A Study on Service-Oriented Smart Medical Systems Combined with Key Algorithms in the IoT Environment
Shan Lu ,Anzhi Wang,Shenqi JingTao ShanXin ZhangYongan Guo, Yun Liu
1 Department of Geriatrics,the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing 210029,China
2 Department of Health Education,the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing 210029,China
3 Engineering Research Center of Health Service System Based on Ubiquitous Wireless Networks,Ministry of Education,Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Nanjing 210003,China
Abstract: A smart medical service system architecture is proposed in this paper to increase medical resource utilization and improve the efficiency of the medical diagnosis process for complex business scenarios in the Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) environment.The resource representation model theory,multi-terminal aggregation algorithm,and the resource discovery algorithm based on latent factor model are also studied.A smart medical service system within the IoT environment is then developed,based on the open source project.Experimental results using real-world datasets illustrate that the proposed smart medical service system architecture can promote the intelligent and efficient management of medical resources to an extent,and assists in the develop towards digitization,intelligence,and precision in the field of medicine.
Keywords: Internet of Things; resource representation model; resource discovery algorithm; smart medical service system
I.INTRODUCTION
The Internet of Things (IoT) bridges the gap between the physical and digital world,enabling users and computers to interact with multitude of items including actuators,sensors,and other objects [1].The application core of IoT in the medical field is the use of sensor technology,GPS technology,radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology,and other information sensing technology to transmit information to mobile terminals,embedded computing devices,and medical information processing platforms through wireless and wired networks.The sensing information can then be exchanged and processed.The application and development of the Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) has attracted a high level of attention worldwide,due to its numerous application prospects in medical fields.For 5G/6G networks,IoT/MIoT is an important scenario,and the convergence of communication combined with computing is essential to support the interaction between users and the remote smart service platform for MIoT.[2]Corresponding with the improvement of living standards,IoT technology has been developed in almost all branches of the medical field.Informationization work in the medical field is now urgently required for the development of technologies.
Currently,the smart medical service system is capable of simple functions such as remote registration,inquiry,and reservation.The system also contains some defects,being unable to carry out the unified management of massive heterogeneous medical resources,including various surgical equipment,laboratory equipment,and hospital beds,whose communication modes and data formats are different from each other [4].Moreover,there is a lack of efficient multi-terminal aggregation algorithms for the tremendous amount of terminal devices in the existing medical service system.This is a key issue to accomplish a service-oriented smart medical system.Furthermore,with the continuous expansion of the network,the growth of data available has been accelerated.Consequently,earlier “passive” semantic searching technology based on keywords on the Internet will no longer be applicable since the number of data,devices and services in IoT is also showing a sharp growth trend and the devices in the perception layer are often in a changing state.
The new generation of smart medical service systems must be oriented to both “business” and “resources”,and fully introduce IoT elements to continuously promote the development of the medical field.In this work,a smart medical service system framework based on MIoT application characteristics is proposed.The system is comprised of a terminal aggregation layer,network management layer,and a service aggregation layer.The resource representation model,multi-terminal aggregation algorithm,and the resource discovery algorithm based on latent factor model (LFM)are also individually studied.The effectiveness of the service-oriented smart medical system framework and the related algorithms proposed in this paper are then evaluated by practical experiment.In addition,based on the proposed system framework,the analysis and evaluation of diabetes treatment mode for patients in existing hospitals will become more efficient.
A design architecture for a smart MIoT service system based on the complex business scenarios in the MIoT environment was proposed.
II.RELATED WORK
The smart MIoT service system has experienced a multi-stage development process since its birth.The original smart MIoT service system refers to the information management system that caters for daily operations in medical institutions [5].Zhu [6]applied the information management system to infections monitoring,carrying out automatic warning and monitoring.This system undertook regulatory functions such as drug grading management and analysis on the use of equipment,so that effective control measures for hospitalization infections could efficiently implemented.With the continuous development of IoT technology,the medical service system has begun to rely on the IoT framework to gradually present more “services” to users.Zhang [7]applied barcode technology to the medical management system.The introduction of this technology facilitates in the dynamic management of patient use of medical equipment,and is conductive to scientific and rational distribution of medical resources.Hanawa et al.[9]designed a skin image system for ordinary clinics,where doctors and patients can use the common tablet to complete a telemedicine interaction,so that people in areas with scarce medical resources can access superior medical resources at low cost.
Although above solutions have promoted the development of a smart MIoT service system to some extent,their functions are too monotonous and tend to focus only on specific scenarios.With the development of IoT,it is becoming a tide to develop and design intelligent medical applications that meet users’ needs and are easy to use.Fine medical service design can improve patients’ medical efficiency and experience,and also facilitate users and medical personnel to conduct selfhealth management and testing,thus providing better medical health services for users.Although many hospitals have their own information service systems,their functions end in availability.However,in the era of big data and cloud computing,the smart MIoT service system should integrate multiple information technologies and interface “medical services”combined with “medical resources”,thus transforming it into a remote smart service platform.To this end,this work will combine the characteristics of “resources” and “services” to propose a smart MIoT service system framework.In the subsequent design process,the resource representation model theory,the multi-terminal aggregation algorithm,and the MIoT resource discovery algorithm based on latent factor model (LFM) signals are studied.
From the perspective of IoT resources,Buckl [10]presented a resource-based model on the basis of representational state transfer(REST) architecture.However,the analysis process of state transition is relatively simple,and cannot apply to the complex business scenarios in IoT.Jia [11]presented a number of key foundational models and algorithms,such as the service ontology model,semantic-based service description language,and service management strategy.Barnaghi [12]proposed a semantic model based on IoT services,initially presenting a number of basic concepts,such as equipment,resources,and entities,combined with interconnections between them.The IoT services were then presented by providing a unified description protocol and an interface for all kinds of services.
