Exosomes as potential diagnosis and treatment for liver cancer
INTRODUCTION
Liver cancer is a common malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer death worldwide[1].It is one of the most challenging cancers to treat.For patients with an early stage of liver cancer,surgical treatment is the standard of care.However,most patients with liver cancer are already in the advanced stage at the initial diagnosis,which results in a poor prognosis[2].Currently,α-fetoprotein (AFP) is the most commonly used serum marker for liver cancer[3].However,AFP has a sensitivity of 41%–64% and a specificity of 80%–94%,which is often missed diagnosis,especially in the early stages of liver cancer[4].Therefore,it is vital to develop more sensitive and specific liver cancer biomarkers to improve patient survival.
Recent studies have shown that exosomes have potential as biomarkers for liver cancer[5].Once considered cellular waste,exosomes are rich in bioactive molecules,such as proteins,lipids,and nucleic acids[6,7].Almost all human cells can secrete exosomes.Tumor cells release more exosomes than normal cells,and the exosome contents of tumor cells are different from those of normal cells[8,9].Additionally,the exosomal envelope protects proteins,nucleic acids,and other substances in exosomes from degradation by extramembrane enzymes[10].The stability and abundance of exosome contents show the advantages of its unique liver cancer biomarkers.
On the other hand, without encouragement talented students may never be motivated to learn, develop skills, or reach their full potential. For example, at the same high school, there was a teacher whose Spanish language classes I attended but from whom I, unfortunately learned very little simply because of the woman’s cold sarcastically8 critical attitude. She seemed to know nothing about encouraging students, and she was gifted speaking contemptuously of those of us who weren’t learning fast enough. Her negativism drove me away. Partly because of this teacher’s negative influence, I am not fluent in Spanish today.
Exosomes are widely involved in cell-to-cell communication.They can deliver their functional RNAs and proteins to recipient cells and affect their physiological functions[11].Therefore,exosomes can also serve as drug delivery vehicles.Here,we summarize the potential of exosome contents in the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer,provide new ideas for the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer,and promote further research on the potential clinical applications of exosomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search
According to the conventional research methods of systematic review[12],a systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed and Web of Science using the following keywords:"exosomal biomarkers","exosomal therapy","exosomal therapy" and "liver cancer" or "HCC".The EndNote software was used to delete duplicate data[13].The latest literature was published in June 2021.Literature search focused on full texts.Two reviewers independently screened the references of each article to remove the irrelevant studies according to our inclusion criteria.The inclusion criteria were as follows:(1) Detection of exosomes or their contents in clinical samples (body fluid or tissue);or (2) Exosomes served as drug carriers or therapeutic factors.Two authors(Xiao-Cui Wei and Li-Juan Liu) independently reviewed the full texts of all retained literature and analyzed the information.
Data extraction
The data collected from each study included the clinical sample,expression level,and application of exosomes divided into three major segments.The first part involved the exosomes isolated from the body fluid samples.The second part meant the data that were relevant to the detection of exosomal contents in the clinical tissue samples.The third part included the collection of data pertinent to the application of exosomes.
RESULTS
Literature selection
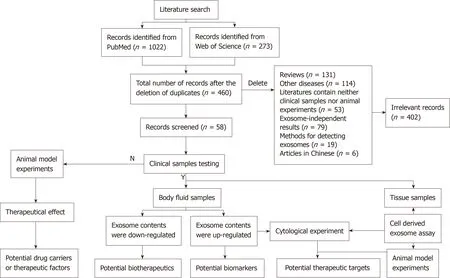
A total of 1295 studies were identified using the systematic literature search.After 835 duplicate studies were found and omitted,460 were screened by two independent reviewers.A further 402 irrelevant studies were excluded,including review articles,other diseases,records containing neither clinical samples nor animal experiments,exosome-independent studies,methods for detecting exosome or articles in Chinese.Finally,58 published papers were included in the study (Figure 1).
Exosomes are identified as potential biomarkers or potential biotherapeutics
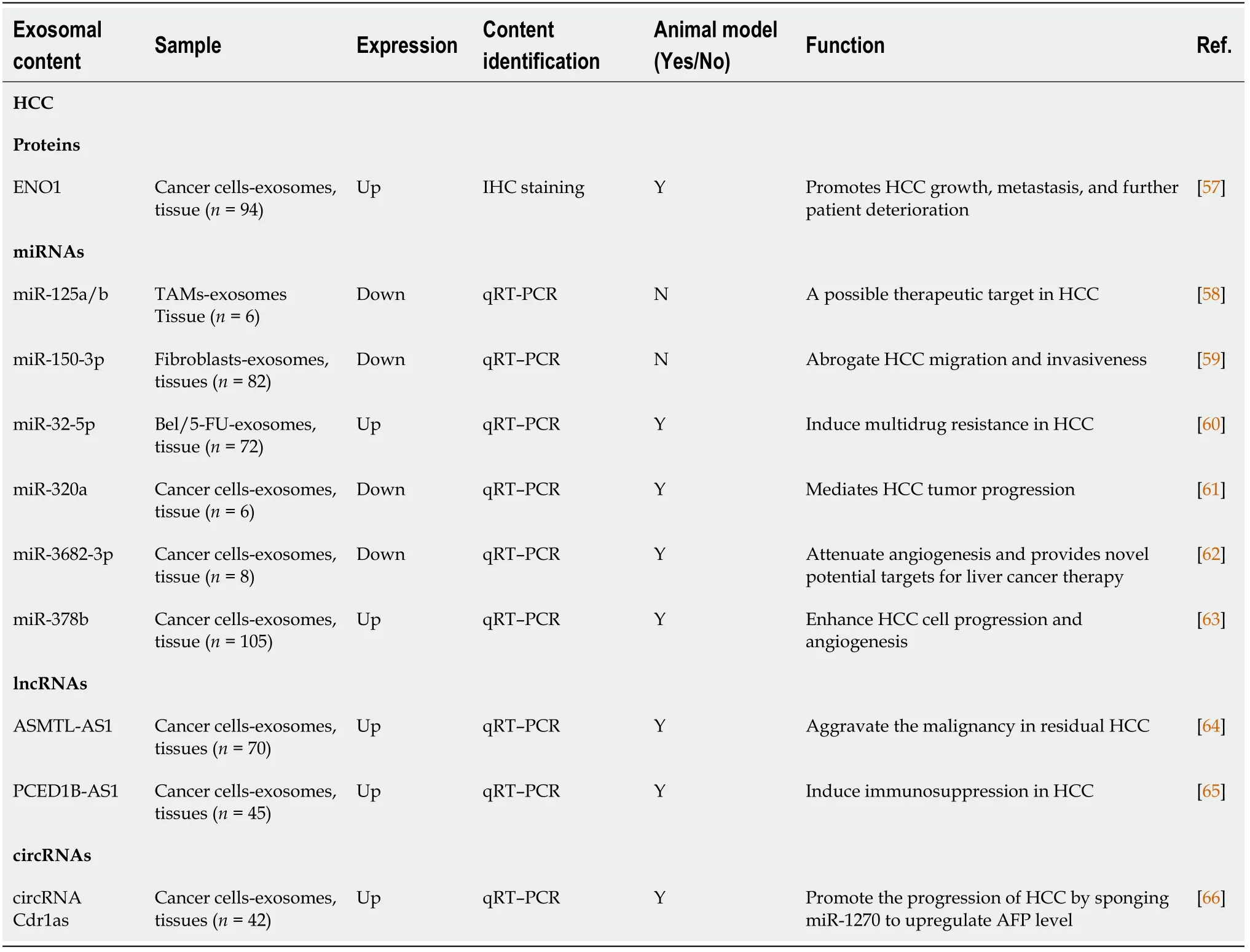
The expression of exosomal contents was detected in liver cancer clinical tissue samples,and cytology or animal experiments were used to identify the role of exosomal contents.Upregulated exosomal contents might enhance hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression,angiogenesis,and drug resistance,while downregulated exosomal contents might attenuate angiogenesis.In Table 3[57-66],all these abnormally expressed exosomal contents may become novel therapeutic targets for liver cancer.

