Comparison of different methods for quantification of proanthocyanidins from grape seeds
ZHOU Li,YANG Fu,ZHANG Minghao,YAO Jiaxu
(The Modernization Engineering Technology Research Center of Ethnic Minority Medicine of Hubei Province & School of Pharmacy,South-Central University for Nationalities,Wuhan 430074,China)
Abstract The effect of extraction temperature,time,solvent and the number of cycles on the solid-liquid extraction yield of total polyphenols and three main phenolic compounds in grape seed extracts were investigated.The optimal extraction conditions were obtained as follows: Extraction temperature 50 ℃ and 60 min of extraction with 80∶20(ethanol/water,V/V) of aqueous ethanol for four successive extractions.Additionally,quantification of proanthocyanidins from grape seeds by vanillin-HCl assay and Folin-Ciocalteu assay in combination with HPLC was evaluated,and compared with acid butanol assay.The results showed that vanillin-HCl-HPLC method and acid butanol assay were more efficient than Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method for the quantification of proanthocyanidin,and there was no significant difference(P>0.05) between vanillin-HCl-HPLC and acid butanol assay.Especially,acid butanol assay provides a simple,fast and effective method to quantify the proanthocyanidin,and could be a better alternative to vanillin-HCl-HPLC method and Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method of analyzing the proanthocyanidin in grape seed extracts or other natural sources.
Keywords grape seed; proanthocyanidin; quantification; Vanillin-HCl assay; Folin-Ciocalteu method; acid butanol assay
Grape seeds,a by-product of winemaking or juice making,are rich in polyphenols.Polyphenols have health-promoting effects such as reducing incidence of atherosclerosis and coronary heart diseases and removing problematic low-density lipoprotein.The phenolic compounds in grape seeds are phenolic acids(e.g.gallic acid),flavonoids including monomeric flavan-3-ols(i,e.,catechin,epicatechin,gallocatechin,epigallocatechin,and epicatechin-3-O-gallate) and proanthocyanidins.Proanthocyanidins is analyzed by UPLC or HPLC coupled with diode array detector(DAD) and mass spectrometry(MS)[1-3].However,most HPLC methods have only been developed for the determination of major compounds of proanthocyanidins,which cannot well reflect the quantities of proanthocyanidins[4-5].Currently there is no uniform method of measuring the content of proanthocyanidins due to the complex composition,although some traditional methods are workable,such as vanillin method,Folin-Ciocalteu assay and acid butanol assay.The vanillin reaction has been widely used to estimate condensed tannin(proanthocyanidin).Folin-Ciocalteu assay measures the total concentration of phenolic hydroxyl groups in the plant extract.Polyphenols in plant extracts react with Folin-ciocalteu reagent to form a blue complex that can be quantified by visible-light spectrophotometry[6].Acid butanol assay is a method specific for the determination of the content of proanthocyanidin,which can be quantified spectrophotometrically following depolymerization under strongly acidic conditions[7-8].The aim of this study was to investigate and compare the three methods in order to evaluate the efficiency of the quantification of proanthocyanidins from grape seed extracts.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Materials
Grape seeds were purchased from local supermarket(Nanjing,China).Solvents used for HPLC analyses were of HPLC grade,and those used for extraction were of analytical grade.HPLC grade of methanol was provided by Hanbon(Jiangsu,China).Distilled deionized water(ddH2O) was produced using a MilliQ Ultrapure water-purification system(Millipore,USA).Formic acid solution(pH 2.5) was prepared by diluting formic acid in ddH2O(2∶998,V/V).Folin-Ciocalteu reagent was purchased from Kayon Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Hydrochloric acid andn-butanol were provided by Lingfeng Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Sodium carbonate,vanillin,ammonium ferric sulfate dodecahydrate and standards of gallic acid,catechin,and epicatechin were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich(USA).Proanthocyanidin(>95%) was purchased from Dalian Meilun Biotech Co.,Ltd.(Dalian,China).
