一個(gè)基于丹磺?;臒晒馓结樀暮铣珊捅碚?/h1>
2013-10-17 03:02王繼猛舒威虎馬志剛陳雪梅
無機(jī)化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào) 2013年1期
張 勇 王繼猛 舒威虎 陳 其 馬志剛 陳雪梅
(湖北理工學(xué)院化學(xué)與材料工程學(xué)院,黃石 435003)
0 Introduction
Fe3+ion plays important role in all living cells.It is present in the structure of many enzymes and proteins and therefore essential for cellular metabolism,however,exceeding concentrations of Fe3+ion can also be detrimental.Thus,detection of Fe3+ion is essential for monitoring the environment and human health.Because of its operational simplicity,low cost,real time monitoring and high selectivity,fluorescent detection has become the promising strategy used for Fe3+detection[1].However,the examples of Fe3+-selective fluorescent probes are still scarce owing to its easy to be interfered by other transition-metal ions,though iron plays an important role in life and environment.At present,there are a few of Fe3+ion fluorescence probes reported[2-8].Therefore,designing a selective sensor for Fe3+is still a challenge.The dansyl group is often chosen as a fluorophore for the construction of the chemosensor due to its strong fluorescence,relatively long emission wavelength in the visible region and structuralflexibility for derivatization[9-10].We show great interest in preparing fluorescent probes bearing the dansyl group that are expected to detect Fe3+ions.In this paper,we report the synthesis,crystal structure and fluorescent properties of a dansyl-based fluorescent sensor.
1 Experimental
All reagents were purchased from commercial companies and directly used unless stated otherwise.Solvents were purified by the most used methods.The melting pointwas determined with an XT4A micromelting point apparatus and was uncorrected.The1H NMR spectra were recorded on a Mercury Plus-400 spectrometer in CDCl3.The IR spectra were measured on a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum BX FT-IR instrument in tablets with potassium bromide.Elemental analyses were carried out on a Vario ELⅢinstrument.UV-Visspectrawererecorded on a Shimadzu UV-265 spectrophotometer.Fluorescence spectra were performed on a FluoroMax-P spectrofluorimeter.
1.1 Preparation of probe 2
The intermediate 1 was prepared as the literature method[11].The synthesis route of fluorescent probe 2 is outlined in Scheme 1.The intermediate 1 (0.31 g,0.1 mmol)and K2CO3(0.28 g,0.2 mmol)was added to a solution of dansyl chloride (0.27 g,0.1 mmol)in MeCN (60 mL).The mixture was refluxed for 12 h under stirring.The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC.After concentration under reduced pressure,the yellow crude product was purified via column chromatography(silica,petroleum ether/AcOEt,4/1,V/V),yield:75%.m.p.173~175 ℃.UV-Vis spectra(λmax,nm(ε,L·mol-1·cm-1)):(MeOH solution)364 (28 970).IR (KBr):2 947,1 572,1 474,1 325,1141,1078,934,802,754 cm-1.1H NMR(400 MHz,CDCl3,ppm): δ 8.39 (dd,J=15.2,8.6 Hz,2H),8.08(dd,J=7.3,1.0 Hz,1H),7.59~7.52 (m,2H),7.51~7.45(m,1H),7.27(s,1H),7.20~7.13(m,4H),7.11(d,J=7.4 Hz,1H),7.05 (dd,J=6.3,2.9 Hz,2H),4.99(s,4H),3.64 (s,6H),2.82 (s,6H).Anal.Calcd.for C30H30N6O2S(%):C,66.89,H,5.61;N,15.60;Found(%):C,66.35;H,5.45;N,15.93.
