Current Situation Analysis of Nursing Students' Professional Attitudes and Employment Intentions during COVID-19 Pandemic
Xiao-Feng Liu, Ya-Nan Wang, Shen Wang, Shu-Rui Wang
1Graduate School of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China; 2Graduate School of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China; 3Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China.
Abstract Objective: To understand the status of nursing students' professional attitudes, professional identity, and employment intention under the new coronary pneumonia pandemic, and to analyze the factors influencing nursing students' employment intention.Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted on 689 nursing students using a questionnaire, and the results were analyzed by multiple unordered and ordered regressions.Results: 47.17% of the nursing students chose to work in clinical nursing in the future; 95.5% of the nursing students preferred to work in Grade III class hospital hospitals; 0.73% of the nursing students actively chose to work in the infectious disease unit in the background of COVID-19 pandemic.In the analysis of professional attitudes, female nursing students scored higher than male nursing students; Senior students and above scored significantly higher than junior nursing students; nursing students who had internship experience scored higher than those who had not; nursing students who had someone close to them who was involved in the rescue work of the COVID-19 pandemic scored higher in professional attitudes.Regression analysis showed that the higher the professional identity score, the more likely the nursing students were to choose a nursing-related job and expect a higher salary; nursing students who chose nursing because it was easy to find a job, followed the advice of others, or had a family income of less than 3000 yuan per capita also expected a higher salary.In the context of the pandemic, nursing students with high career attitude scores were less likely to choose clinical nursing jobs; students without nursing practitioners at home were less likely to choose hospitals and health management organizations; nursing students with high career identity were more likely to choose Grade III class hospitals. Conclusion: The outbreak of COVID-19 has influenced the employment intention of nursing students, in the background of pandemic, about half of them still choose to engage in clinical nursing work; most of them recognize the outstanding contribution and professional value of nurses in the fight against epidemic.Meanwhile, through this research, it is believed that nursing students at school have insufficient awareness of infectious diseases and other public health emergencies.It is recommended that relevant colleges and universities strengthen knowledge and related courses on the prevention and control of infectious diseases and public health emergency events.
Keywords: Nursing student; COVID-19; Professional attitudes; Employment intention; The questionnaire survey; Cross-sectional study; Nursing education
Introduction
COVID-19 is a major public health emergency with the fastest spreading, the widest range of infection, and the most difficult prevention and control since the founding of the People's Republic of China.Nurses play a huge role and bear the pressure and challenges in fighting against this unknown and threatening pandemic [1].When public health events such as disasters and infectious diseases break out, nurses practice the Nightingale spirit with their actions, actively participate in the anti-pandemic rescue work, and interpret the connotation of nursing with moral and professional responsibilities [2].Although studies have shown that public health emergency events tend to change people’s perceptions of nurses and make them more valued, understood, and evaluated [3], there are still 75.35% of nurses believe that their work is a low-level job [4].This conception affects their professional identity and professional attitude, thereby indirectly affecting the construction of the nursing team [5].Professional attitude refers to an individual's understanding and emotion of the industry he/she is engaged in, and the relatively lasting tendency of the occupational value is formed accordingly [6].In contrast, professional identity is the psychological embodiment of the tendency of an individual's occupational behavior [7].Research shows that nurses with stronger professional identity are more likely to stick to their nursing posts in the future and have better nursing service quality [8].As the successor of the nursing career, nursing students' professional identity is an important part of their core competence training.A higher professional identity is the basis for their firm professional position, which can improve nursing students' employment rate and prevent losing the nurse workforce [9,10].
To study and analyze nursing students' professional attitude, professional identity, and the present situation of the employment intention and its influencing factors, a cross-sectional investigation and study were conducted in April 2020.The results are discussed and analyzed to strengthen the construction of the nursing team and to provide valuable data and theoretical arguments for nursing departments and colleges.
Methods
Data source and participants
A cross-sectional survey with 689 nursing students were conducted in April 2020.Full-time undergraduate and graduate nursing students aged 17 to 28 in two universities in Tianjin were selected as the investigation subjects.They all voluntarily participated in this study with a consent to release the research outcomes.
