Stochastic convergence analysis of cubature Kalman filter with intermittent observations
SHI Jie,QI Guoqing,LI Yinya,and SHENG Andong
1.School of Automation,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing 210094,China;
2.NARI Group Corporation/State Grid Electric Power Research Institute,Nanjing 211000,China
Abstract:The stochastic convergence of the cubature Kalman filter with intermittent observations(CKFI)for general nonlinear stochastic systems is investigated.The Bernoulli distributed random variable is employed to describe the phenomenon of intermittent observations.According to the cubature sample principle,the estimation error and the error covariance matrix(ECM)of CKFI are derived by Taylor series expansion,respectively.Afterwards,it is theoretically proved that the ECM will be bounded if the observation arrival probability exceeds a critical minimum observation arrival probability.Meanwhile,under proper assumption corresponding with real engineering situations,the stochastic stability of the estimation error can be guaranteed when the initial estimation error and the stochastic noise terms are sufficiently small.The theoretical conclusions are verified by numerical simulations for two illustrative examples;also by evaluating the tracking performance of the optical-electric target tracking system implemented by CKFI and unscented Kalman filter with intermittent observations(UKFI)separately,it is demonstrated that the proposed CKFI slightly outperforms the UKFI with respect to tracking accuracy as well as real time performance.
Keywords:cubature Kalman filter(CKF),intermittent observation,estimation error,stochastic stability.
1.Introduction
The nonlinear state estimation problem is a hot research topic that has attracted considerable interest during the past decades.A great deal of suboptimal approaches have been proposed to deal with the nonlinear filtering problem,such as extended Kalman filter(EKF)[1],unscented Kalman filter(UKF)[2,3],and particle filter(PF)[4,5].These methods mentioned above have been successfully adopted in many applications,including simultaneous localization and mapping(SLAM)problem[6],state estimation in power systems[7],maneuvering target tracking with a multistatic radar system[8],and so forth.
In 2010,a new nonlinear filter called cubature Kalman filter(CKF)was proposed by Arasaratnam and Haykin[9,10].The CKF was developed on the basis of the spherical-radial cubature rule that is a useful way to numerically compute multivariate moment integrals encountered in the nonlinear Bayesian filtering problems[11].Similar to the UKF,it is also not necessary to compute the Jacobian matrix which is the basis of EKF.The CKF only propagates 2n equal-weighted cubature points through a nonlinear function to approximate the mean and covariance of state and measurement vector[12].Meanwhile,the sigma points of UKF have some adjustment parameters that should be set reasonably while the weights of cubature points of CKF are fixed.The CKF can achieve better estimation performance compared to the EKF and UKF,especially for high-dimensional nonlinear filtering problems,e.g.,state estimation of chemical reaction[13],spacecraft attitude and position estimation[14],maneuvering target tracking[15],bearings-only tracking[16],GPS/IMU tightly-coupled navigation system[17],etc.Most importantly,in[18,19],by the linearization of the nonlinear model,the convergence analysis and the estimation performance of CKF for nonlinear discrete-time systems were investigated.
In practical engineering,however,the estimator may be implemented under the condition that the observations contain missing measurements.Generally,the reasons for the phenomenon of intermittent observations can be classified into the following two aspects.For one thing,it is quite common in practice that the observations may not be acquired caused by the high maneuver ability of the tracked target,intermittent sensor failures or accidental loss of some collected data[20,21].For another,the observations could be lost or delayed due to the transmission failure and signal fluctuation of the communication channel between the sensor and estimator[22,23].Therefore,the effect of intermittent observations in practical engineering applications must be highly considered.Early interesting results on linear estimation with intermittent observations can be traced back to[24].In[24],the arrival of observations was modeled as an independent,identically distributed(i.i.d)Bernoulli process and the existence of a corresponding critical probability has been shown to guarantee the boundedness of the error covariance matrix(ECM).Afterward,a two state Markov chain was introduced to model the arrival of observations in [25], where the sufficient condition for the boundedness of peak ECM was presented.Recently,a necessary condition and a sufficient condition were derived for the boundedness of the expected value of the ECM of the Kalman filter with intermittent observations[26].
On the other hand,in the case of nonlinear filtering with intermittent observations,considerable publications can be retrieved in the literature(see,e.g.[27-31]and the references therein).The stochastic stability problems of the EKF-based estimation methods for general nonlinear systems with intermittent observations were investigated in[27,28].In[27],under appropriate assumptions,a critical probability also existed to ensure the boundedness of the prediction ECM,and the estimation error was exponentially bounded in mean square if the ECM and the initial estimation error remain bounded.The stochastic stability analysis of a new extended filtering(EF)subject to measurement packet losses was presented in[28].Similar to the case in[27],conditions for guaranteeing the stochastic stability of the UKF with intermittent observations(UKFI)have been developed in[29,30].In addition,the peak ECM stability ofUKFI was studied in[31],where the arrival of observations was modeled as a two state time homogeneous Markov process.
Above all,the stochastic convergence analysis of CKF with complete observations has been conducted in[18].In contrast to the theoretical research of[18],we focus on the CKF-based state estimation problem for nonlinear systems with intermittent observations,which often occur in practical applications such as target tracking.The main contribution of this work can be highlighted as follows:
(i)The Taylor series expansion is adopted to derive the estimation error and ECM of the CKF with intermittent observations(CKFI),which enables us to analyze the stochastic convergence of CKFI.
(ii)The conditions are provided regarding the boundedness of ECM and the stochastic stability of estimation error,respectively.
(iii)To compare the estimation performances of the proposed CKFI and UKFI,both algorithms are implemented in the optic-electric target tracking system.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows:Section 2 establishes the filtering framework of CKFI.The estimation errors and ECM of CKFI are derived in Section 3.The theoretical results on the boundedness of ECM and the stochastic stability of estimation error are provided in Section4and Section5,respectively.Section6 presents two illustrated examples and the optic-electric target tracking system implemented by CKFI and UKFI.A summary of conclusion is given in Section 7.
The notation used in this article is fairly standard.Rndenotes the n dimensional Euclidean space,Rm×nis a set of real matrices with dimension m×n,the superscript“T”stands for matrix transposition.Indenotes the identity matrix with dimension n,and I denotes the identity matrix with suitable dimension.The norm of vectorrepresents the Euclidean norm,the norm of matrixrepresents the spectral norm.The E(x)stands for the expectation value of x.
2.Problem formulation
We consider the nonlinear discrete-time stochastic system with intermittent observations[24]:
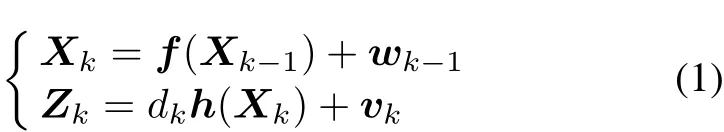
where Xk∈Rnxis the state vector,Zk∈Rnzis the measurement vector.wkand vkare unrelated zero-mean white Gaussian vectors with covariance Qkand Rk,respectively.We use dkto indicate whether the observation Zkis received.dkis a scalar binary Bernoulli distributed random variable taking values on 0 and 1,and the random variable dkcan be characterized by probability λ with Prob(dk=1)= λ and Prob(dk=0)=1-λ.The observation noise vkis defined as
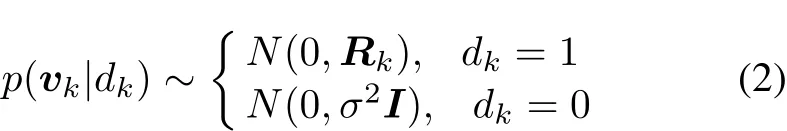
the absence of observation corresponds to the limiting case of σ2→ ∞.