Multi-terminal aggregation in IoT is a collaborative behavior process to support distributed ubiquitous business requirements.The term “collaboration” in terminal collaborative management refers to the process or ability to coordinate two or more different resources or individuals to achieve a certain goal in coordination [13].In the far reaching environment of MIoT,an effective multi-terminal collaborative aggregation algorithm is of great importance to realize the intelligence and automation of MIoT services.Su [14]proposed the service-oriented device composer (SODC),based on the batch priority of the combined service mechanism.This solved the resource combination and allocation problem for multiple business requests,however,the mechanism requires users to set weight parameters in advance,making it difficult to support business diversity.Kalasapur [15]proposed a new service composition mechanism for ubiquitous computing.The service-oriented middleware platform pervasive information communities’organization (PICO) was used to build the model.The mechanism uses attribute graphs to describe the service,which can dynamically synthesize multiple underlying services into complex services,but maintaining relative balance among businesses is difficult.Goo et al.[13]put forward a more business-oriented terminal aggregation algorithm,adapting the multi-user environment benefit model of terminal polymerization.However,for a large number of heterogeneous and constrained terminals,adaptive business configuration and collaborative control are still required.
From the aspect of MIoT resource discovery,Ostermaier [16]proposed a real-time search engine that allows users to search for entities in the physical world with certain attributes.This system associates web pages with physical entities that contain multiple sensor devices,and adopts additional structured metadata to describe the sensor.This approach takes full advantage of the historical data of the user and device interactions,but ignores the relationship between device contexts to a certain degree.Yao et al.[17]mapped environmental context information to a separate graph,using the weight values between the vertices to reflect the degree of correlation between different devices.However,the description structure of the graph does not fully capture the relationship between heterogeneous devices.In the process of compressing multi-dimensional information into graphs,it will inevitably experience some loss of useful information.
III.A FRAMEWORK OF SMART MIOT SERVICE SYSTEM COMBINED WITH ITS KEY ALGORITHMS
There is no doubt that IoT technology has great potential in medical field.It can help hospitals to realize intelligent medical treatment and the management of things.Also,it can meet the needs of medical health information,medical equipment and supplies,and intelligent management and monitoring of public health safety,so as to solve the prob-lems of weak support of medical platform,low level of medical service and hidden danger of medical safety production.
With the growing demands for MIoT technology by patients and doctors,more explorations and attempts regarding its application have been made in the medical field.Medical IoT was first developed to promote the development of the medical service model.It serves the medical and health field by integrating optical technology,pressure-sensitive technology,and RFID technology,and combines various medical sensors.The MIoT can exchange information using mobile terminals,embedded computing devices,and a medical information processing platform using sensor networks in accordance with determined protocols [18].
To adapt to the above characteristics of the MIoT environment,a framework of a smart MIoT service system based on the traditional three-tier architecture of the IoT is proposed in this work,as shown in figure 1.In hospitals,the IoT consists of a large amount of addressable communication sensor systems,medical equipment,hospital information systems,and building systems [19].
For the terminal aggregation layer,the first step is to abstract the MIoT resource representation model,construct it into a virtual terminal,and to provide an interface for the upper platform.Additionally,based on the particularity of the MIoT environment,optimally allocating the terminal set for each user’s business under limited resources is a key issue for MIoT to implement the smart processing of services.Due to limited network resources and terminal capabilities,competition may occur when multiple users simultaneously initiate service requests.To protect the quality of service,effective multi-terminal collaboration and aggregation cannot affect the quality of service of other users.
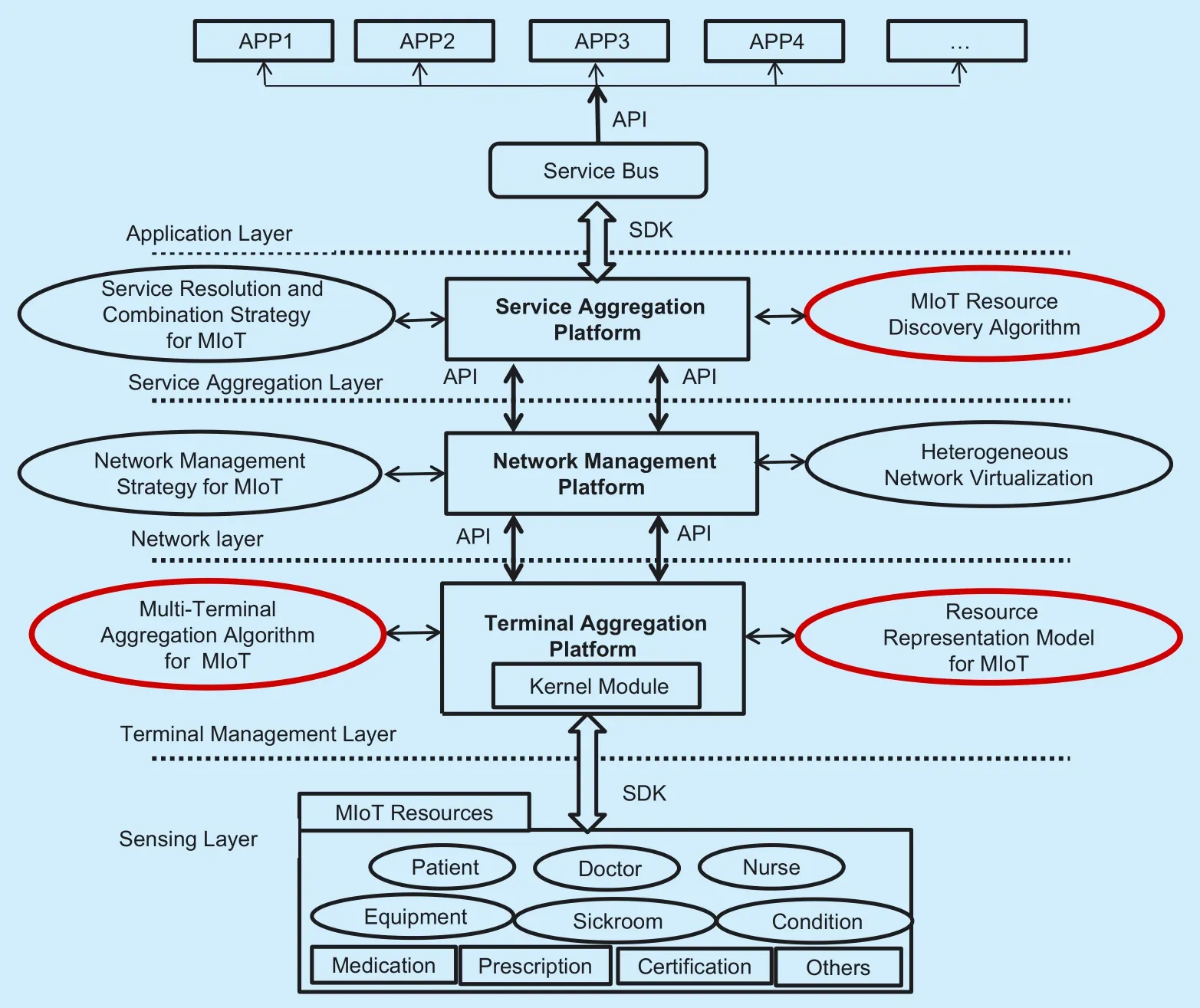
Fig.1.The proposed framework of smart MIoT service system in this work.
