Malignant Syphilis as an Initial Presentation of HIV Infection:A Case Report
Khairuddin Djawad?
Department of Dermatology and Venereology,Faculty of Medicine,Hasanuddin University,Makassar,South Sulawesi90245,Indonesia.
Abstract
Keywords:malignant syphilis,human immunodeficiency virus infection,case report
Introduction
Malignant syphilis(MS)is a rare form of secondary syphilis which is frequently associated with human immunodeficiency virus(HIV)infection.1Since the beginning of the HIV epidemic,the incidence of MS has been steadily rising,making it a disease of vital recognition for any patient with suspicious cutaneous lesions.MS,also referred in the literature as syphilis maligna praecox,lues maligna,or rupioid syphilis,is defined as the presence of pleomorphic multiple round to oval papules,papulopustules,or nodules with ulceration,without central clearing,and occasionally exhibit a lamellate brown to black rupioid crust.This disease is characterized by marked prodromal constitutional symptom,such as fever,malaise,myalgia,headache,and weight changes over the span of4 weeks before the appearance of skin lesions.1
Characteristic morphology of lesions,positive serological tests for syphilis,characteristic histopathology,and resolution of lesions following administration of penicillin therapy confirmed the clinical diagnosis of MS.1Fisher et al.2defined the classical diagnostic criteria for MS as:compatible macroscopic and microscopic skin lesions,high serology titer,Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction(JHR)upon starting antibiotic treatment,and rapid clinical resolution with treatment.Here we report a case of MS and this was the initial presentation of HIV infection.
Case report
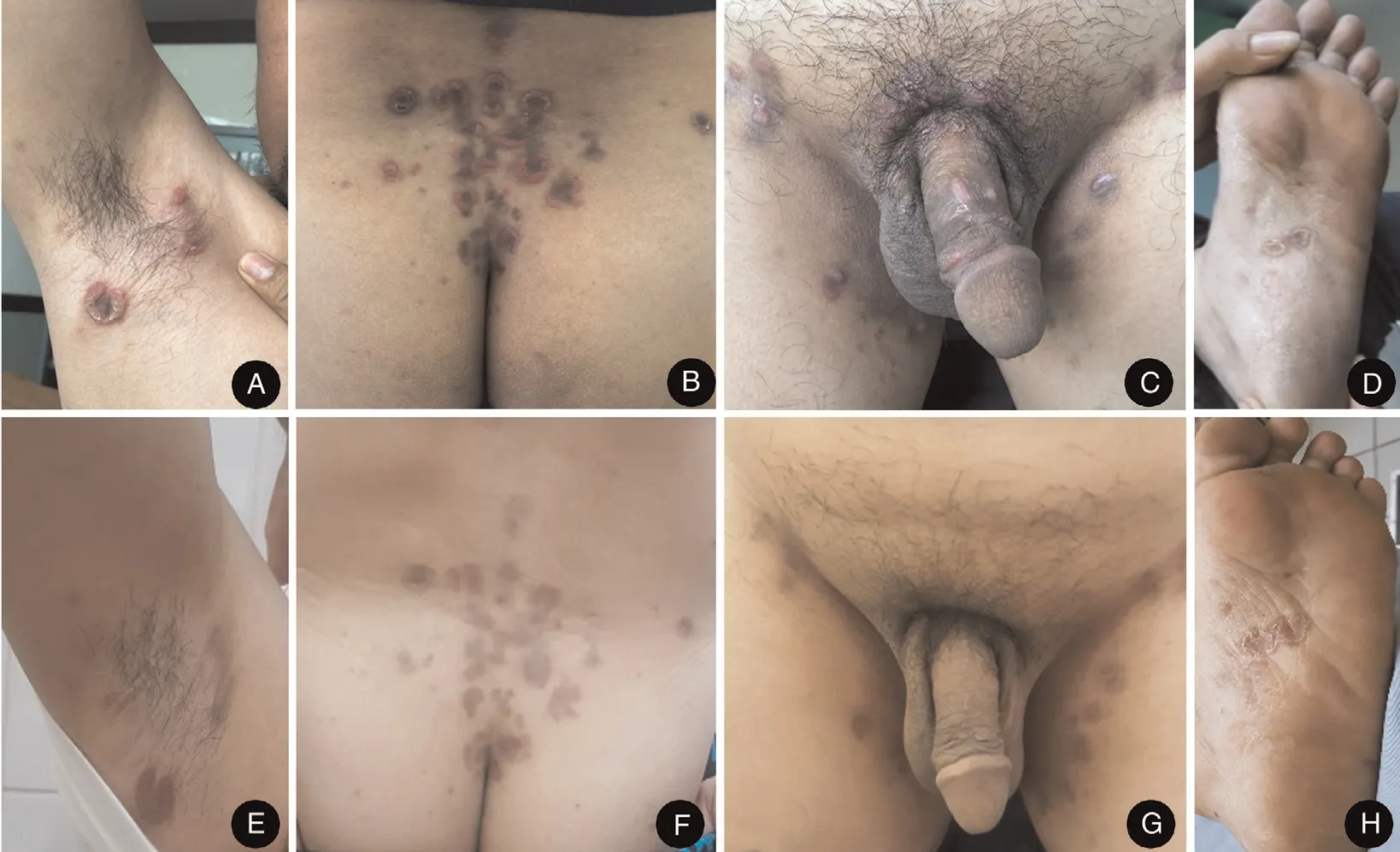
Figure1.Clinical presentation of the HIV patient with malignant syphilis.(A–D)Erythematous nodules multiple erythematous nodules occasionally ulcerative with round configuration.Rupioid lesions with central necrosis were found over the plantar regions.(E–H)Post-treatment showed post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and a few residual scars.