Assume the posterior density functionis known at time step k-1.The procedure for implementing the CKFI can be summarized as
Step 1 Evaluate cubature points,i=1,2,...,m
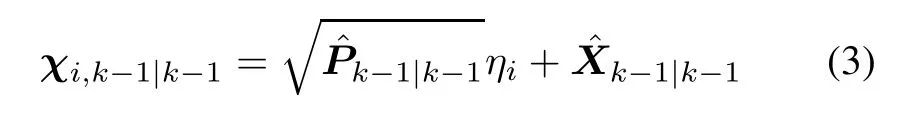
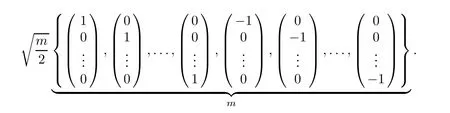
where m=2nx,nxis the dimension of state vector.?is the matrix square root of,andis the ith element of the following vector set:
Step 2 Time update
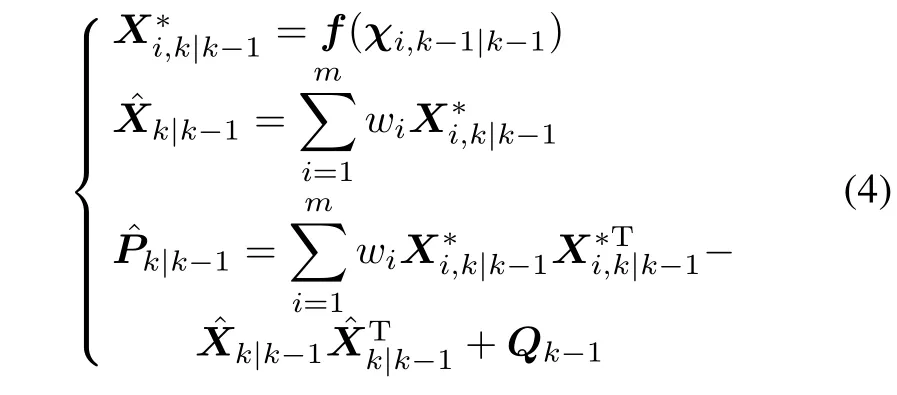
where wi=1/m.is the state prediction,andis the state error covariance prediction.
Step 3 Measurement update
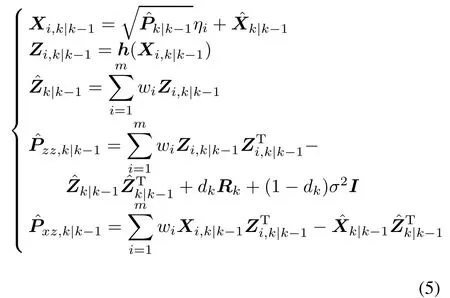

Taking the limit with σ2→ ∞,it can be obtained that
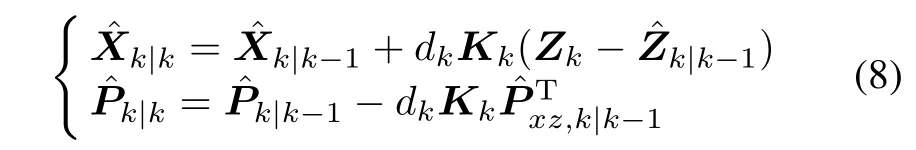
where
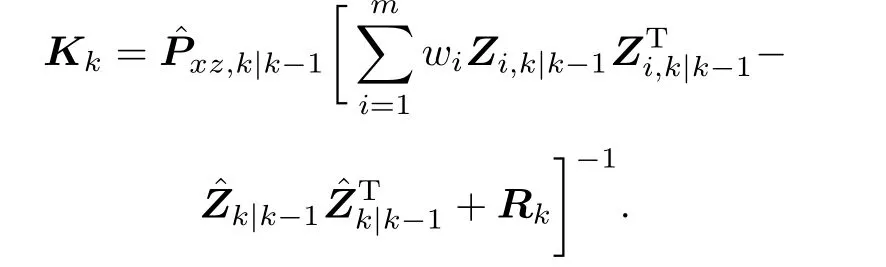
Step 4 Repeat Steps 1-3 for the next sample.
3.Estimation error and ECM of CKFI
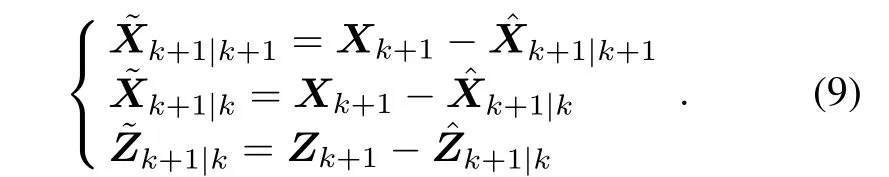
Expending Xk+1by Taylor series aboutyields
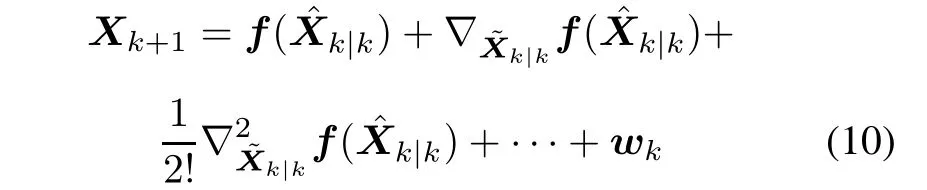
The sampling cubature points can be represented as
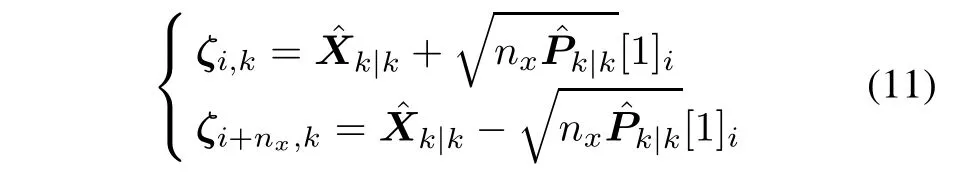
where i=1,...,nx.Denote Δi,k=ζi,k-.By using cubature transformation,we expendby Taylor series[19]:
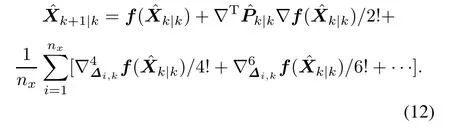
Combing(10)and(12)we establish that
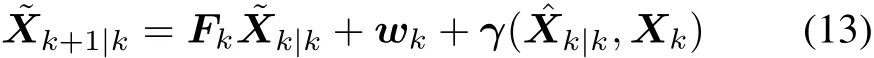
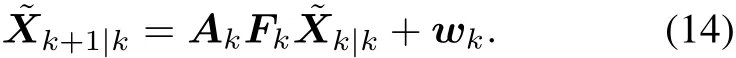
We denote σi,k+1=πi,k+1-,where the cubature points are calculated as
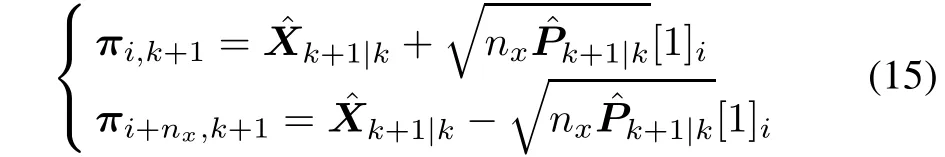
where i=1,...,nx.Similar to the calculating of state prediction error,it can be derived that
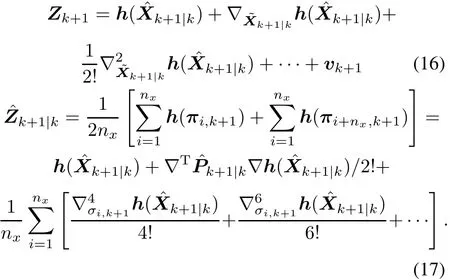
With(16)and(17),we can obtain an exact equality for the observation prediction error.