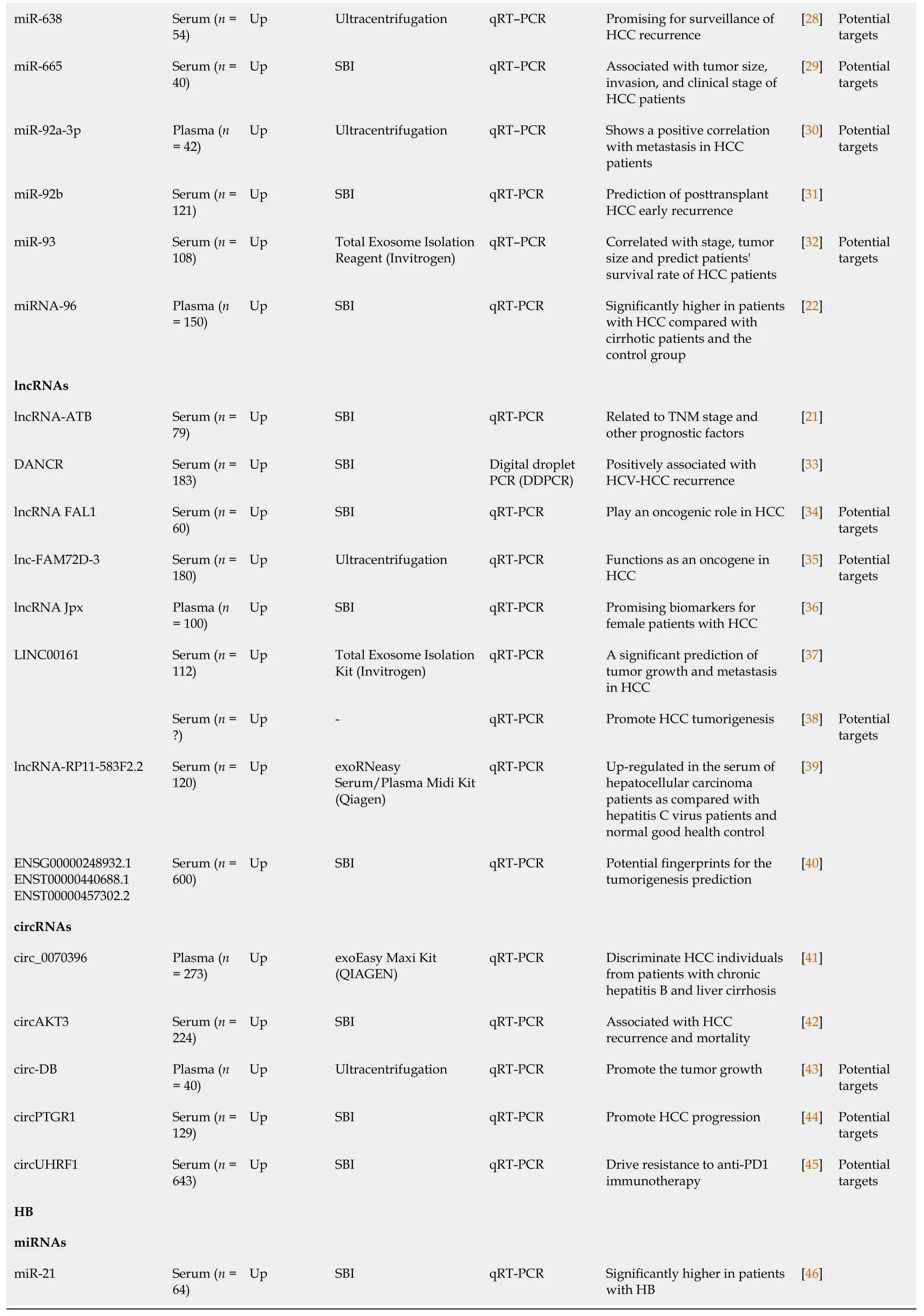
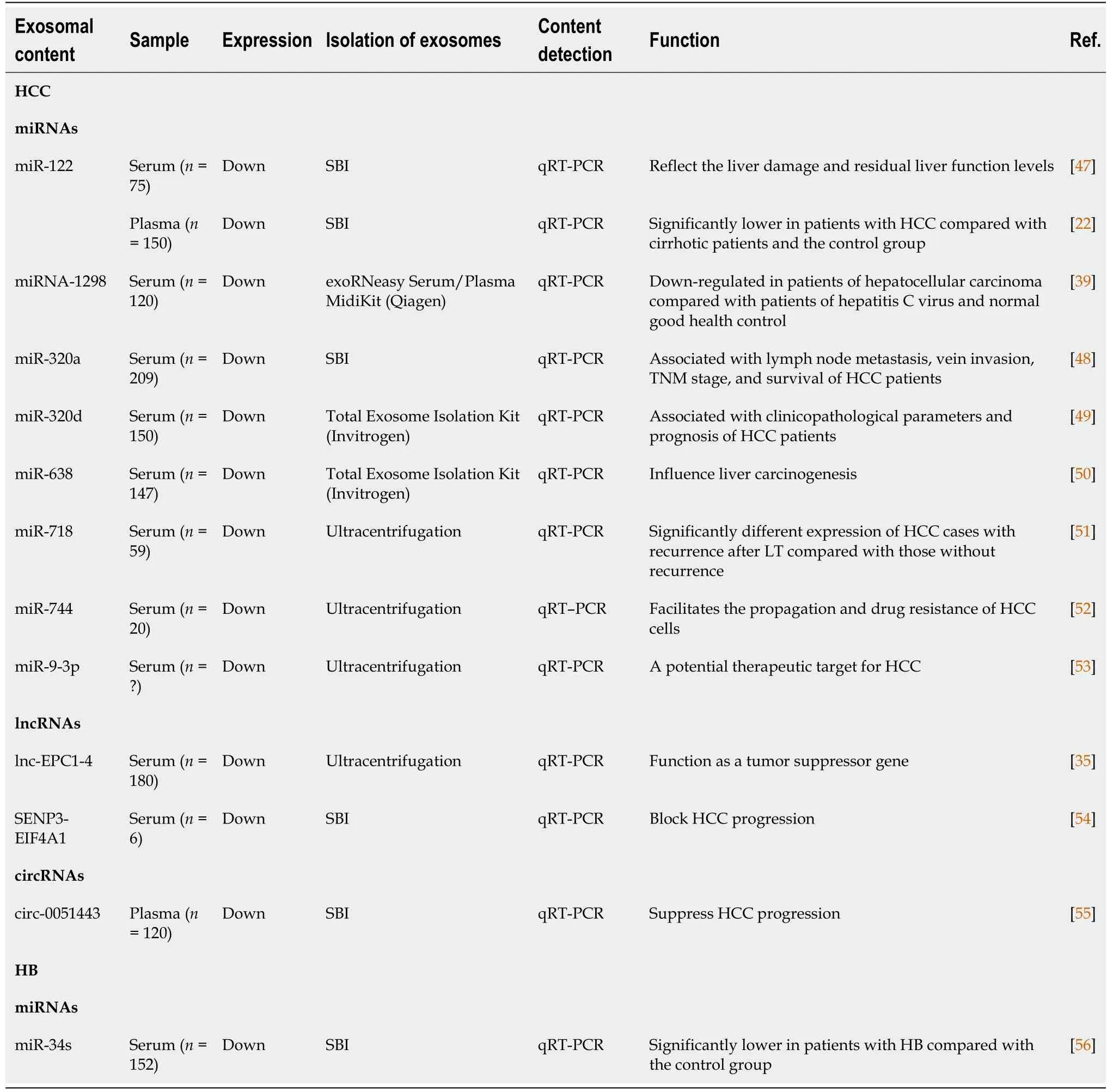
Table 2[22,35,39,47-56] includes potential biotherapeutics of exosomal contents for liver cancer.Those downregulated exosomal contents in blood liver cancer samples might serve as possible biotherapeutic drugs.
5.Into the forest:The forest is a place of change. It can also be a place of danger. There is also a connection to meeting gods in the forest, and when the devil appears in the forest he is being connected to the old gods (Biedermann 158).Return to place in story.
Exosomal contents are identified as potential therapeutic targets
In some literature,exosomes were isolated from liver cancer patients’ blood samples.Then,the level of exosomal molecular contents was detected.Table 1[14-46] lists the potential biomarkers for liver cancer.In these studies,exosomal contents that were upregulated in blood exosomes might be potential exosomal biomarkers.
Exosomes serve as drug carriers and therapeutic factors
In addition to being carriers,some researchers have reported the therapeutic effect of exosomes.As early as 1998,Zitvogel
[86] found that dendritic-cell-derived exosomes (DEXs) could activate tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and inhibit tumor growth