1.2 Sample preparation
The grape seeds were grounded,and the obtained powder was lyophilized(Telstar LyoQuest,HT-40 Beijer electronics).The grape seed powder(1.0 g) was extracted with 20 mL of aqueous ethanol(ethanol/water,80∶20,50∶50 or 20∶80,V/V),water or ethanol with different temperatures(30~70 ℃) for the duration from 30 to 120 min.The suspension was centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 10 min,and the organic phase containing total polyphenols was collected,evaporated under vacuum using a rotary evaporator(40 ℃) and dried under a gentle stream of N2,affording the grape seed extract.
1.3 Folin-Ciocalteu assay
One milliliter of 10 fold diluted Folin-Ciocalteu reagent,2.0 mL of 10% sodium carbonate and 0.2 mL of grape seed extracts(1.0 mg/mL) were mixed well[9].The absorbance was measured at 747 nm after 60 min of heating at 30 ℃.A mixture of water and reagents was used as a blank.The calibration curve was made with standard solutions of proanthocyanidins in the range 1-10 mg/mL.The content of total polyphenols was expressed as gallic acid equivalents.
1.4 Vanillin-HCl assay
Firstly,vanillin reagent was prepared by solution A and B.Solution A,1% vanillin in methanol(1.0 g vanillin up to 100 mL with absolute methanol); Solution B,8% concentrated HCl in methanol(8.0 mL concentrated HCl brought to 100 mL with absolute methanol).Then,solution A and B were mixed(1∶1,V/V) and stored for use in a dark bottle at 4 ℃.
One milliliter of the sample or standard solution of proanthocyanidin(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4 and 0.5 mg/mL) was added 5.0 mL of the vanillin reagent.The reaction was carried out in a water bath at 30 ℃ for 30 min.Measure was carried out at 500 nm.The calibration curve was made with standard solutions of proanthocyanidins in the range 1-10 mg/mL.Total polyphenols content of grape seed extract was expressed as mg proanthocyanidin equivalents/1 mg grape seed extracts.
1.5 Acid butanol assay
An aliquot(1.0 mL) of extract or standard solution of proanthocyanidin(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4 and 0.5 mg/mL) was added to 10.0 mL volumetric flask containing 5.0 mLn-butanol-hydrochloric acid(95∶5,V/V),and 0.2 mL 2% ammonium ferric sulfate solution was then added into the flask.The solution was mixed well and heated in the water bath at 95 ℃ for 40 min.The absorbance was measured against prepared reagent blank at 550 nm.Total polyphenols content of grape seed extract was expressed as mg proanthocyanidin equivalents/1 mg grape seed extracts.
1.6 Determination of individual polyphenols byHPLC
HPLC-DAD analysis was done on an Agilent 1100 series HPLC(dwell volume,1.2 mL) consisted of a model G1379A degasser,a model G1311A pump with a low-pressure gradient mixer(G1311-69701),a model G1316A column oven,and a model G1315B DAD system.The separation was achieved on a TSKgel ODS-80TsQA column(150 mm × 4.6 mm,5 mm,Tosoh).The temperature of column oven was set at 40 ℃.The flow rate of the mobile phase was 0.7 mL/min,and gradient flow was used with 2 mobile phases which are formic acid solution(pH 2.5) as mobile phase A and 100% methanol as mobile phase B,the analysis time was 40 min.The gradient program was as follows: 0-20 min,90%-40% A,20-30 min,40%-90% A,30-40 min,90% A.Grape polyphenol extract samples were dissolved in methanol,filtered on a 0.45 mm filter,and injected(20 mL) in the chromatographic system.The DAD acquisition wavelength was set in the range of 200-600 nm.Chromatographic data were collected and integrated using Agilent Chemstation software.Calibration plots were constructed with authentic standards by plotting peak areas from the DAD absorbance signal at 280 nm versus standard concentrations.
1.7 Validation of vanillin-HCl assay,Folin-Ciocalteu assay,acid butanol assay and HPLC
The parameters of precisions and recovery were evaluated for the validation to ensure the validity and reliability of vanillin assay,Folin-Ciocalteu assay,acid butanol assay and HPLC method.
The precision of the method was established by the relative standard deviations(RSD) of the respective measurements from five repeated runs of sample solution.The recovery of the method was determined by standard addition method.The standards of proanthocyanidin,gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin were spiked with samples,five replicates were analyzed and the results were compared with an unspiked sample analyzed under the same conditions.
