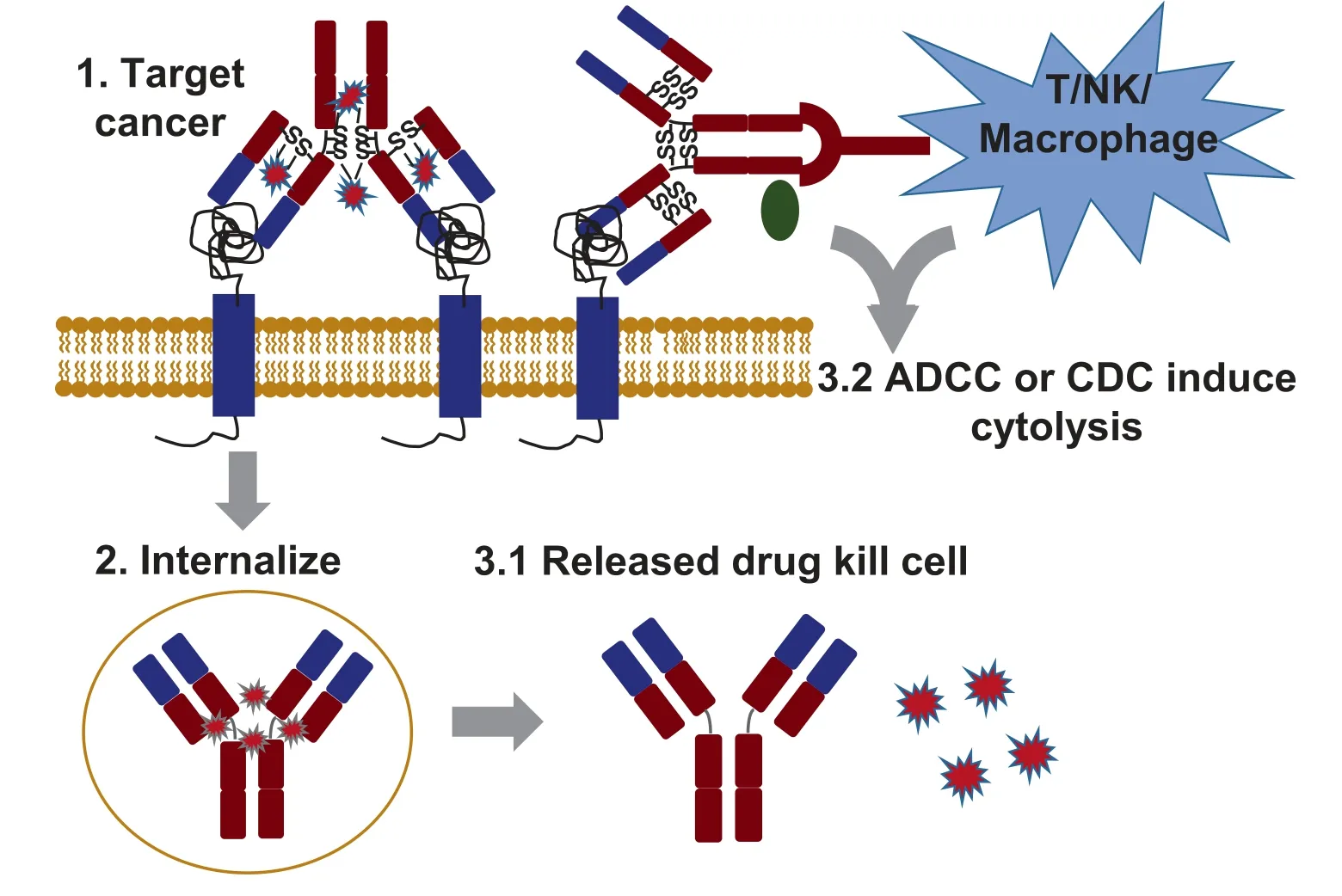
Fig.1.The anti-cancer mechanisms of mAb and ADC.1.mAb or ADC specifically targets cancer cells by binding the overexpressed surface receptor;2.ADC internalizes mediated with receptor;3.1.Released cytotoxic drug causes cancer cell death;and 3.2.mAb-mediated ADCC or CDC leads to cytolysis.