.DEXs have been used in several clinical trials.Researchers have processed DEXs derived from melanoma patients,loaded them with melanoma antigens,and observed an enhanced antimelanoma immunity after selfinoculation[87].Another trial indicated that DEX therapy increases natural killer cells(NKs) lytic activity in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[88].Besse’s group has conducted phase II clinical trials in NSCLC and confirmed the capacity of DEXs to boost the NK cell arm of antitumor immunity in patients with advanced NSCLC[89].In addition to injecting DEXs,Dai and colleagues have found that the immunotherapy of colorectal cancer (CRC) with ascites-derived exosomes in combination with granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor can serve as a choice for immunotherapy of advanced CRC[90].In liver cancer,however,there have been no such clinical trials.
The main result that the authors are concerned about is discovering the great potential of exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer.
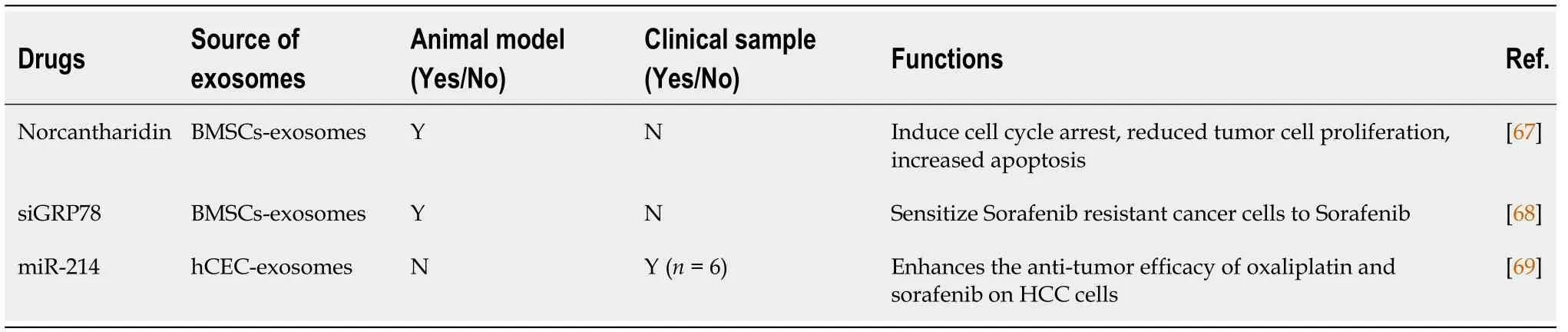
Table 5[70,71] shows the self-derived exosomes from dendritic cells as potential therapeutic factors.Data showed exosomes isolated from dendritic cells could inhibit tumor growth and improve the immune response.This indicated that exosomes serve as potential therapeutic factors.
DISCUSSION
Liver cancer is a global disease with high morbidity and mortality[72].Despite the continuous development of novel treatment options,the 5-year survival rate of liver cancer patients is still low because of the delayed diagnosis[73,74].Scientists are still trying to find new markers for early diagnosis and individualized treatments.