1.2 X-ray crystallography

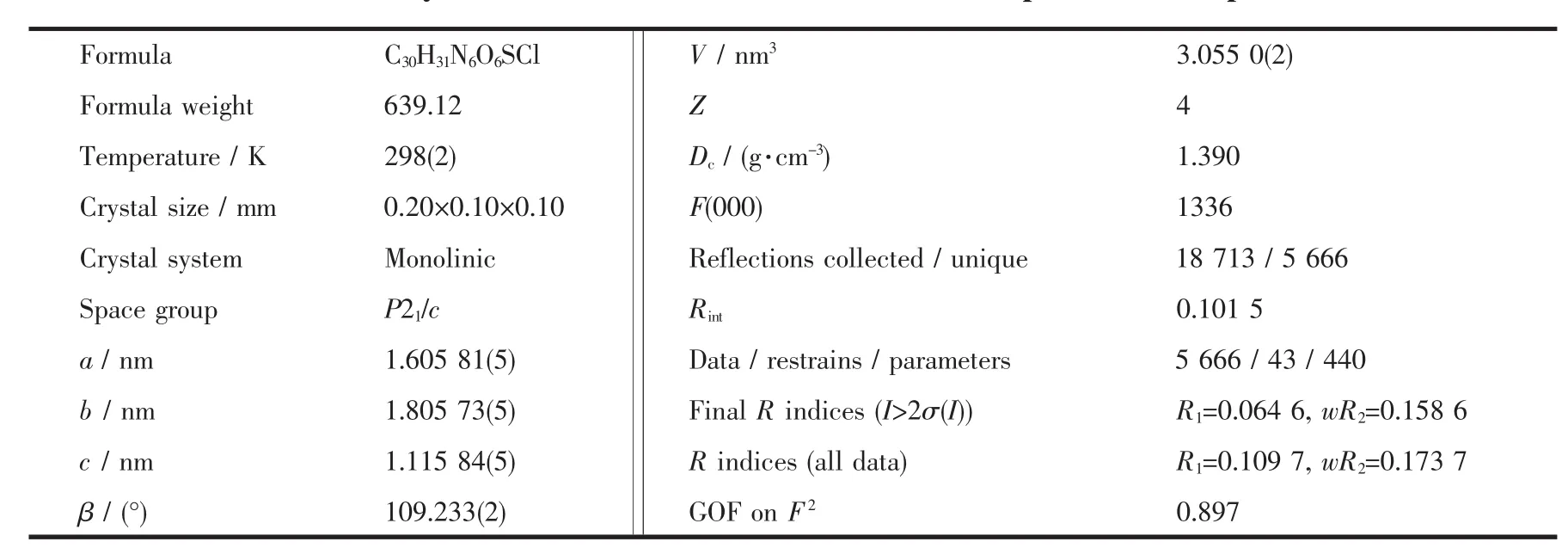
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinements of the perchlorate of probe 2
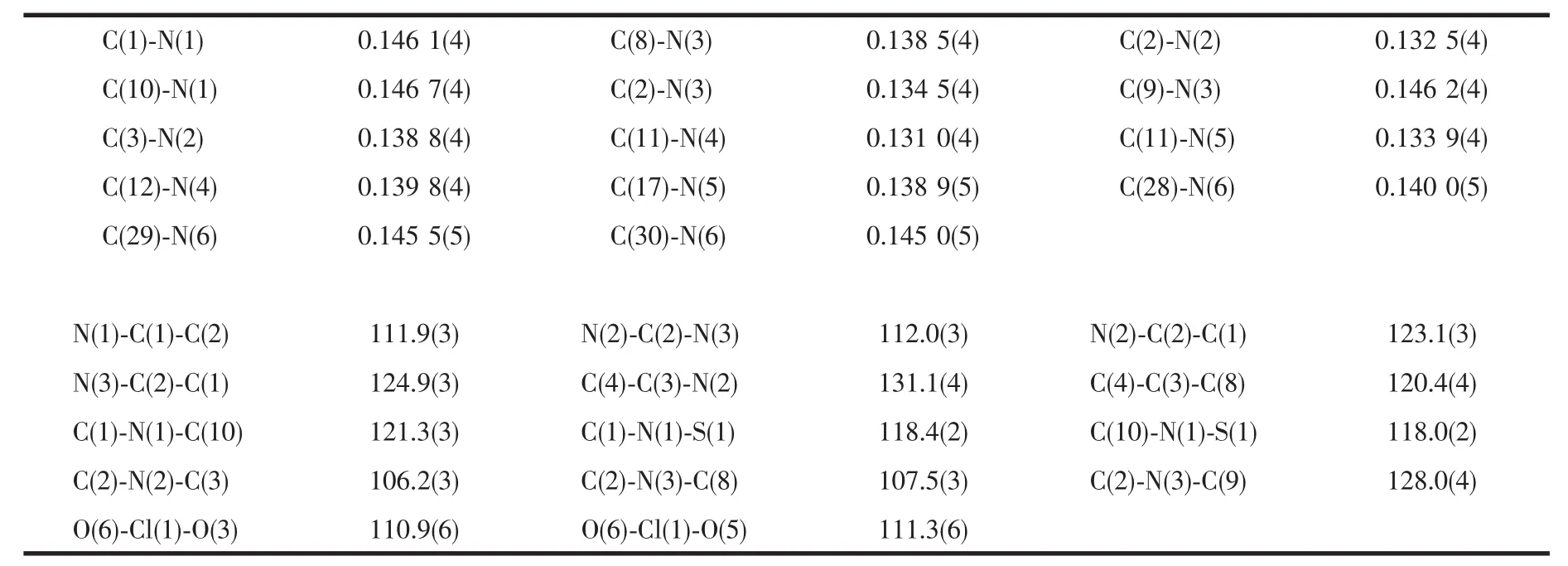
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)of the perchlorate of probe 2
To confirm the structure of probe 2,a few drops of perchloric acid was added to methane solution of probe 2,Yellow crystals of its perchlorate salt suitable for X-ray diffraction were got by slow evaporation at room temperature.Thetitlecompound 2 having approximate dimensions of 0.2 mm ×0.10 mm ×0.10 mm was mounted on a glass fibre in a random orientation at 298(2)K.The determination of unit cell and the data collection were performed with Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)on a Bruker Smart APEX-CCD diffactometer with a ψ-ω scan mode.A total of 18 713 reflections were collected in the range of 1.75°<θ<25.50°at room temperature.The structures were solved by direct methods and semi-empirical absorption corrections were applied.The non-hydrogen atoms were located by direct and were refined on F2by full matrix least squares,while the hydrogen atoms for non-water protons were treated using the riding mode.All calculations were carried out on a PC using SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97 programs[12-13].The detailed crystallographic data are listed in Table 1,and the selected bond parameters are given in Table 2.
CCDC:867156.
1.3 Fluorescent assay
Fluorescence spectra measurements were performed on a FluoroMax-P spectrofluorimeter.All pH measurements were made with a Model pHS-3C pH meter (Shanghai,China).The solutions of metal ionswereprepared from theirchloride saltsof analytical grade.A 1.0 mmol·L-1stock solution of probe 