1.8 Statistical analysis
The results were analyzed by SPSS version 16.0(SPSS Inc.,USA).Any significant difference was determined by one-way analysis of variance(ANOVA) followed by the Tukey test for multiple comparisons atP<0.05 level.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Effects of extraction parameters on the yields of main phenolic compounds
To achieve total extraction,conditions such as extraction temperature,time,solvents and number of cycles,are important parameters[10].This preliminary work compared the contents of total polyphenols in the extracts which were obtained in the extractions with different temperatures from 30 to 70 ℃.Polyphenol extracts from grape seeds were investigated for the presence of various phenolic compounds.Using reversed phase chromatography,well-separated peaks could be obtained.The major phenolic compounds,gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin,were identified by authentic standards(Fig.1).
The quantitative content of each compound was determined by external calibration models obtained by using standard solutions with concentrations ranging from 0.001 to 0.006 mg/mL cover to the concentrations of phenolic compounds in grape seeds.Catechin and epicatechin accounted for proportion higher than gallic acid in grape seed extracts.As far as the extraction temperature was concerned,the yield of each phenolic compounds increased and reached a maximum at 50 ℃ and then slightly decreased in the extraction condition with 80∶20(V/V) of ethanol/water for 60 min of one cycle extraction(Fig.2).The results are in line with the previous report[11].However,that higher temperature shows positive effect on the extraction yield cannot be increased infinitely,because the stability of polyphenols of grape pomace and the denaturation of membranes can happen at temperature above 50 ℃.Thus,the suitable temperature was set at 50 ℃.
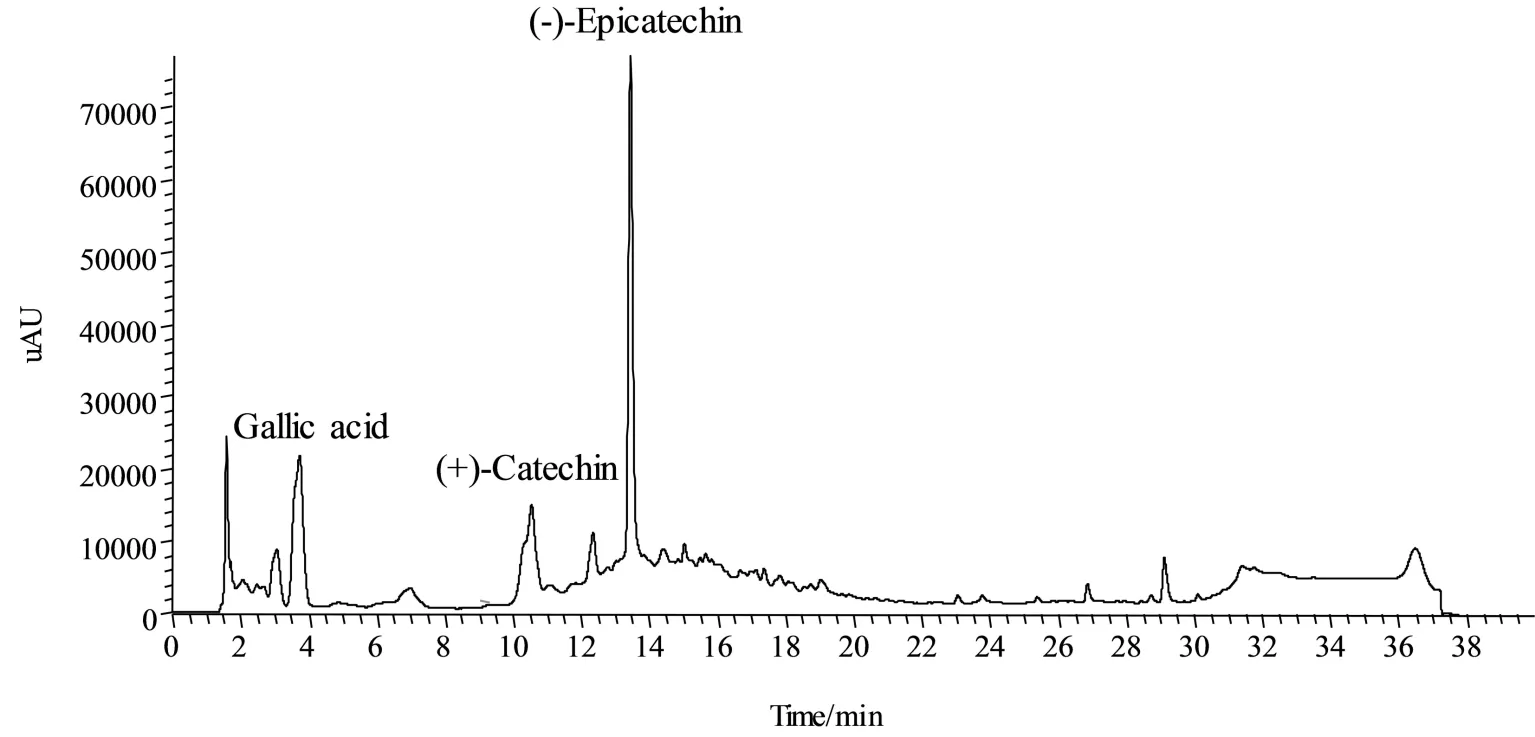
Fig.1 Chromatogram of phenolic compounds identified in grape seed extract using HPLC-DAD圖1 HPLC-DAD法測(cè)定葡萄籽提取物中酚類化合物
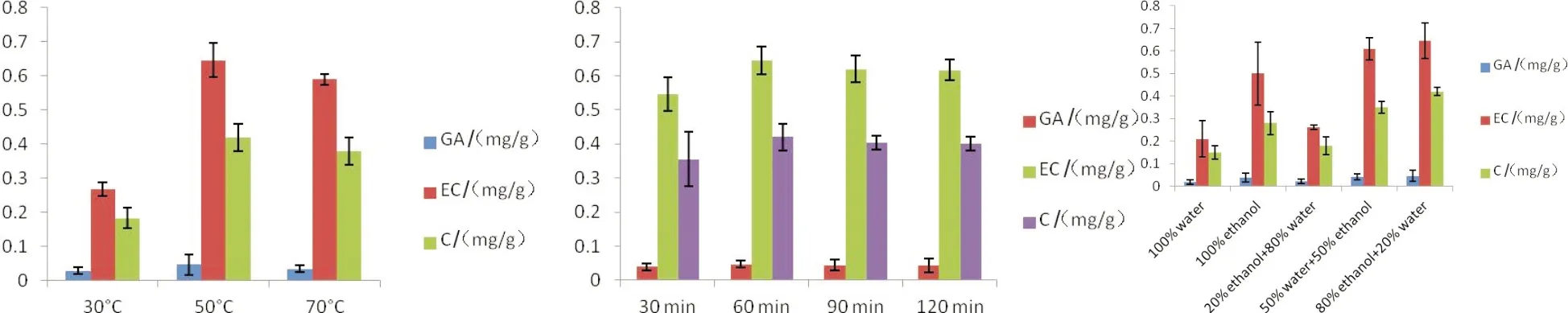
(a) (b) (c)Fig.2 Effect of extraction temperature(a),time(b) and extraction solvent(c) on the yields of each phenolic compounds圖2 提取溫度(a)、時(shí)間(b)和提取溶劑(c)對(duì)各種酚類化合物提取量的影響 GA:gallic acid; C:catechin; EC:epicatechin
Fig.2B shows the influence of extraction time on the recovery of each phenolic compound.The results showed that the contents of them increased until 60 min,then slightly decreased.In other words,no significant difference(P>0.05) in extraction efficiency was observed with extraction of 90 min or 120 min,indicating no benefit in using contact times above 60 min.The result is in agreement with the previous study[12].Therefore,the duration of extraction was set at 60 min for further experiments.
