Diagnosing isolated superior mesenteric artery dissection and thrombosis using point-of-care ultrasonography: A case series
Sin Youl Park, Won Joon Jeong
1 Department of Emergency Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu 42415, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Emergency Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon 301721, Republic of Korea
Dear editor,
Most superior mesenteric artery (SMA) dissections occur along with aortic dissections; isolated SMA dissections are rare (incidence rate of 0.06%).A diagnosis of SMA dissection is generally made using contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT);however, bedside point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS)may hasten the process. Herein, we present a case series of isolated SMA dissections that were suspected and conf irmed using POCUS and CECT, respectively.
CASE
Case 1
A 75-year-old woman was admitted to the emergency department (ED) with abdominal pain 5 h ago. Her vital signs were normal. She complained of epigastric and periumbilical pain; however, physical examination revealed that her abdomen was soft and flat, without a definite area of tenderness. Bedside POCUS (Mylab Seven Ultrasound system; Esaote, Italy) was performed, and duplex ultrasounds demonstrated no SMA blood flow compared to the aorta, suggesting a SMA thrombosis. An intimal f lap was not visible in the aorta or the SMA on POCUS (Figure 1A). A CECT was performed to confirm the diagnosis(Figure 1B). There was no evidence of bowel ischemia or necrosis on POCUS or CECT. The patient’s symptoms were improved after receiving anticoagulants.
Case 2
A 51-year-old man was admitted to the ED with a 1-day history of abdominal pain. His vital signs were normal. He complained of vague abdominal pain from the epigastric to the periumbilical areas, and physical examination revealed mild epigastric tenderness without rebound tenderness. His medical history, laboratory data,and radiographs were unremarkable. An intimal SMA flap was detected by POCUS. Duplex and pulse wave ultrasounds demonstrated the presence of a true and a false lumen within the SMA, along with thrombosis of the false lumen (Figure 1C, supplementary Videos 1 and 2). No findings suggestive of bowel ischemia were observed on POCUS. The diagnosis was conf irmed using CECT (Figure 1D). The patient was improved after treatment with anticoagulants and was discharged.
Case 3
A 55-year-old man visited the ED after experiencing sudden abdominal pain for 1 h. His vital signs were nonspecific. Physical examination revealed epigastric tenderness without rebound tenderness. His medical history revealed a previous diagnosis of atrial fibrillation that had not been treated. Laboratory data and radiographs were unremarkable. Color and pulse wave Doppler mode on POCUS demonstrated the absence of SMA blood f low,suggesting thrombosis or a false lumen in the SMA. An intimal flap was not visible in the aorta or SMA (Figure 2A, supplementary Video 3). No findings suggestive of bowel ischemia were observed on POCUS. CECT was performed to confirm the diagnosis (Figure 2B). The bowel was well-perfused. The patient was improved after treatment with anticoagulants and was discharged.
DISCUSSION
The presumed mechanism of SMA dissection is an intimal or vasa vasorum tear that leads to hemorrhage in the medial and adventitial layers.Many patients who initially present with a sudden onset of abdominal pain are misdiagnosed with gastroenteritis, or gastric or nonspecific pain, only to return within a week to be correctly diagnosed with SMA dissection.SMA dissection may induce occlusion with thrombosis (which is potentially life threatening) and bowel ischemia,which requires immediate revascularization. Therefore,a fast and accurate diagnosis is important for patients presenting to the ED with abdominal pain. Although CECT is currently the preferred imaging modality for identifying SMA dissections, there are various reports that bedside POCUS may hasten the diagnosis of SMA dissection.
During ultrasonography, SMA dissection is diagnosed if an intimal flap is visible in the vessel.POCUS is useful for observing an intimal f lap, although flap visualization is inconstant.Occasionally, the intimal flap may be too faint to detect using POCUS in emergency settings.The intimal f lap can be missed on ultrasound compared to CECT because the flap is sometimes hidden behind the thrombus of the false lumen.Furthermore, an absent Doppler signal throughout the cardiac cycle in an adequately visualized SMA is a pathognomonic sign of occlusion.In accordance with our cases,duplex ultrasound is a sensitive and accurate method for detecting SMA dissection and may be used to screen patients with abdominal pain.
The normal SMA diameter is 5.7–7.3 mm in ultrasound images.Huang et alsuggested that when the SMA diameter is >10 mm, clinicians should suspect SMA dissection and perform additional imaging for confirmation. Unfortunately, the diameter of the SMA could not be accurately measured in these three cases.We could recognize complete or partial obstruction of SMA blood flow using color Doppler ultrasound. In one case, the intimal f lap and false lumen were detected by POCUS, while SMA blood flow was detected in the true lumen. In the other two cases, the intimal flap was undetected and SMA blood flow was completely absent in color Doppler ultrasound. In addition to direct visualization of SMA vessels, circumferential or focal echogenic dots in the bowel wall on POCUS may indicate air in the bowel wall (pneumatosis intestinalis),suggestive of bowel ischemia;these were not observed in this case series.