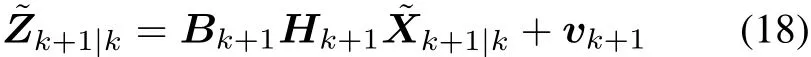
where
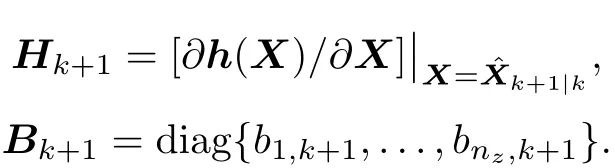
According to(14),the actual state prediction error covariance Pk|k+1can be obtained by
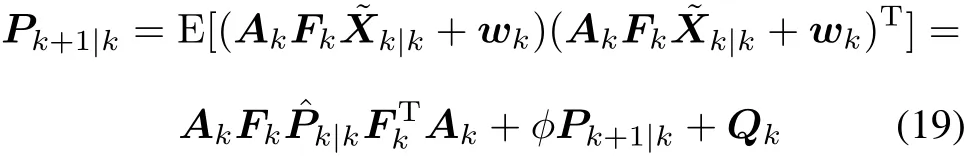
where φPk+1|kis the difference betweenand
Following[19],substituting(11)and(12)into(4)gives the prediction ECM:
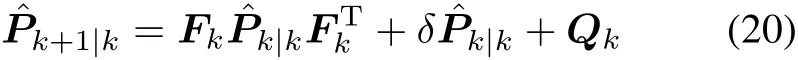
Therefore,it can be obtained that
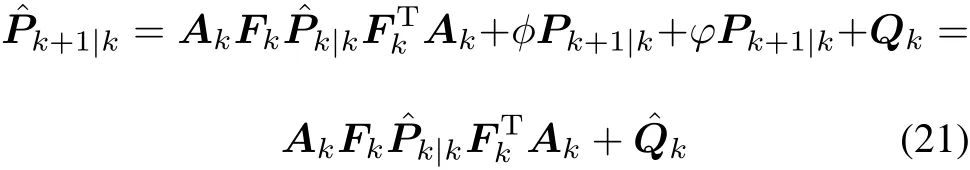
where
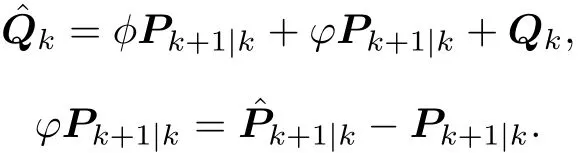
Similarly,the following covariance can be expressed as
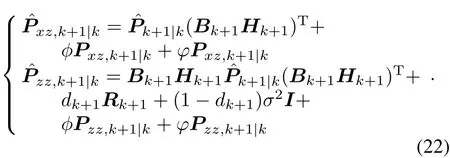
Introducing the stochastic matrix μk+1∈ Rnx×nx[3],we have
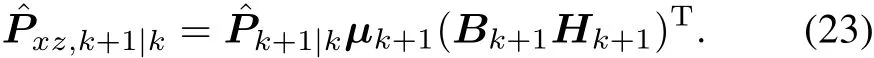
It can be obtained that

4.Boundedness of the ECM of CKFI
Before establishing the sufficient condition to ensure the boundedness of the ECM of CKFI,the following lemma and assumption are introduced.
Lemma 1[27]For symmetric positive-definite matrices C,D ∈ Rn×n,(C+D)-1> C-1-C-1DC-1holds.
Assumption 1 As pointed out in[28]:exists.There also exist real numbers fmax,hmin,μmin,μmax,amax,bmin,,>0,such that
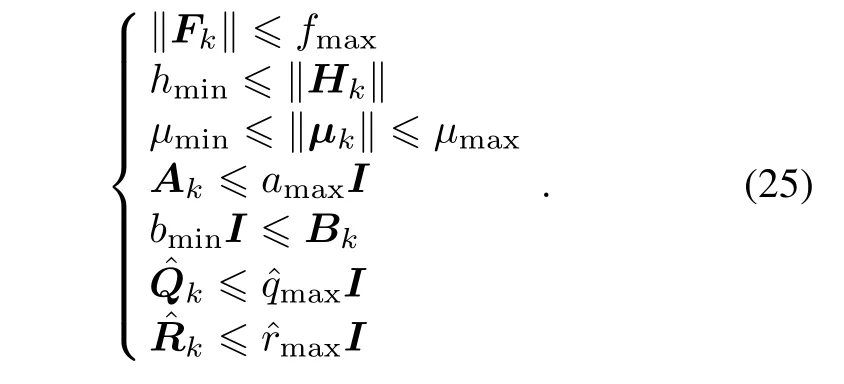
Theorem 1 If Assumption 1 is satisfied and the linear form of the nonlinear system in(1)is uniformly observable as in[27],there exists a critical valuesuch that the ECMs are bounded for the observation arrival probability λ > λc.That is,there exists a positive real constant pmaxsuch that
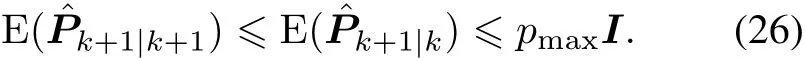
Proof Substituting(24)into(21)gives
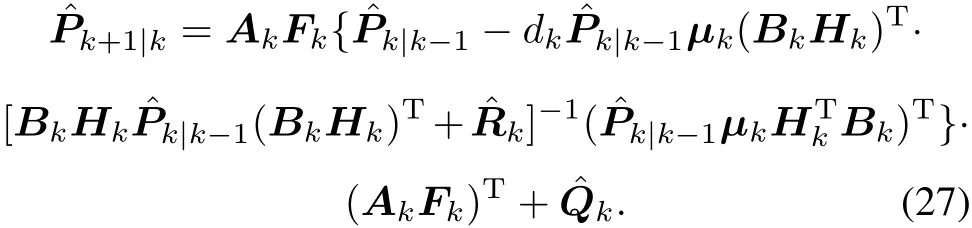
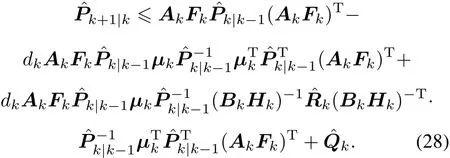
Considering Assumption 1,it can be derived that
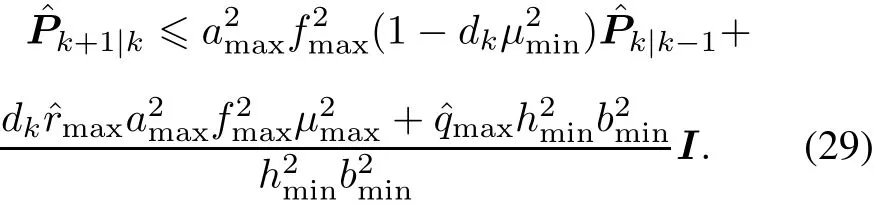
Taking the mean value from both sides of(29)gives
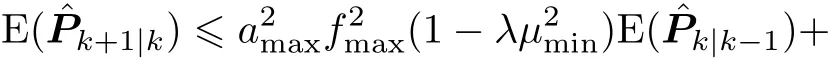

Recursively,we reach(31)below.
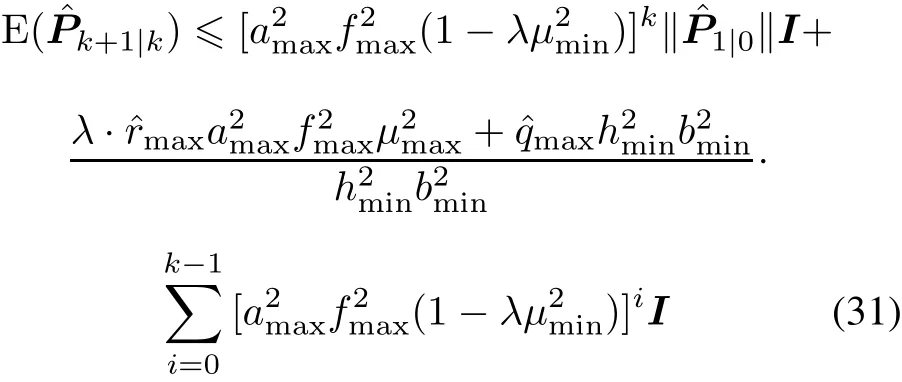
Denote
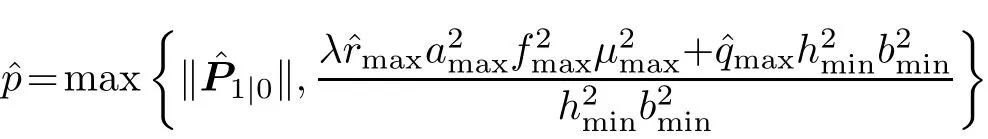
then we have
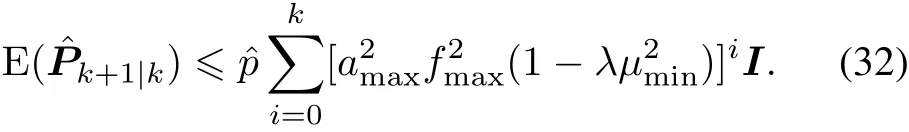
It is obvious that under the assumption
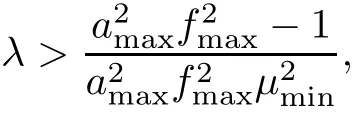
the sum in(32)converges to
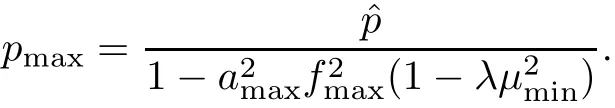
Remark 2 Generally,the ECM for the nonlinear tracking filter is not in accordance with the state estimation error[28].That is,the boundedness of ECM cannot necessarily guarantee the convergence of the estimation error.Therefore,the stochastic behavior of the estimation errorshould be further studied.