2 was prepared in absolute DMSO.For the selective fluorescent response experiments,to 5 mL glass tubes with 3.96 mL Tris-HCl buffer(100 mmol·L-1,pH 7.4)containing different amount of metal ions,40 μmol·L-1of probe 2 stock solution was added to each tube by a pippet to obtain solutions of 10 μmol·L-1probe 2 (VH2O∶VDMSO=9∶1).After well mixed,the samples were incubated for10 min atroom temperature prior to measurements.The excitation wavelength was 365 nm.The quantum yield (ΦF)for fluorescence emission was determined by comparison with the integrated and corrected emission spectrum of quinine sulfate (a standard),whose quantum yield in 0.05 mol·L-1H2SO4was assumed to be 0.55(excitation at 366 nm).10 μmol·L-1probe 2 in DMSO solution wasprepared.Theconcentration ofthe reference was adjusted to match the absorbance of the test sample at the wavelength of excitation.Emission for probe 2 was integrated from 480 to 660 nm with excitation at 365 nm.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Synthesis and structure
The perchlorate salt of probe 2 was characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction,as shown in Fig.1.In the crystal,N(4)of the benzimidazole ring is found to be protonized.The C-N bond distances range from 0.131 0(4)to 0.146 7(4)nm,and the C-N(amino)bonds are longer than the C-N (benzothiazolyl)bonds(Table1).Thedihedralanglebetween the two benzothiazole ring systems is 12.99°,while that between the naphthalene ring and each benzothiazole ring is 82.25°and 71.15°,respectively.Atoms N6 and S1 are located approximately in the naphthalene ring plane with their deviations being 0.002 5 and 0.002 4 nm.The torsion angles of S1-N1-C1-C2 and S1-N1-C10-C11 are 80.88°and-106.47°,which lead to Y-shape of the whole molecule.