Since the FDA approved the first anti-cancer chimeric mAb in 1997,anti-CD20 Rituximab,a treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma [38,39],32 more mAbs have been approved for cancer treatment in the USA [40,41](Table 1).The CD19-targeting Tafasitamab-cxix and anti-TROP-2 Sacituzumab govitecan were approved in 2020 for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and triple-negative breast cancer,respectively.There are five additional new antibody therapeutics undergoing FDA review in 2020 [8].In addition to cancer treatment,the mAbs can also be used to diagnose cancers,construct antibody-drug conjugate,or direct the targeted delivery of various therapies [42–47].
2.Antibody Structure
Of the five classes of immunoglobin family (IgA,IgD,IgE,IgM,and IgG),IgG is the most effective antibody for cancer treatment[48,49].IgG is comprised of two identical heavy chains (HC,50000) and two identical light chains (LC,25000) that are held together by four interchain disulfide bonds and arranged in a Y shape (Fig.2A) [50,51].The HC consists of one variable domain(VH),a discrete folded region containing 110 amino acids,three constant domains (CH1,CH2 and CH3),and a hinge linker.The LC consists of one variable domain (VL) and constant domain(CL) with two subtypes,lambda(λ) and kappa(κ).The domains of VH,VL,CL and CH1 form the fragment antigen binding (Fab)region which recognizes and binds a specific antigen.The CH2 and CH3 form the fragment crystallizable(Fc)region that mediates the recruitment of immune cells through interaction with Fc gamma receptors (FcγR) [52,53].The four subclasses of IgG(IgG1-4) are highly conserved and differ in their hinge region length,the number and location of interchain disulfide bonds,and the upper CH2 domains [51].The Fc region of IgG subclasses leads to their functional difference in ADCC and CDC [40,54,55].
3.Engineering of Therapeutic mAb
Immunogenicity is one of the major factors that hinders the therapeutic application of murine mAb.For instance,obvious human anti-murine antibody responses in the circulation can be detected within one to three weeks post-murine mAb administration and the serum half-life of murine mAb is only 15–30 h[56,57].Although chimeric and humanized mAbs have been successfully developed,their immunogenicity is still challenging [58–60].Phage display [61–63]and transgenic mice [64–68]have enabled the development of clinically indistinguishable mAbs (Table 1).To date,over 500 therapeutic mAbs have been evaluated in clinical trials worldwide,with more than 80 mAbs (32 of them for cancer treatment)approved by the US FDA for clinical use(Fig.3).Here we use representative FDA-approved mAbs to review a multitude of advanced antibody engineering technologies.
3.1.Cetuximab (chimeric antibody)
A chimeric antibody can be generated by fusing the variable region of a murine antibody with the constant region of a human antibody,containing the consensus sequences for N-linked glycosylation and the N-terminal amino acid cyclized as pyroglutamic acid [7,27–31,69].Cetuximab (Erbitux) is a 152000 chimeric mAb containing a human IgG1 constant region and a murine Fv variable region,which was developed to treat metastatic colorectal cancer,metastatic non-small cell lung cancer,and head and neck cancer by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).Compared to murine antibodies,Cetuximab showed significantly improved anti-cancer efficacy,reduced immunogenicity,higher affinity to antigen,and reduced dosage [70–72].For example,the combination of Cetuximab with platinum-based therapy using fluorouracil has resulted in overall survival (OS),progression-free survival(PFS),and objective response rate (ORR) of 10.1 months,5.5 months,and 35.6%,respectively,in the treatment of K-Ras wild-type and EGFR-positive head and neck cancer patients.In combination with the chemotherapeutic drug FOLFIRI,the Cetux-imab extended the OS,PFS,and ORR to 23.5 months,9.5 months,and 57%from 19.6 months,8.9 months,and 46%respectively[73].