5.Stochastic stability of the estimation error of CKFI
In this section,the estimation error results from the proposed CKFI will be shown to be bounded,if the following assumption and condition hold.
Lemma 2[19] Assume that ξkis the stochastic process,and there is a stochastic process Vk(ξk)satisfying the following conditions for every k∈N:
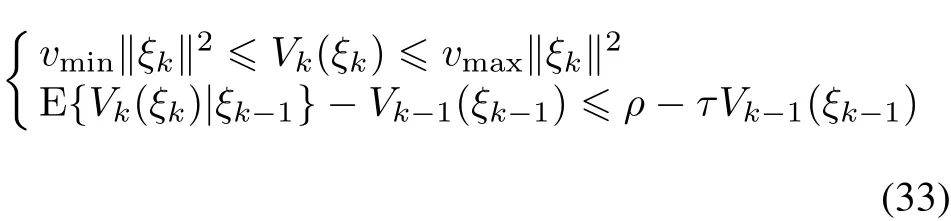
where vmin,vmax,ρ>0 and 0<τ?1.Then the stochastic process ξkis bounded in the mean square,and
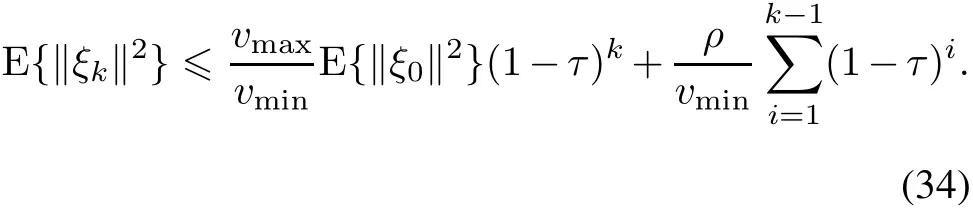
Assumption 2 There exist real constants fmax,hmax,μmax,amax,bmax,,,pmin,pmax>0,such that the following bounds are fulfilled for every k∈N:
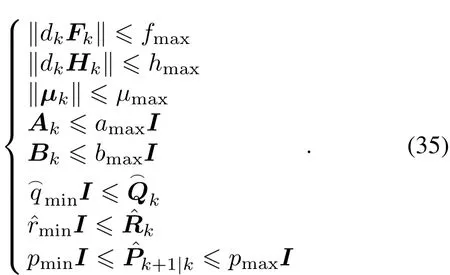
Theorem 2 Under Assumption 2,consider the nonlinear stochastic system described by(1)and the CKFI given by(3)-(8).If the initial estimation error satisfies?ε for small real constant ε>0,and there exists a bound δ> 0 for the stochastic noise such thatThen the estimation error?Xk|kis exponentially bounded in the mean square and bounded with probability one.
Proof According to(8),(14)and(18),it can be obtained that
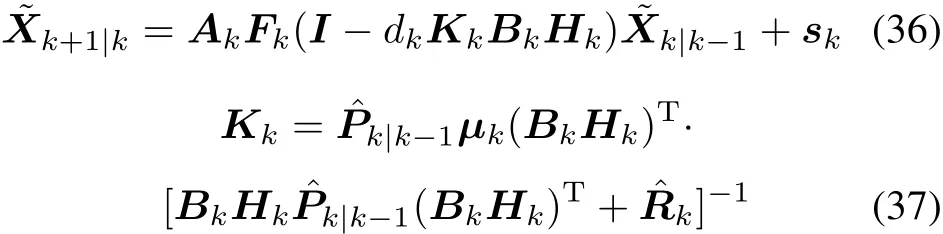
where we denote
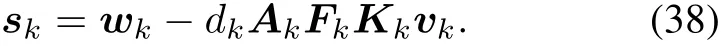
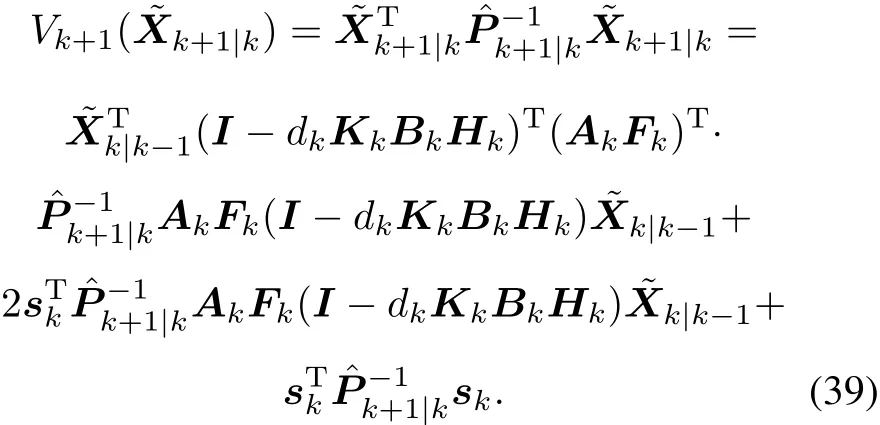
Therefore,taking conditional expectation yields
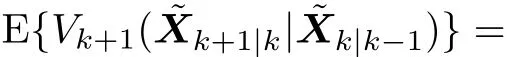

At the next step we take care of the first term above

Based on(36),it follows
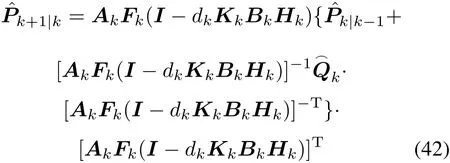
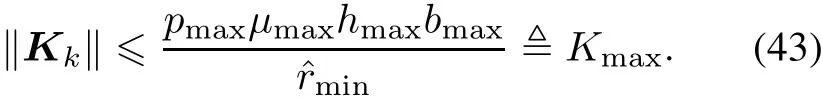
On the basis of the characteristic of the matrix norm,it can be verified that
From(35)and(37),we have
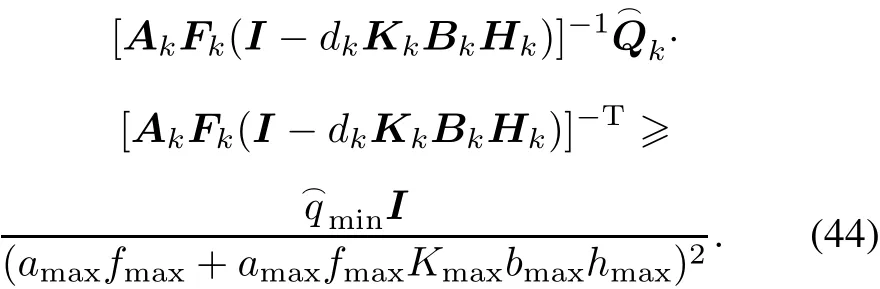
According to(42),we establish that
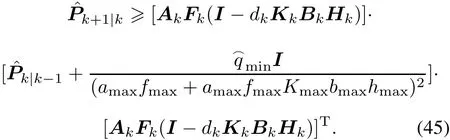
Taking the inverse of both sides of(45),it can be further derived that Using(35)we can obtain(47)below.