Fig.2C shows the yields of phenolic compounds using water,ethanol,ethanol/water(20∶80,V/V),ethanol/water(50∶50,V/V) and ethanol/water(80∶20,V/V).Notably,extract with 80∶20(V/V) of ethanol/water contained a highest quantity of phenolic compounds.And the yields of catechin and epicatechin were higher than gallic acid.The yield of gallic acid ranged from 0.019 to 0.046 mg/g grape seed powder,which is in accordance with the report of Liang et al[13].In addition,extraction cycles were investigated in order to recovery total amounts of each phenolic compounds.Fig.3 shows that the quantity extracted was plotted against the number of extractions,which indicated that four successive extractions were necessary to recover all of the phenolic compounds(P>0.05).The total contents of gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin of grape seed extracts with four successive extractions were 0.09,0.66,1.42 mg/g grape seed powder,respectively.In summary,the best conditions for total polyphenols extraction were the use of 80∶20(V/V) of aqueous ethanol with an extraction temperature of 50 ℃ for 60 min and with four successive extractions.
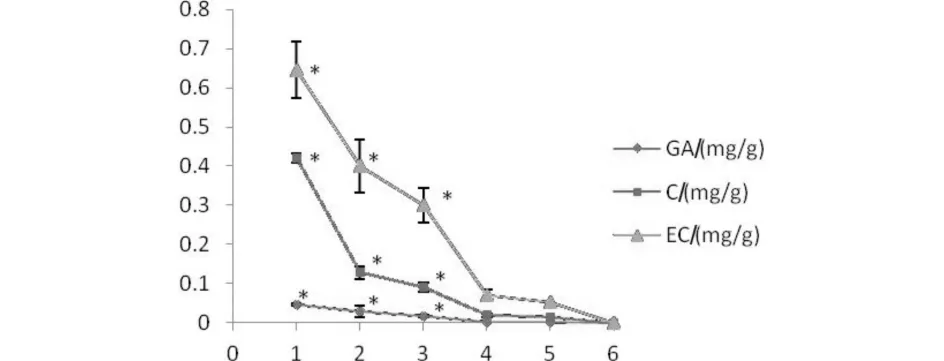
Fig.3 Effects of number of extraction cycles on the yields of each phenolic compounds圖3 提取次數(shù)對(duì)各種酚類化合物提取量的影響 GA:gallic acid; C:catechin; EC:epicatechin; *significant at P0.05
2.2 Validation of the three methods
The content of total polyphenols determined by vanillin-HCl assay,Folin-Ciocalteu assay and acid butanol assay were 21.74%,18.76% and 19.35%,respectively.As for the HPLC method for the determinations of gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin,the content of each phenolic compound was 0.08%,1.06% and 0.68%,respectively(Tab.1).In addition,the RSD was less than 2%,which proved that the precision of all the methods was good and sufficient.
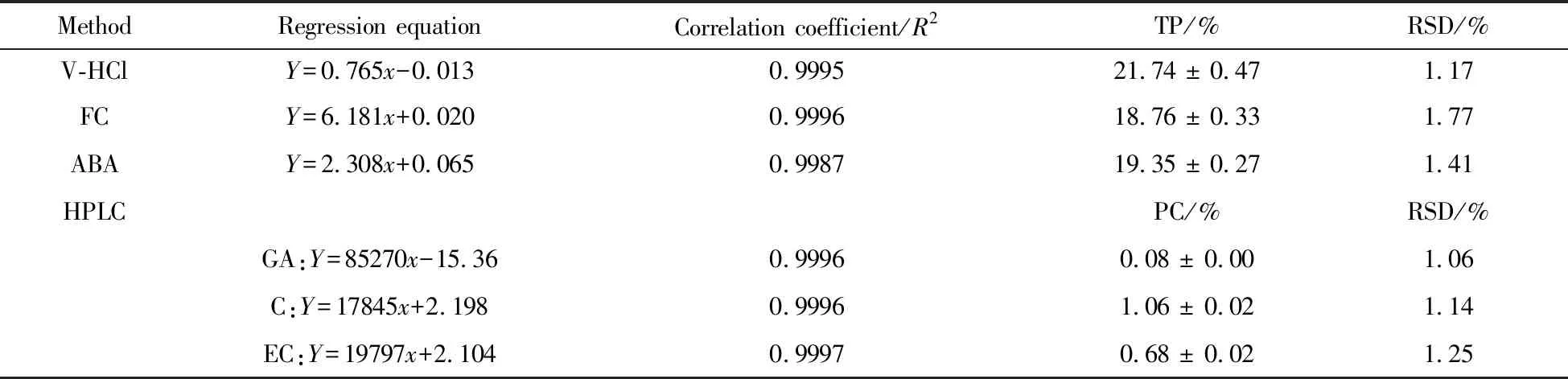
Tab.1 Determination of phenolic compounds by different methods 表1 不同方法測(cè)定酚類化合物含量
The recoveries of proanthocyanidin,gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin were determined by standard addition method.Tab.2 shows the results of the recovery tests.The recoveries were within the range of 98.1%~103.3% and the RSD values of proanthocyanidin,gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin were less than 2%,proving that the methods used in this study were credible and accurate.
