Comparison of Status of Mental Health of Male Nursing Students between China and Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Chao-Kai He, Jung Chang Suk, Minchae Park, Sunwoong Nam
1School of Nursing, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China; 2Department of Nursing, Daegu Haany University, Gyeongsan, Korea.
Abstract Objective: To compare the mental health status among Chinese and Korean male nursing students and further clarify the predictors of the mental health.Methods: Research data was collected from 86 undergraduate male nursing students of China and Korea by using the SCL-90-R questionnaire.The collected data was analyzed by using SPSS version 22.0.Results: Findings showed Chinese male nursing students reported higher scores of SCL-90-R than the Chinese norms, and Korean group scored lower than Chinese group and the Korean norms.The key predictors of male nursing students' mental health include having a male role model in the nursing field, receiving positive career guidance from teaching staff and having the support and respect of family and friends. Conclusion: Chinese male nursing students need to improve their mental health level more urgently than Korean male nursing students.Chinese educators need to pay more attention to role model education and spread more excellent male nurse models for male nursing students, and Korean educators need to support male nursing students with enthusiastically and provide more positive guidance for their study and career planning.
Keywords: Male nursing students; Mental health; Psychological symptom dimension; Checklist-90-Revised
Introduction
Nursing students, as indispensable professionals in the health system will work in challenging and high-pressure environments, and as such require that they should have good mental health to be competent and safe nurses to provide quality nursing care [1].Walker et al.[2] suggested that educating the future nursing workforce needs to develop their person-centred attitude and psychomotor skills to facilitating students toward becoming well rounded.A comprehensively developed person would have good emotional management skills to maintain his or her healthy mentality, and researchers have also found that managing emotions is positively correlated with academic success [3].Nursing students are more prone to stress, anxiety, loneliness, depression and nervousness than non-medical students because of the challenges in difficult professional knowledge, skills and clinical experience, and also the higher ethical standards of the nursing profession [4,5].If these psychological emotions are not dealt with adequately, some physiological adverse reactions may occur, such as, lack of sleep and hypertension, which in turn can affect the student's academic and clinical performance [6,7].Although many previous studies have indicated the poor mental health status of nurse students [8,9], there are few literatures that independently focused on the psychological status of male nursing students.As we all know, males are very different from females on both physically and psychologically.Therefore, the mental health of male nursing students is a problem worthy of close attention and in-depth study.
Since the Nightingale period, nursing has always been considered a females’ profession, and under the influence of this concept, the main force of the nursing industry has consistently been dominated by females [10,11].Compare with female nurses, male nurses have great advantages in physical strength, critical thinking ability, and cool-headedness [12], and they also can increase the diversity of nursing and thus promote an inclusive culture that has a negative effect on the quality care [13].Some researchers also reported that it serves would improve the quality of patient care provided by improving nursing workforce diversity to be representative of the public, and it would make diversity a key initiative [14,15].However, the experience of male nursing students in their nursing education program is not optimistic, and they have to overcome many challenges due to gender.Powers [16] pointed out male nursing students were subject to gender discrimination from their faculty in their education programs.In addition, studies have shown that there is a certain relationship between the support of family and friends and the psychological emotions of male nurse students, however, their family members and friends also didn’t understand why they have chosen to work as a male nurse, or even ridiculed, and they won’t be trusted by patients for gender reasons in clinical internships [17].Male nursing students face a variety of stereotypes, such as laziness [18], they won’t work and study hard like female students [19], and men who have entered into nursing career are normally stereotyped as troublemakers, effeminate, or gay [20].Some researchers also found that male nursing students had a sense of isolation, which leaded them to choose to keep silent in the corner of the classroom [21,22].On the other hand, male nursing students always be picked on or put in the spotlight more often because of standing out as the minority in the classroom [18,23].Based on these literature reports, we speculate that the degree of understanding of nursing disciplines, the support of family, friends, and school have a great correlation with the mental health of male nursing students during nurse training programs.
As we all know, the cultural environment is an important factor affecting human social behavior.In East Asian culture, gender roles are strictly regulated due to the influence of traditional Chinese Confucian culture.Men are usually responsible for raising a family, they are the main person in charge of a family's economy, and women are mainly responsible for housework and caring for their families.Affected by this concept, males are taught to seek success in their professions and reluctant to engage in nursing [17].Nursing work is mainly based on caring, and it includes some basic life care such as bed making.Therefore, Asian patriarchal society insists that men should not be engaged in nursing because nursing is considered a female occupation.The social culture of China and South Korea is highly similar to a certain extent.Under the similar cultural background, the impact of different education systems on the education of male nursing students is worth looking forward to.
