Effects of 5-azacytidine-2’-deoxycytidine on the proliferation,cell cycle,and apoptosis of fetal bovine fibroblast cells
YU Mengfei,WANG Wenlu,YI Jianming
(1.Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory for Protection and Application of Special Plant Germplasm in Wuling Area of China/Institute for Medical Biology,College of Life Sciences,South-Central University for Nationalities,Wuhan 430074,China;2.Key Laboratory of Agricultural Animal Genetic,Breeding,and Reproduction of Ministry of Education,College of Animal Science&Technology,Huazhong Agricultural University,Wuhan 430070,China)1
Abstract Fetal bovine fibroblast cells(FBFCs)are widely used in cellular reprogramming and methylation.In this study,the effects of 5-azacytidine-2’-deoxycytidines(5-Aza-CdR),a DNA methylation inhibitor on the physiological characteristics of FBFCs were investigated.The FBFCs derived from a bovine fetus were treated with 5-Aza-CdR at different concentrations for 24,48 and 72 h,respectively,to determine the changes of cell proliferation,viability,cell cycle distribution and apoptosis rates.The results demonstrated that 5-Aza-CdR treatment in the FBFCs resulted in a decrease of cell proliferation,cell viability,and an increase of total cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner.The best treatment strategy for 5-Aza-CdR was less than 0.1 μmol/L for 24 h,which showed minimal adverse effects on FBFCs.The above results indicate that the low dose DNA demethylation inhibitor treatment in FBFCs is beneficial for cell reprogramming.
Key words 5-azacytidine-2’-deoxycytidines;cell proliferation;cell cycle;cell apoptosis
Terminally differentiated somatic cell nuclei can be reprogrammed to totipotency when transferred into enucleated mature oocytes[1-2].However,the success rate of somatic cell nuclear transfer(SCNT)remains quite low,frequently due to abnormal genomic imprinting.In some mammals,genomic imprinting is an important epigenetic mechanism that ensures the expression of parental origin-specific monoallelic genes.Imprinted genesplay essentialrolesin diversebiological phenomena,notably in the regulation of placental and postnatal growth and/or adult behaviors[3].
Methylation imprints are established during germ cell development and are protected from genomewide demethylation and re-methylation during early embryonic development.DNA methylation plays an important role in gene expression,which influences early embryonic development and subsequent growth[4].In natural reproduction,DNA methylation levels in gametes are relatively low,and further demethylation occurs during early development.However,terminally differentiated somatic cells exhibit higher levels of DNA methylation.In SCNT,these highly methylated somatic cells are used as donor cells,which will in turn result in abnormal hypermethylation in cloned embryos[5].To improve the efficacy of SCNT,several epigenetic remodeling drugs such as the DNA methylation inhibitor 5-azacytidine-2’-deoxycytidines(5-Aza-CdR)and histone deacetylase inhibitors as Trichostatin A have been used to enhance the early developmental potential of cloned embryos[6-7].Although epigenetic modification agents such as 5-Aza-CdR can improve the cloning efficacy,the mechanisms underlying the developmental improvement in cloned embryos still require further investigation.In this study,we explored the effects of different concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR on common SCNT donor cells(fetal bovine fibroblast cells,FBFCs).
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Reagents
Unless otherwise stated,all chemicals and media were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich(St Louis,MO,USA).
1.2 Cell culture
The isolation of FBFCs was performed as previously described[8].Briefly,FBFCs were obtained from a bovine fetus of a slaughterhouse.The FBFCs were isolated from a skin biopsy and cultured in DMEM(Gibco,Life Technology,Carlsbad,CA,USA)supplemented with 10%fetal bovine serum(Gibco,Life Technology)in a 37.5℃incubator with the humidified atmosphere of 5%CO2and 95%air.
1.3 Experimental design
FBFCs at passage 6 were used.At 24 h after cell seeding,the FBFCs were treated with different concentrations(0,0.01,0.1,0.5 and 1.0 μmol/L)of the DNA methyltransferase(DNMT1)inhibitor 5-Aza-CdR.The cells at different time points were used for the analysis of proliferation,cell cycle,apoptosis,and mRNAexpression of DNMT1.