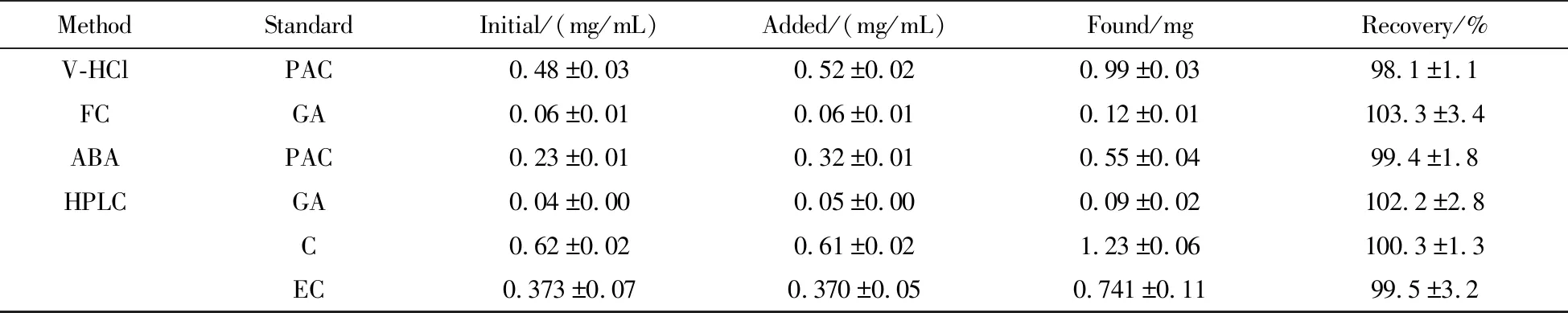
Tab.2 Recovery of phenolic compounds determined by standard addition method 表2 加標(biāo)法測(cè)定酚類化合物的回收率
As previously mentioned,the total polyphenols contained not only proanthocayanidin,but also three main phenolic compounds(gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin).Therefore,it was necessary to evaluate the specificity of vanillin-HCl assay,Folin-Ciocalteu assay and acid butanol assay.Tab.3 shows the absorbance of sample(grape seed extract) and samples added standards determined by different methods.The data indicated that there was significant difference(P0.05) for the determination of the absorbance between the samples with the sample added gallic acid,catechin or epicatechin by either vanillin-HCl assay or Folin-Ciocalteu assay.In contrast,there was no significant difference(P>0.05) when determined by acid butanol assay.It demonstrated that gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin would not involve in the reaction of acid butanol assay.In other words,acid butanol assay is specific for the determination of proanthocyanidins content,which is in agreement with the previous report[14].Moreover,it was necessary to combine vanillin-HCl assay and Folin-Ciocalteu assay with HPLC for the determination of proanthocyanidins.