The discussion above explained the importance of male nurses in promoting the diversity of nursing professions and improving the quality of care.A literature review described the current state of education of male nursing students and some of their experiences in nursing programs.The nursing education method and workforce policy in China and Korea are different, and these have caused many different outcomes for nursing workforces.Chinese nursing education is more traditional and emphasizes a teacher-centered approach, and it is dominated by low-level (diploma programs) education [24].On the contrary, Korean higher education in nursing developed earlier than China and occupied a large proportion, and Korean nursing education advocates a student-centered approach to education and focuses more on developing students' skills of critical thinking, Evidence-Based Practice and Team-Based learning [25].In addition, due to socio-cultural and educational levels of nurses, Korean nurses generally have higher social status than Chinese nurses, and their salary is better than China [26].The purpose of this study was to explore the mental health status and its influencing factors of male nursing students among China and Korea under different education systems.The findings of this study were used to compare the differences of male nursing students’ psychological problems in both two countries and then analyzed what caused these mental health issues.This study would benefit to help male nursing students build resilience in nursing programs and reflect on how to provide them with the necessary support to improve their mental health.
Methods
Study Design
This cross-sectional study used a questionnaire survey to measure the psychological symptom level of male nursing students among China and Korea.Through the comparison of these three groups: Chinese male nursing students and Korean male nursing students, Chinese male nursing students and Chinese norms, Korean male nursing students and Korean norms, the mental health status of male nursing students in the two countries was explored, and the influencing factors were analyzed.
Participants
A convenience sampling of male nursing students was recruited from Chinese university and Korean university.All participants were from four-year undergraduate nursing programs and volunteered to participate in the study and signed informed consent.Inclusion criteriaMale nursing students attending of the two countries; Aged 18 years or above; Voluntary participation in the study.
Exclusion criteriaStudents in military service; International students.
Data collection
A paper questionnaire was used to evaluate for Korean students.Before starting the assessment, the research staff explained the general scoring method and requirements to the participants.Then the students were requested 20 minutes to make an independent self-assessment, which was unaffected by anyone and filled it in with a pencil.The time range of the assessment was the actual feeling of ‘now’ or ‘last week’.The ‘Questionnaire Star’ APP was used for Chinese students to complete the questionnaire on online.A brief description of the project and informed consent were displayed in the link.The participants were informed the requirements of completing the questionnaire.All participants were also informed that participation was voluntary, and all information provided would be kept confidential.
The data collection was undertaken over a month period from May 1st to May 31st, 2019.After the data collection was completed, it was immediately handed over to the staff not associated with the study for safekeeping, and then two data entry staffs entered the data independently from back to back.After the completion, the data table was exchanged for checking for integrity.
Instruments
The self-made socio-demographic questionnaire was used to investigate the basic information of male nursing students, and the Checklist-90-Revised (CL-90-R) was used to measure psychological symptomatology in this project.The self-made socio-demographic scale was based on the research results of previous literature [16,17,27] and the results of education expert consultations to select the items that may have the greatest relationship with the mental health of male nursing students.The Symptom Checklist-90-Revised (SCL-90-R) consists of 90 items designed for individuals from the community and individuals with psychiatric conditions to measure psychological symptoms and psychological distress.It uses a five-point Likert scale ranging from "not at all"(0) to "extremely"(4).The SCL-90-R assesses psychological distress in terms of nine primary symptom dimensions28:Somatization, Obsessive-Compulsive,Interpersonal Sensitivity, Depression, Anxiety, Hostility, Phobic Anxiety, Paranoid Ideation and Psychoticism.The SCL-90-R was translated into Chinese and Korean in this study.The average reliability of each factor of the Chinese version was measured to have a Cronbach alpha value of 0.981, and the Cronbach’s alpha of Korean version is 0.967.
Ethical considerations
This study did not use any interventions or cause any harm to the participants, and the ethical approval was not necessary.The research assistant has explained in detail the purpose and procedures of the study to all participants and informed them that participation in the study is completely voluntary and that refusal to participate will not affect their study and life at the university.Participants completed the questionnaire anonymously.All participants have signed informed consent and all data was locked and accessible only by researchers.
Data analysis
The data collected by the socio-demographic questionnaire and the SCL-90-R questionnaire were counted, and then the average scores of the nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R were calculated according to the scoring criteria.
The collected data was analyzed by using SPSS version 22.0 for Windows (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).The frequency and percentage of each item in the socio-demographic questionnaire were calculated.T-Test was performed to calculate the mean values and standard deviations of the Chinese group and the Korean group, while, it was compared with the norms of China29 and Korea30.The Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test was used to verify the normal distribution of the data between the two groups in China and Korea.The results showed that the data was non-normally distributed, so the Wilcoxon rank sum test was used for analyzing the difference of the scores on nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R between Chinese and Korean male nursing students.After that, Correlation analysis was carried out to estimate the degree of correlation between independent variables and dependent variables, and then screen out three to five important related factors.Finally, these factors were included in a multivariate regression analysis, and it was conducted to analyze the influence of these factors on nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R.