For the network management platform,the communication protocols of the terminal or devices in the MIoT environment are diverse.On the one hand,to achieve multi-dimensional joint optimization of communication,computing,storage,and other resources,heterogeneous network virtualization technology is required.Using heterogeneous physical network resource modeling,abstraction,allocation,and other mechanisms,multiple heterogeneous virtual networks are built in parallel on the physical network.These heterogeneous virtual networks coexist,and share the underlying public physical network resources.This allows users to configure and manage the required resources so that each virtual network can customize its own architecture and protocols according to service needs,so as to improve network utilization.On the other hand,the MIoT is usually oriented for complex business scenarios,and the network transmission and control platform is the backbone platform of the hospital network,which generally uses Ethernet,machine to machine (M2M),mobile communication,and other technologies to transmit the information acquired by the sensing layer.Therefore,it is necessary to reasonably schedule and manage network resources based on network management strategies for MIoT complex business scenarios.
The service aggregation platform receives the business request sent by the application layer,and allocates the virtual terminal resource or the network link resource based on the parsing and combination strategy of the service in the MIoT business scenario.Then,the calculation result is fed back to the network management platform in time,in order to invoke the corresponding virtual terminal access interface of the terminal aggregation control platform to execute the specific application.With the continuous expansion of the MIoT,the growth of data available on the Internet has accelerated rapidly.Furthermore,the status of devices in the sensing layer is often unstable.Consequently,previous “passive” semantic searching technology based keywords on the Internet will no longer be applicable.A method to analyze the tremendous interactive information between users and devices to recommend the most relevant equipment resources according to user preference is the key to the resource discovery algorithm in the MIoT.Therefore,an IoT resource discovery algorithm based on LFM is included in the service aggregation platform,so to support efficient resource discovery in the MIoT environment.As the MIoT is an extremely large and complex system,the study of its architecture is fundamental to the work,and a key to future development [18].Thus,this paper initially proposes a smart MIoT service system framework based on the complex business scenarios in the MIoT.The resource representation model,multi-terminal aggregation algorithm,and the MIoT resource discovery algorithm based on LFM are then examined,so as to promote the intelligent and efficient management of medical resources.
3.1 Resource representation model basis for MIoT service
The MIoT is composed of interrelated “objects” as well as addressable virtual resources[20].However,this feature imposes a great challenge to the representation of the MIoT services as it lacks the same unity as Web services.The inevitability of the MIoT resource representation model is clearly perceived based on the following features: (1) The heterogeneity of “things”; (2) The “massive”nature of MIoT data; and (3) The diversity of MIoT services,and the complexity of business scenarios.Therefore,a unified representation model is required for massive heterogeneous resources and services in the MIoT environment,which facilitates service managing and searching operations of the MIoT management platform.
3.1.1 Service representation model basis
To achieve wider sharing and interoperability,the representation model of MIoT services must have a broad application base.Furthermore,the representation model should be able to support a more comprehensive description of the MIoT service,and support the association with other domain knowledge ontology.Due to the difference of application scenarios compared with Web services,services in the MIoT generally have unique feature requirements,including context features and user experience quality features.Therefore,the logical structure of the MIoT resource representation model must be more diverse and customizable.
Possessing a strong expressive ability as well as a concise description structure,Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a computational logic-based language.Considering IoT services cover diverse areas,the proposed approach herein is based on OWL.In this study,the description of the main structure is provided in figure 2.In this diagram,profile represents the outline of services or describes the purpose of the application of services; model refers to processing models,mainly for service providers to describe the internal processes of services; and grounding refers to the service foundation,predominantly explaining how to access the services.The IoT resources are used to describe the collection of physical resources that can provide the services,and specified ontology refers to the specific domain ontology model,as some scholars have attempted to model different domain ontologies,such as social ontology and Gene Ontology [10].
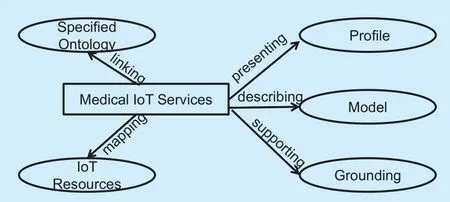
Fig.2.Extended OWL structure for MIoT service description.
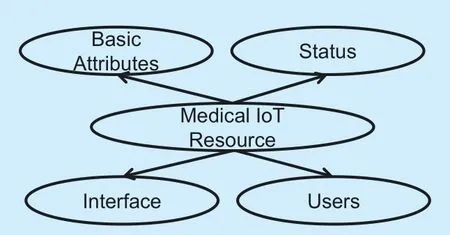
Fig.3.Description structure of MIoT resources.
3.1.2 Resource representation model basis
As an increasing amount of devices are connected to MIoT applications,the complexity of the network also increases.Therefore,a method to establish a unified MIoT resource representation model will be the basis of information exchange for various MIoT applications.