Over the past decade,exosomes have received widespread attention.Many studies have found that the differential expression of exosome proteins and RNAs has diagnostic significance for various cancers.Previous studies have suggested that exosomes may serve as liquid biopsies to help diagnose malignancies such as breast,pancreatic and lung cancer,and glioblastoma[75-78].Here,we listed exosomal contents that have been identified as possible biomarkers for liver cancer in recent years.We found multiple research reports about miR-21[21-24,46] and LINC00161[37,38].There are five papers on exosomal miR-21.These studies indicate that expression level of miR-21 in serum exosomes of liver cancer patients is higher than that of healthy people,suggesting that it is the most likely marker for early liver cancer screening.Among the contents of liver cancer serum with downregulated exosomal expression,miR-122 has been reported most often.These studies suggest that miR-122 may be the most likely biotherapeutic drug for liver cancer[22,47].
The servants came to the door, and finding it locked, they knocked; but the frozen breath on the window replied in Prince Milan s voice, I am coming directly
In addition to serving as disease markers in patients’ serum,exosomes are involved in the occurrence,development and prognosis of various cancers[79].Bai
[80] have shown that exosomes secreted by gastric cancer cells deliver miR-135b to tumor cells and promote angiogenesis by negatively regulating intracellular forkhead box O1.This study provides a potential target for antiangiogenic therapy.Huang and his collaborators demonstrated that colon cancer cells secrete Wnt4-rich exosomes delivered to normoxic cells to activate β-catenin signaling and enhance their metastatic behavior.They found that β-catenin inhibitors ICG-001 can inhibit this metastatic behavior,which provides a new target for treating metastatic colon cancer[81].In this paper,we listed the previous studies on the mechanism of exosomal contents involved in the development of liver cancer.Therefore,developing drugs targeting these exosomal contents may be a potential therapy for liver cancer.
As drug carriers,exosomes have the characteristics of stability in circulation,good biocompatibility,low immunogenicity,and low toxicity[82,83].Liang
[84] have shown that exosomes loaded with 5-fluorouracil and miR-21 inhibitors can effectively improve cancer cell drug resistance and colon cancer treatment efficiency.Zhang and his group also found that HEK293T-cell-derived exosomes deliver exogenous si-c-Met to gastric cancer cells and enhance gastric cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin[85].In this paper,we reviewed recent studies on the therapeutic effect of exosomes as carriers in HCC.
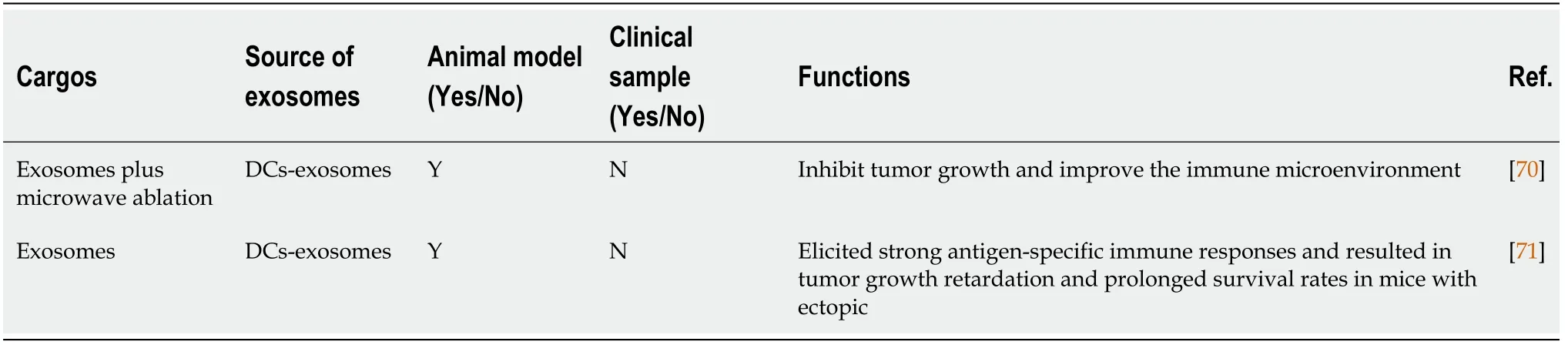
Table 4[67-69] focuses on the carrier roles of exosomes in HCC.Drug-carrying exosomes were injected into tumor-prone mice to observe the effects of the drugs.These studies indicated that exosomes could serve as drug carriers that made cancer cells sensitive to antitumor drugs or enhanced their antitumor efficacy.
22. Poisonous comb: The second temptation relates to Snow White s head and her hair. Combs were an attribute of Aphrodite, the Sirens and mermaids all symbols of female desirability. Hair is a symbol of fertility and virility, but the comb tames its wildness and its poison nearly kills her. IRReturn to place in story.
CONCLUSION
Exosomes are composed of a lipid bilayer membrane structure,which has the advantages of rich content,high stability,ability to reflect the state of disease,and cellular communication.These features make them a research hotspot for liver cancer for potential biomarkers,biotherapeutics,therapeutic targets,drug carriers,and therapeutic factors.
Although exosomes present good application value,there are still problems with their clinical application.Firstly,the separation and purification of exosomes are complex.Secondly,the contents in exosomes are not unique.Thirdly,not all exosomes secreted by cells are suitable for use as carriers.Although there are currently smallscale clinical trials,the actual application of exosomes in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer still needs more in-depth studies.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Liver cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors with high morbidity and mortality because of lacking early diagnosis and treatment.Exosomes have been a newly discovered cellular communication tool with high biocompatibility,low immunogenicity,and high transport efficiency.They show great potential for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Research motivation
This review aimed to consolidate the evidence on exosomes as biomarkers for the diagnosis and therapeutics for liver cancer in a systematic fashion.
Research objectives
Then he summoned his son, and revealed to him that he had got the false bride, who was nothing but a waiting-maid, while the real one, in the guise31 of the ex- goose-girl, was standing at his side
Research methods
A systematic literature search was performed using PubMed and Web of Science.The latest literature was published in June 2021.
Research results
Fifty-eight studies were included in this systematic review.Blood-derived exosomes could be biomarkers or biotherapeutics.Cell-derived exosomes,which were used to explore underlying mechanisms of differentially expressed exosome contents in clinical tissue samples,might serve as potential therapeutic targets for liver cancer.Exosomes might also serve as drug carriers or therapeutic factors.
They took them both in their arms, and asked him to tell about his sorrowful lot during the twenty years he had lived in the forest as a hideous lindorm
Research conclusions
Existing studies show that exosomes have great potential for clinical application as potential novel diagnostic and therapeutic markers of liver cancer.