1.4 Cell proliferation assay
The proliferation of FBFCs treated with 5-Aza-CdR was detected[9].Briefly,harvested FBFCs were seeded onto 96-well culture plates at a density of 5 000 cells/well and cultured for 24,48 and 72 h.The cells treated with different concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR were then incubated with 10 μL of Cell Counting Kit(CCK)-8(Dojindo,Kumamoto,Japan)solution for 4 h at 37℃.The proliferation of FBFCs was measured using the CCK-8 according to the manufacturer’s protocol.Absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a spectrophotometer.
1.5 Cell viability assay
The viability of FBFCs treated with different concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR was measured[10].Briefly,the FBFCs were seeded onto 96-well plates and treated with 0,0.01,0.1,0.5 or 1.0 μmol/L of 5-Aza-CdR for 24,48,72 or 96 h.Then,10 μL of CCK-8 solution was added,and the cells were incubated for 4 h.Cell viability was analyzed using the CCK-8.The optical density(OD)values were measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader(Model 680,Bio-Rad,Hercules,CA,USA).
1.6 Cell cycle assay
The cellcycle was analyzed as reported elsewhere[11]with some modifications.Briefly,the FBFCs were seeded onto six-well microplates at a final density of 1×106cells/well.After 24 h incubation,the cells were treated with different concentrations of the DNMT1 inhibitor 5-Aza-CdR.At 24,48 and 72 h after 5-Aza-CdR treatment,the cells were trypsinized,washed,and fixed in 70%ethanol at-20℃for 24 h.For flow cytometric analysis,the cells were incubated in RNase at 37℃for 30 min,treated with propidium iodide(PI)and suspended in 300 μL of Dulbecco’s phosphate buffer solution(DPBS).The cell cycle distribution was examined by measuring the DNA content on a FACSCalibur(BD,Immunocytometry Systems,San José,CA,USA).
1.7 Detection of apoptosis
The procedure used to detect apoptotic cells was conducted as described[12]with some modifications.Briefly, the FBFCs were seeded onto sixwell microplates at a final density of 1×106cells/well in 100 μL of complete medium.After 24 h,the cells were treated with different concentrations of the DNMT1 inhibitor 5-Aza-CdR.After 24,48 or 72 h,apoptotic FBFCs in the early and late stages were determined via annexin V-FITC and PI staining,respectively.Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)was performed to analyze the apoptotic changes in the FBFCs.The rate of early apoptosis was defined as the sum of the apoptotic cells(Annexin V-FITC-positive/PI-negative)/total cells in the early stages.The rate of late apoptosis was defined as the sum of the apoptotic cells (Annexin V-FITC-positive/PI-positive)/total cells in the late stages.The rate of total apoptosis was the sum of the rates of early apoptosis to late apoptosis.
1.8 Real-time polymerase chain reaction(PCR)
Total RNA was isolated from fetal bovine fibroblasts at passage 6 using TRIzol(Invitrogen,Carlsbad,CA,USA)according to the manufacturer’s instructions.TotalRNA wasmeasured usinga NanoDrop-2000 spectrophotometer at wavelengths of 260 and 280 nm(Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.,Waltham, USA). Reverse transcription was performed with M-MuLV reverse transcriptase(Promega,WI,USA).The expression of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH)was used for normalization.Amplification was performed using SYBR green master mix(Life Technologies,USA).The amplification conditions were as follows:40 cycles of denaturation at 94℃for 20 s,annealing at 60℃for 20 s,and primer extension at 72℃for 20 s.The primer sequences were as follows:5′-GTAGTG GACGACAAGAAGTTTG-3′(forward),5′-ATCTC AGGGAGGTCAGACAT-3′(reverse),101 bp for DNMT1,and 5′-CTGCCCGTTCGACAGATAG-3′(forward),5′-CTCCGACCTTCACCATCTTG-3′(reverse),76 bp for GAPDH.