Questionnaire design
In order to understand as much as possible the influencing factors that affect the professional identity and professional attitude of nursing students during the pandemic, we designed a questionnaire based on the actual situation, which mainly contains 4 parts include basic information, professional attitude scale, employment factor scale and open question.The details of 4 parts are list blow.What needs to be pointed out is that to ensure the completeness, appropriateness and accuracy of the questionnaire, the scale used in this study was reviewed and modified by three experts in related fields.
Basic informationGender, age, the only child or not, grade, place of origin, per capita monthly family income, reasons for studying the major, clinical practice experience, family has a nurse worker or not, whether there are people around to participate in the frontline anti-pandemic work or not.
Professional attitudeThis scale is divided into 2 dimensions and 8 items: dimension 1 contains 4 items named occupational identity, which includes (1) Think nursing is a sacred profession before the outbreak; (2) Think nursing is a sacred profession after the outbreak; (3) Before the outbreak, the nursing career had an optimistic outlook; (4) After the outbreak, the nursing career is considered optimistic.Dimension 2, which named professional attitude, contains 4 items, including (1) Your family's attitude towards your nursing career after the outbreak; (2) The level of preference for the nursing profession before the outbreak; (3) The level of preference for the nursing profession after the outbreak; (4) Are you willing to join the first-line clinical work of anti-pandemic during this COVID-19 pandemic? The professional attitude scale adopts Likert 5 rating method.It is divided into 1."strongly disagree", 2."disagree", 3."neutral", 4."agree" and 5."strongly agree".The higher the score is, the higher the student's recognition degree is.Before the start of the study, the researchers first conducted a pre-survey of 36 nursing students to assess the clarity of the content.For dimension 1, the Cronbach 'α coefficient is 0.845 and content validity is 0.664.For dimension 2, the Cronbach 'α coefficient is 0.758 and content validity is 0.656.For total, the Cronbach 'α coefficient is 0.859, content validity is 0.769, expert validity is 0.92, which can be considered to have good reliability and validity.
Employment intentionThe main content includes the desire to work, preferred work unit, preferred work hospital level, preferred work department, expected monthly salary, etc.
Open questionFrom the perspective of nursing student, what should be added to the school's curriculum on infectious diseases and natural disasters?
Ethical consideration
The Deans of the nursing college approved the questionnaire before distributing the questionnaire to the students.The questionnaire was sent to the WeChat groups of students.Participation is all voluntary, and the collected data is used only for academic research.The respondents completed the questionnaire independently and submitted the questionnaire on the platform.The survey was anonymous, and a total of 689 questionnaires were collected.They are all valid, with a significant recovery rate of 100%.
Statistical analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics v26 was used for data analysis.Counted data were represented by frequency and percentage, while measurement data were represented by the mean and standard deviation.In the general data of nursing students and the professional attitude scale, the two dimensions of professional attitude and professional identity were analyzed by double independent samplet-test and single factor variance.The regression analysis of the influencing factors of nursing students' employment intention adopts the multivariate logistics regression analysis method to evaluate the independent influencing factors of nursing students' employment intention.WhenP< 0.05, this factor can be considered as statistically significant.
Results
General Information
The age range of our survey participants covers 17 to 37 years old, among which the undergraduates are 17 to 28 years old, and the postgraduates are 22 to 37 years old.Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of the study participants.The mean participant age was 20.52 years old; 91.3% were female.67.8% of participants were living in town or countryside and 67.8 of them at least two children in the family.It should be noted that up to 89.4% of respondents have nursing-related jobs in their homes.Regarding the question of whether anyone around the participants is involved in the fight against the pandemic, which is important to this study, 78.5% participants answered yes.
Table 2 present the proportion of nursing students’ job seeking preferences.For desired position 47.17% of participants prefer clinical nursing.More than half of participants (50.36%) hope to work in a hospital.Among all level of hospital, obviously, 3rd grade class-A general hospital (The highest level in China) is the most popular, 79.39% of participants chose this option.Among all the departments in the hospital, operating room, surgery, and medical department are the most popular three departments, with 23.66%, 20.46% and 13.35% of participants choosing these three departments, respectively.As for salary, 44.56 % of participants expect to earn more than 15,000 yuan per month.