Ontology language has a rich expressive ability,and a high level of grammar and semantics [20].Therefore,this paper will model the MIoT resources based on the ontology construction method to carry out the unified description of heterogeneous resources.
The basic description structure of MIoT resources is provided in figure 3.In this diagram,basic attributes are used to describe the attribute information carried by the device itself,including the unique symbol ID,the name of the device,and the information related to the manufacturer (i.e.,the date of manufacturing,serial number,etc.).Status is generally used to describe the related state information of a device.Due to the different environments of the MIoT,the operation of devices is is largely challenged by environmental factors.In addition,interface is used to describe the relevant information of the device,mainly involving the particular constraints on the input and output instance,and properties of access links to the device.The user attribute is mainly used to record user attribute information.On the one hand,to facilitate the discovery and selection of devices,recent user information attribute should be added.On the other hand,for the safety and stability of devices,configuration of various privileges for different users should be carried out.
3.1.3 Mapping relationship between resource and service
As the service provider,the MIoT resource entity needs to establish a reasonable mapping relationship between the resource and the service in order to configure the optimal device set for the business in the application layer.There are multiple devices with the capability of providing this service.However,some devices may be required to provide different services and are integrated for a composite service.Hence,the authors’ attempt to add property classes called “Resource Set: for each service,possessing two basic attributes: device list and state list”.The device list is generally used to indicate which devices can provide the service,and state list is typically utilized to indicate whether these devices are operating normally.The structure of the Resource Set is illustrated in figure 4.The device list is provided with the vectorDL,whose elements are the entities of the IoT resource.The state list is represented by the vectorSL,whose element is 0 or 1,0,indicating that the device does not operate normally,and conversely is represented by 1.
3.2 Multi-terminal aggregation algorithm for MIoT service
3.2.1 Basic concepts
To solve the MIoT terminal aggregation problem,the MIoT service model (SM) and resource model (RM) are modeled based on ontology theory.The RM is a comprehensive model of the network layer and the ubiquitous sensing layer in the overall architecture,while SM is the representation model of ubiquitous service in the application layer,depending on the support of the network layer and the sensing layer.The terminal aggregation set (TAS)corresponding to the service is then constructed.The models are represented in the form of a logical diagram [21],which are respectively expressed asGSM(Pi,Ci,Qi) andGRM(T,L).The research problem focuses on the proper way to mapGSM(Pi,Ci,Qi) toGRM(T,L),so as to select the best set of terminals to provide services.
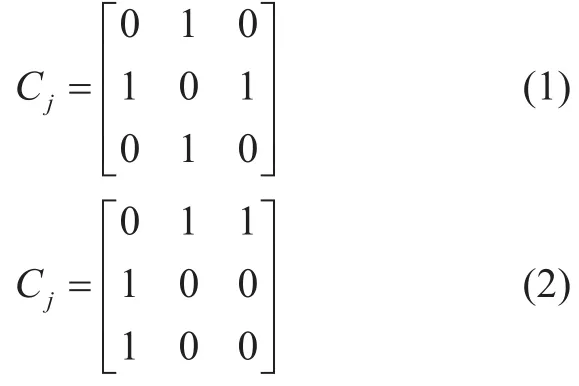
SM: Each ubiquitous businessi(i=1,2,···,n)is represented byGSM(Pi,Ci,Qi),including business setbusiness relationship matrixand business quality index setLetpiv,represent thevthsub-business in businessi.To represent the relationships between the various businesses,a transfer matrixis introduced.The value of the matrix element(0 or 1) represents the connection or disconnection between various sub-services,which is convenient for the analysis and processing of computer language.For example,(1) is the execution sequence ofwhile (2) isThe difference lies in the order of service execution,in which (1) is a serial order,and (2) is in the order of parallel execution.Note thatqiv,is the quality indicator for thevthsub-business of generic businessi.
RM: In the ubiquitous MIoT environment,terminals interact with each other through wired or wireless communication.The corresponding logical diagram can be expressed asGRM(T,L),consisting of a terminal setand a network communication link setbetween different terminals.
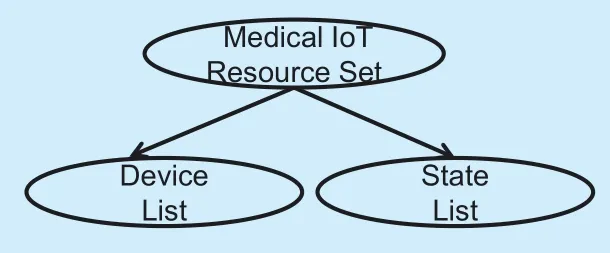
Fig.4.ThemainpropertiesoftheMIoTResource Set.
TAS: For each ubiquitous businessi,there are multiple optional terminal collaboration sets corresponding to it,denoted asCis,,wheresrepresents thesthterminal synergy set related to the ubiquitous businessPi.Moreover,the TAS corresponding to each generic business should meet the corresponding resource capacity constraints of (3) and (4).Among them,Tkw,represents thekthkind of upper limit ability of the terminal,andwis the selected terminal.SubscriptLerepresents upper limit carrying capacity of the link occupiede.
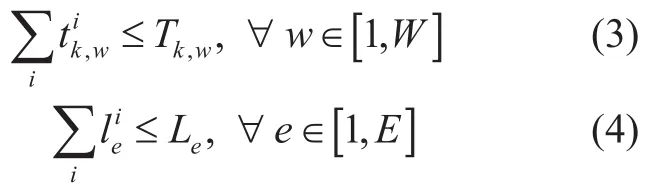
Based on the service,resource,and terminal aggregation models,the multi-terminal aggregation problem (MTAP) of the MIoT service is predicated on the mapping algorithm from SM to RM,which is responsible for providing the optimal terminal combination and allocation scheme for lots of MIoT businesses in the application layer.
3.2.2 MTAP
The MTAP in the MIoT business scenario can be expressed as (5) using the model in [13].