Results
Socio-demographic data
The Chinese questionnaire was open online and a total of 42 samples were collected, including 40 valid questionnaires.A total of 46 Korean questionnaires were distributed in this study, and 46 valid questionnaires were collected.The demographic characteristics of the sample are shown in Table 1.
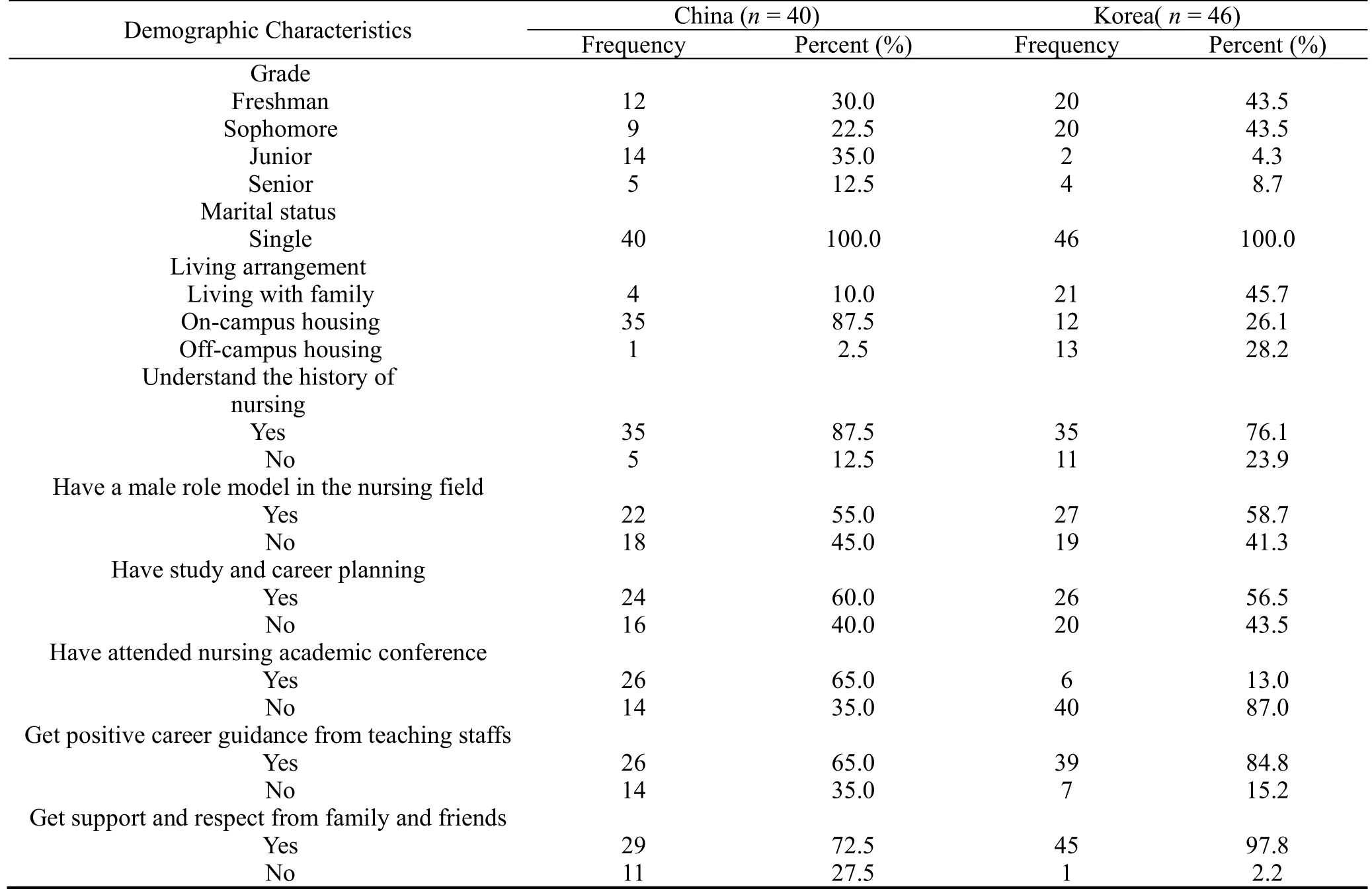
Table 1.Demographic characteristics of the two samples
Comparison of SCL-90-R outcomes between the male nursing students and norm samples of China and Korea
Results of the comparison of SCL-90-R outcomes between the male nursing students and norm samples of China and Korea are shown in Table 2.For Chinese group, all scores of the symptom dimensions were higher than the norms, and all of symptom dimensions had significant statistical differences (P< 0.001,P< 0.01,P< 0.05), except the Interpersonal sensitivity (P= 0.076).For Korean group, all of the scores in the symptom dimensions of male nursing students were lower than the scores of norms.Among these symptom dimensions, Interpersonal sensitivity, Anxiety, Hostility, Paranoid ideation and Psychoticism were significantly different (P< 0.01).In addition, the Somatization, Depression and Phobic anxiety had statistical differences (P< 0.05), and the Obsessive-Compulsive was not significantly different (P= 0.074).