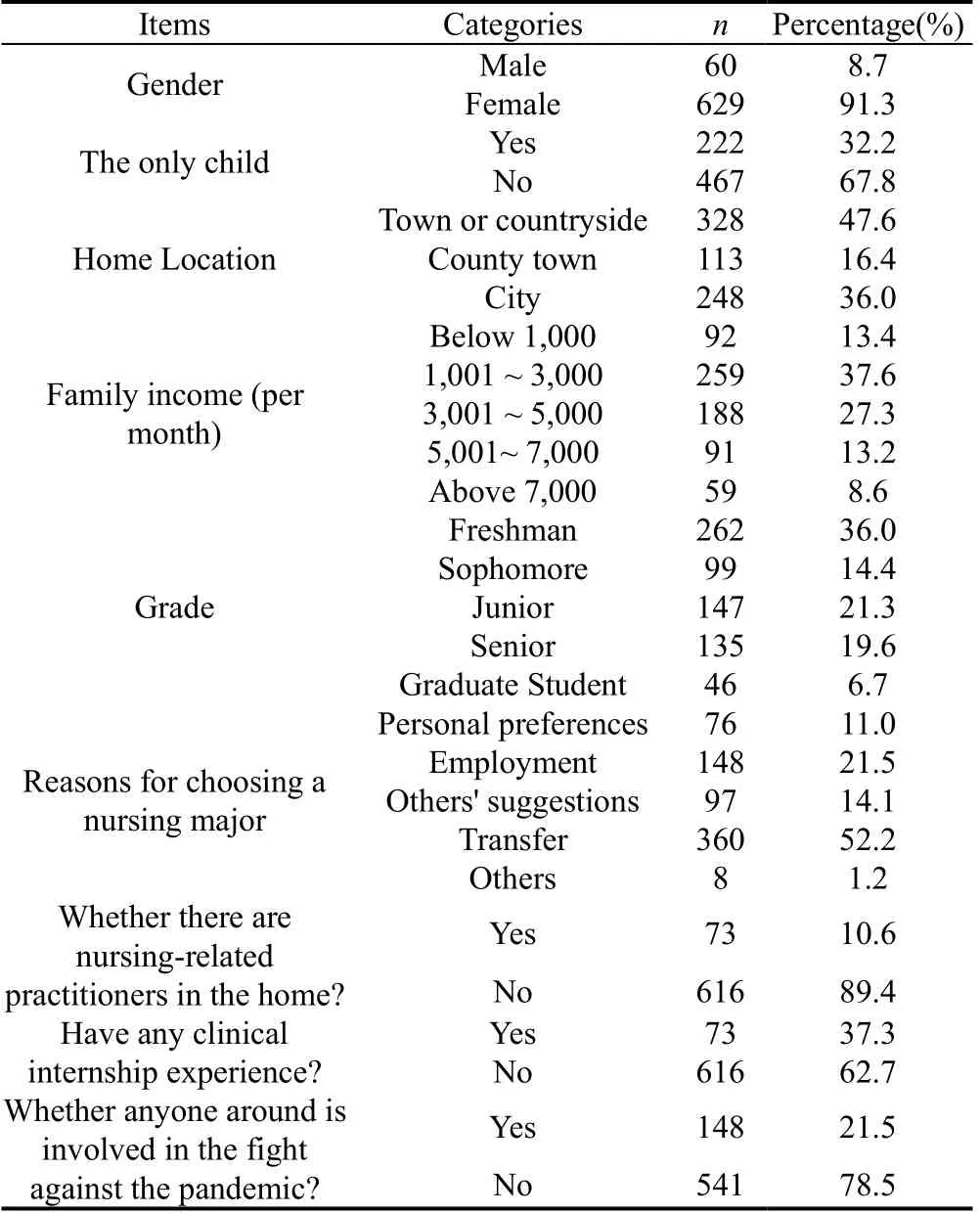
Table 1.Baseline characteristics of participants (n = 689)

Table 2.Nursing student job seeking preferences (n = 689)
Professional attitude analysis
The professional attitude and professional identity were divided into dependent variables including gender, whether it was an only child, birthplace, per capita monthly household income, reasons for choosing a nursing major, grade, whether there were nursing practitioners at home, and whether there was clinical internship experience, and whether anyone around him/her participates in the first-line clinical anti-pandemic work.Single factor variance andt-test were used in this analysis.