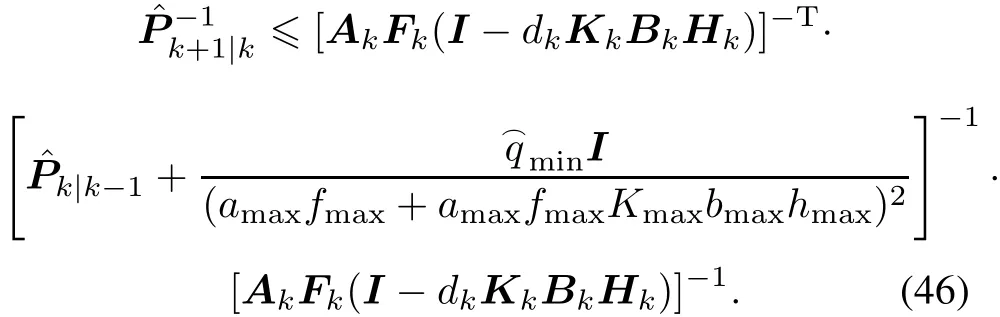
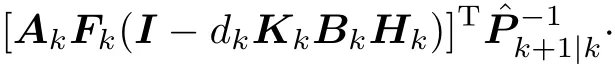
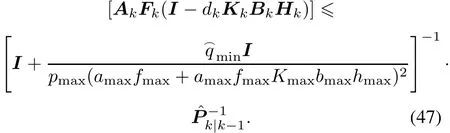
Define
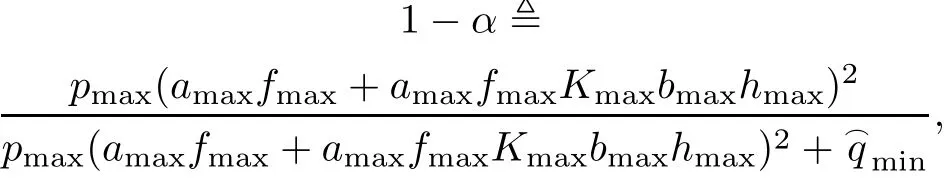
0<α<1,the first term of(40)is bounded.
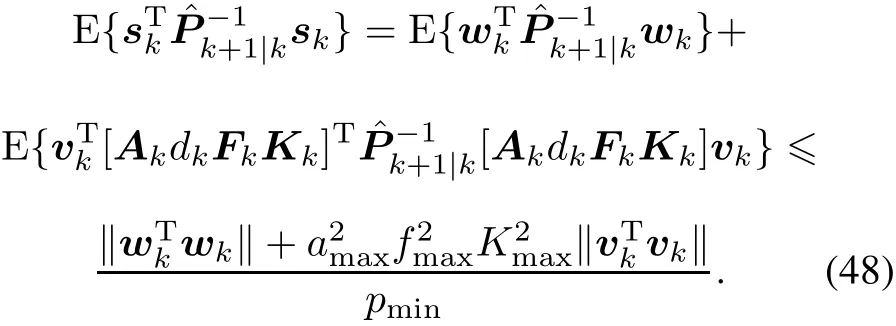
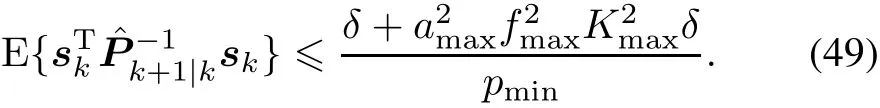
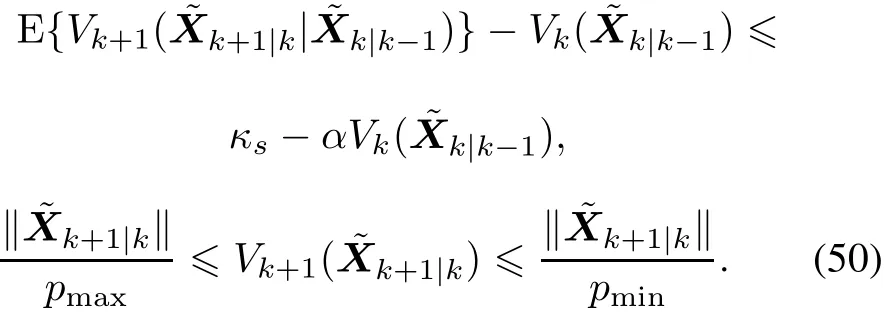
Thus,by applying Lemma 2,the estimation errormeets
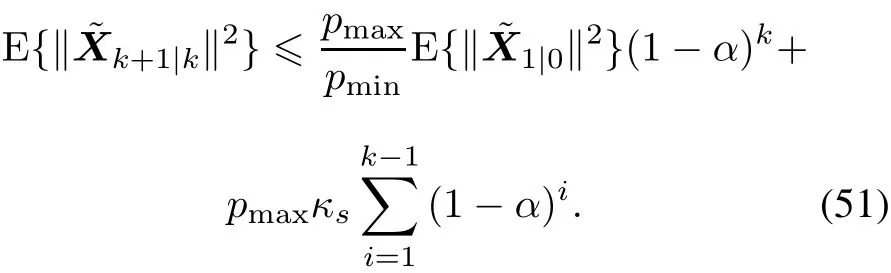
By(14),it can be easily derived that
Hence,we can easily draw the conclusion that the estimation error?Xk|kof the CKFI is bounded in mean square.
6.Illustrative examples
Example 1 The first nonlinear system that we consider can be described[30]as
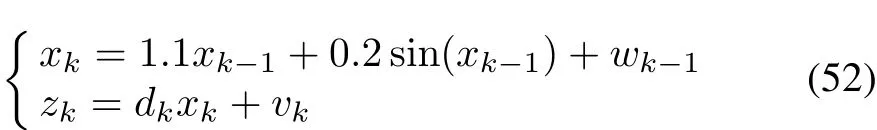
where wk,vkare the zero-mean white Gaussian noises with covariance Qk=0.01 and Rk=6,respectively.The initial conditions are x0=0.1,=0,the initial state error covariance is?p0|0=1.02.
From(52),we can derive that Fk= ?[f(x)]/?xk=1.1+0.2cos(xk),thus it can be verified by numerical simulation that fmax=1.30,μmin=0.92,amax=0.83.According to Theorem 1,the sufficient condition for boundedness of the ECM is
As can be seen from Fig.1,for the nonlinear system given in(52),there exists a critical value λc=0.16 for the observation arrival probability such that the ECM is bounded,which verifies the theoretical result in Theorem 1.
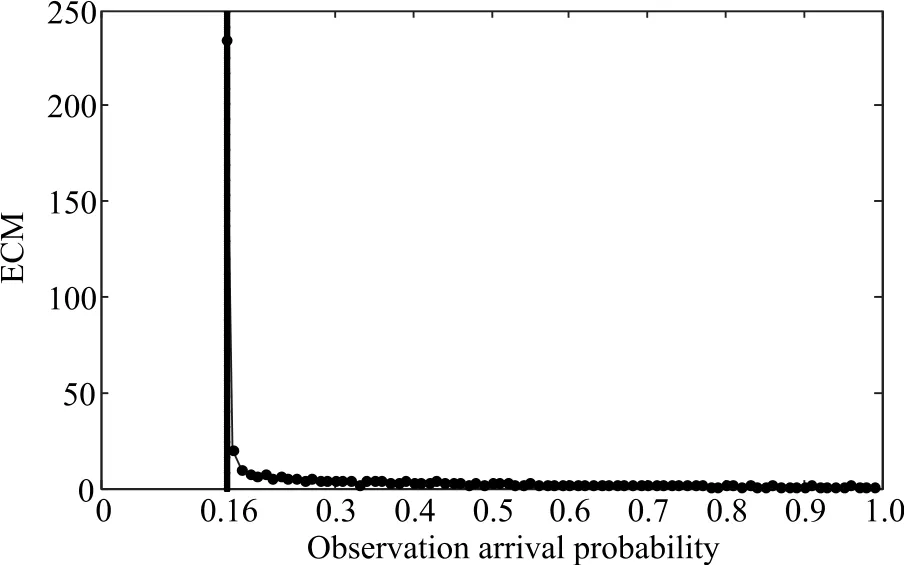
Fig. 1 ECM of the CKFI with different observation arrival probabilities
Example 2 The second numerical example concerns another nonlinear stochastic system[1,3],where τ=0.006,covariance matrices of the state noise wkand measurement noise vkare Qk=0.0032I,Rk=0.012,respectively.The initial state is given as X0=[0.8 0.2]T.
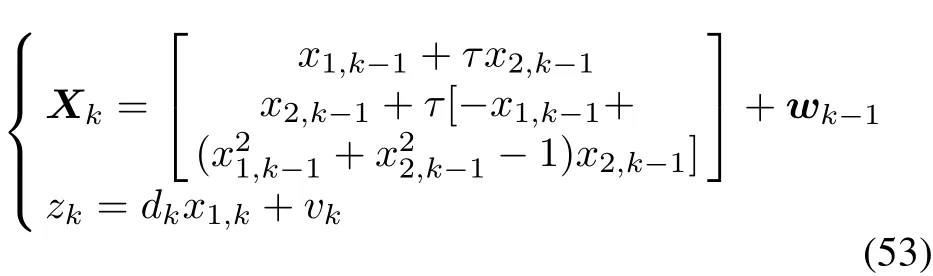
According to Theorems 1-2,the estimation error of the proposed CKFI will be bounded under some assumptions and appropriate initial conditions.Hence,in our simulation,three cases are taken into consideration:small initial error with a high observation arrival probability,small initial error but with a low observation arrival probability,and large initial error as well as a high observation arrival probability.The detailed parameters are demonstrated in Table 1.