Comparison in the nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R between Chinese and Korean male nursing students
The results of Wilcoxon rank sum test showed that the medians of the Chinese students were significantly higher than the Korean students among Hostility (Z = -2.891,P< 0.01), Phobic anxiety (Z = ?2.694,P< 0.01), Paranoid ideation (Z = ?2.878,P< 0.01) and Psychoticism (Z = ?2.521,P< 0.05).Comparison in the Somatization,Obsessive-Compulsive, Interpersonal sensitivity, Depression and Anxiety between Chinese and Korean Male Nursing Students, there were no significant statistical differences (P> 0.05).The results of comparison in the nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R between Chinese and Korean male nursing students are shown in Table 3.
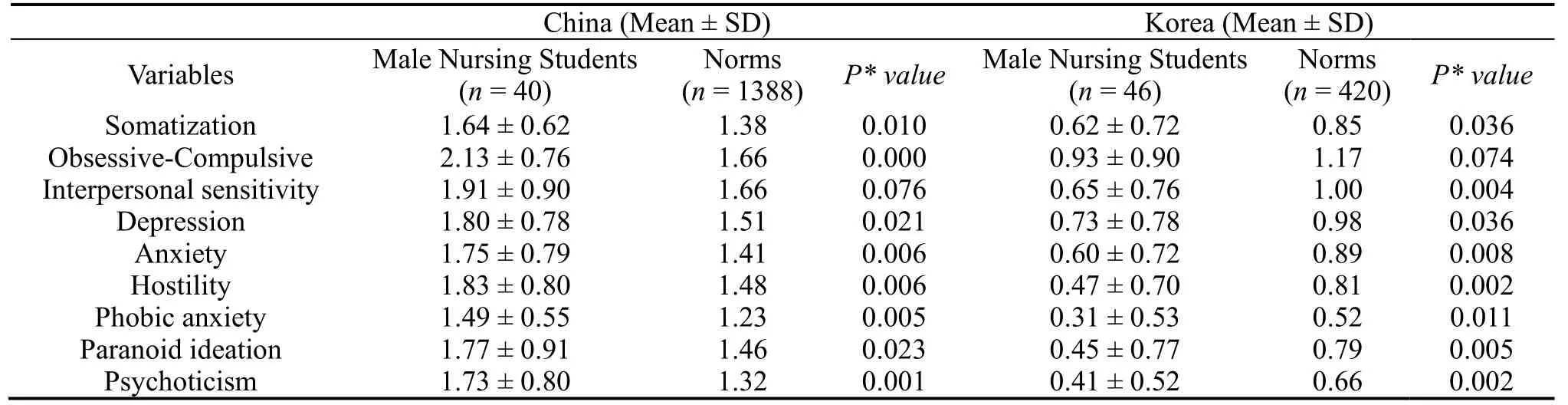
Table 2.Summary of the nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R for both male nursing students and norm samples in China and Korea
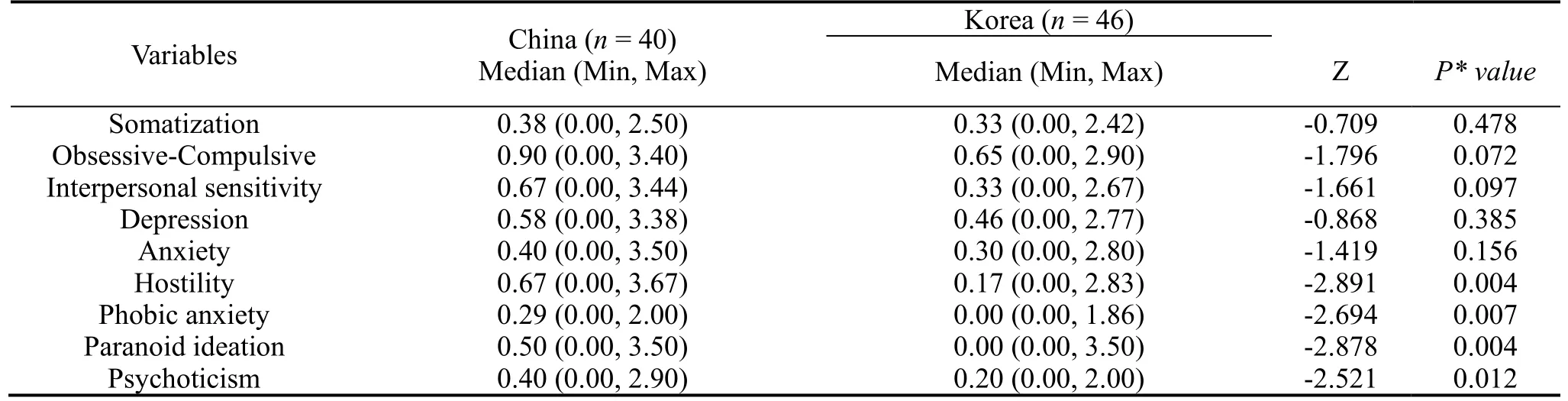
Table 3.Summary of the comparison about the nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R between Chinese and Korean male nursing students
Regression models to predict psychological symptom level in male nursing students
There were six demographic variables significantly correlated with the nine symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R, and all of these demographic variables were included in further analysis.In the multivariate regression analysis, dummy variables were set for the disordered multi-category variables of grade and living arrangement, and these were used the ‘Enter’ method to incorporate into the regression equation.The other demographic variables were used the method of ‘Stepwise’ to carry out the regression analysis.
Chinese groupThe results of the multivariate regression analysis on predicting psychological symptom level in Chinese male nursing students are shown in Table 4.
● Have a male role model in the nursing field