1.9 Statistical analysis
Values are shown as the mean±standard error of the mean(SEM).The statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test for two groups and one-way analysis of variance for multiple comparisons.Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 17.0(SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).Differences were considered statistically significant when P<0.05.
2 Results
2.1 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the proliferation of FBFCs
FBFCs were widely used in exploring the mechanisms of cellular reprogramming.Therefore,FBFCs were used as materials to explore the effects of 5-Aza-CdR on cellular physical events(Fig.1A).the FBFCs at passage 6 were used for further experiments(Fig.1B).
It is possible that demethylation treatment in FBFCs may change cell proliferation.Therefore,the OD values of FBFCs treated with different concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR were assessed using the CCK-8 method.As shown in Fig.2,5-Aza-CdR produced inhibitory effects on FBFCs in a dosedependent manner.At 24 and 48 h after 5-Aza-CdR treatment,the OD value in the 1.0 μmol/L group was significantly lower than that in the control group(P<0.05).At 72 h after 5-Aza-CdR treatment,the OD value in the 1.0 μmol/L group was significantly lower than that of the 0.5 μmol/L group.Similarly,at 96 h,the OD value of the 1.0 μmol/L treatment group was significantly lower than those of the control and the 0.5 μmol/L groups(P<0.01).Meanwhile,the OD valueofthe0.5 μmol/L treatmentgroup was significantly lower than that of the control group.However,no differences were observed at different time within the same treatment group.These results suggest that the FBFCs with treatment of 5-Aza-CdR produce a harmful effect on the proliferation of FBFCs in a dose-and time-dependent manner.
Fig.1 Primary fetal bovine fibroblast cells(A)and fetal bovine fibroblast cells at passage 6(B)
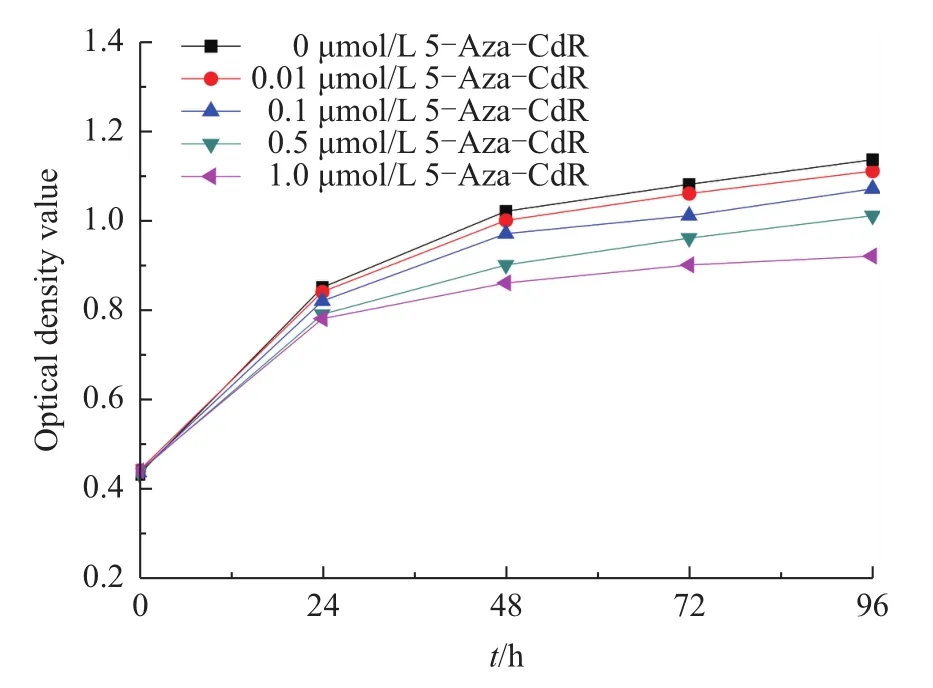
Fig.2 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the proliferation of FBFCs
2.2 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the cell viability of FBFCs
Demethylation drug treatment may exert harmful effects of cell characteristics,such as cell viability.Therefore,the effect of 5-Aza-CdR on the viability of FBFCs was detected using the CCK-8 method at 450 nm.As shown in Fig.3,5-Aza-CdR inhibited the growth of FBFCs in a time-and dose-dependent manner.At 24 and 48 h after 5-Aza-CdR treatment,the viability of FBFCs in the 1.0 μmol/L group was significantly lower than that of the control group(P<0.05).At 72 and 96 h after treatment,the cell viability in the 1.0 μmol/L group was significantly lower than those of the control and 0.01 μmol/L groups(P<0.05).Similarly,the cell viability in the 0.5 μmol/L group was significantly lower than that of the control group(P<0.05).Moreover,no significant differences were found among other groups and among the same treatment group at different time points.