I advise you to do what you think will turn out to yourhappiness, said the girl. Be kind and good to her, but rememberthis; from the hour we part we shall never see each other again. Years passed; then one day she met the old friend and sweetheartin the street; he looked ill and miserable15, and she could not helpasking him, How are you?
Research perspectives
This present review might be helpful as a reference for clinical research on exosomes in liver cancer.
We are grateful to Wang Ying for her skillful statistical analysis guidance.
1 Bray F,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,Siegel RL,Torre LA,Jemal A.Global cancer statistics,2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries.
2018;68:394-424 [PMID:30207593 DOI:10.3322/caac.21492]
2 Hollebecque A,Malka D,Ferté C,Ducreux M,Boige V.Systemic treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:from disillusions to new horizons.
2015;51:327-339 [PMID:25559615 DOI:10.1016/j.ejca.2014.12.005]
3 Johnson PJ.Role of alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
1999;14 Suppl:S32-S36 [PMID:10382636 DOI:10.1046/j.1440-1746.1999.01873.x]
4 Gupta S,Bent S,Kohlwes J.Test characteristics of alpha-fetoprotein for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C.A systematic review and critical analysis.
2003;139:46-50 [PMID:12834318 DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-139-1-200307010-00012]
5 Liu H,Li B.The functional role of exosome in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;144:2085-2095 [PMID:30062486 DOI:10.1007/s00432-018-2712-7]
6 Wortzel I,Dror S,Kenific CM,Lyden D.Exosome-Mediated Metastasis:Communication from a Distance.
2019;49:347-360 [PMID:31063754 DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011]
7 Roma-Rodrigues C,Fernandes AR,Baptista PV.Exosome in tumour microenvironment:overview of the crosstalk between normal and cancer cells.
2014;2014:179486 [PMID:24963475 DOI:10.1155/2014/179486]
8 Henderson MC,Azorsa DO.The genomic and proteomic content of cancer cell-derived exosomes.
2012;2:38 [PMID:22649786 DOI:10.3389/fonc.2012.00038]
9 Bebelman MP,Smit MJ,Pegtel DM,Baglio SR.Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer.
2018;188:1-11 [PMID:29476772 DOI:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.013]
10 Li W,Li C,Zhou T,Liu X,Li X,Chen D.Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis.
2017;16:145 [PMID:28851367 DOI:10.1186/s12943-017-0706-8]
11 Ratajczak J,Miekus K,Kucia M,Zhang J,Reca R,Dvorak P,Ratajczak MZ.Embryonic stem cellderived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors:evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery.
2006;20:847-856 [PMID:16453000 DOI:10.1038/sj.leu.2404132]
12 Muka T,Glisic M,Milic J,Verhoog S,Bohlius J,Bramer W,Chowdhury R,Franco OH.A 24-step guide on how to design,conduct,and successfully publish a systematic review and meta-analysis in medical research.
2020;35:49-60 [PMID:31720912 DOI:10.1007/s10654-019-00576-5]
13 Bramer WM,Milic J,Mast F.Reviewing retrieved references for inclusion in systematic reviews using EndNote.
2017;105:84-87 [PMID:28096751 DOI:10.5195/jmla.2017.111]
14 Xie JY,Wei JX,Lv LH,Han QF,Yang WB,Li GL,Wang PX,Wu SB,Duan JX,Zhuo WF,Liu PQ,Min J.Angiopoietin-2 induces angiogenesis
exosomes in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;18:46 [PMID:32183816 DOI:10.1186/s12964-020-00535-8]
15 Xu H,Dong X,Chen Y,Wang X.Serum exosomal hnRNPH1 mRNA as a novel marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;56:479-484 [PMID:29252188 DOI:10.1515/cclm-2017-0327]
16 Cui Z,Li Y,Gao Y,Kong L,Lin Y,Chen Y.Cancer-testis antigen lactate dehydrogenase C4 in hepatocellular carcinoma:a promising biomarker for early diagnosis,efficacy evaluation and prognosis prediction.
2020;12:19455-19467 [PMID:33035196 DOI:10.18632/aging.103879]
17 Cho HJ,Eun JW,Baek GO,Seo CW,Ahn HR,Kim SS,Cho SW,Cheong JY.Serum Exosomal MicroRNA,miR-10b-5p,as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
2020;9 [PMID:31968558 DOI:10.3390/jcm9010281]
18 Fang T,Lv H,Lv G,Li T,Wang C,Han Q,Yu L,Su B,Guo L,Huang S,Cao D,Tang L,Tang S,Wu M,Yang W,Wang H.Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer.
2018;9:191 [PMID:29335551 DOI:10.1038/s41467-017-02583-0]
19 Liu W,Hu J,Zhou K,Chen F,Wang Z,Liao B,Dai Z,Cao Y,Fan J,Zhou J.Serum exosomal miR-125b is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
2017;10:3843-3851 [PMID:28814883 DOI:10.2147/OTT.S140062]
20 Muhammad Yusuf AN,Raja Ali RA,Muhammad Nawawi KN,Mokhtar NM.Potential biomarkers in NASH-induced liver cirrhosis with hepatocellular carcinoma:A preliminary work on roles of exosomal miR-182,miR-301a,and miR-373.
2020;42:377-384 [PMID:33361718]
21 Lee YR,Kim G,Tak WY,Jang SY,Kweon YO,Park JG,Lee HW,Han YS,Chun JM,Park SY,Hur K.Circulating exosomal noncoding RNAs as prognostic biomarkers in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
2019;144:1444-1452 [PMID:30338850 DOI:10.1002/ijc.31931]
22 Wang S,Yang Y,Sun L,Qiao G,Song Y,Liu B.Exosomal MicroRNAs as Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
2020;13:2021-2030 [PMID:32210570 DOI:10.2147/OTT.S232453]
23 Wang H,Hou L,Li A,Duan Y,Gao H,Song X.Expression of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
2014;2014:864894 [PMID:24963487 DOI:10.1155/2014/864894]
24 Zhou Y,Ren H,Dai B,Li J,Shang L,Huang J,Shi X.Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancerassociated fibroblasts.
2018;37:324 [PMID:30591064 DOI:10.1186/s13046-018-0965-2]
25 Cui Y,Xu HF,Liu MY,Xu YJ,He JC,Zhou Y,Cang SD.Mechanism of exosomal microRNA-224 in development of hepatocellular carcinoma and its diagnostic and prognostic value.
2019;25:1890-1898 [PMID:31057302 DOI:10.3748/wjg.v25.i15.1890]
26 Liu Y,Tan J,Ou S,Chen J,Chen L.Adipose-derived exosomes deliver miR-23a/b to regulate tumor growth in hepatocellular cancer by targeting the VHL/HIF axis.