The results showed that having a male role model in the nursing field had positive and significant predications regarding most of the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R.Having a male role model in the nursing field could predict a lower level on symptom dimensions of Somatization (β = 0.322,P< 0.05), Obsessive-Compulsive (β = 0.426,P< 0.01), Interpersonal sensitivity (β = 0.383,P< 0.05), Anxiety (β = 0.359,P< 0.05), Phobic anxiety (β = 0.325,P< 0.05), Paranoid ideation (β = 0.379,P< 0.05) and Psychoticism (β = 0.379,P= 0.01).
● Get positive career guidance from teaching staffs
Getting positive career guidance from teaching staffs had positive and significant predictions on Somatization (β = 0.430,P< 0.01), and students got more positive career guidance, the scores of Somatization were less.
● Have attended nursing academic conference
Having attended nursing academic conference had positive and significant predictions on Depression (β=0.370,P< 0.05), and students reported a lower score on this symptom dimension.
Korean groupThe results of the multivariate regression analysis on predicting psychological symptom level in Korean male nursing students are shown in Table 5.
● Get positive career guidance from teaching staffs
Getting positive career guidance from teaching staffs was found to have positive and significant predications regarding of Obsessive-Compulsive (β = 0.349,P< 0.05), Interpersonal sensitivity (β = 0.462,P= 0.001), Depression (β = 0.413,P< 0.01), Anxiety (β = 0.321,P< 0.05), Phobic anxiety (β = 0.307,P< 0.05) and Paranoid ideation (β = 0.275,P< 0.05), with reporting lower scores of these symptom dimensions.
● Get support and respect from family and friends Getting support and respect from family and friends had positive and significant predictions on Somatization (β = 0.312,P< 0.05), Anxiety (β = 0.307,P< 0.05) and Paranoid ideation (β = 0.502,P< 0.001).The students got support and respect from family and friends reported lower scores of these three symptom dimensions.