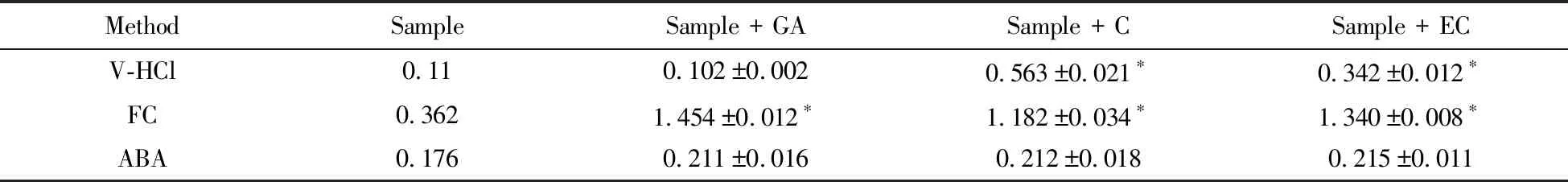
Tab.3 Absorbance of samples added standards determined by different methods 表3 不同方法測(cè)定加標(biāo)樣品的吸光度
2.3 Comparisons of the three methods for the determination of proanthocyanidins content
Folin-Ciocalteu assay and vanillin-HCl assay measured the content of total polyphenols.Three main phenolic compounds including gallic acid,catechin and epicatechin were separated and quantified by HPLC.The results showed that the contents of total polyphenols determined by vanillin-HCl method and by Folin-Ciocalteu method were 21.74% and 18.76%,respectively,while the total quantity of the three phenolic compounds in the grape seed extracts determined by HPLC was 1.82%.The content of proanthocyanidin quantified by vanillin-HCl-HPLC method and Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method was 19.92% and 16.94%(Tab.4),respectively,which was represented by the subtraction between amounts of total polyphenols and the total quantity of three phenolic compounds.Another method for the determination of the content of proanthocyanidins was acid butanol assay.The result showed that the content of proanthocayanidins was 19.35%(Tab.4).

Tab.4 Comparison of the three methods for the determination of the content of PAC 表4 3種測(cè)定原花青素方法的比較
It is noteworthy that the content of proantho-cayanidins detected by Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method was lower than vanillin-HCl-HPLC method and acid butanol assay.The reason was probably that the standard for detection by Folin-Ciocalteu assay was gallic acid,while the content of gallic acid in grape seed extract was very low(0.15%),the value of the content of proanthocayanidins was thereby lower than actual value when detected by Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method.Moreover,a comparison among the three methods showed that there was no significant difference(P>0.05) in extraction efficiency between vanillin-HCl-HPLC and acid butanol assay.However,Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method has significant difference either with vanillin-HCl-HPLC or acid butanol assay(P<0.05).Therefore,vanillin-HCl-HPLC and acid butanol assay were suitable to be used to determine the content of proanthocayanidins of grape seeds.However,as far as the ease of operation,acid butanol assay seems more convenient than vanillin-HCl-HPLC method,because vanillin-HCl-HPLC method needs the use of spectrophotometer and HPLC,while acid butanol assay only needs spectrophotometer,which offers the advantages of reducing the organic solvent consumption and the analytical time.Therefore,acid butanol assay provides a simple,fast,and effective method to quantity the proanthocyanidins of grape seeds.
3 Conclusion
This study applied solid liquid extraction to extract total polyphenols of grape seeds,the optimal extraction conditions was investigated.Three main phenolic compounds,gallic acid,cathechin,epicathechin were determined by HPLC.Moreover,the efficiency of three methods including Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC,vanillin-HCl-HPLC and acid butanol assay for the quantification of proanthocyanidins from grape seed extracts were evaluated.The results showed that vanillin-HCl-HPLC method and acid butanol assay were more efficient than Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method for the quantification of proanthocyanidin,and there was no significant difference(P>0.05) between vanillin-HCl-HPLC and acid butanol assay.It demonstrates that the acid butanol assay is a method specific for the determination of the content of proanthocyanidin.The method can be a better alternative to vanillin-HCl-HPLC method and Folin-Ciocalteu-HPLC method.
 中南民族大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)(自然科學(xué)版)2021年1期
中南民族大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)(自然科學(xué)版)2021年1期
- 中南民族大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)(自然科學(xué)版)的其它文章
- 基于FS-YOLOv3及多尺度特征融合的棉布瑕疵檢測(cè)
- 基于顯著性檢測(cè)和Grabcut算法的茶葉嫩芽圖像分割
- 基于RSU協(xié)作的V-NDN數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)方法研究
- 子句級(jí)別的自注意力機(jī)制的情感原因抽取模型
- Gallium-incorporated zinc oxide films deposited by magnetron sputtering and its microstructural properties
- 稻瘟病抗性基因Pita2的克隆及其介導(dǎo)的防御相關(guān)基因表達(dá)分析