The degree of luminal stenosis and the presence or absence of blood f low within the false lumen are known to have important prognostic value.In our cases, the type of SMA dissection that was suggested by Sakamoto et alcould not be distinguished through POCUS.We believe that is one of the limitations of POCUS.However, the cause of acute abdominal pain in these patients was identified at the bedside using POCUS in the ED, and SMA dissection could be suspected quickly.In the present cases, we were able to check the flow and intimal f lap of SMA, and this allowed us to suspect SMA dissection and to proceed with further evaluations including CECT.
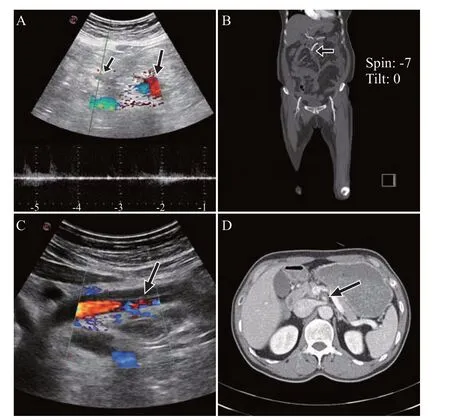
Figure 1. C olor Doppler ultrasound or contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) coronary images of patients 1 (A and B) and 2 (C and D). A: color Doppler ultrasound of the SMA (short arrow) demonstrated that blood f low was absent compared to the aorta (long arrow); B: CECT showed the cut-off point of the SMA enhancement (arrow); C: a true and a false lumen of SMA between the intimal f lap (arrow) were compared using color Doppler to visualize blood flow; D: CECT demonstrated the true lumen and false lumen between the intimal f lap of the SMA (arrow).
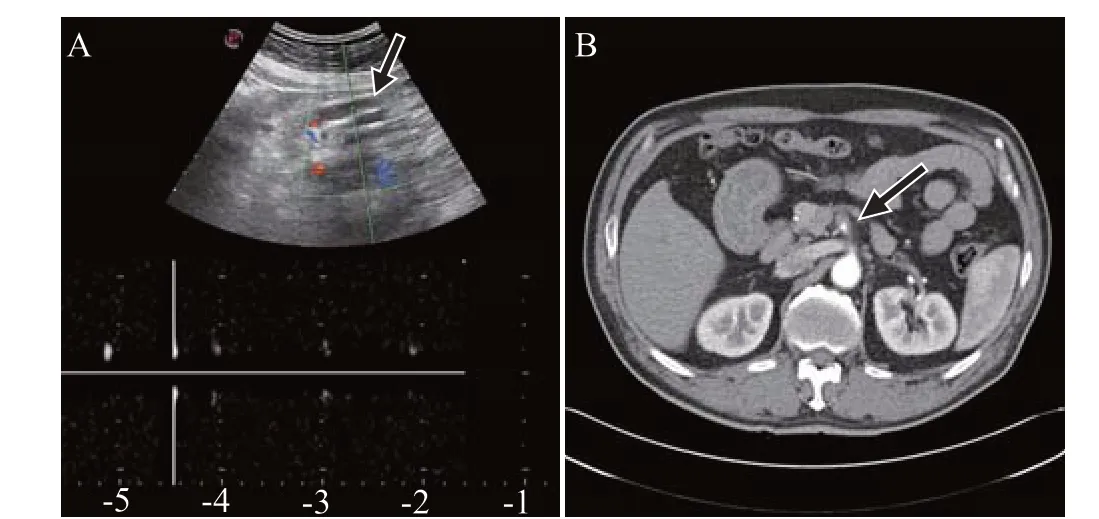
Figure 2. Color Doppler ultrasound or contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) coronary images of patient 3. A: color Doppler ultrasounds demonstrated that SMA (arrow) blood flow was absent,suggesting thrombosis or a false lumen; B: CECT showed enlargement of the SAM with narrowing of the patent lumen, suggesting thrombosis (arrow).
CONCLUSIONS
POCUS may be used for early detection of SMA dissection. SMA dissection should be considered if the blood flow of SMA is undetected using color Doppler ultrasound, irrespective of intimal flap visibility. Thus,POCUS with duplex mode may be used to screen patients with acute abdominal pain, thereby hastening early diagnosis and surgical consultation for SMA dissection and thrombosis.
None.
Not needed.
The authors have no commercial associations or sources of support that might pose a conflict of interest.
SYP proposed the study and wrote the first draft.Both authors contributed the design and interpretation of the study and to further drafts.
All the supplementary files in this paper are available at http://wjem.com.cn.
 World Journal of Emergency Medicine2022年3期
World Journal of Emergency Medicine2022年3期
- World Journal of Emergency Medicine的其它文章
- Mortality-related electrocardiogram indices in methanol toxicity
- The combination of creatine kinase-myocardial band isoenzyme and point-of-care cardiac troponin/contemporary cardiac troponin for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction
- Increasing angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) 2/ACE axes ratio alleviates early pulmonary vascular remodeling in a porcine model of acute pulmonary embolism with cardiac arrest
- Shrinking lung syndrome in autoimmune inflammatory diseases: A case series and review of literature
- Traumatic tension pneumocephalus: A case report
- Blunt myocardial injury and gastrointestinal hemorrhage following Heimlich maneuver: A case report and literature review