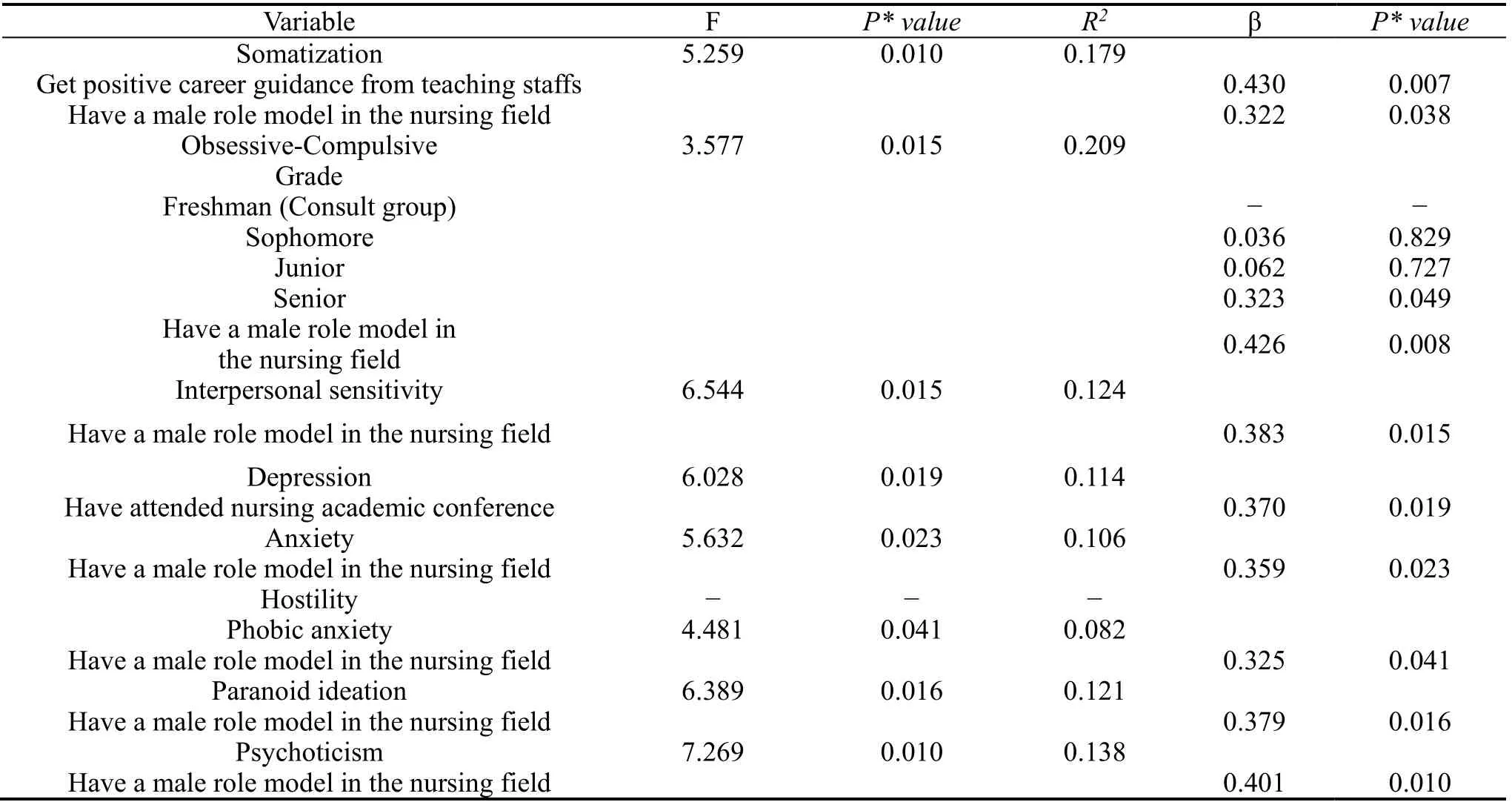
Table 4.Regression models to predict psychological symptom level in Chinese male nursing students
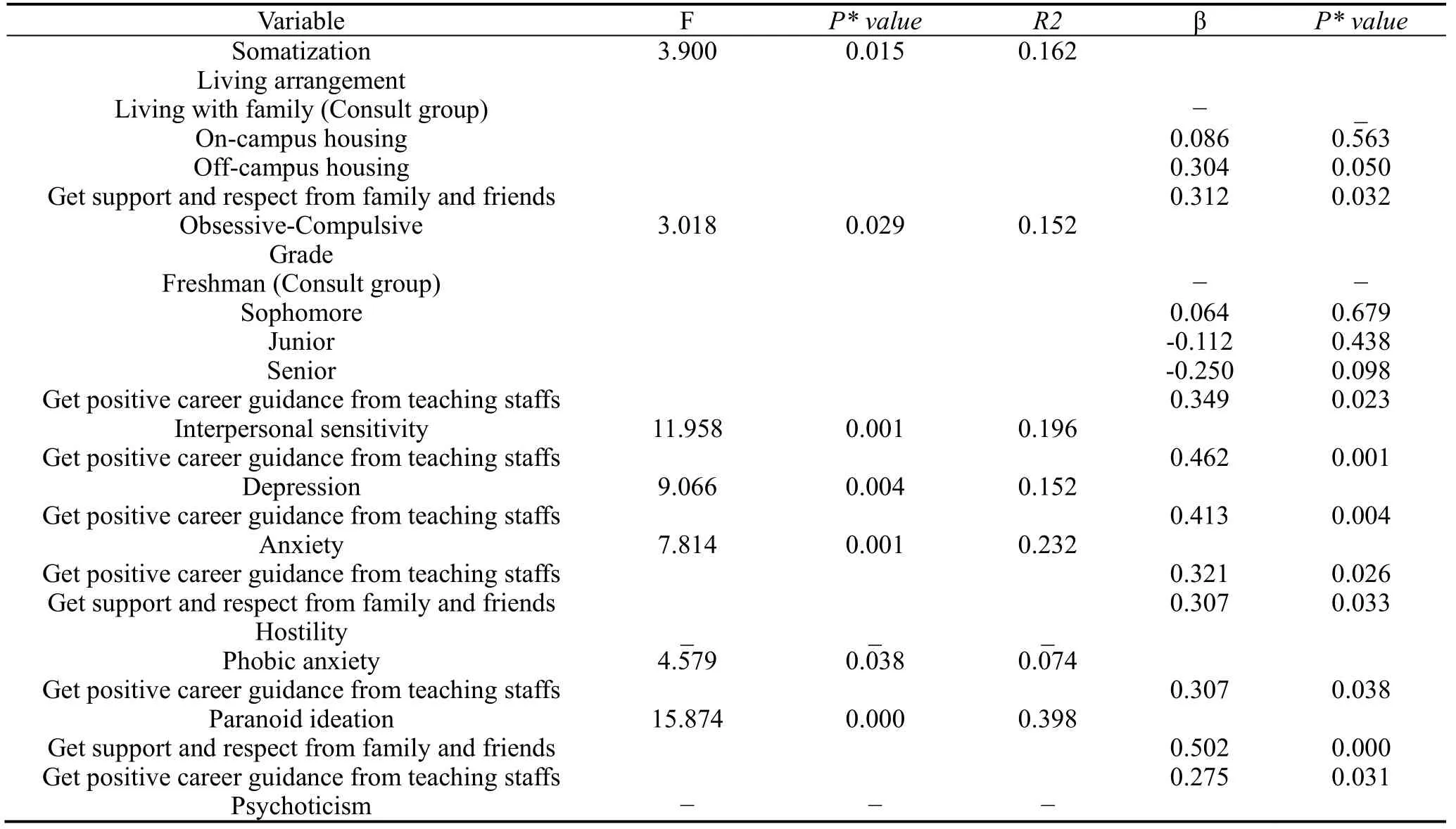
Table 5.Regression models to predict psychological symptom level in Korean male nursing students
Discussion
This cross-sectional study was conducted to compare the mental health symptom status and identify the predictors of the symptom dimensions of male nursing students in China and Korea.
For mental health symptom status, this study indicated that Chinese male nursing students have scored higher on the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R than the norms of community samples except the Interpersonal sensitivity.Previous studies have also provided evidences support for this result.Sun Haiya [31] pointed out that Chinese undergraduate male nursing students reported higher scores of SCL-90-R than the norms.Chinese male nursing students generally had psychological and emotional problems such as inferiority, depression and obsessive-compulsive [32], and 36.4% of male nursing students had problems in interpersonal communication [33].Another systematic review and Meta-analysis in 2018 also supported this result and showed that Chinese medical students scored significantly higher than the national norms on the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R [34].
Korean male nursing students reported lower scores on the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R compared with norms.However, this result is different from previous research, which indicated that Korean nursing students have experienced higher academic stress and poor psychological well-being [27,35].This may be related to the closer attention to Korean male nursing students and more support and guidance provided by the Korean nursing educators in recent years.
Compared with Korea, Chinese male nursing students scored significantly higher on the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R.This indicates that the overall mental health of Korean students is better than that of Chinese students, and this may be closely related to the differences in the nursing education system, nursing work environment and salary treatment in the two countries.There is also a noteworthy point that men are given higher expectations and responsibilities in the society in China.It is widely believed for Chinese people that nursing is not a man's job, and men should be more successful in their ‘careers’, obviously not nursing [17,21].Despite this, Korean male nursing students have better prospects for their career development.