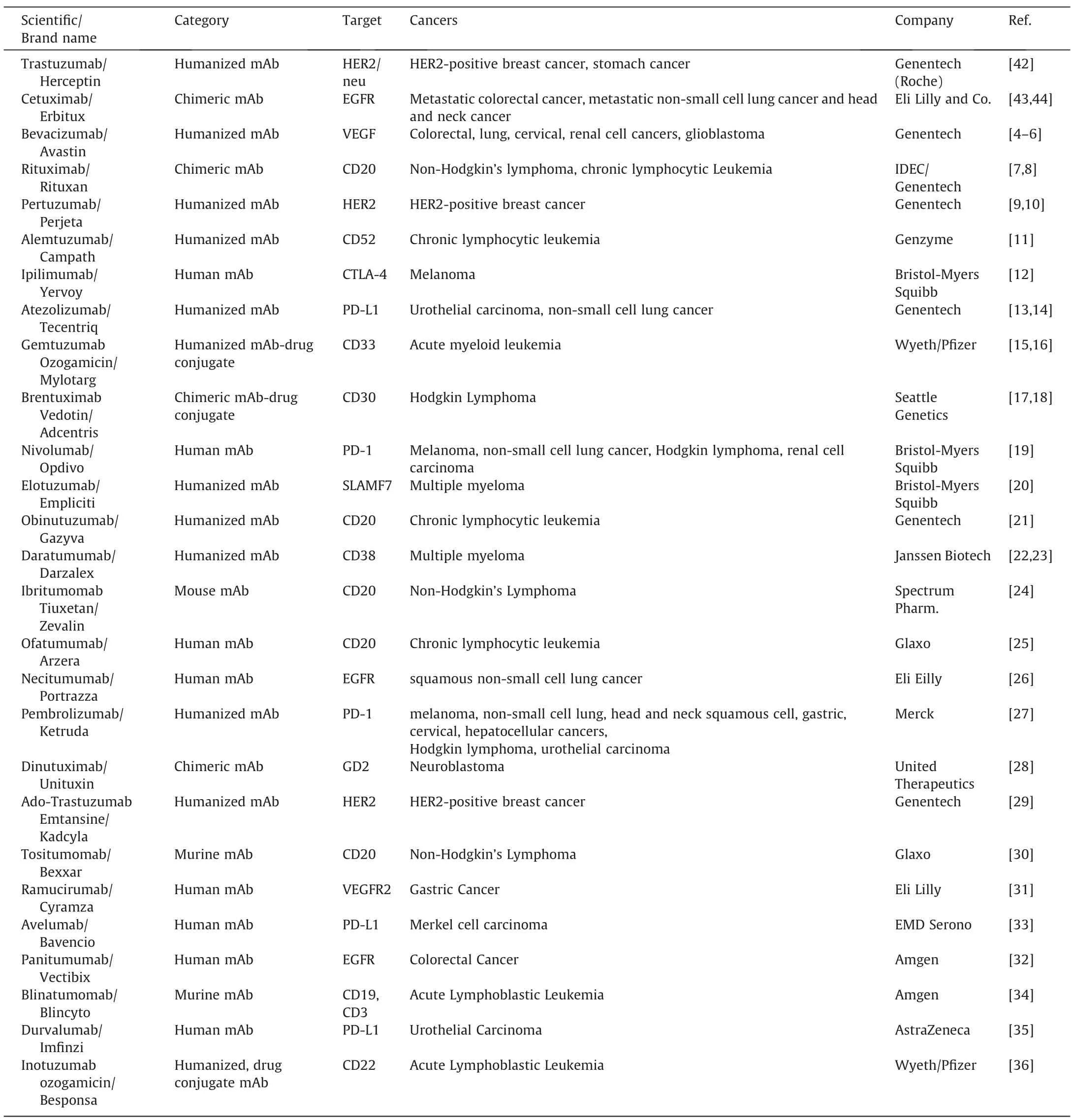
Table 1 Summary of commercialized mAb-based anti-cancer therapies.