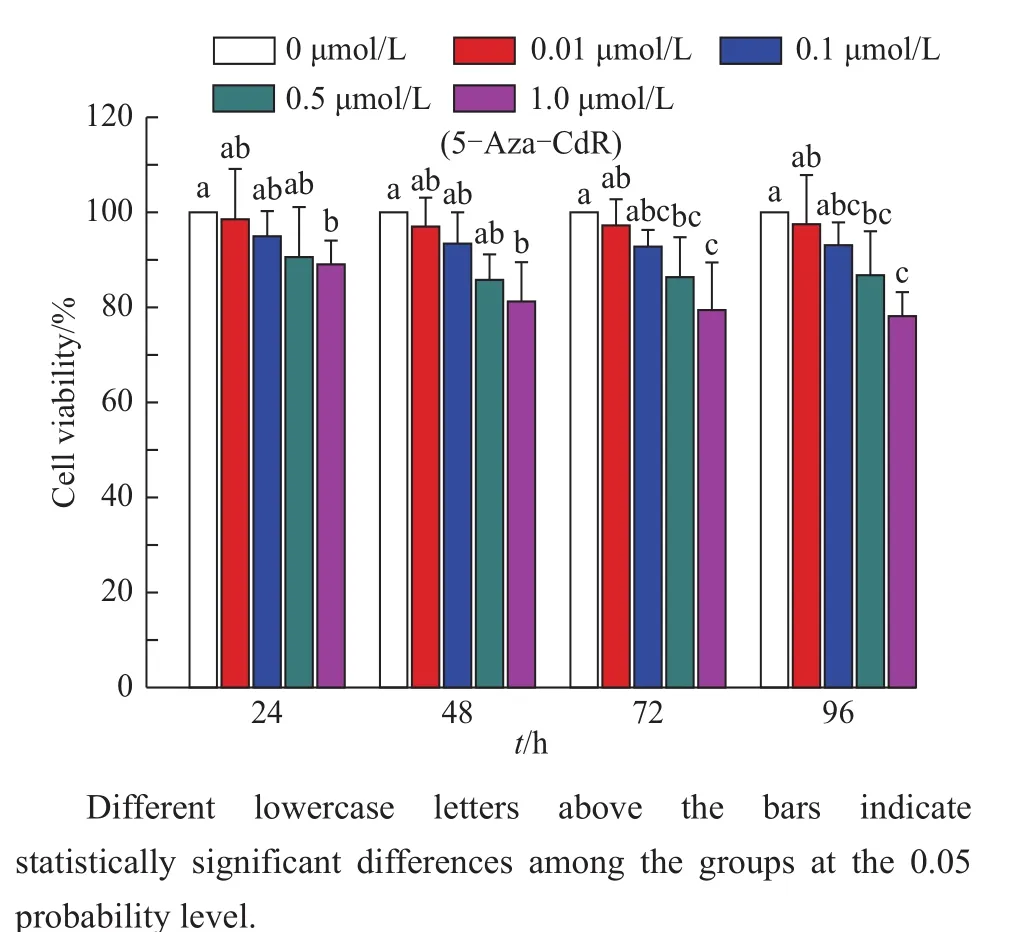
Fig.3 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the viability of FBFCs
2.3 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the cell cycle distribution of FBFCs
The efficacy of reprogramming in the somatic cells vary with dependence on the different stages of cell cycles.Therefore,the cell cycle distribution of FBFCs treated by 5-Aza-CdR was measured by using flow cytometry.As indicated in Fig.4,the rate of FBFCs arrested at the G0/G1stage was significantly higher in the 1.0 μmol/L group than in the control and 0.01 μmol/L groups at 24,48 and 72 h(P<0.05 and 0.01).Meanwhile,the rate in the 0.5 μmol/L group was significantly higher than that in the control group(24 and 48 h,P<0.05;72 h,P<0.01)and in the 0.01 μmol/Lgroup(24 and 48 h,P<0.05;72 h,P<0.01).The rates of the FBFCs in the S stage in the 1.0 μmol/L and 0.5 μmol/L groups were significantly lower than that of the control group(P<0.05)at 24 h.Similarly,at 48 h,the rates in the 1.0 and 0.5 μmol/L groups were significantly lower than that of the control group(P<0.05),while the rate in the 1.0 μmol/L group was also significantly lower than that of the 0.01 μmol/Lgroup(P<0.05).These data indicate that 5-Aza-CdR treat-ment arrested the cells at the G0/G1stage in a dose-and time-dependent manner.