2019;75:391-401[PMID:31321740 DOI:10.1007/s13105-019-00692-6]
27 Cho HJ,Baek GO,Seo CW,Ahn HR,Sung S,Son JA,Kim SS,Cho SW,Jang JW,Nam SW,Cheong JY,Eun JW.Exosomal microRNA-4661-5p-based serum panel as a potential diagnostic biomarker for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;9:5459-5472 [PMID:32537885 DOI:10.1002/cam4.3230]
28 Yokota Y,Noda T,Okumura Y,Kobayashi S,Iwagami Y,Yamada D,Tomimaru Y,Akita H,Gotoh K,Takeda Y,Tanemura M,Murakami T,Umeshita K,Doki Y,Eguchi H.Serum exosomal miR-638 is a prognostic marker of HCC
downregulation of VE-cadherin and ZO-1 of endothelial cells.
2021;112:1275-1288 [PMID:33426736 DOI:10.1111/cas.14807]
29 Qu Z,Wu J,Ji A,Qiang G,Jiang Y,Jiang C,Ding Y.Exosomal miR-665 as a novel minimally invasive biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis.
2017;8:80666-80678 [PMID:29113334 DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.20881]
30 Yang B,Feng X,Liu H,Tong R,Wu J,Li C,Yu H,Chen Y,Cheng Q,Chen J,Cai X,Wu W,Lu Y,Hu J,Liang K,Lv Z,Zheng S.High-metastatic cancer cells derived exosomal miR92a-3p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of low-metastatic cancer cells by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;39:6529-6543 [PMID:32917956 DOI:10.1038/s41388-020-01450-5]
31 Nakano T,Chen IH,Wang CC,Chen PJ,Tseng HP,Huang KT,Hu TH,Li LC,Goto S,Cheng YF,Lin CC,Chen CL.Circulating exosomal miR-92b:Its role for cancer immunoediting and clinical value for prediction of posttransplant hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence.
2019;19:3250-3262 [PMID:31162867 DOI:10.1111/ajt.15490]
32 Xue X,Wang X,Zhao Y,Hu R,Qin L.Exosomal miR-93 promotes proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting TIMP2/TP53INP1/CDKN1A.
2018;502:515-521 [PMID:29859935 DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.208]
33 Wang SC,Li CY,Chang WT,Cheng WC,Yen CH,Tu WY,Lin ZY,Lin CC,Yeh ML,Huang CF,Huang JF,Dai CY,Chuang WL,Chen YL,Yu ML.Exosome-derived differentiation antagonizing non-protein coding RNA with risk of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence.
2021;41:956-968 [PMID:33346937 DOI:10.1111/Liv.14772]
34 Li B,Mao R,Liu C,Zhang W,Tang Y,Guo Z.LncRNA FAL1 promotes cell proliferation and migration by acting as a CeRNA of miR-1236 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
2018;197:122-129 [PMID:29421439 DOI:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.006]
35 Yao Z,Jia C,Tai Y,Liang H,Zhong Z,Xiong Z,Deng M,Zhang Q.Serum exosomal long noncoding RNAs lnc-FAM72D-3 and lnc-EPC1-4 as diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;12:11843-11863 [PMID:32554864 DOI:10.18632/aging.103355]
36 Ma X,Yuan T,Yang C,Wang Z,Zang Y,Wu L,Zhuang L.X-inactive-specific transcript of peripheral blood cells is regulated by exosomal Jpx and acts as a biomarker for female patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
2017;9:665-677 [PMID:29344104 DOI:10.1177/1758834017731052]
37 Sun L,Su Y,Liu X,Xu M,Chen X,Zhu Y,Guo Z,Bai T,Dong L,Wei C,Cai X,He B,Pan Y,Sun H,Wang S.Serum and exosome long non coding RNAs as potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;9:2631-2639 [PMID:30087703 DOI:10.7150/jca.24978]
38 You LN,Tai QW,Xu L,Hao Y,Guo WJ,Zhang Q,Tong Q,Zhang H,Huang WK.Exosomal LINC00161 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis
regulating miR-590-3p/ROCK axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2021;28:719-736 [PMID:33414518 DOI:10.1038/s41417-020-00269-2]
39 Matboli M,Labib ME,Nasser HE,El-Tawdi AHF,Habib EK,Ali-Labib R.Exosomal miR-1298 and lncRNA-RP11-583F2.2 Expression in Hepato-cellular Carcinoma.
2020;21:46-55[PMID:32655298 DOI:10.2174/1389202920666191210111849]
40 Lu Y,Duan Y,Xu Q,Zhang L,Chen W,Qu Z,Wu B,Liu W,Shi L,Wu D,Yang Y,Sun D,Chen X.Circulating exosome-derived bona fide long non-coding RNAs predicting the occurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;24:1311-1318 [PMID:31811749 DOI:10.1111/jcmm.14783]
41 Lyu L,Yang W,Yao J,Wang H,Zhu J,Jin A,Liu T,Wang B,Zhou J,Fan J,Yang X,Guo W.The diagnostic value of plasma exosomal
for hepatocellular carcinoma.
2021;15:359-371 [PMID:33666515 DOI:10.2217/bmm-2020-0476]
42 Luo Y,Liu F,Gui R.High expression of circulating exosomal circAKT3 is associated with higher recurrence in HCC patients undergoing surgical treatment.
2020;33:276-281 [PMID:32561093 DOI:10.1016/j.suronc.2020.04.021]
43 Zhang H,Deng T,Ge S,Liu Y,Bai M,Zhu K,Fan Q,Li J,Ning T,Tian F,Li H,Sun W,Ying G,Ba Y.Exosome circRNA secreted from adipocytes promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting deubiquitination-related USP7.
2019;38:2844-2859 [PMID:30546088 DOI:10.1038/s41388-018-0619-z]
44 Wang G,Liu W,Zou Y,Wang G,Deng Y,Luo J,Zhang Y,Li H,Zhang Q,Yang Y,Chen G.Three isoforms of exosomal circPTGR1 promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis
the miR449a-MET pathway.
2019;40:432-445 [PMID:30630697 DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.062]
45 Zhang PF,Gao C,Huang XY,Lu JC,Guo XJ,Shi GM,Cai JB,Ke AW.Cancer cell-derived exosomal circUHRF1 induces natural killer cell exhaustion and may cause resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;19:110 [PMID:32593303 DOI:10.1186/s12943-020-01222-5]
46 Liu W,Chen S,Liu B.Diagnostic and prognostic values of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in children with hepatoblastoma:a Chinese population-based study.