2.2 Fluorescent response of probe 2 to Fe3+
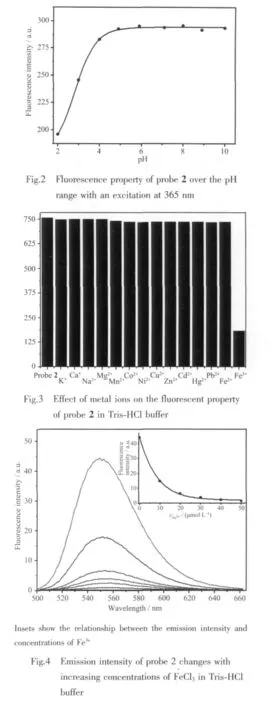
The maximum excitation (λex)and emission(λem)wavelengths of fluorescent probe 2 were 365 and 545 nm,respectively.It exhibited a relatively high fluorescence quantum yield (ΦF=0.67).The fluorescence property of probe 2 was not significantly changed in the differentsolvents such as MeOH,CH2Cl2,CH3COOCH2CH3,DMSO and so on.The emission intensity at 545 nm of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)remained nearly constant in the range of pH 5.0~10.0 at room temperature (Fig.2),which indicated it was stable under the physiological pH condition.It′s found that the fluorescence spectra of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)were not altered by addition of the tested metal ions(10 μmol·L-1)except Fe3+at the given concentrations,and no such significant response was noticed in other metal ions(Fig.3).The fluorescence intensity of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)was nearly quenched 70%when reacted with Fe3+(10 μmol·L-1),showed that probe 2 was selective in the detection Fe3+.When the concentration of Fe3+was increased from 0 to 50 μmol·L-1and keptotherfactorsunchanged undernearly physiological conditions,the fluorescence of probe 2 was quenched little by little(Fig.4).The selectivity of probe 2 toward Fe3+was further confirmed by the competition experiment (Fig.5).Thefluorescence changes of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)were measured by the treatment of 1 equiv Fe3+ion in the presence of 10 equiv other interfering metal ions in the presence of representative alkali metals,alkali earth metals and other transition-metal salts.The tested background metal ions showed small or no interference with the detection of Fe3+.To further investigate the interaction of probe 2 and Fe3+,a fluorescence titration experiment was carried out.Binding analysis using the method of continuous variations(Job′s plot)established that the stoichiometry of the probe 2-Fe3+complex was estimated to be 1∶1 (Fig.6).It can be concluded that two N atoms of the benzimidazole rings and the N atom of sulfamide group of probe 2 were coordinated with Fe3+.

3 Conclusions
In summary,we have synthesized a novel dansylbased fluorescent probe 2,the structure of its perchlorate was characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction.Our fluorescent study showed that probe 2 was selective to Fe3+and formed a 1∶1 complex with Fe3+.
[1]de Silva A P,Gunaratne H Q N,Gunnlaugsson T,et al.Chem.Rev.,1997,97:1515-1566
[2]Hu Z Q,Feng Y C,Huang H Q,et al.Sens.Actuat.B:Chem.,2011,156:428-432
[3]Yao J N,Dou W,Qin W W,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2009,12:116-118
[4]Peng R G,Wang F,Sha Y W.Molecules,2007,12:1191-1201
[5]Zhang Y,Ma Z G,Ku Z J.J.Chem.Res.,2011,11:626-627
[6]Ma Y,Luo W,Quinn P J,et al.J.Med.Chem.,2004,47:6349-6362
[7]Weizman H,Ardon O,Mester B,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,1996,118:12368-12375
[8]YI Wei-Guo(易衛(wèi)國),CAO Zhong(曹忠),YIN Dong(鄢東),et al.Chinese J.of Anal.Chem.(Fenxi Huaxue),2012,40(7):113-118
[9]Kavallieratos K,Rosenberg J M,Chen W Z,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2005,127:6514-6515
[10]Lim M H,Lippard S J.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45:8980-8989
[11]Casella L,Carugo O,Gullotti M,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1996,35:1101-1113
[12]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,A Program for the Solution of Crystal Structures,University of G?ttingen,Germany,1997.