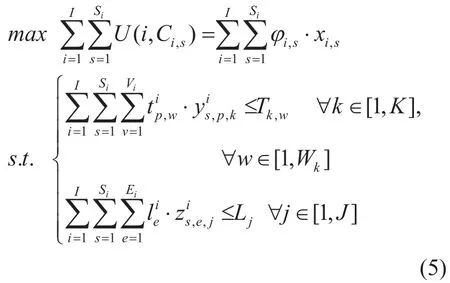

It can be seen from (5) that the MTAP is a linear integral planning problem with multi-dimensional constraint conditions [22].However,it is very difficult to solve this optimization problem,so it should be simplified by dimensional reduction processing.Therefore,the MTAP is transformed into the multiple-choice multi-dimension knapsack problem (MMKP)by dimensional reduction processing [23],that is,the two constraints in MTAP on terminal and link capacities are combined into the one-dimensional constraintThe transformation formula is provided in (7).
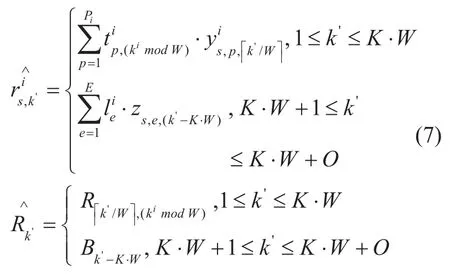
Then the MATP can be transformed into the one-dimensional MMKP,as shown in (8).


The MMKP problem is an NP-hard problem.Many practical problems can be described by the MMKP model,including inventory compression and distributed computing system processor allocation problems.In this study,the ant colony optimization (ACO) [24]algorithm is introduced to solve the MMKP problem,which has been successfully applied to traveling salesman problems (TSP),quadratic assignment,and sorting problems.A modified ACO algorithm to adapt to the MMKP model is proposed,namely ant colony optimization-multi-terminal aggregation(ACO-MTA).The main process of the ACO-MTA is as follows.
When the ACO is applied in different scenarios,the pheromone updating model is not alike.The pheromone updating process of each TAS in this work is as shown in (10).
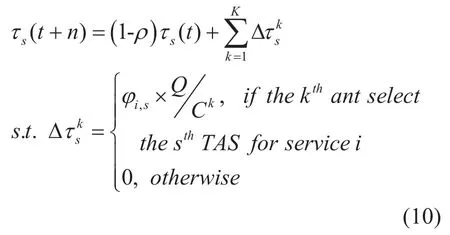
Note thatQis a constant and can be set to 1.Subscriptis the pheromone increment generated when thekthant passes thesthTAS,andρ∈[0,1]represents the degree of volatilization of pheromones.The closer the value is to 1,the more volatile the pheromones are,and vice versa.SubscriptCkrepresents the total benefit of all TAS selected by thekthant.It can be seen from the above formula that the higher the benefit values of TAS,the greater the corresponding pheromone increment.By the subsequent iteration,all ants will calculate the select probabilityps(k) of TAS according to the newly updated pheromone vectorτs(t+n) [26].Note thatps(k) can be obtained as follows.
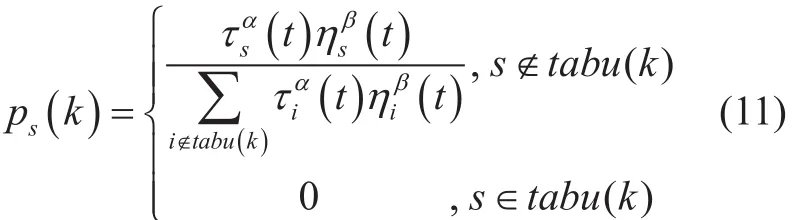
Additionally,let
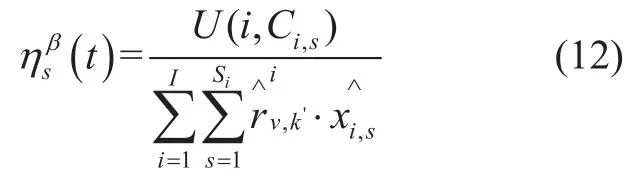
3.3 Resource discovery algorithm based on LFM
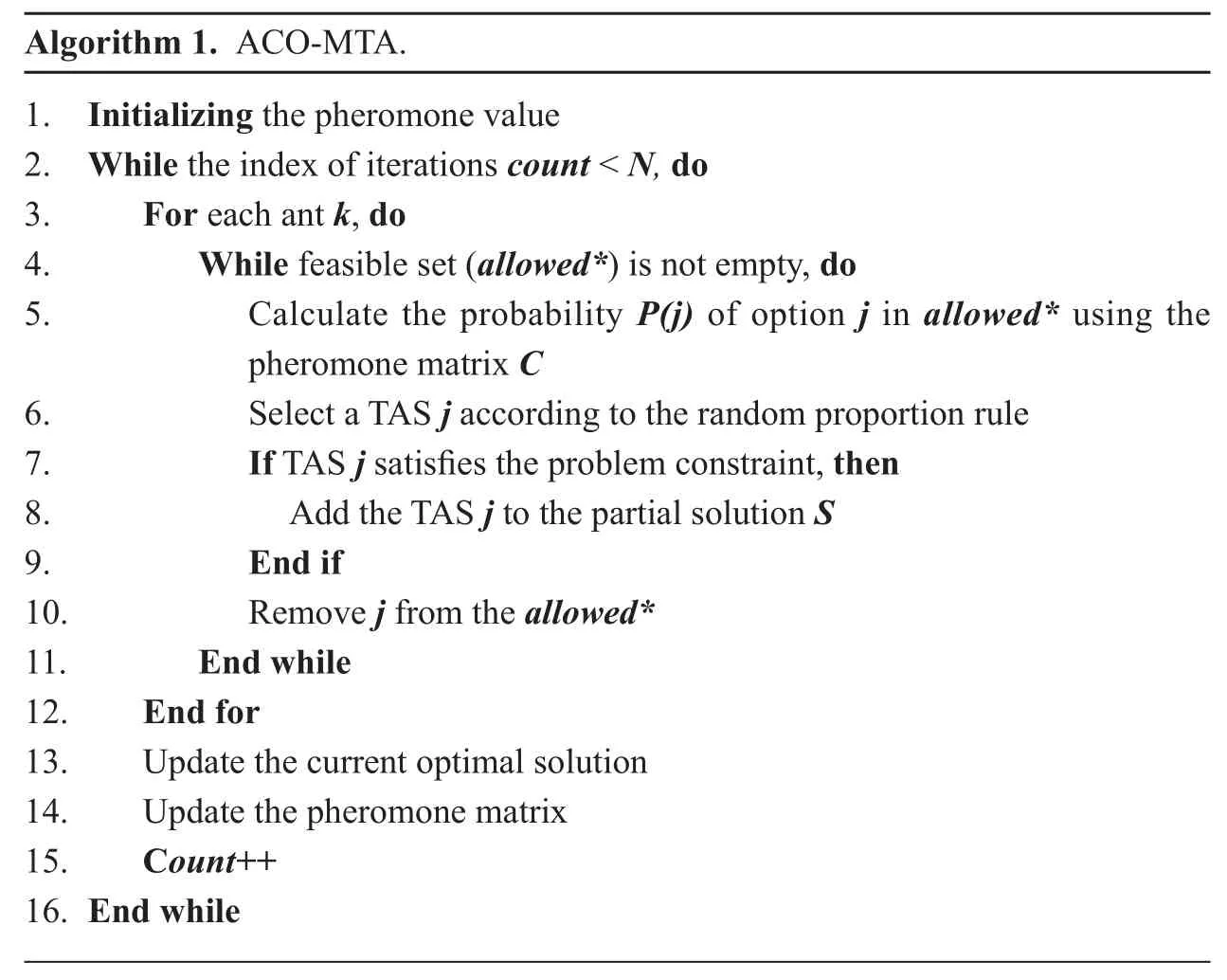
Algorithm 1.ACO-MTA.1.Initializing the pheromone value 2.While the indexof iterations count < N, do 3.For each ant k,do 4.While feasible set (allowed*) is not empty,do 5.Calculate the probability P(j) of option j in allowed* using the pheromone matrix C 6.Select a TAS j according to the random proportion rule 7.If TAS j satisfies the problem constraint,then 8.Add the TAS j to the partial solution S 9.End if 10.Remove j from the allowed*11.End while 12.End for 13.Update the current optimal solution 14.Update the pheromone matrix 15.Count++16.End while