3.2.Trastuzumab (humanized antibody)
A humanized antibody can be generated by substituting the CDR of a murine antibody with the corresponding CDR graft of a human antibody,which has a higher proportion of human regions(90%–94%) and more similarity to fully human antibody than chimeric antibody [7,27–31].Trastuzumab (Herceptin) is a humanized mAb utilized to treat the HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer,stomach cancer and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinomas.The anti-HER2 murine mAb was first developed through hybridoma technology by immunizing mice with NIH 3T3 cells that highly express human HER2 receptor.The hybridoma clone with high anti-HER2 mAb productivity and high HER2 selectivity was then screened.Finally,the variable region of mouse anti-HER2 antibody was grafted onto human antibody backbone,generating the humanized Trastuzumab [24,74–77].Trastuzumab can be used to treat breast cancer as a monotherapy or in combination with the thermotherapy paclitaxel.
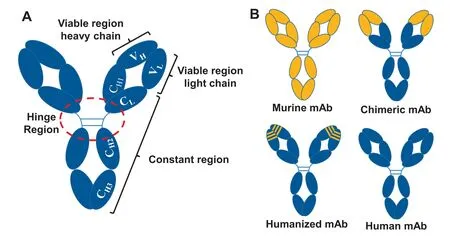
Fig.2.The structures of mAbs.A.Overall structure of mAb;B.Structures of mouse,chimeric,humanized,and fully human mAbs.
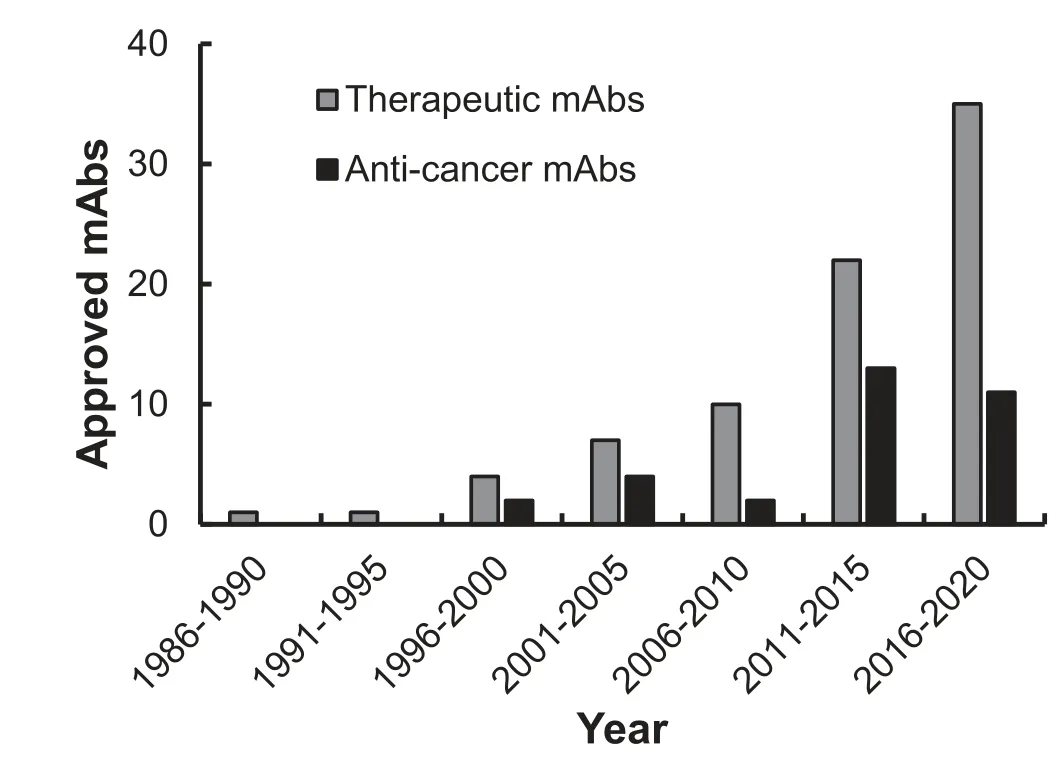
Fig.3.The USA FDA approved therapeutic mAbs.