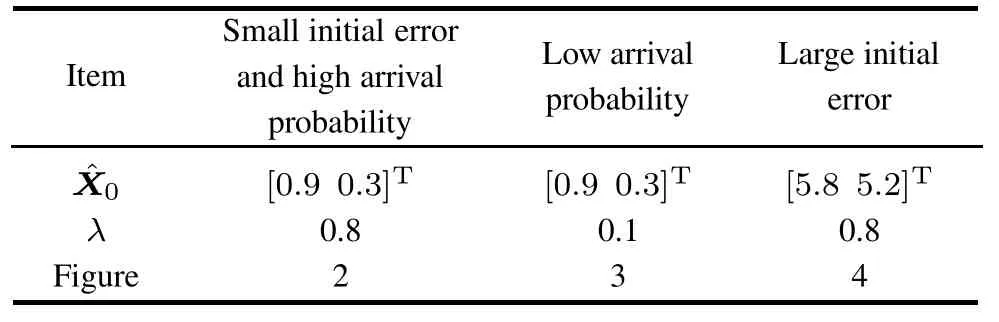
Table 1 Initial error and arrival probability
The simulation results are demonstrated in Figs.2-4,where the true state x2,k,the estimated stateand the estimation errorare depicted for three conditions in Table 1.From Fig.2,we can see that the estimation error keeps bounded for the small initial error and a high observation arrival probability.As shown in Fig.3,the low observation arrival probability will result in the divergence of the ECM and lead to the unbounded estimation error,which is in accordance with Theorem1.According to Theorem 2,the estimation error will also diverge due to the large initial error as demonstrated in Fig.4.
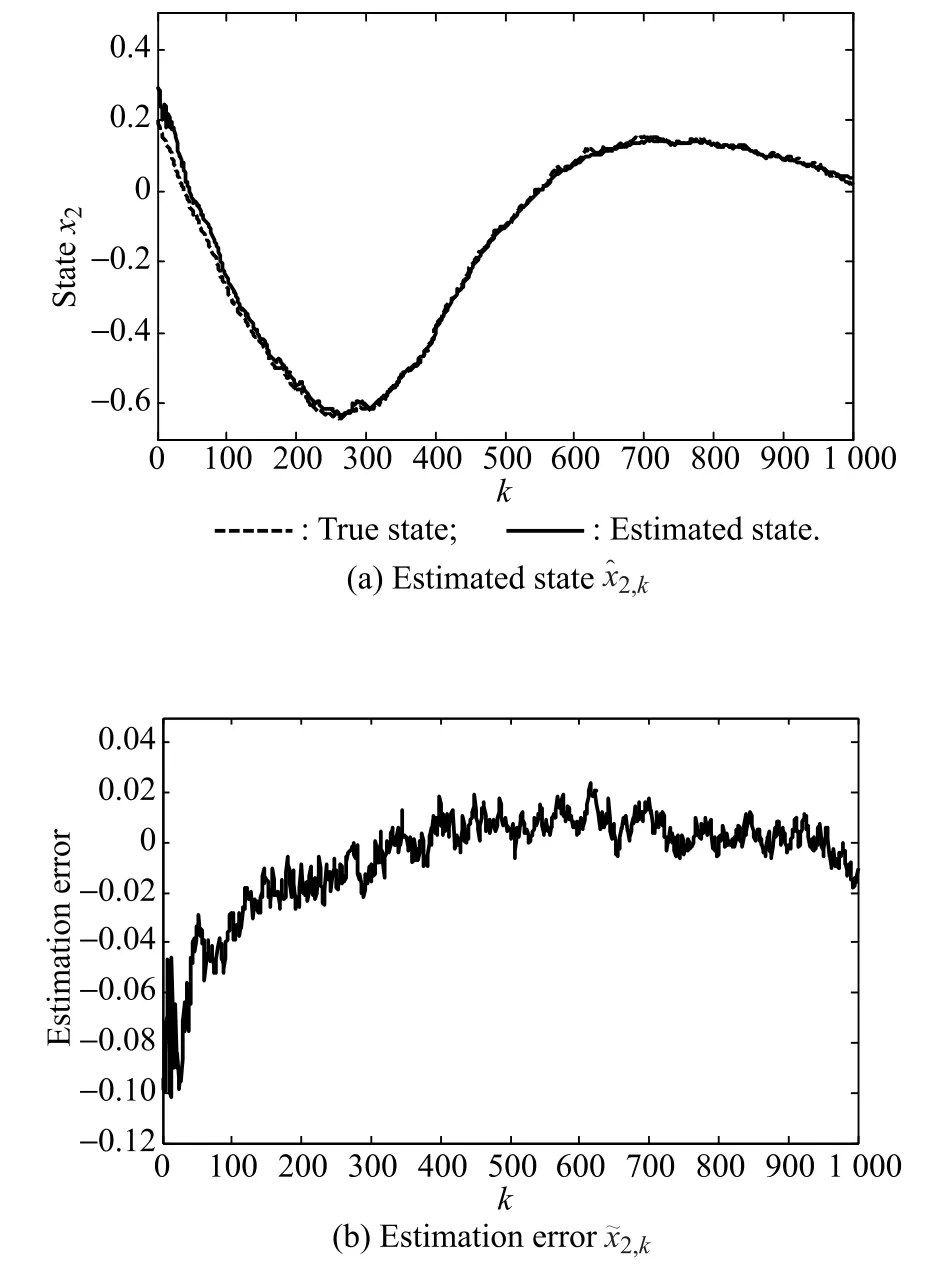
Fig.2Simulation results with=[0.9 0.3]Tand λ=0.8
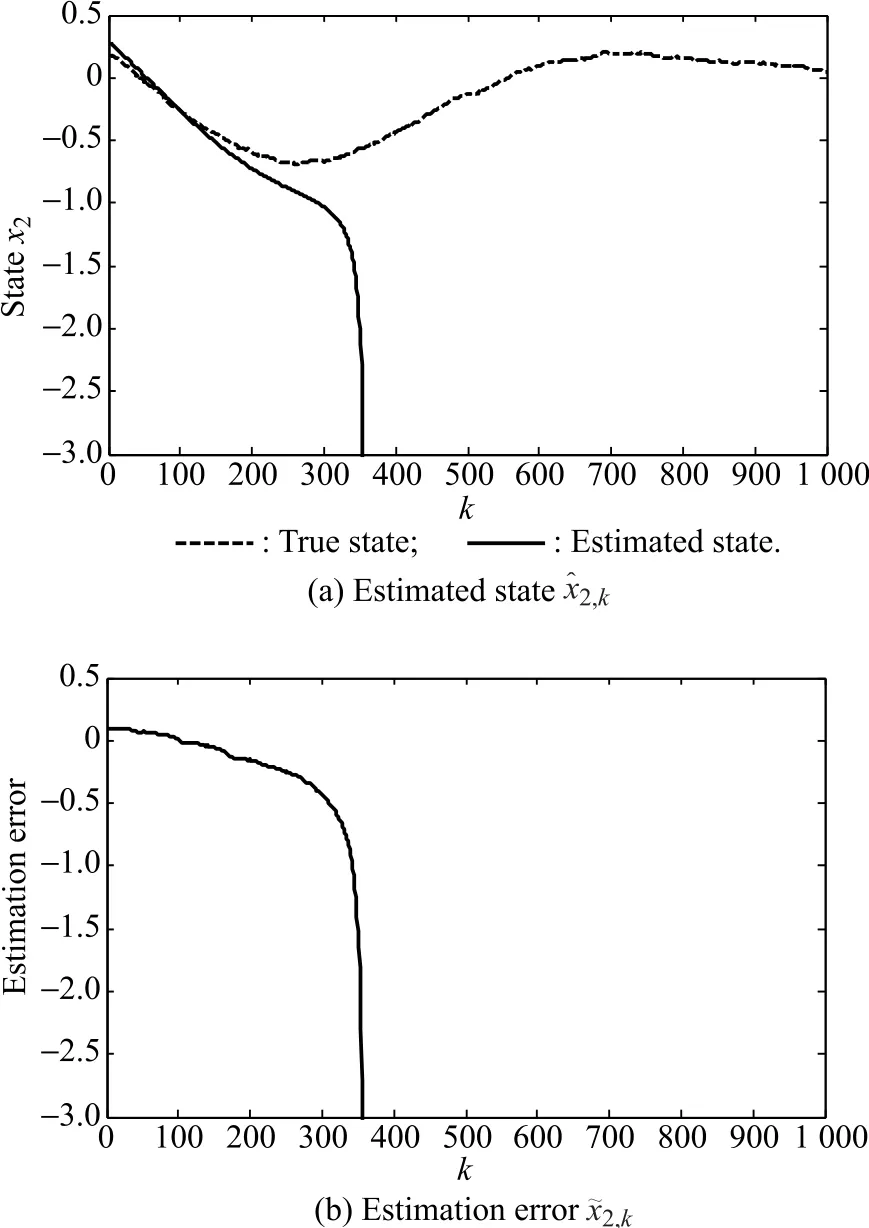
Fig.3Simulation results with=[0.9 0.3]Tand λ=0.1
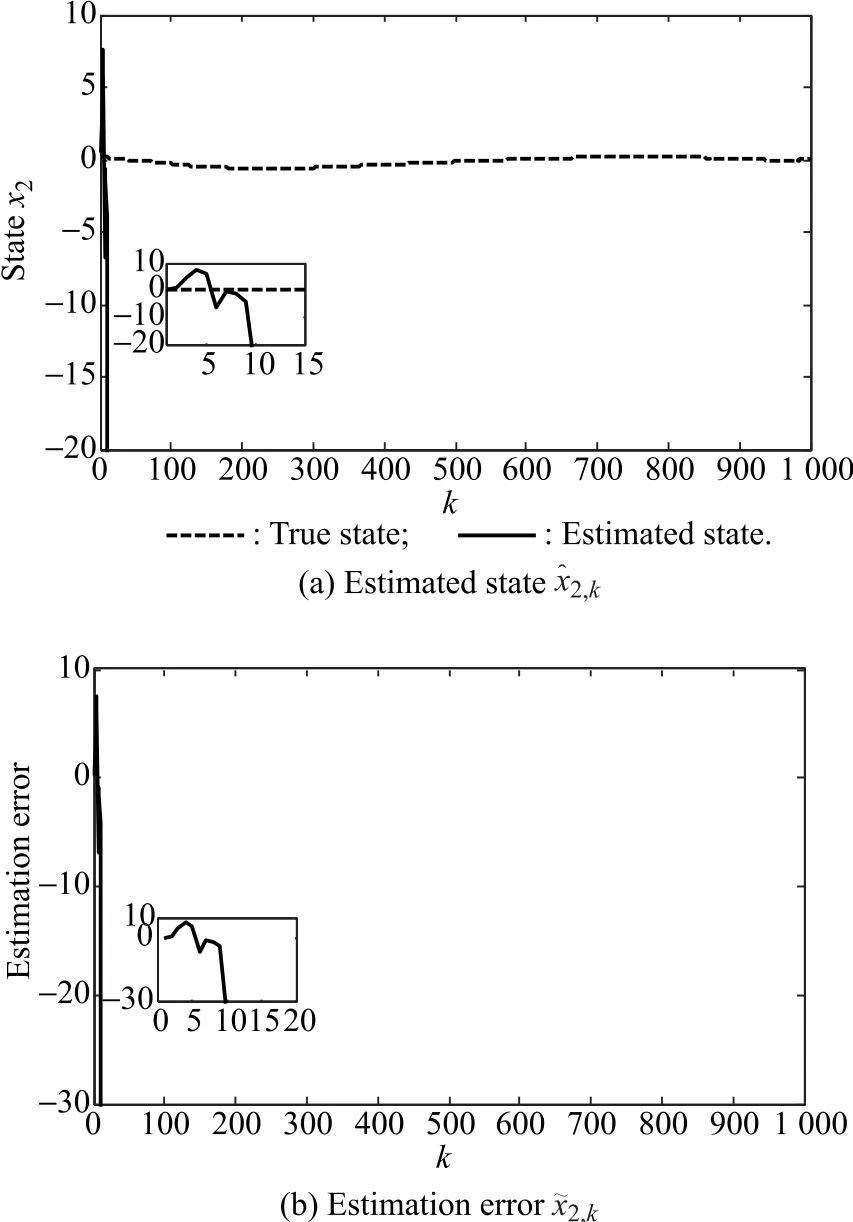
Fig.4Simulation results with=[5.8 5.2]Tand λ=0.8
Example 3 Application to the optic-electric tracking system
The previous two examples have been utilized to verify the theoretical results in this article.To evaluate the estimation performance of the filtering framework provided in Section 2,the proposed CKFI will be applied to the optic-electric tracking system in this example.As shown in Fig.5,the azimuth angle βk,elevation angle εkare measured