2016;32:1059-1065 [PMID:27601233 DOI:10.1007/s00383-016-3960-8]
47 Suehiro T,Miyaaki H,Kanda Y,Shibata H,Honda T,Ozawa E,Miuma S,Taura N,Nakao K.Serum exosomal microRNA-122 and microRNA-21 as predictive biomarkers in transarterial chemoembolization-treated hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
2018;16:3267-3273[PMID:30127924 DOI:10.3892/ol.2018.8991]
48 Hao X,Xin R,Dong W.Decreased serum exosomal miR-320a expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;48:300060519896144 [PMID:32339037 DOI:10.1177/0300060519896144]
49 Li W,Ding X,Wang S,Xu L,Yin T,Han S,Geng J,Sun W.Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-320d predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;34:e23239[PMID:32125733 DOI:10.1002/jcla.23239]
50 Shi M,Jiang Y,Yang L,Yan S,Wang YG,Lu XJ.Decreased levels of serum exosomal miR-638 predict poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;119:4711-4716 [PMID:29278659 DOI:10.1002/jcb.26650]
51 Sugimachi K,Matsumura T,Hirata H,Uchi R,Ueda M,Ueo H,Shinden Y,Iguchi T,Eguchi H,Shirabe K,Ochiya T,Maehara Y,Mimori K.Identification of a bona fide microRNA biomarker in serum exosomes that predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation.
2015;112:532-538 [PMID:25584485 DOI:10.1038/bjc.2014.621]
52 Wang G,Zhao W,Wang H,Qiu G,Jiang Z,Wei G,Li X.Exosomal MiR-744 Inhibits Proliferation and Sorafenib Chemoresistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PAX2.
2019;25:7209-7217 [PMID:31553714 DOI:10.12659/MSM.919219]
53 Tang J,Li Y,Liu K,Zhu Q,Yang WH,Xiong LK,Guo DL.Exosomal miR-9-3p suppresses HBGF-5 expression and is a functional biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;109:15-23 [PMID:28750499 DOI:10.23736/S0026-4806.17.05167-9]
54 Wang J,Pu J,Zhang Y,Yao T,Luo Z,Li W,Xu G,Liu J,Wei W,Deng Y.Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA
suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;12:11550-11567 [PMID:32602848 DOI:10.18632/aging.103302]
55 Chen W,Quan Y,Fan S,Wang H,Liang J,Huang L,Chen L,Liu Q,He P,Ye Y.Exosometransmitted circular RNA hsa_circ_0051443 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
2020;475:119-128 [PMID:32014458 DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.01.022]
56 Jiao C,Jiao X,Zhu A,Ge J,Xu X.Exosomal miR-34s panel as potential novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with hepatoblastoma.
2017;52:618-624 [PMID:28277300 DOI:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.09.070]
57 Jiang K,Dong C,Yin Z,Li R,Mao J,Wang C,Zhang J,Gao Z,Liang R,Wang Q,Wang L.Exosome-derived ENO1 regulates integrin α6β4 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis.
2020;11:972 [PMID:33184263 DOI:10.1038/s41419-020-03179-1]
58 Wang Y,Wang B,Xiao S,Li Y,Chen Q.miR-125a/b inhibits tumor-associated macrophages mediated in cancer stem cells of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CD90.
2019;120:3046-3055 [PMID:30536969 DOI:10.1002/jcb.27436]
59 Yugawa K,Yoshizumi T,Mano Y,Itoh S,Harada N,Ikegami T,Kohashi K,Oda Y,Mori M.Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression through downregulation of exosomal miR-150-3p.
2021;47:384-393 [PMID:32883551 DOI:10.1016/j.ejso.2020.08.002]
60 Fu X,Liu M,Qu S,Ma J,Zhang Y,Shi T,Wen H,Yang Y,Wang S,Wang J,Nan K,Yao Y,Tian T.Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
the PI3K/Akt pathway.
2018;37:52 [PMID:29530052 DOI:10.1186/s13046-018-0677-7]
61 Zhang Z,Li X,Sun W,Yue S,Yang J,Li J,Ma B,Wang J,Yang X,Pu M,Ruan B,Zhao G,Huang Q,Wang L,Tao K,Dou K.Loss of exosomal miR-320a from cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to HCC proliferation and metastasis.
2017;397:33-42 [PMID:28288874 DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.004]
62 Dong SS,Dong DD,Yang ZF,Zhu GQ,Gao DM,Chen J,Zhao Y,Liu BB.Exosomal miR-3682-3p Suppresses Angiogenesis by Targeting ANGPT1
the RAS-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
2021;9:633358 [PMID:33869178 DOI:10.3389/fcell.2021.633358]
63 Chen W,Huang L,Liang J,Ye Y,He S,Niu J.Hepatocellular carcinoma cells-derived exosomal microRNA-378b enhances hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis.
2021;273:119184[PMID:33577844 DOI:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119184]
64 Ma D,Gao X,Liu Z,Lu X,Ju H,Zhang N.Exosome-transferred long non-coding RNA ASMTLAS1 contributes to malignant phenotypes in residual hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation.
2020;53:e12795 [PMID:32722884 DOI:10.1111/cpr.12795]
65 Fan F,Chen K,Lu X,Li A,Liu C,Wu B.Dual targeting of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by PCED1B-AS1
sponging hsa-miR-194-5p induces immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2021;15:444-458 [PMID:33219943 DOI:10.1007/s12072-020-10101-6]
66 Su Y,Lv X,Yin W,Zhou L,Hu Y,Zhou A,Qi F.CircRNA Cdr1as functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
2019;11:8183-8203 [PMID:31581132 DOI:10.18632/aging.102312]
67 Liang L,Zhao L,Wang Y.Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Enhanced When Norcantharidin Is Encapsulated in Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
2021;18:1003-1013 [PMID:33527831 DOI:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00976]
68 Li H,Yang C,Shi Y,Zhao L.Exosomes derived from siRNA against GRP78 modified bone-marrowderived mesenchymal stem cells suppress Sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;16:103 [PMID:30572882 DOI:10.1186/s12951-018-0429-z]
69 Semaan L,Zeng Q,Lu Y,Zhang Y,Zreik MM,Chamseddine MB,Chopp M,Zhang ZG,Moonka D.MicroRNA-214 enriched exosomes from human cerebral endothelial cells (hCEC) sensitize hepatocellular carcinoma to anti-cancer drugs.