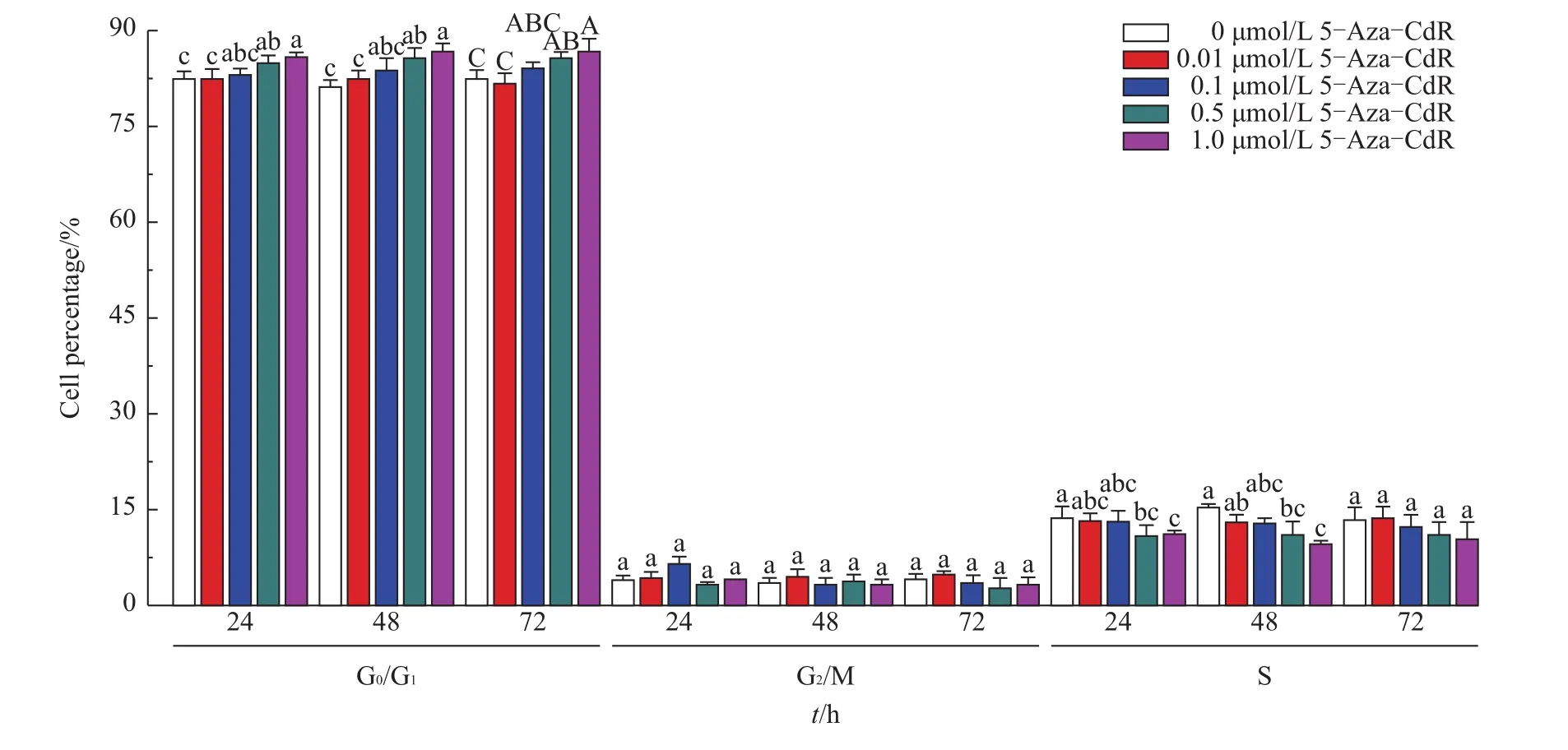
Fig.4 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the cell cycle distribution of FBFCs
2.4 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the apoptosis of FBFCs
Drug treatment in somatic cells may result in an increase of apoptosis.Therefore,the effect of 5-Aza-CdR on the apoptosis of FBFCs was analyzed using TUNEL.As indicated in Fig.5A,the effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the rate of early apoptosis in FBFCs were as follows.The rates in the 1.0 μmol/L group were significantly higher than those of the other four groups at 24,48 and 72 h(P<0.01).Meanwhile,the early apoptotic rate in the 0.5 μmol/L group was significantly higher than those in the control(48 and 72 h,P<0.01)and 0.01 μmol/L(48 and 72 h,P<0.01)groups.Similarly,the early apoptotic rates in the 0.1 and 0.01 μmol/L groups were significantly higher than those of the control group at 48 and 72 h(P<0.05).The effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the rate of late apoptosis were as follows(Fig.5B).The rate in the 1.0 μmol/L group was significantly higher than those in the control and 0.01 μmol/L groups at 24,48 and 72 h,respectively(P<0.05 and 0.01).The rate of late apoptosis in the 0.5 μmol/L group was also significantly higher than that in the control group(48 h,P<0.05;72 h,P<0.01)and the 0.01 μmol/L group,respectively(48 h,P<0.05).No significant differences were found among the other groups.The rate of totalapoptosis showed no significant difference between the 0.01 μmol/L and the control group(24 h,P>0.05),while the differences among the other groups were all significant(P<0.01)(Fig.5C).These results demonstrated that 5-Aza-CdR induced apoptosis of FBFCs in a dose-and timedependent manner.
2.5 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on DNMT1 expression levels
The effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the expression of DNMT1 mRNA were measured by using qPCR.As shown in Fig.6,the mRNA expression levels of DNMT1 in the 0.01 and 0.1 μmol/L groups were not significantly different from the control group.In contrast,the DNMT1 mRNA levels in the 0.5 and 1.0 μmol/L groups were significantly decreased as comparison with that of the control group(decreasing by 14.0%and 24.0%,respectively).