According to Table 3, the results showed that gender reasons for choosing a nursing major, grade, clinical practice experience, and whether anyone around is involved in the fight against the pandemic? had statistical significance (P< 0.05) on the professional attitude of nursing students.Family per capita monthly income, reasons for choosing a nursing major, grade, and clinical practice experience had statistical significance (P< 0.05) for nursing students' professional identity.See Table 3 for details.
Table 3.Comparison of scores of professional attitude and professional identity among nursing students in the school (± s, n = 689)
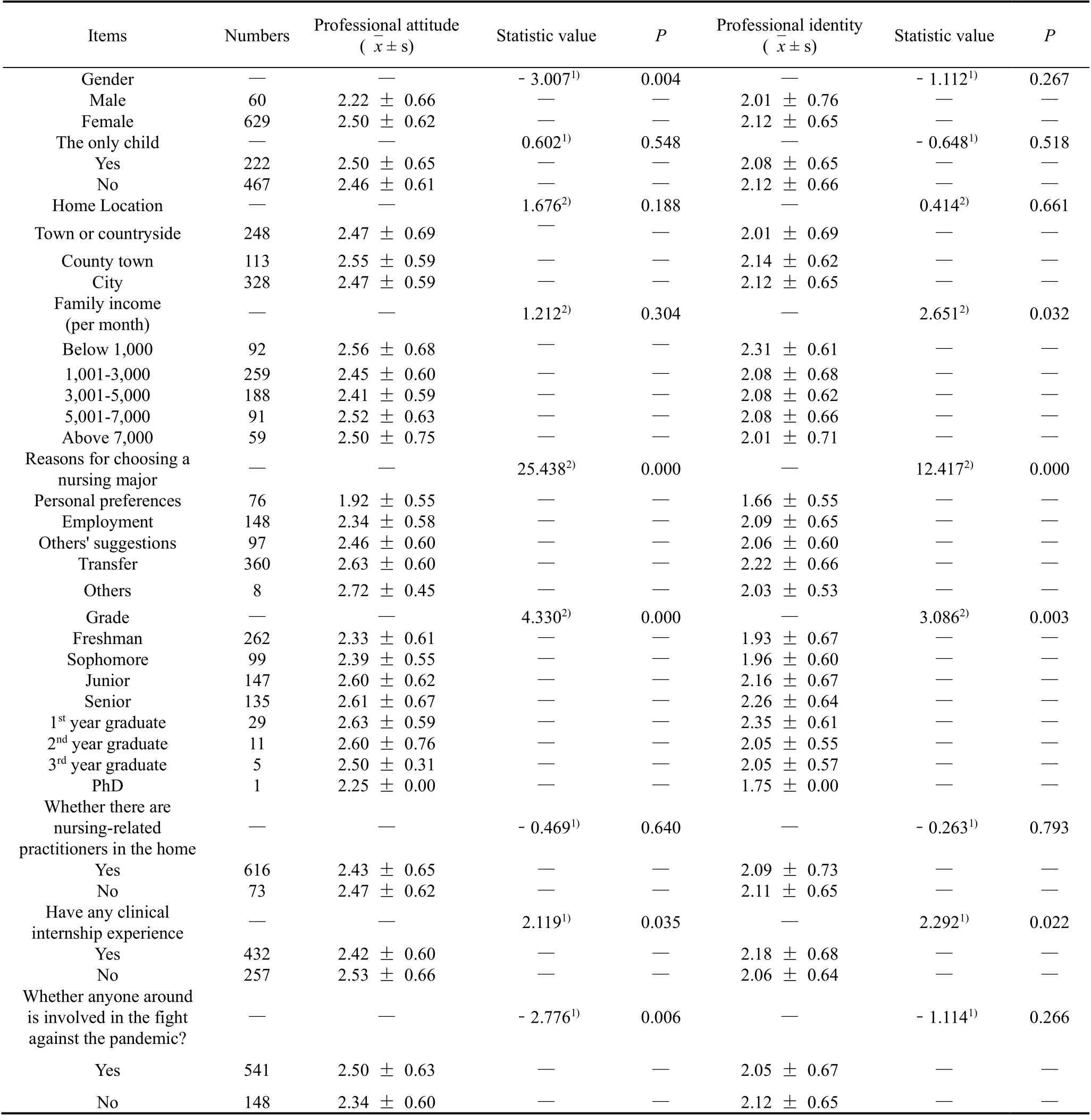
Table 3.Comparison of scores of professional attitude and professional identity among nursing students in the school (± s, n = 689)
Note: In the table, superscript 1) represents the T statistic , and 2) represents the F statistic.