according to the visible/infrared image-based target tracking,also the laser range finder is adopted to obtain the target distance Dk.Combining with the practical application,the observations of the optic-electric tracking system may be lost due to the cloud cover,a high noise environment,intermittent sensor failures,accidental loss of some collected data,etc.
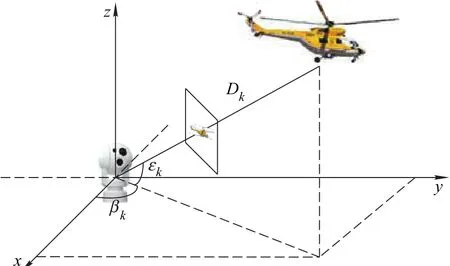
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of the optic-electric tracking system
We define the target state as
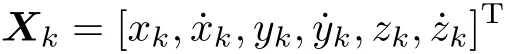
where[xk,yk,zk]Tindicates the target position in the Cartesian coordinate,and[]denotes the corresponding target velocity,the tracking equation of the optic electric tracking system can be obtained by
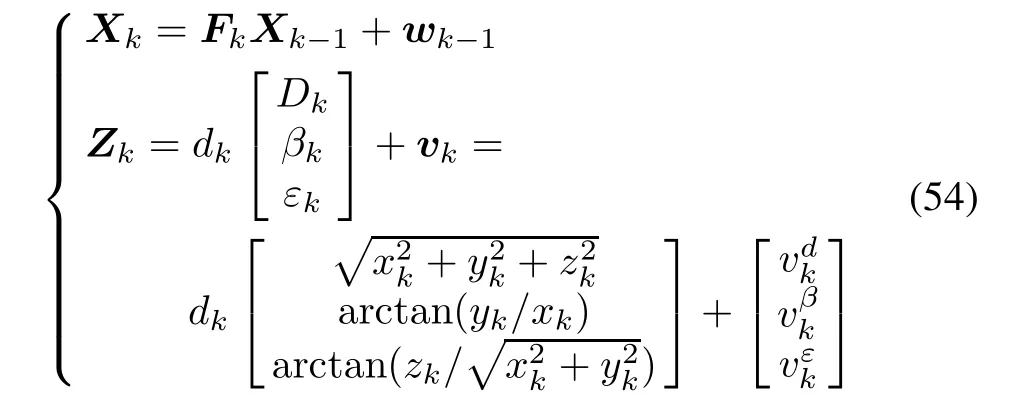
where Fk∈ R6×6is the state transitional matrix.wk∈R6is white Gaussian noise with zero mean and covariance matrix Qk∈R6×6.,andare independent white Gaussian noises with covariance,and,respectively.dkis a scalar binary Bernoulli distributed random variable that indicates whether the observations are achieved.Without loss of generality,the constant velocity(CV)target model is adopted in our example[21],and we have
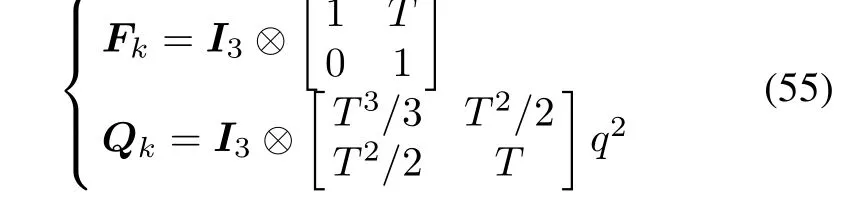
where?is the Kronecker product,T is the sample interval,and q is the process noise intensity.