[13]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,A Program for the Refinement ofCrystalStructures,University ofG?ttingen,Germany,1997.
猜你喜歡
黃石國家公園慶祝150年蠻荒歲月——這是怎樣的歷史英語文摘(2022年5期)2022-06-05 奮力創(chuàng)造建設(shè)現(xiàn)代化新黃石的嶄新業(yè)績黨員生活(2022年2期)2022-04-24 基于FANUC數(shù)控系統(tǒng)的馬波斯探針標(biāo)定原理及應(yīng)用裝備制造技術(shù)(2020年1期)2020-12-25 黃石俱樂部度假別墅現(xiàn)代裝飾(2020年11期)2020-11-27 黃石高速公路改造項(xiàng)目中互聯(lián)網(wǎng)+工程建設(shè)管理系統(tǒng)的應(yīng)用中國交通信息化(2019年11期)2019-08-13 N-月桂?;劝彼猁}性能的pH依賴性中國洗滌用品工業(yè)(2017年2期)2017-04-16 多通道Taqman-探針熒光定量PCR鑒定MRSA方法的建立現(xiàn)代檢驗(yàn)醫(yī)學(xué)雜志(2016年3期)2016-11-15 當(dāng)代化工研究(2016年2期)2016-03-20 N-脂肪?;被猁}的合成、性能及應(yīng)用中國洗滌用品工業(yè)(2016年2期)2016-02-28 α-甲氧甲?;?γ-丁內(nèi)酯和α-乙氧甲酰基-γ-丁內(nèi)酯的合成及表應(yīng)用化工(2014年5期)2014-08-08
張 勇 王繼猛 舒威虎 陳 其 馬志剛 陳雪梅
(湖北理工學(xué)院化學(xué)與材料工程學(xué)院,黃石 435003)
0 Introduction
Fe3+ion plays important role in all living cells.It is present in the structure of many enzymes and proteins and therefore essential for cellular metabolism,however,exceeding concentrations of Fe3+ion can also be detrimental.Thus,detection of Fe3+ion is essential for monitoring the environment and human health.Because of its operational simplicity,low cost,real time monitoring and high selectivity,fluorescent detection has become the promising strategy used for Fe3+detection[1].However,the examples of Fe3+-selective fluorescent probes are still scarce owing to its easy to be interfered by other transition-metal ions,though iron plays an important role in life and environment.At present,there are a few of Fe3+ion fluorescence probes reported[2-8].Therefore,designing a selective sensor for Fe3+is still a challenge.The dansyl group is often chosen as a fluorophore for the construction of the chemosensor due to its strong fluorescence,relatively long emission wavelength in the visible region and structuralflexibility for derivatization[9-10].We show great interest in preparing fluorescent probes bearing the dansyl group that are expected to detect Fe3+ions.In this paper,we report the synthesis,crystal structure and fluorescent properties of a dansyl-based fluorescent sensor.
1 Experimental
All reagents were purchased from commercial companies and directly used unless stated otherwise.Solvents were purified by the most used methods.The melting pointwas determined with an XT4A micromelting point apparatus and was uncorrected.The1H NMR spectra were recorded on a Mercury Plus-400 spectrometer in CDCl3.The IR spectra were measured on a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum BX FT-IR instrument in tablets with potassium bromide.Elemental analyses were carried out on a Vario ELⅢinstrument.UV-Visspectrawererecorded on a Shimadzu UV-265 spectrophotometer.Fluorescence spectra were performed on a FluoroMax-P spectrofluorimeter.