3.3.Nivolumab (fully human antibody)
A fully human mAb can be generated by display technologies[25,26],transgenic animals [35,36],and human B cells [78–80].Nivolumab (Opdivo) is a PD-1-targeted IgG4 human antibody created from transgenic mice.In clinical applications,Nivolumab treats patients with metastatic melanoma,metastatic squamous cell or squamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma,and advanced renal cell carcinoma as a monotherapy or in combination with Ipilimumab (Yervoy) [80].The combination of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab improved the OS,PFS,and ORR in patients with metastatic melanoma compared to Nivolumab alone.
3.4.Catumaxomab (bispecific antibody)
A Bispecific Antibody(BsAb)can recognize two distinct antigen targets or epitopes simultaneously.BsAbs can be constructed by employing quadroma technology (biological) that somatically fuses two antibodies producing parent hybridomas into a hybridhybridoma cell[81–84],chemical conjugation that uses a chemical cross linker to couple different mAbs or fragments at their hinge cysteine residues [84–87],or recombinant DNA technologies (genetic) such as knobs-into-holes,leucine zippers,minibodies,diabodies,and single chain structures [30,31,82,83].Compared to traditional mAbs,BsAbs are advantageous in redirecting immune cells to tumor cells to maximize tumor killing,simultaneously blocking two different antigens to prevent activation of deleterious downstream pathways,increasing binding affinity,and avoiding potential antigen-loss relapse.Catumaxomab (Removab) is a bispecific antibody containing two binding specificities towards the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) and the T-cell antigen CD3[30,31,88,89].This BsAb is produced in a mouse-rat quadroma that contains one mouse IgG2a heavy-light chain and one rat IgG2b heavy-light chain.
4.Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC)
In addition to monotherapy,mAbs can be conjugated with highly potent chemotherapies to construct antibody-drug conjugates(ADCs)viathe conjugation sites(e.g.,free amines and thiols)and a chemical linker [90,91].Linkers with high stability in acidic and protease-rich environments both extracellularly and intracellularly have been developed,such as acid labile,reducible,enzyme-cleavable,and peptide-based linkers.As effective anticancer biopharmaceuticals,ADCs integrate the advantages of mAbs,which can specifically bind a tumor associated surface receptor and mediate cytotoxicity,with the potent cytotoxicity of small molecule chemotherapeutics.The mAb enables an ADC circulating through the bloodstream to bind the tumor specific surface antigen.After binding,the ADC is internalizedviareceptormediated endocytosis,a late endosome is formed,and lysosomal degradation releases cytotoxic drug into the cytoplasm,ultimately leading to cancer cell death [92].Multiple ADCs have been developed to effectively treat cancers in clinics while minimizing side effects in normal cells [93–99].Here we use three FDA approved ADCs as examples to describe the construction,anti-cancer mechanisms,and clinical applications of this mAb-directed therapy.
4.1.Gemtuzumab ozogamicin
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg) has been developed to treat CD33-positive acute myeloid leukemia(AML)[100–106].This ADC is composed of a humanized anti-CD33 IgG4 mAb (hP67.6)and N-acetyl gamma calicheamicin,a DNA-binding cytotoxic antibiotic,combined through an acid-cleavable hydrazone linker.The utilization of the lysine attachment site on the mAb can synthesize active hydrazone conjugates without oxidation of the carbohydrates.After targeting the surface CD33 receptor and internalizing,the hydrazone linker is hydrolytically cleaved and the potent payload is released intracellularly.The released Nacetyl gamma calicheamicin dimethyl hydrazide induces doublestranded DNA breaks and further leads to the apoptosis of cancer cells.The clinical data demonstrated that the gemtuzumab ozogamicin treatment group achieved event-free survival (EFS),relapse-free survival (RFS) and OS of 40.8% (32.8–50.8),50.3%(41.0–61.6) and 53.2% (44.6–63.5),respectively,without severe toxicity compared to EFS of 17.1% (10.8–27.1),RFS of 22.7%(14.5–35.7) and OS of 41.9% (33.1–53.1) in control group [107].