Items Numbers Professional attitude (ˉx ± s) Statistic value P Professional identity (ˉx ± s) Statistic value P ?Gender — — ﹣3.0071) 0.004 — ﹣1.1121) 0.267 Male 60 2.22 ± 0.66 — — 2.01 ± 0.76 — — Female 629 2.50 ± 0.62 — — 2.12 ± 0.65 — — The only child — — 0.6021) 0.548 — ﹣0.6481) 0.518 Yes 222 2.50 ± 0.65 — — 2.08 ± 0.65 — — No 467 2.46 ± 0.61 — — 2.12 ± 0.66 — — Home Location — — 1.6762) 0.188 — 0.4142) 0.661 Town or countryside 248 2.47 ± 0.69 — — 2.01 ± 0.69 — — County town 113 2.55 ± 0.59 — — 2.14 ± 0.62 — — City 328 2.47 ± 0.59 — — 2.12 ± 0.65 — — Family income (per month) — — 1.2122) 0.304 — 2.6512) 0.032 Below 1,000 92 2.56 ± 0.68 — — 2.31 ± 0.61 — — 1,001-3,000 259 2.45 ± 0.60 — — 2.08 ± 0.68 — — 3,001-5,000 188 2.41 ± 0.59 — — 2.08 ± 0.62 — — 5,001-7,000 91 2.52 ± 0.63 — — 2.08 ± 0.66 — — Above 7,000 59 2.50 ± 0.75 — — 2.01 ± 0.71 — — Reasons for choosing a nursing major — — 25.4382) 0.000 — 12.4172) 0.000 Personal preferences 76 1.92 ± 0.55 — — 1.66 ± 0.55 — — Employment 148 2.34 ± 0.58 — — 2.09 ± 0.65 — — Others' suggestions 97 2.46 ± 0.60 — — 2.06 ± 0.60 — — Transfer 360 2.63 ± 0.60 — — 2.22 ± 0.66 — — Others 8 2.72 ± 0.45 — — 2.03 ± 0.53 — — Grade — — 4.3302) 0.000 — 3.0862) 0.003 Freshman 262 2.33 ± 0.61 — — 1.93 ± 0.67 — — Sophomore 99 2.39 ± 0.55 — — 1.96 ± 0.60 — — Junior 147 2.60 ± 0.62 — — 2.16 ± 0.67 — — Senior 135 2.61 ± 0.67 — — 2.26 ± 0.64 — — 1st year graduate 29 2.63 ± 0.59 — — 2.35 ± 0.61 — — 2nd year graduate 11 2.60 ± 0.76 — — 2.05 ± 0.55 — — 3rd year graduate 5 2.50 ± 0.31 — — 2.05 ± 0.57 — — PhD 1 2.25 ± 0.00 — — 1.75 ± 0.00 — — Whether there are nursing-related practitioners in the home — — ﹣0.4691) 0.640 — ﹣0.2631) 0.793 Yes 616 2.43 ± 0.65 — — 2.09 ± 0.73 — — No 73 2.47 ± 0.62 — — 2.11 ± 0.65 — — Have any clinical internship experience — — 2.1191) 0.035 — 2.2921) 0.022 Yes 432 2.42 ± 0.60 — — 2.18 ± 0.68 — — No 257 2.53 ± 0.66 — — 2.06 ± 0.64 — — Whether anyone around is involved in the fight against the pandemic? — — ﹣2.7761) 0.006 — ﹣1.1141) 0.266 Yes 541 2.50 ± 0.63 — — 2.05 ± 0.67 — — No 148 2.34 ± 0.60 — — 2.12 ± 0.65 — —
Regression analysis of influencing factors of employment intention
To further understand the influencing factors of nursing students' employment intention, each item in this category was taken as the dependent variable.The general information in demographic statistics was taken as the independent variable, and the total scores of the two dimensions of occupational attitude and occupational identity were taken as the covariable to conduct logistics regression analysis.For two or more independent variables and dependent variables case, multiple unordered logistics regression analysis is adopted.When the dependent variable is an ordered classification variable, multiple ordered logistics regression analysis was adopted.In multiple ordered and unordered logistics regression analyses,P< 0.05 is considered as statistically significant.Positive B value indicated a positive correlation between dependent variables and independent variables, and a negative correlation was the opposite.See Table 4 and Table 5 for details.