In the MIoT,devices are usually function-oriented,and there is a strong correlation between devices with similar functions.Devices with different functions also face different populations,and pairwise devices show similarities or complementarities in functions,such as printers and computers,heart rate monitor,and sphygmomanometers [25].The cross-correlation between devices will be reflected in specific usage scenarios and modes,and fully exploiting this potential correlation will provide some reference value to the resource recommendations in the MIoT.
The resource discovery problem in the MIoT business scenario should focus on how to analyze the tremendous historical interaction information between users and devices,so to obtain a cross-correlation matrix between different devices.Then,according to user preferences,the recommendation list of the device is generated,and the efficiency of IoT resource searching can be improved to some extent based on this “active” resource discovery method.Herein,the form of four tuples in(13) is used to describe every user’s behavior record on the device in the MIoT environment,whererepresent user set,device set,location set,and timestamp set,respectively.Each usage record can be represented by
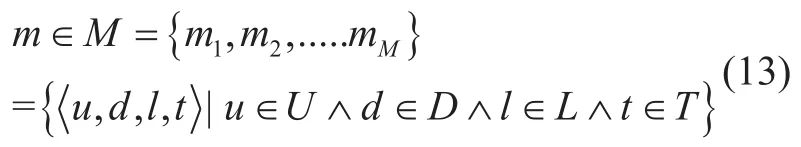
The above usage record can be used to analyze the usage frequency of different devices by the user,which can be expressed in the form of a pair of “user-device” tuples,denoted asThe usage frequencyrij,corresponds to (,)i jwith mapping criteria in (14).
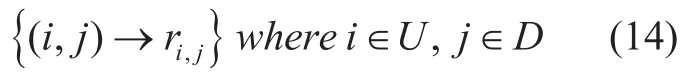
This paper aims to calculate the implicit correlation between the users and devices by analyzing the knownrij,and then predict users’interestin unknown devices.Finally,the sorting function was used to generate a list of device recommendations for the specific user.The solution process of this problem is shown in figure 5.
(1) Model based on hypergraph theory:Owing to the comprehensiveness of the relationship between users and devices,a unified hypergraph is required.Here,by analyzing the user’s behavior usage logon the devices,a representation model MG of MIoT user-device interaction based on the hypergraph theory [26]is presented,and the corresponding representation matrixRUI×is designed.SubscriptUandIrepresent the number of users,and the number of devices,respectively.Finally,the resource recommendation problem is proposed based on this model.
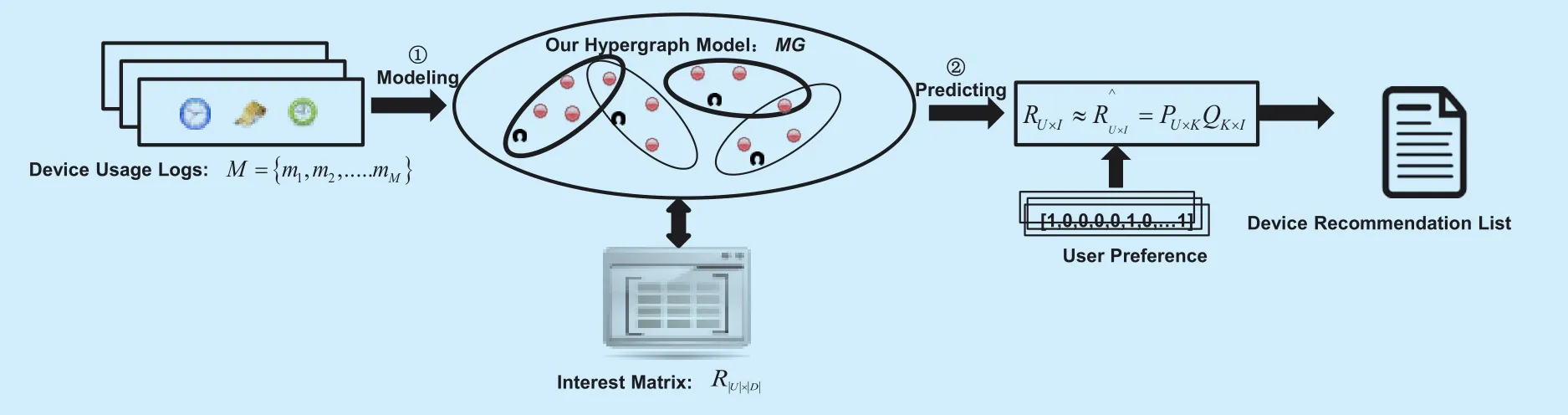
Fig.5.Schematic diagram of the proposed IoT resource discovery algorithm.