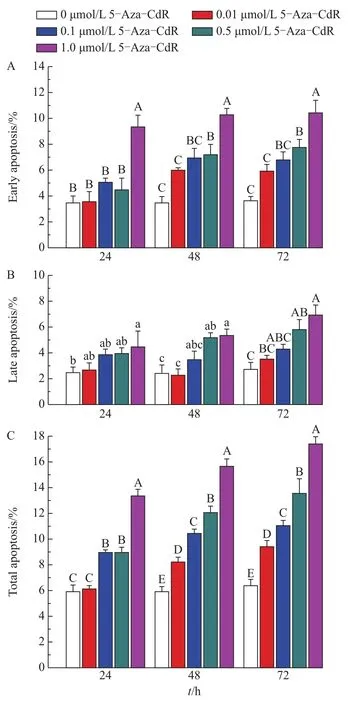
Fig.5 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the apoptosis of FBFCs
3 Discussion
In the present study,we aimed to explore a method for treating donor cells for SCNTs.The results demonstrated that the FBFCs with the treatment of 5-Aza-CdR producedose-andtime-dependenteffects.A concentration of 5-Aza-CdR of less than 0.1 μmol/L will not affect the cell cycle distribution,apoptosis,and DNMT1 mRNA expression level in the FBFCs.The optimal treatment time of FBFCs with 5-Aza-CdR is 24 h.
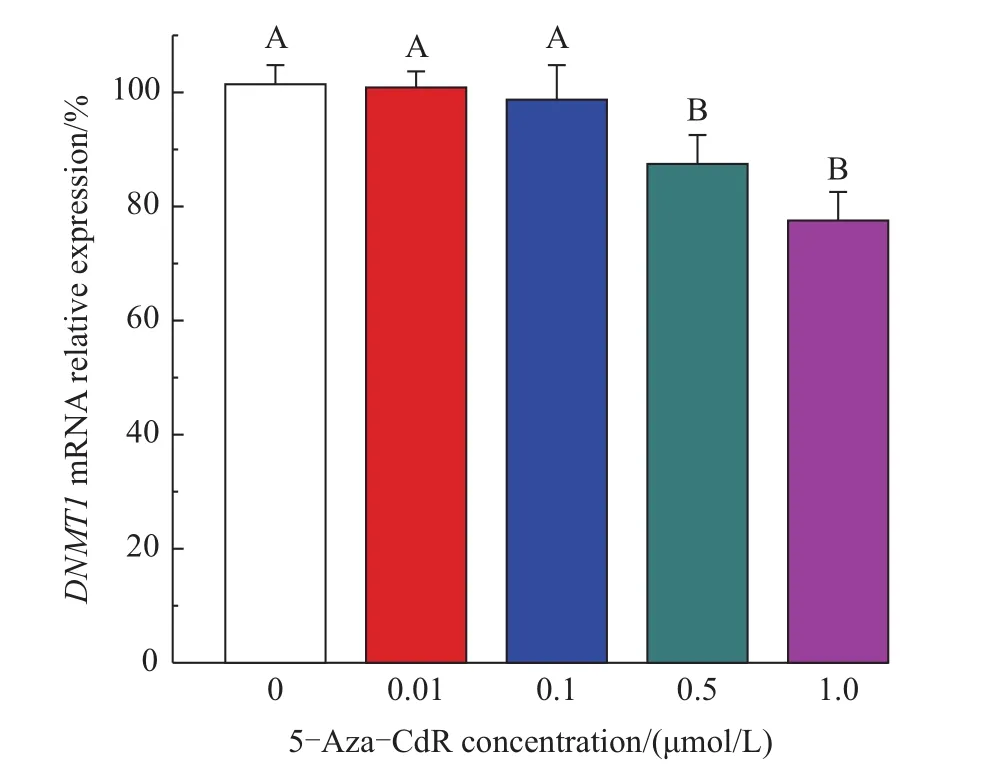
Fig.6 Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on the mRNA expression of DNMT1
The DNA demethylating agent 5-Aza-CdR has been used to activate the expression of silent imprinted genes[13].Due to this characteristic,it has also been used to enhance genomic methylation reprogramming and regulate the transcription of early embryo developmentassociated genes in embryos undergoing SCNT,thereby resulting in the improvement of the efficacy of SCNT[14-15].However,it is also a teratogenic agent and can result in defects in the developing embryos after implantation.Therefore,the effects of 5-Aza-CdR on SCNT donor cells were need to be explored.We first investigated the effects of different concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR on the cell viability of FBFCs.The OD values indicated that 5-Aza-CdR reduced the viability of FBFCs in a dose-and time-dependent manner,suggesting that 5-Aza-CdR exerted potential harmful effects on somatic cells.This result may explain to some extent the inhibitory effect of 5-Aza-CdR against the developmentalpotentialof preimplantation[16]or implanted embryos[17].Meanwhile,different concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR induced dose-dependent apoptosis in the FBFCs,the levels of which were significantly higher than those of the control group,further suggesting that 5-Aza-CdR at relatively high concentrations exerted harmful effects on the treated cells.These inhibitory effects induced by 5-Aza-CdR may be due to DNA damage and/or gene mutations that activated the expression of apoptosis-associated genes and inhibited the viability and proliferation of the treated cells.