In China, nursing was not the first-choice major for male students,36 and lots of Chinese male nursing students were adjusted their major into nursing by the university admission office according to their NCEE score rank or accepted their parental advice to choose nursing major, even if they never had nursing in mind.However, Korean researchers reported that about half of male nursing students choosing nursing as their first-choice major influenced by themselves [37].Different choices lead to different attitudes, and this may also lead Korean male nursing students to have better satisfaction with their major, which leads them better mental health.Compared to China, Korea offers various nursing courses more focused on specific nursing [26], and Chinese nursing courses are more likely similar to those taught in medicine [38].Differences in the education system lead to differences in students’ professional cognition.Chinese male nursing students don’t have a high awareness of the nursing profession [39].They don’t understand the value of nursing and what can they do in nursing field, so they always experience confused, anxious and depressed.Another reason may be due to differences in the working environment.Due to the large population of China and the serious shortage of nurses and patients, each nurse has to work overtime every day [40], and they have to work normally on statutory holidays.Korea’s working hours will be relatively better than China’s, and there will be more vacations for Korean nurses.Meanwhile, the relationship between nurses and patients is nervous.Doctors and nurses are often attacked by patients and injured or even killed.These have a great negative impact on Chinese nursing students.In addition, remuneration is also an important factor affecting the mental health of male nursing students.According to the Economist, a report showed that “a Big Mac costs 4,500 Won in South Korea and 21.00 Yuan in China.The implied exchange rate is 214.29.The difference between this and the actual exchange rate (171.48) suggests the South Korean Won is 25% overvalued [41]”.We used the Big Mac index to measure the monthly per capita income of nurses in China and South Korea.The result showed that Chinese nurses monthly earned 4,863 Yuan and the income of Korean nurses was 12,611 Yuan per month.It suggested South Korean nurses earn more than twice as much as Chinese nurses.
Some new suggestions were found in this study about the predictors of the psychological symptom dimensions of Chinese and Korean male nursing students.Having a male role model in the nursing field is an important predictor of the psychological symptom dimensions of Chinese male nursing students.Previous studies in the field of male nursing students have also reported that a lot of participants complained for lack of male role models in the nursing field.Here are the original texts of some reports “Almost all the nursing school lectures and clinical faculty members are female.I feel lack professional idols [17]”, “Having a male role model in the nursing field that I could have talked to run these things by would have been nice [16]”.Lu R [42] also suggested that the real deeds and growth experiences of excellent male nurses can provide a clear reference system for male nursing students and promote the emotional identity of male nursing students to nursing professionals.Furthermore, getting positive career guidance from teaching staffs can also predict the symptom dimensions of Somatization.Having a male role model in the nursing field is a predictor of the symptom dimensions of Depression, and this may be due to attending academic conferences that expose them to the industry's cutting-edge information, which leads them to find their own interests and hope for nursing.
For Korean male nursing students, the main predictor of the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R is getting positive career guidance from teaching staffs, followed by getting support and respect from family and friends.Professors can have substantial effects on happiness of students [43].In a sense, the professor is the guide of the student's career, and may also be the object of the most trust and worship of the student.Therefore, the attitudes and guidance of teaching staffs to students are very important to the professional attitude and mental health of students in the process of completing their degree.However, some studies have shown that male nursing students receive less help from professors in learning and career planning than female nurses [16].A participant in Wang's research reported that a professor said to him “Doing the nursing job as a man will give you no good future and value [21]”.This discriminatory language not only reduces the students' self-confidence in the field of nursing, but also cause trauma to the students' psychology.On the other hand, several suggestions can be made to support the important of the support and respect from family and friends.When people make a decision or do something, they often refer to the opinions and feelings of people from close relationships.Powers K [16] suggested that the reaction male nursing students received from their friends and family had a great impact for them when they decided to pursue a nursing degree.Jo KH [44] also indicated that nursing students who were supported and recognized by family and friends reported more happiness.
Limitations
Although the sample size of this study was sufficient and the results were significant, due to the funding and time constraints, the data collected in this study was only from one university in each country.It is hoped that future research will be able to collect data in universities in various regions of China and Korea to increase the diversity of data.Due to location constraints, the research team was unable to conduct a paper survey in China, different data collection methods were used in two countries.It may affect participants to complete the questionnaire accurately.The data of norms was investigated in 1986 and 1983.It is old, but there is no data of norms with higher reliability and recognition.
Conclusion
This study reports the scores and the predictors of the symptom dimensions of SCL-90-R among the male nursing students in China and Korea.Chinese male nursing students need to improve their mental health level more urgently than Korean male nursing students.To promote the mental health for male nursing students, Chinese educators need to pay more attention to role model education and spread more excellent male nurse models for male nursing students, and male nurses should also go to nursing campus to share their experiences of working as male nurses.; for Korean male nursing students, educators need to support them with enthusiastically and provide more positive guidance for their study and career planning; the news media should actively publicize the image of male nurses to increase recognition of male nurses in the whole society, and this will not only inspire male nursing students, but also lead their family and friends to support and respect their choices of being nurses.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- The application progress of auricular therapy in diabetes
- Neonatal Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome: A Case Report
- Effects of Modern Online and Traditional Offline Exercise Programs on the Frailty, Physical function, Emotional, and Social Support on Chinese Community-Dwelling Frail Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trail
- Current Situation Analysis of Nursing Students' Professional Attitudes and Employment Intentions during COVID-19 Pandemic