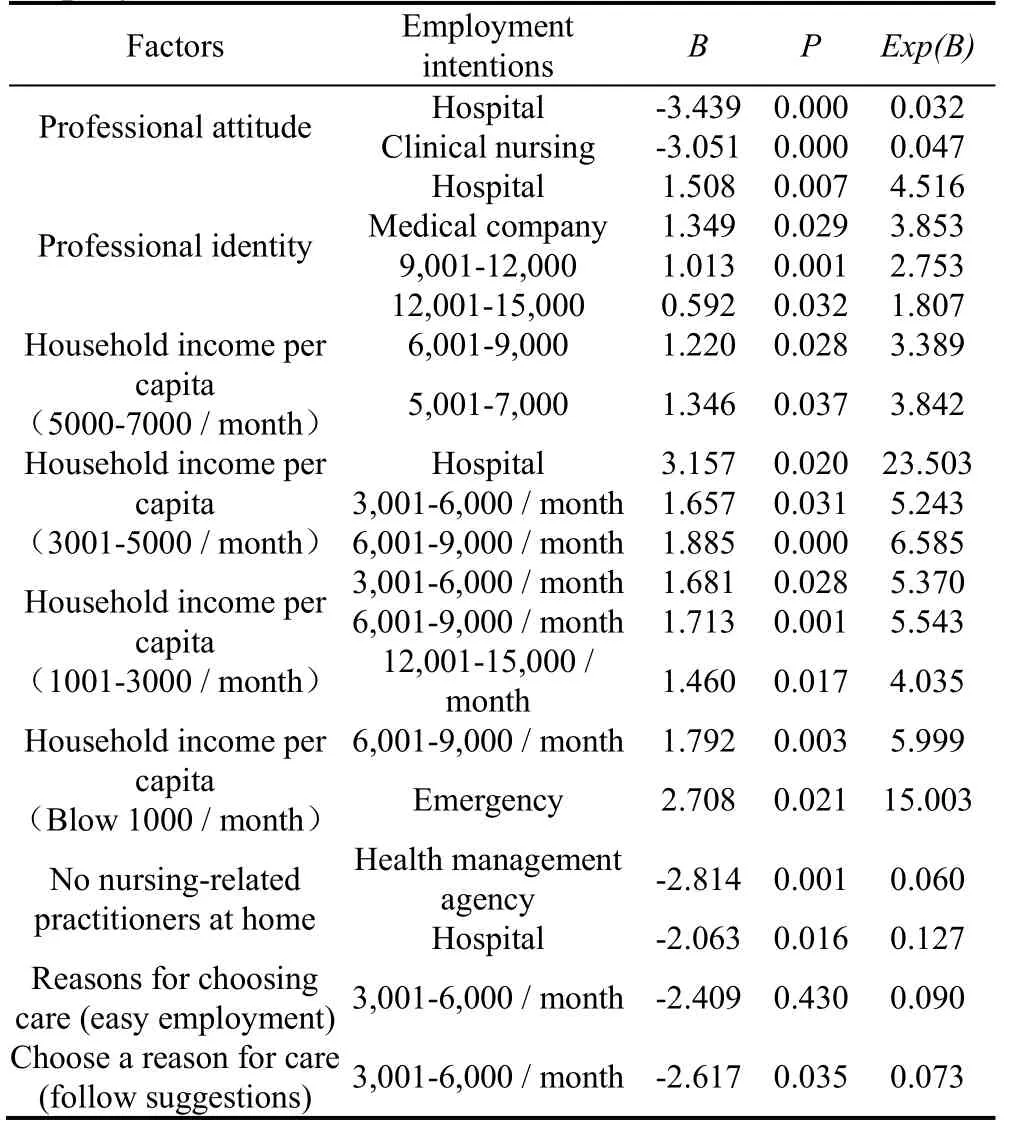
Table 4.Multiple unordered logistics regression analysis of influencing factors of nursing students' employment intention (n = 689)
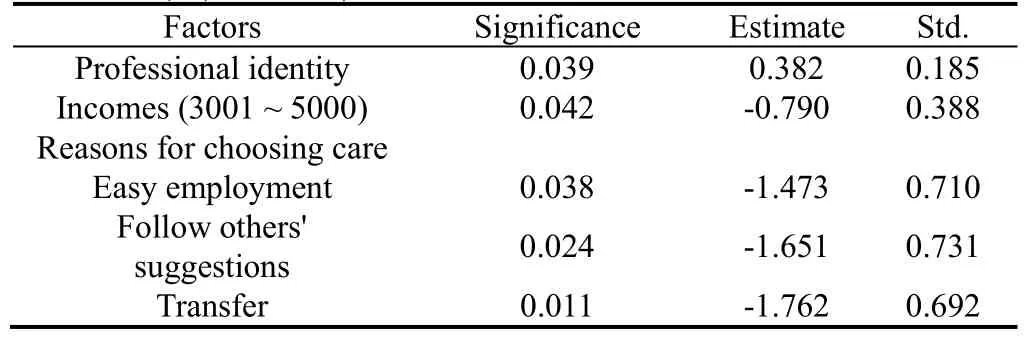
Table 5.Multiple ordered logistics regression analysis of nursing students' employment intention (hospital selection) (n = 689)
Discussions
Employment intention of nursing students
This study investigated the employment intention of nursing students in schools.The results showed that most students wanted to pursue a nursing-related career, among which 47.17% chose clinical nursing, and 30.19% chose nursing education.95.50% of the students said that they wanted to work in 3rd grade class-A hospital (top level in China).23.66% of students want to work in the operating room.In the context of the pandemic, the number of nursing students who actively chose the infectious department was 0.73%.Studies have shown that nursing students have varying degrees of safety concern and nervousness after their internship in the infectious diseases department, which may be caused by the lack of knowledge about infectious diseases [11].More students are willing to work in the operating room because the nursing work in the operating room is more special and there is less contact with patients and family members.In addition, the nurse-patient relationship is simpler, and a higher compensation is expected there.Studies have shown that the expected monthly pay for mid-career nurses is more than 4,000 yuan [12].This study shows that 89.84% of nursing students with a bachelor's degree or higher expect a monthly salary of more than 6,000 yuan, indicating that the higher the education, the higher the expectation of monthly salary.
Occupational attitudes and identity with different demographic characteristics
The analysis of this study showed that gender, grade, reasons for choosing a nursing major, clinical practice experience, and whether there were people around to participate in the frontline work of COVID-19 had statistical significance with the professional attitude of nursing students (P< 0.05).There were statistically significant differences between grade, family monthly income, reasons for choosing a nursing major, clinical practice experience, and nursing students' professional identity (P< 0.05).The professional attitude score of female students is higher than that of male students, which is consistent with the findings from Wu Linfeng et al.