Somatic cells at the G0/G1stage were preferentially used as donor cells to enhance the efficacy of SCNT.Serum starvation was used to synchronize the cell cycle of donor cells.However,this method resulted in DNA damage and apoptosis.In the present study,the demethylating reagent 5-Aza-CdR also affected the cell cycle distribution in a dose-dependent manner.These results were consistent witha previous studythat 5-Aza-CdR at the concentration of less than 0.05 μmol/L had no deleterious effect on the chromosomes[18].However,a previous study suggested that the concentration of 5-Aza-CdR for treating bovine donor cells for SCNT was less than 0.01 μmol/L[19].The difference in the concentrations of 5-Aza-CdR may be due to the differences in the cell types,cell passages or cell culture conditions.The influence mechanism of 5-Aza-CdR on the cell cycle distribution may be due to the increased expression of p21,which inhibits the activity of cyclindependent kinases and cell proliferation[20].
Apoptosis plays an importantrole during development,homeostasis,and many diseases.In the present study,5-Aza-CdR treatment resulted in apoptosis of FBFCs in a dose-dependent manner.These results are consistent with a previous study,which showed that 5-Aza-CdR treatment led to increased sensitivity to apoptotic signals in melanoma[21].Similarly,in cancer cells,apoptosis induced by 5-Aza-CdR may be due to the activation of cancer inhibitory genes[22].5-Aza-CdR treatment will induce apoptosis in cells and is cumulative over time[23].This apoptosis may be due to DNA damage or the interaction with apoptosis-inducing cytokines,which in turn activate pro-apoptosis cytokines.These data suggest that 5-Aza-CdR is best used at a relatively low concentration and over a short time period.
As a demethylating reagent,5-Aza-CdR can significantly reduce the methylation level of the genome via interactions with the key enzymes associated with genomic methylation.A previous study demonstrated that 5-Aza-CdR could covalently bind with DNMT1.This binding subsequently induced the degradation of DNMT1[24].The down-regulation of DNMT1 induced by 5-Aza-CdR was also confirmed by the present study.However,5-Aza-CdR at a concentration of 0.01 μmol/L or lower failed to down-regulate the expression of DNMT1 mRNA in the FBFCs.5-Aza-CdR was used to treat donor cells/embryos before SCNT to improve the cloning efficacy by reducing the methylation level of the genome.However,high-dose of 5-Aza-CdR inhibited the developmental potential and implantation of embryos[25].Therefore,the concentrationof5-Aza-CdR usedtoimproveSCNT efficacy should be optimized according to the experimental conditions,including the donor cell type,species,and enucleation methods,among others.
4 Conclusions
The DNA demethylating reagent 5-Aza-CdR can reduce cell viability,inhibit cell proliferation,increase apoptosis,and affect the cell cycle distribution.5-Aza-CdR treatment(>0.5 μmol/L)can significantly down-regulate the expression of DNMT1(P<0.01),which is beneficial for improving SCNT efficacy.Due to the cumulative effect of 5-Aza-CdR,its appropriate concentration and time for the treatment of FBFCs are less than 0.1 μmol/L for 24 h.Further investigations are needed to improve the efficacy of SCNT.