A35-year-old married male was admitted to the dermatology and venereology clinic of Wahidin Sudirohusodo Hospital,Makassar,South Sulawesi,Indonesia,with a1-month history of extensive erythematous nodular rash affecting the axilla,trunk,back,inguinal,penis,and soles accompanied with fever and malaise.Some lesions were ulcerated with annular configuration(Fig.1A–D).The lesions were painful and itchy with brown-black thick crust.No mucosal lesions were seen.He reported history of sexual intercourse with more than one partner.Past medical history was significant for gonorrhea,which was successfully treated and cured.
On clinical examination the patient had a temperature of 38.2°C,while other vital signs were within normal limit.He also complained of general malaise and headache.A skin biopsy was taken from the back and histological examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining showed epidermal hyperplasia with hyperkeratosis and acanthosis.In the dermis,lymphocytes,and histiocytes(Fig.2A)and very dense perivascular and periadnexal plasma cells(Fig.2B)were observed.These findings were consistent with syphilis.
Laboratory investigation revealed normal complete blood count,reactive rapid plasma reagin(1:128),and positive Treponema pallidum hemagglutination(1:5,120).The Hepatitis B surface antigen and anti-hepatitis C virus were non-reactive.Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for HIV was reactive with CD4cell count of291cells/mm3.
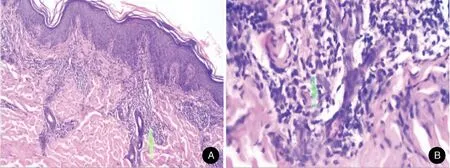
Figure2.Histological examination of the skin lesion from the HIV patient with malignant syphilis.(A)Hyperplastic epidermis with hyperkeratosis and acanthosis were found.In the dermis,there are lymphocytes,histiocytes,and very dense plasma cells in the perivascular interstitial area(arrow)(H&E,×40).(B)Periadnexa was found(arrow)(H&E,×200).
With the above clinical,laboratory,and histopathologic data taken into consideration,a diagnosis of MS with HIV infection was made.The patient was decided to be treated with intramuscular injection of2.4million units of benzathine penicillin G for three consecutive weeks.He was also treated with antiretroviral therapy with tenofovir 300mg,lamivudine300mg,and efavirenz600mg per day.Topical fusidic acid cream was also applied on ulcerative lesions to avoid bacterial superinfection.He responded very well to benzathine penicillin G and no JHR was seen during treatment.On follow-up visit,1week after the third injection,the patient presented with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and a view residual scars(Fig.1E–H).The patient gave his agreement for case publication.