4.2.Brentuximab vedotin
Brentuximab vedotin(Adcetris)is constructed by conjugating a 153-kDa chimeric anit-CD30 IgG1 antibody with monomethyl auristatin Eviaa protease-cleavable linker with a drug-antibody ratio of approximate 4[108–111].Brentuximab vedotin was developed to treat classical Hodgkin lymphoma,systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma,and any CD30-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas.The mAb-delivered monomethyl auristatin E induces cancer cell apoptosis and cell death by binding the microtubule and disrupting its networks.Significant improvements in objective response and survival benefit were observed in brentuximab vedotin treated patients compared to conventional therapies [112].For instance,a Phase III clinical study with 128 enrolled patients showed that the objective response rate lasting at least 4 months(ORR4) was 56.3% in treatment groupversus12.5% in the conventional physician’s choice group.The brentuximab vedotin also extended the median progression-free survival to 17.2 months from 3.5 months in control group.
4.3.Trastuzumab emtansine
Trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla) is constructed by conjugating a humanized anti-HER2 IgG1 mAb with a microtubule inhibitory mertansine by a thioether chemical linker with a drugantibody ratio of about 3.5 to treat patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer [108,113–116].After the initial binding to the IV sub-domain of HER2 receptor,the ADC undergoes receptor-mediated internalization and lysosomal degradation.The cytotoxic small molecule released in breast cancer cells binds tubulin,disrupts microtubule synthesis,and ultimately leads to apoptosis and cell death.The clinical data showed that trastuzumab emtansine treatment improved the median progression-free survival of 6.2 (95% CI 5.59–6.87) with reduced incidence from 3.3 months (2.89–4.14) in control group [117].
5.Market Value and Technical Trend of mAb-based Therapies
With high therapeutic efficacy,mAbs have emerged as a major targeted treatment strategy of cancers,where the global market value of therapeutic mAbs was about 150 billion USD in 2019.Considering the numerous mAbs evaluated in clinical trials,the market will continue to grow with an estimated value of 300 billion USD by 2025 [7].The ADCs-based cancer therapies have made promising progress over the past decade because of the combined therapeutic values.The development and modification of new drugs,development of novel cancer-targeted mAbs (e.g.humanized mAbs),and design of new linkers to improve plasma stability and achieve controlled drug release in tumor could further advance the ADCs technologies.
6.Conclusions
mAb has evolved as an important biopharmaceutical in targeted anti-cancer delivery as monotherapy or as a conjugated therapy.Multiple platforms or technologies of therapeutic antibody development,including hybridoma technology,phage display,and transgenic mice,have been developed.Various engineered antibodies,such as chimeric,humanized,and fully human antibodies,have been developed to overcome the limitation of murine antibodies and are widely used in clinics.The other antibodyfacilitated targeted therapies,such as antibody-drug conjugates and antibody tagged polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery,have also been rapidly developed.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health R21CA226491-01A1 (X.M.L.),1R01CA238273-01A1 (X.M.L.) and 1R01CA242917-01A1 (X.M.L.).
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2021年2期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2021年2期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Molecular design,synthesis strategies and recent advances of hydrogels for wound dressing applications
- Recent advances in systemic and local delivery of ginsenosides using nanoparticles and nanofibers
- State of arts on the bio-synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles and their biological application
- Concepts,processing,and recent developments in encapsulating essential oils
- Engineering organoid microfluidic system for biomedical and health engineering:A review
- The potential of ionic liquids in biopharmaceutical engineering