1.1 Preparation of probe 2
The intermediate 1 was prepared as the literature method[11].The synthesis route of fluorescent probe 2 is outlined in Scheme 1.The intermediate 1 (0.31 g,0.1 mmol)and K2CO3(0.28 g,0.2 mmol)was added to a solution of dansyl chloride (0.27 g,0.1 mmol)in MeCN (60 mL).The mixture was refluxed for 12 h under stirring.The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC.After concentration under reduced pressure,the yellow crude product was purified via column chromatography(silica,petroleum ether/AcOEt,4/1,V/V),yield:75%.m.p.173~175 ℃.UV-Vis spectra(λmax,nm(ε,L·mol-1·cm-1)):(MeOH solution)364 (28 970).IR (KBr):2 947,1 572,1 474,1 325,1141,1078,934,802,754 cm-1.1H NMR(400 MHz,CDCl3,ppm): δ 8.39 (dd,J=15.2,8.6 Hz,2H),8.08(dd,J=7.3,1.0 Hz,1H),7.59~7.52 (m,2H),7.51~7.45(m,1H),7.27(s,1H),7.20~7.13(m,4H),7.11(d,J=7.4 Hz,1H),7.05 (dd,J=6.3,2.9 Hz,2H),4.99(s,4H),3.64 (s,6H),2.82 (s,6H).Anal.Calcd.for C30H30N6O2S(%):C,66.89,H,5.61;N,15.60;Found(%):C,66.35;H,5.45;N,15.93.
1.2 X-ray crystallography


Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinements of the perchlorate of probe 2

Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)of the perchlorate of probe 2
To confirm the structure of probe 2,a few drops of perchloric acid was added to methane solution of probe 2,Yellow crystals of its perchlorate salt suitable for X-ray diffraction were got by slow evaporation at room temperature.Thetitlecompound 2 having approximate dimensions of 0.2 mm ×0.10 mm ×0.10 mm was mounted on a glass fibre in a random orientation at 298(2)K.The determination of unit cell and the data collection were performed with Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)on a Bruker Smart APEX-CCD diffactometer with a ψ-ω scan mode.A total of 18 713 reflections were collected in the range of 1.75°<θ<25.50°at room temperature.The structures were solved by direct methods and semi-empirical absorption corrections were applied.The non-hydrogen atoms were located by direct and were refined on F2by full matrix least squares,while the hydrogen atoms for non-water protons were treated using the riding mode.All calculations were carried out on a PC using SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97 programs[12-13].The detailed crystallographic data are listed in Table 1,and the selected bond parameters are given in Table 2.
CCDC:867156.
1.3 Fluorescent assay
Fluorescence spectra measurements were performed on a FluoroMax-P spectrofluorimeter.All pH measurements were made with a Model pHS-3C pH meter (Shanghai,China).The solutions of metal ionswereprepared from theirchloride saltsof analytical grade.A 1.0 mmol·L-1stock solution of probe 2 was prepared in absolute DMSO.For the selective fluorescent response experiments,to 5 mL glass tubes with 3.96 mL Tris-HCl buffer(100 mmol·L-1,pH 7.4)containing different amount of metal ions,40 μmol·L-1of probe 2 stock solution was added to each tube by a pippet to obtain solutions of 10 μmol·L-1probe 2 (VH2O∶VDMSO=9∶1).After well mixed,the samples were incubated for10 min atroom temperature prior to measurements.The excitation wavelength was 365 nm.The quantum yield (ΦF)for fluorescence emission was determined by comparison with the integrated and corrected emission spectrum of quinine sulfate (a standard),whose quantum yield in 0.05 mol·L-1H2SO4was assumed to be 0.55(excitation at 366 nm).10 μmol·L-1probe 2 in DMSO solution wasprepared.Theconcentration ofthe reference was adjusted to match the absorbance of the test sample at the wavelength of excitation.Emission for probe 2 was integrated from 480 to 660 nm with excitation at 365 nm.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Synthesis and structure
The perchlorate salt of probe 2 was characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction,as shown in Fig.1.In the crystal,N(4)of the benzimidazole ring is found to be protonized.The C-N bond distances range from 0.131 0(4)to 0.146 7(4)nm,and the C-N(amino)bonds are longer than the C-N (benzothiazolyl)bonds(Table1).Thedihedralanglebetween the two benzothiazole ring systems is 12.99°,while that between the naphthalene ring and each benzothiazole ring is 82.25°and 71.15°,respectively.Atoms N6 and S1 are located approximately in the naphthalene ring plane with their deviations being 0.002 5 and 0.002 4 nm.The torsion angles of S1-N1-C1-C2 and S1-N1-C10-C11 are 80.88°and-106.47°,which lead to Y-shape of the whole molecule.