Discussion
HIV infection may make clinical manifestations of syphilis more severe and/or atypical.Humoral and cellular immunity against Treponema pallidum depend on the stage of HIV infection and host defence;impairment in immunity may lead to changes in the clinical presentations and natural course of syphilis,increased number of syphilis lesion and degree of infectiousness,and shortened incubation time.A treponemal infection may act as a facilitator or aggravator forHIVtransmission from co-infectedpatients.3Co-infection of syphilis and HIV alters the course of both diseases.The clinical impact of HIV and syphilis coinfection is bidirectional;HIV alters the course of syphilis and syphilis also appears to adversely impact HIV disease progression and transmissibility.It is also associated with decreased CD4+T-cell counts and increased HIV viral loads.4Immunologic events that facilitate the development ofMS areunknown,but it isreasonable topostulate that the loss of helper T cells is responsible.One study found80%of HIV patients with MS had a CD4count greater than200 cells/mm3.5Our patient’s presenting CD4count was291 cells/mm3.These findings suggest that people with acute HIV infection,whose CD4count is still relatively high,maybe an at-risk population.
Although MS was described well before the HIV pandemic,more cases of MS have been described in people with HIV infection.Persons living with HIV/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome are60times more likely to present with this form of syphilis.5The onset of MS is characterized by prodromal symptoms composed of arthralgia,malaise,and fever.The lesions are characterized by erythematous-violaceous or reddish-coppery ulcerated papules,nodules,or blisters,followed by necrosis of the center of the lesion that may give rise to rupioid crusts that resemble an oyster shell.In some cases,they form small ulcers with welldefined edges,covered with purulent secretion without perilesional inflammatory reaction.The lesions mainly affect the trunk and extremities,but involvement of the mucosae,palms,soles,and scalp is also common.6
Fisher et al.2defined the classical diagnostic criteria for MS as compatible macroscopic and microscopic skin lesions,a high serology titer,JHR upon starting antibiotic treatment;and rapid clinical resolution with treatment.Based on the clinical presentation of the disease,darkfield microscopy performed on the fluid obtained from the lesional skin,syphilis serology,and histopathology characterized by dermal plasma cell admixed with lymphocytes,histiocytes,and neutrophilic venulitis is describe as a pattern of syphilis maligna,but spirochetes are infrequently found.7In this case,we were not able to identify spirochetes in dark-field microscopy;however,syphilis serology was highly positive and the histopathology was typical with the findings of numerous plasma cell infiltrates in the dermis.Intramuscular injection of benzathine penicillin G2.4million units weekly for three consecutive weeks is the recommended treatment option for MS.As has been previously described in literature our patient also responded very quickly to the antibiotic therapy with Benzathine-penicillin G.
While JHR is one of the diagnostic criteria in MS as proposed by Fisher has been widely reported in several studies and case reports,Bjekic′8and Fustà-Novell et al.9have also described MS patients with no JHR.JHR is an acute febrile inflammatory reaction that happens after antibiotic treatment of syphilis especially as well as of other spirochetal infections.The symptoms include fever,chills,headache,myalgias,exacerbation of cutaneous lesions,tachycardia,and hyperventilation during the first 24hours after the treatment.Our case exhibited a similar phenomenon,where although both the treponemal and non-treponemal titers were high,no JHR occurred upon administration of intramuscular Benzathine-penicillin G.However,the absence of this reaction was not considered a reason to rule out a diagnosis of MS,nor did it appear to have any bearing on the specific clinical presentation.
In conclusion,the diagnosis of MS should be considered in all HIV-infected individuals with noduloulcerative skin lesions.This approach might avoid unnecessary efforts or more complex investigations in such patients.
- 國(guó)際皮膚性病學(xué)雜志的其它文章
- Mask on Followed by Gloves on:Do We Have a Choice?
- Mobilization of Melanocytes During NB-UVB Treatment of Vitiligo
- Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Melasma in China(2021Version)#
- Retiform Hemangioendothelioma
- Treatment of Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome by Surgery Combined With ALA-PDT:A Case Report
- Scrofuloderma:A Rare Case Report of Sequelae of Intestinal Tuberculosis