2021;12:185-198 [PMID:33613846 DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.27879]
70 Zhong X,Zhou Y,Cao Y,Ding J,Wang P,Luo Y,Liu H,Zhu Z,Jing X.Enhanced antitumor efficacy through microwave ablation combined with a dendritic cell-derived exosome vaccine in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2020;37:1210-1218 [PMID:33100037 DOI:10.1080/02656736.2020.1836406]
71 Lu Z,Zuo B,Jing R,Gao X,Rao Q,Liu Z,Qi H,Guo H,Yin H.Dendritic cell-derived exosomes elicit tumor regression in autochthonous hepatocellular carcinoma mouse models.
2017;67:739-748 [PMID:28549917 DOI:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.05.019]
72 Forner A,Reig M,Bruix J.Hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;391:1301-1314 [PMID:29307467 DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2]
73 Anwanwan D,Singh SK,Singh S,Saikam V,Singh R.Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches.
2020;1873:188314 [PMID:31682895 DOI:10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188314]
74 De Stefano F,Chacon E,Turcios L,Marti F,Gedaly R.Novel biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma.
2018;50:1115-1123 [PMID:30217732 DOI:10.1016/j.dld.2018.08.019]
75 Corcoran C,Friel AM,Duffy MJ,Crown J,O'Driscoll L.Intracellular and extracellular microRNAs in breast cancer.
2011;57:18-32 [PMID:21059829 DOI:10.1373/clinchem.2010.150730]
76 Skog J,Würdinger T,van Rijn S,Meijer DH,Gainche L,Sena-Esteves M,Curry WT Jr,Carter BS,Krichevsky AM,Breakefield XO.Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers.
2008;10:1470-1476[PMID:19011622 DOI:10.1038/ncb1800]
77 Cui S,Cheng Z,Qin W,Jiang L.Exosomes as a liquid biopsy for lung cancer.
2018;116:46-54 [PMID:29413050 DOI:10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.12.012]
78 Melo SA,Luecke LB,Kahlert C,Fernandez AF,Gammon ST,Kaye J,LeBleu VS,Mittendorf EA,Weitz J,Rahbari N,Reissfelder C,Pilarsky C,Fraga MF,Piwnica-Worms D,Kalluri R.Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer.
2015;523:177-182 [PMID:26106858 DOI:10.1038/nature14581]
79 Kalluri R.The biology and function of exosomes in cancer.
2016;126:1208-1215[PMID:27035812 DOI:10.1172/JCI81135]
80 Bai M,Li J,Yang H,Zhang H,Zhou Z,Deng T,Zhu K,Ning T,Fan Q,Ying G,Ba Y.miR-135b Delivered by Gastric Tumor Exosomes Inhibits FOXO1 Expression in Endothelial Cells and Promotes Angiogenesis.
2019;27:1772-1783 [PMID:31416776 DOI:10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.06.018]
81 Huang Z,Yang M,Li Y,Yang F,Feng Y.Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Colorectal Cancer Cells Transfer Wnt4 to Normoxic Cells to Elicit a Prometastatic Phenotype.
2018;14:2094-2102 [PMID:30585272 DOI:10.7150/ijbs.28288]
82 Das CK,Jena BC,Banerjee I,Das S,Parekh A,Bhutia SK,Mandal M.Exosome as a Novel Shuttle for Delivery of Therapeutics across Biological Barriers.
2019;16:24-40 [PMID:30513203 DOI:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00901]
83 Peer D,Karp JM,Hong S,Farokhzad OC,Margalit R,Langer R.Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy.
2007;2:751-760 [PMID:18654426 DOI:10.1038/nnano.2007.387]
84 Liang G,Zhu Y,Ali DJ,Tian T,Xu H,Si K,Sun B,Chen B,Xiao Z.Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer.
2020;18:10 [PMID:31918721 DOI:10.1186/s12951-019-0563-2]
85 Zhang Q,Zhang H,Ning T,Liu D,Deng T,Liu R,Bai M,Zhu K,Li J,Fan Q,Ying G,Ba Y.Exosome-Delivered c-Met siRNA Could Reverse Chemoresistance to Cisplatin in Gastric Cancer.
2020;15:2323-2335 [PMID:32308384 DOI:10.2147/IJN.S231214]
86 Zitvogel L,Regnault A,Lozier A,Wolfers J,Flament C,Tenza D,Ricciardi-Castagnoli P,Raposo G,Amigorena S.Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine:dendritic cellderived exosomes.
1998;4:594-600 [PMID:9585234 DOI:10.1038/nm0598-594]
87 Escudier B,Dorval T,Chaput N,André F,Caby MP,Novault S,Flament C,Leboulaire C,Borg C,Amigorena S,Boccaccio C,Bonnerot C,Dhellin O,Movassagh M,Piperno S,Robert C,Serra V,Valente N,Le Pecq JB,Spatz A,Lantz O,Tursz T,Angevin E,Zitvogel L.Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes:results of thefirst phase I clinical trial.
2005;3:10 [PMID:15740633 DOI:10.1186/1479-5876-3-10]
88 Morse MA,Garst J,Osada T,Khan S,Hobeika A,Clay TM,Valente N,Shreeniwas R,Sutton MA,Delcayre A,Hsu DH,Le Pecq JB,Lyerly HK.A phase I study of dexosome immunotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
2005;3:9 [PMID:15723705 DOI:10.1186/1479-5876-3-9]
89 Besse B,Charrier M,Lapierre V,Dansin E,Lantz O,Planchard D,Le Chevalier T,Livartoski A,Barlesi F,Laplanche A,Ploix S,Vimond N,Peguillet I,Théry C,Lacroix L,Zoernig I,Dhodapkar K,Dhodapkar M,Viaud S,Soria JC,Reiners KS,Pogge von Strandmann E,Vély F,Rusakiewicz S,Eggermont A,Pitt JM,Zitvogel L,Chaput N.Dendritic cell-derived exosomes as maintenance immunotherapy after first line chemotherapy in NSCLC.
2016;5:e1071008[PMID:27141373 DOI:10.1080/2162402X.2015.1071008]
90 Dai S,Wei D,Wu Z,Zhou X,Wei X,Huang H,Li G.Phase I clinical trial of autologous ascitesderived exosomes combined with GM-CSF for colorectal cancer.
2008;16:782-790[PMID:18362931 DOI:10.1038/mt.2008.1]
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2022年1期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2022年1期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Comment on “Outcomes of curative liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis”
- Liquid biopsy:Precise diagnosis and therapy for cholangiocarcinoma
- Increased risk of colorectal neoplasia in inflammatory bowel disease patients with post-inflammatory polyps:A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of cognitive behavior therapy combined with Baduanjin in patients with colorectal cancer
- Intertwined leukocyte balances in tumours and peripheral blood as robust predictors of right and left colorectal cancer survival
- Digestive cancer incidence and mortality among young adults worldwide in 2020:A population-based study