[13].The reasons are analyzed here.On the one hand, the number of male nurses is much less than female students, and the low social recognition of male nurses can affect their views on the profession.On the other hand, the profession of nurses may not meet the expectations of male students for their future [14].The professional attitude of nursing students has a remarkable effect on the professional identity of junior, senior, and graduate nursing students.From the results, Junior students and above have significantly higher professional identity and professional attitude than entry level students do.This finding shows that with the deepening of the courses, students have a profound understanding of the nursing industry, and they have more professional knowledge.As a result, students have more positive attitudes towards careers, and their sense of professional identity has gradually improved.The internship is also an important factor affecting professional recognition.During the internship process, nursing students enter the clinics and experience the clinical nursing environment.The professional attitude scores of students who have clinical internship experience are higher than those who have not.The instructors in the clinics often positively guide the students to increase their confidence in the profession and improve their professional attitude.The occupational identification scores of students with clinical internship experience are lower than those of students who have no clinical internship experience.It is assumed that clinical nursing work is onerous.The nurse-patient relationship is intense, bringing greater physical and mental pressure to nursing students, thus affecting their sense of identity in the nursing profession.The professional attitudes of nursing students with people, who have participated in the front line of the pandemic, around them have relatively high scores.Such nursing students can truly feel the social value and sense of social responsibility of the nursing profession through real example deeds around them, thereby improving their attitude towards the profession.Family per capita monthly income can also affect nursing students' professional identity towards the nursing field.Among them, nursing students whose family per capita monthly income is less than 1000 yuan have higher professional identity scores than others.Nursing students in this category may want to choose a more stable career because they are burdened by their families, so they recognize the nursing industry more.