(2) Resource recommendation based on LFM:After the matrixRUI×is obtained,the resource recommendation problem can be transformed into a correlation prediction problem based matrix decomposition.That is,the dependence matrixRUI×to the device can be decomposed into two matrices: one is the user’s preference matrixPUK×for the implicit features of the device,and the other matrixQKI×indicates the implicit weight of features contained in different devices.SubscriptKis the number of implicit features.The decomposition process is as shown in (15).
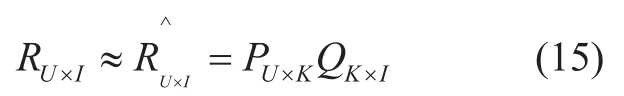
To calculate the matrix parametersPUK×andQKI×,a training set is required.For each useru,the training set contains device interaction data that is more dependent or independent.The above model parameters can be obtained by learning this training data set.To measure the accuracy of the prediction,the loss function is defined as (16).
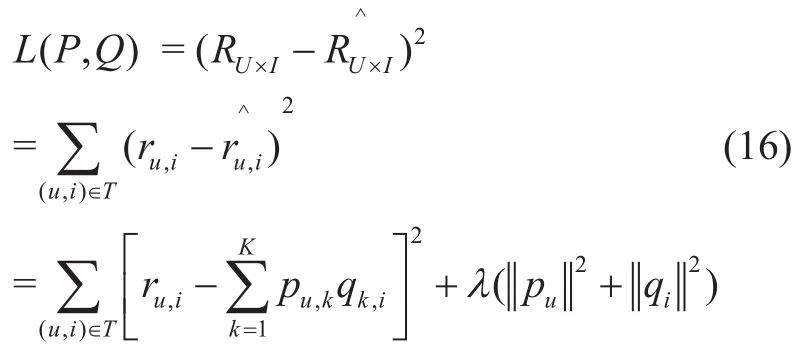
At this point,the IoT resource recommen-dation problem based on the LFM has been transformed into a single-objective optimization problem,namely how to minimizeL(P,Q).As the variablespuandqiare coupled together,the solution process will become very complicated,so the alternating least squares (ALS) [27]method is introduced.That is,QK×Iis first fixed,then the derivative zero method is used to solvePU×K,as shown in (17).Following this,PU×Kis fixed,then the derivative zero method is used to solveQK×I,as shown in (18).This is alternately calculated multiple times until the convergence or iteration number has been determined (also called the ALS solution).
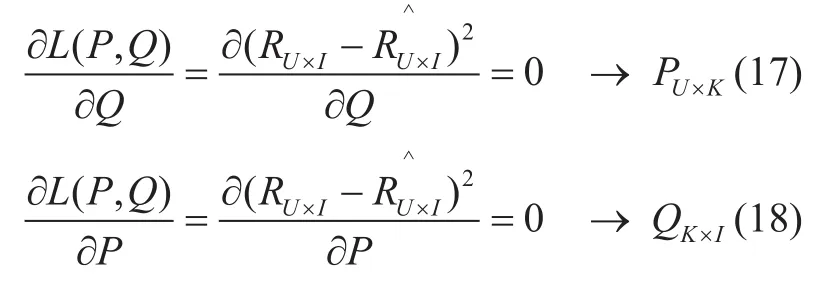
According to the solution [27]of ALS,puandqican be obtained as (19) and (20),whereru(1×I) is theuthrow ofRU×I,ri(U×1) is theithcolumn ofRU×I,andEis the identity matrix.A resource recommendation algorithm (LFMALS) based on the latent factor model is then proposed.
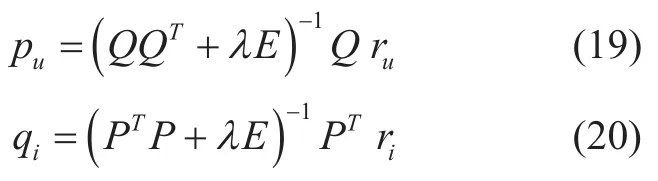
IV.EVALUATIONS
4.1 The developed smart MIoT service system based on Kaa
As the smart MIoT service system is still a relatively new field,it is hard to find large-scale public testing tools.Thus,a service-oriented smart medical service platform is built here based on the open source project Kaa [28].With reference to the experimental environment setup in [25],several typical application scenarios are set up on this platform,such as outpatient hall,ward,operating room,and laboratory.There are approximately 300 sensors or devices connected to the platform,including printers,computers,sphygmomanometers,heart rate monitors,and thermometers.Each physical device has a corresponding virtual terminal on the platform,which provides the Web service invocation interface in the form of RESTful for the application program upward,and communicates with the physical device in the perception layer downward,using software development kit (SDK) to receive the sensor data in real time.The platform supports the generation of SDKs for different IoT hardware operating systems,such as Linux,Android,and Raspberry.Furthermore,MongoDB is embedded with the cloud platform,and is used to record individual historical usage data.Administrators can view this in real time by logging in to the background system.