2.2 Fluorescent response of probe 2 to Fe3+
The maximum excitation (λex)and emission(λem)wavelengths of fluorescent probe 2 were 365 and 545 nm,respectively.It exhibited a relatively high fluorescence quantum yield (ΦF=0.67).The fluorescence property of probe 2 was not significantly changed in the differentsolvents such as MeOH,CH2Cl2,CH3COOCH2CH3,DMSO and so on.The emission intensity at 545 nm of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)remained nearly constant in the range of pH 5.0~10.0 at room temperature (Fig.2),which indicated it was stable under the physiological pH condition.It′s found that the fluorescence spectra of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)were not altered by addition of the tested metal ions(10 μmol·L-1)except Fe3+at the given concentrations,and no such significant response was noticed in other metal ions(Fig.3).The fluorescence intensity of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)was nearly quenched 70%when reacted with Fe3+(10 μmol·L-1),showed that probe 2 was selective in the detection Fe3+.When the concentration of Fe3+was increased from 0 to 50 μmol·L-1and keptotherfactorsunchanged undernearly physiological conditions,the fluorescence of probe 2 was quenched little by little(Fig.4).The selectivity of probe 2 toward Fe3+was further confirmed by the competition experiment (Fig.5).Thefluorescence changes of probe 2 (10 μmol·L-1)were measured by the treatment of 1 equiv Fe3+ion in the presence of 10 equiv other interfering metal ions in the presence of representative alkali metals,alkali earth metals and other transition-metal salts.The tested background metal ions showed small or no interference with the detection of Fe3+.To further investigate the interaction of probe 2 and Fe3+,a fluorescence titration experiment was carried out.Binding analysis using the method of continuous variations(Job′s plot)established that the stoichiometry of the probe 2-Fe3+complex was estimated to be 1∶1 (Fig.6).It can be concluded that two N atoms of the benzimidazole rings and the N atom of sulfamide group of probe 2 were coordinated with Fe3+.


3 Conclusions
In summary,we have synthesized a novel dansylbased fluorescent probe 2,the structure of its perchlorate was characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction.Our fluorescent study showed that probe 2 was selective to Fe3+and formed a 1∶1 complex with Fe3+.
[1]de Silva A P,Gunaratne H Q N,Gunnlaugsson T,et al.Chem.Rev.,1997,97:1515-1566
[2]Hu Z Q,Feng Y C,Huang H Q,et al.Sens.Actuat.B:Chem.,2011,156:428-432
[3]Yao J N,Dou W,Qin W W,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2009,12:116-118
[4]Peng R G,Wang F,Sha Y W.Molecules,2007,12:1191-1201
[5]Zhang Y,Ma Z G,Ku Z J.J.Chem.Res.,2011,11:626-627
[6]Ma Y,Luo W,Quinn P J,et al.J.Med.Chem.,2004,47:6349-6362
[7]Weizman H,Ardon O,Mester B,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,1996,118:12368-12375
[8]YI Wei-Guo(易衛(wèi)國),CAO Zhong(曹忠),YIN Dong(鄢東),et al.Chinese J.of Anal.Chem.(Fenxi Huaxue),2012,40(7):113-118
[9]Kavallieratos K,Rosenberg J M,Chen W Z,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2005,127:6514-6515
[10]Lim M H,Lippard S J.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45:8980-8989
[11]Casella L,Carugo O,Gullotti M,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1996,35:1101-1113
[12]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,A Program for the Solution of Crystal Structures,University of G?ttingen,Germany,1997.
[13]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,A Program for the Refinement ofCrystalStructures,University ofG?ttingen,Germany,1997.