Regression analysis of factors influencing employment intention of nursing students
Nursing students'professional attitudes and professional identity influence their choice of jobs and salary expectations in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.The study showed that nursing students with high scores on their professional attitudes were less likely to choose a clinical nursing job than those with high scores on their attitudes.Analysis of different demographic characteristics and professional attitudes and identity showed that nursing student who had someone, who was involved in the fight against the pandemic, close to them scored higher in their professional attitudes.This may be due to the risks of nursing, as demonstrated by the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the overwhelming responsibilities and pressures of nursing [15].In addition, the relative lack of education on infectious disease protection may also lead to nursing students' anxiety and fear of working in clinical nursing.
We also found that nursing students with higher professional identity scores were more likely to choose a nursing-related job and to expect higher pay.This may be due to the fact that nursing students with a higher professional identity recognize the intrinsic value system of the hospital and healthcare company, the professional competencies required of nurses, and the nurses' own recognition of their profession and the professional competencies it entails, while at the same time believing that they are worthy of higher rewards for their efforts.
Nursing students who chose a nursing profession because it was easy to find employment, followed the advice of others and had a family income of less than 3,000 per capita per month had higher salary expectations.Nursing students who chose a nursing profession because of the ease of employment and the advice of others may have had higher salary expectations when they chose the nursing profession.In addition, nursing students' salary expectations are to some extent influenced by family income, and students from lower income families may tend to expect a higher salary to improve their financial situation.
The presence or absence of nursing-related professionals in the home influences the nursing student's desired workplace.Nursing student who do not have a nursing-related practitioner at home are less likely to choose a hospital or health management facility.This may be due to the lack of awareness of the nursing profession among students who do not have nursing staff at home, as well as long-standing societal prejudices about nursing that result in low motivation for nursing-related jobs.
Occupational identity, per capita monthly household income of 3001-5000 yuan, and the reason for choosing the nursing profession had a significant impact on the level of hospital in which nursing students expected to work.The higher the nursing students' occupational identity, the more likely they are to choose a higher-level hospital, indicating that occupational identity has a positive impact on their own requirements and the higher their requirements for employment.Those nursing students who transferred to a nursing program because of ease of employment, following the advice of others, were more likely to choose a lower-ranked hospital.This may be because lower-ranked hospitals tend to have less competitive pressure and are more employable.Nursing students with a per capita monthly family income of 3001 to 5000 yuan may be more likely to seek employment in a lower-ranked hospital with less work pressure due to their own better family circumstances.
Moreover, according to the analysis of the open-ended questions in this questionnaire, the nursing students would like the university to increase: (1) the education on the risks and hazards of infectious diseases and the corresponding first aid measures and protection; (2) the emergency preparedness measures for natural disasters and their drills; (3) the lecturers to increase the education on infectious diseases (such as Ebola) that have not been pandemic in China and the use of real-time records of the working life of health care workers in infected areas in order to better understand the nursing students; (4) the psychological counseling channel to provide effective psychological intervention for nursing students in case of a major public health emergency.
Conclusion
The results of this study show that although the COVID-19 outbreak has affected the employment intention choices of nursing students to some extent, nursing students in the context of the pandemic still mostly choose to work in clinical nursing.In this outbreak, nursing students recognized the outstanding contribution and professional value of nurses in the fight against the pandemic.However, the relative lack of knowledge about the prevention and control of infectious diseases and public health emergencies may have contributed to the psychological burden of nursing students.Therefore, universities should increase the knowledge and courses related to the prevention and control of infectious diseases and public health events, and strengthen the psychological guidance to nursing students; at the same time, universities should also increase the opportunities for clinical apprenticeship for junior nursing students and increase the publicity of nurses' outstanding contribution and professional value in the fight against pandemic, so as to cultivate nursing students' recognition and affection for their profession and to strengthen the nursing team.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- The application progress of auricular therapy in diabetes
- Neonatal Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome: A Case Report
- Effects of Modern Online and Traditional Offline Exercise Programs on the Frailty, Physical function, Emotional, and Social Support on Chinese Community-Dwelling Frail Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trail
- Comparison of Status of Mental Health of Male Nursing Students between China and Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study