The main design structure of the above-mentioned smart medical service platform is illustrated in figure 6,which is a service-oriented system architecture that enables cross-industry and cross-platform resource information sharing and interconnection.The design structure includes the following parts:a heterogeneous terminal cluster environment,IoT ubiquitous heterogeneous network,Kaa core-based terminal control system (Ubuntu,deployed on Tencent Cloud server),service resolution and management system (Windows,deployed in Alibaba Cloud Server),and various industry application systems.The core feature of the platform is the use of Kaa’s superior cross-platform and cross-network features to manage the heterogeneous terminal clusters.The heterogeneous network works as a bridge to receive feedback from the sensing layer,and to construct a virtual terminal based on service requests of the application layer.
The evaluations of the proposed algorithms in this paper are mainly developed from two aspects of the medical diagnosis process.On the one hand,the effectiveness of the proposed ACO-MTA for MIoT ubiquitous service was demonstrated by the comparison with the random selection (RS) algorithm and the greedy algorithm (GA) in terms of comprehensive bene fits,effective utilization of resources,and business success rate.On the other hand,the MIoT resource discovery algorithm based on latent factor model was proposed,the simulation proved that our approach outperforms item-based collaborative filtering (ItemCF)[29]algorithm in terms of root mean square error (RMSE) [25]and mean absolute error(MAE) [25].The results will be expanded in the following sections.
4.2 Results
4.2.1 Experimental results of the proposed ACO-MTA
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach,the comprehensive benefits,utilization of resources,and business success rate of the experiment is compared with the RS and the GA.
For comprehensive benefits,ACO-MTA increased the total business benefit of the RS algorithm or the GA by 2 % to 39 %.Additionally,the ACO-MTA demonstrates obvious advantages over RS as the number of requests increases.For the resource utilization aspect,the ACO-MTA algorithm’s resource utilization is approximately 2 % to 10 % higher than the RS or GA algorithm.Although the performance of ACO-MTA is similar to that of the GA,the performance of the GA is not stable because it easily falls into local optimum,in which case determining the global optimum solution is very hard.Finally,for the business success rate aspect,under the condition of the same number of requests,the business success rate of the ACO-MTA is approximately 6 % to 12 % higher than the RS or the GA.
4.2.2 Experimental results of the proposed LFM-ALS
Approximately five months of historical usage data from 100 participants (including patients,doctors,and nurses) in the hospital was collected as a data set for the experiments in this paper,which included 99,821 user-device interaction records.To verify the accuracy of the LFM-ALS algorithm proposed in this paper,the approach is compared with the ItemCF[29]in terms of MAE [25]and RMSE [25].
From the aspect of MAE,as the training set data set becomes larger,the average absolute error of the two algorithms both decrease to different levels.In the case of a small training set (10 % to 50 %),the ItemCF based on cosine algorithm demonstrates higher prediction accuracy.When the training set size accounts for 60 % to 70 % of the total data,the performance of the LFM-ALS algorithm proposed in this paper and the ItemCF based on cosine have similar capabilities.When the training set is large (90 %),the advantage of LFM-ALS algorithm becomes gradually obvious,as the latent factor model needs to analyze a large number of historical data to obtain implicit features.
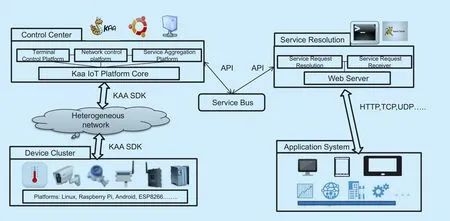
Fig.6.Main design structure of the proposed smart medical service platform.
From the aspect of RMSE,experimental results are consistent with the MAE mentioned above,since both MAE and RMSE are reference values to measure the prediction accuracy of the recommendation algorithm,and the difference between them lies only in the calculation methods.
Additional,experimental results illustrate that as the number of iterations in the LFMALS algorithm increases,MAE and RMSE all tend to decrease overall,but the algorithm consumes more computing resources and time cost with the increase of iteration number.It can be found that RMSE fluctuates more with the number of iterations than MAE,which is related to the increased penalties for prediction errors in the RMSE.The results in [27]show that the values of MAE and RMSE tend to be stable when the number of iteration increases to a certain extent.
V.CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
As a vital aspect of people’s lives,smart medical service systems have gained increasing attention from industry and academia for hospital information construction.It is foreseeable that smart MIoT service systems will become an indispensable part of people’s lives.The significance facing both “service”and “resource” as a necessary requirement for the new generation of smart MIoT service system was initially discussed in this paper.To this end,design architecture for a smart MIoT service system based on the complex business scenarios in the MIoT environment was proposed.The resource representation model,multi-terminal aggregation algorithm for MIoT services,and the resource discovery algorithm based on LFM were then individually examined.Finally,a simple smart MIoT service platform was built based on the open source project Kaa [28],and the effectiveness of the proposed framework combined with the related algorithms was demonstrated using a practical experiment.Furthermore,the module of monitoring and controlling the blood sugar level of diabetic patients in the proposed system framework is found to play an important role in reducing the incidence of diabetes.This provides a drastic improvement compared with previous hospital information management systems.
The MIoT service system is an extremely large and complex system,and the study of its architecture is both a fundamental work and a key to future development.Thus,the heterogeneous network virtualization and network management strategy for complex business scenarios mentioned in the overall architecture remain important directions for future research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China(2018YFC1314901),the Natural Science Foundation of China(61871446),and the Scientific Research Starting Foundation for New Teachers of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications(NY217033).
- China Communications的其它文章
- Convolutional Neural Networks Based Indoor Wi-fiLocalization with a Novel Kind of CSI Images
- Research on Multicloud Access Control Policy Integration Framework
- Towards the Design of Ethics Aware Systems for the Internet of Things
- LLR Processing of Polar Codes in Concatenation Systems
- Cooperative Relay Based on Exploiting Hybrid ARQ
- Initialization for NMF-Based Audio Source Separation Using Priors on Encoding Vectors