In our implementation,the sample interval T =0.2 s,the process noise intensity q = 1 m/s2.The optic-electric tracking system is static and at the origin of the coordinate system,while the target is at location(4 000 m,4 000 m,1 500 m)with the velocity(50 m/s,-50 m/s,0 m/s).The observation arrival probability λ=0.8[21].The measurement accuracy can be given as σd=5 m,σβ= σε=5 mil,(2π =6 000 mil).Generally,the estimation performance of the tracking filter can be evaluated by the root mean square error(RMSE)and accumulative root mean square error(ARMSE),the Monte Carlo runs M=100.
The error comparisons are performed between the proposed CKFI and the UKFI.In Fig.6,the estimated target trajectories by two filters are shown.Meantime,the RMSEs of CKFI and UKFI are depicted in Fig.7.
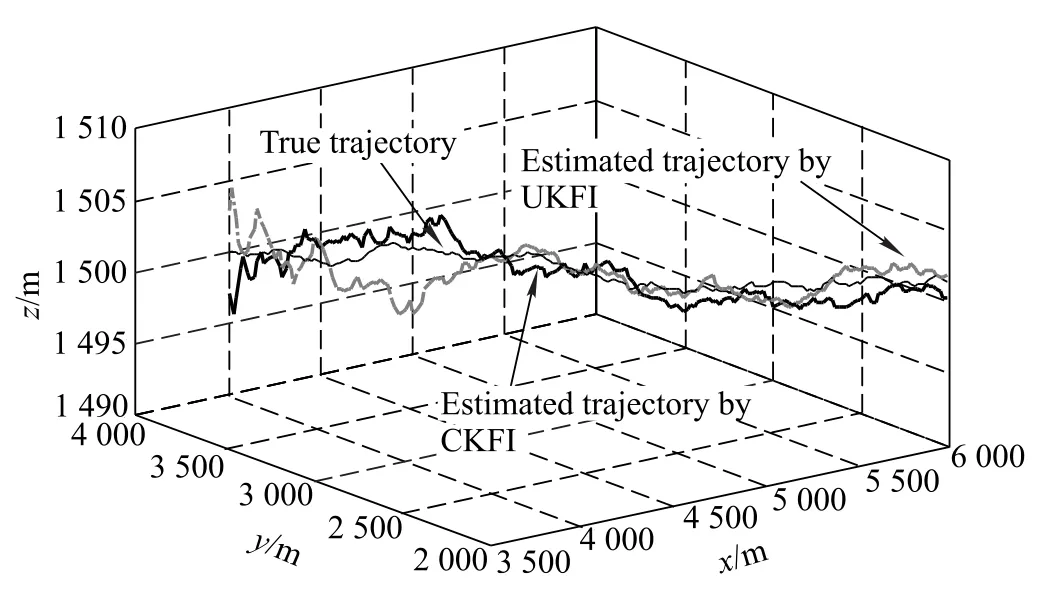
Fig.6 The estimated trajectories by CKFI and UKFI
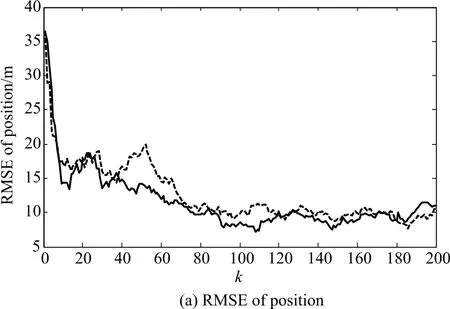
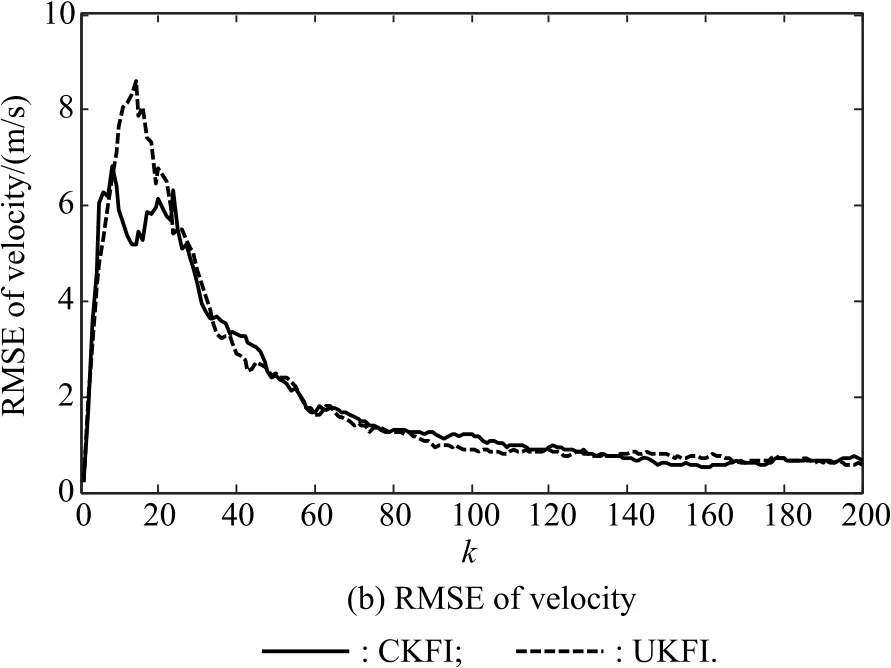
Fig.7 Comparison of RMSEs with the proposed CKFI and UKFI
Furthermore,in Table 2,the ARMSEs of position and velocity,as well as the mean computational time per filtering running in Matlab 2014a on a 3.0 GHz,4G memory based Windows workstation are presented.
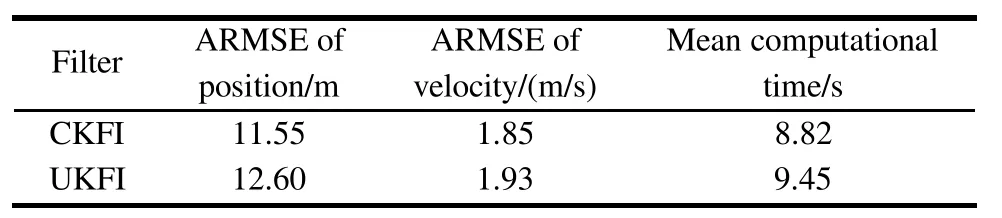
Table 2 Performance metrics of the CKFI and UKFI
It can be concluded from Fig.7 and Table 2 as follows:
(i)The CKFI slighter outperforms the UKFI in terms of tracking accuracy,that is,both the RMSEs and ARMSEs of the CKFI are a bit smaller than that of the UKFI.
(ii)As compared to the UKFI,the CKFI is an effective method with shorter mean computational time,which is of significance in practical target tracking.The main reason for this conclusion is that the CKFI uses fewer sampling points than the UKFI.
In addition,to test the influence of the observation arrival probability on filtering performance,as shown in Table 3,λ are designed as λ =0.6,λ =0.7 and λ =0.8.From Table 3,it is obvious that the estimation precision of CKFI is higher with the higher observation arrival probability.According to Fig.7 and Tables 2-3,it is clear that the CKFI is practical and effective;meantime,the estimation performance of the CKFI can be influenced by the observation arrival probability.

Table3 Comparison of ARMSEs of the CKFI with different probabilities
7.Conclusions
This study addresses the stochastic stability of CKF for discrete-time nonlinear systems with intermittent observations.The estimation error and ECM of CKFI are firstly obtained by Taylor expansion.Then,it can be proven that there exists a critical minimum observation arrival probability such that the ECM is bounded,and certain conditions for guaranteeing the stability of the estimation error are deduced.Finally,as compared to UKFI,the better performances of CKFI are demonstrated through the application to the optic-electric target tracking system.
Further research topic could be the extension of CKF for the stochastic nonlinear systems with Markovian observation dropouts.Moreover,it is of significance to study the CKF-based estimation methods under the condition of random observation delays.
 Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2018年4期
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2018年4期
- Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics的其它文章
- Application of deep autoencoder model for structural condition monitoring
- On redundancy-modified NAND multiplexing
- A dual channel perturbation particle filter algorithm based on GPU acceleration
- Multi-channel signal parameters joint optimization for GNSS terminals
- Output regulation of singular linear systems with input saturation by composite nonlinear feedback control
- Multiple UAVs cooperative formation forming control based on back-stepping-like approach
