Effects of Modern Online and Traditional Offline Exercise Programs on the Frailty, Physical function, Emotional, and Social Support on Chinese Community-Dwelling Frail Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trail
Yan Zhu,Hui Xie,Li Zhang*,Xiao-Juan Su,Hong-Yu Wang
1School of Nursing, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu, Anhui, China; 2School of Sports and Art, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu,Anhui,China
Abstract Objective: The aim of this study were to explore the effects of 12-week modern online and traditional offline exercise programs on physical function, frailty status, emotional, and social support of pre-frail older adults.Methods: The traditional offline exercise programs were offered at a local community center, and the modern online programs were done partly at home and partly modern online.Sixty older adults were randomly allocated into the traditional offline group (n =30;66.96± 4.43 years)and the modern online+traditional offline groups(n=30;65.85±5.61 years).The exercise programs for both groups included strength,balance,and gait exercises and were done twice/week for 60 min/session.We recorded the study parameters (demographic features, frailty, and physical function) at the baseline as well as at the end of the exercise program. Results: Maximum subjects observed a reversal of the pre-frail status with an increase in physical function and a decrease in fat mass in both groups;however,the CB group showed a relatively significant improvement in physical function.Conclusion:The modern online+ traditional offline exercise programs were not only effective in improving the physical condition,but also enhanced psychological status, social support,and adherence.Thus, based on these results,modern online+traditional offline exercise programs were preferable for improving the overall health of pre-frail older adults.
Keywords:Frailty,Home-based exercise,Older adults,Supervised exercise
Introduction
The global aging population has had a significant impact on the alterations in the societal demographic outline.This phenomenon has been observed in China as well, where the National Bureau of Statistics revealed that in 2018, the population of older adults(60 y and 65 y) reached 249 million (17.9%) and 167 million (11.9%), respectively [1].There exists a direct correlation between aging and the increase in the incidence of age-linked chronic diseases, which translates into increased healthcare costs that impose a substantial financial burden on the family on an individual level and the society as a whole.
Studies have shown a steady increase in frailty with age, causing both functional and physical decline[2].Although there is no specific definition of frailty,the commonly observed symptoms include exhaustion,weight loss, decreased activity, sarcopenia, and slow gait speed [3].The functional domains that characterize frailty involve balance, mobility, and muscle strength.Physical and psychological health,social factors, comorbidities, lifestyle, environmental conditions, and nutrition are some of the risk factors for frailty in older adults [4,5].Thus, frail older adults are susceptible to physical disability,falls, difficulty in performing activities of daily living (ADL)independently,increased healthcare costs,hospitalization,and mortality.
Some of the essential interventions to improve the levels of independence and physical function in older adults include exercise and physical activity [6,7,8].A recent study on frail institutionalized nonagenarians showed that a 12-week resistance exercise program enhanced strength, muscle output, the cross-sectional area of the muscle, and fat infiltration, along with improved functional activity and dual-task performance [9].Thus, these studies recommended muscle power training for frail older adults to improve their overall physical health and prevent disability[10].
Exercise programs can be done at a local center(such as supervised group exercise at a senior center)or at home.Home-based (HB) exercise programs are supervised either indirectly by phone calls or directly through home visits [11].Center-based (CB) exercise programs have been shown to increase muscle strengthen [12], functional capacity [13], and reverse frailty [14,15,16].Unlike HB programs, CB programs involve cognitive challenges, given the need to plan transportation, travel time, and social interaction with other participants [17,18].However, the difficulty of movement,need for transportation,and dependency on family members to travel to the center may compromise participation [19,20].Although HB exercise programs with indirect supervision may reduce these participation barriers, they might not be as effective as supervised CB programs.
With the rapid development of the social economy in China, most people are focusing on improving their health.Sports health management has emerged as the key to build a good lifestyle.The emergence of the information platform provides good technical support for health management.First, the sports and health management model was established,followed by the development of the sports management process, and the mobile health hut was built again.Finally, the exercise prescription, tracking,and feedback management were implemented to form a one-stop sports and health management platform.Therefore,this study explored the effects of a 12-week modern online exercise at-home program and an traditional offline multicomponent exercise program at the center on the frail older subjects to improve their frailty status, physical function, body composition, as well as psychological and social status.
Methods
Study design and participants
We performed a randomized, single-center,open-label,controlled trial in pre-frail older adults in China.The community screening model was adopted to identify potential subjects.The eligibility criteria included: (1)60 y, (2) pre-frail (fulfilled items 1-4 of the 15-item simple Tilburg frailty indicator, TFI), (3)community-dwelling, (4) the ability to understand,execute simple instructions, and walk independently,and(5)the ability to use a smartphone.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) severe cognitive impairment or mental illness, (2) severe skeletal and muscular disorders and serious diseases of the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys, and (3) to be hospitalized in the next six months or unable to complete the training for other reasons.
The Ethics Committee of the Bengbu Medical College (reference number[2018]no.45)approved the experimental procedures involved in this study.The survey was completed anonymously, and the participation was completely voluntary.The potential subjects were personally and comprehensively informed regarding the study aims, data collection and processing,and its further use.
Randomization
Each study subject provided written informed consent.Post-baseline assessment, the subjects were randomly allocated to the control or treatment group based on computer-generated numbers.We achieved an equal sample size for each treatment group through block randomization.An independent investigator managed the allocation schedule.
Development of sports and health management platform
It collects the health test and physical test data simultaneously, and integrates all types of peripherals,opening up the channel of communication of information.The data is automatically synchronized,and the collected information is automatically evaluated and formulated for display in mobile phones,computers,cloud servers,web pages,and browsers.(1)Steps: Collection of health data; Risk assessment of health and ability to exercise; Health and exercise interventions.(2)Process:Collect health data,evaluate sports ability tests,establish sports health archives,and prescribe exercise and health intervention.
Intervention
Based on the results of physical examination and exercise,advanced information management technology was used to establish a scientific,professional,and perfect individual exercise and health archives and exercise intervention methods for individuals to be achieved in a 12-week exercise and health management program.
My mommy says that you lost your daughter and you re very, very sad with a broken heart. Susie held her hand out shyly. In it was a Band-Aid. This is for your broken heart. Mrs. Smith gasped5, choking back her tears. She knelt down and hugged Susie. Through her tears she said, Thank you, darling girl, this will help a lot.
Traditional offline intervention
An experienced physical trainer conducted the multicomponent exercise program to improve balance,strength, and endurance.The program was 12-week long and was designed by referencing specific literature reports[21-25], which involved the expertise of the respective authors as well as their field experiences (Table 1).The intervention was based on the American College of Sport Medicine’s (ACSM)recommended exercise and physical activity guidelines for older adults[26].Training attendance was recorded for each session.The supervised sessions were conducted twice/week for 45 min to improve balance and strength, and a minimum interval of 48 h was maintained between two training sessions.
Each session included a 5-min brief warm-up(range-of-motion exercises for the wrists, neck,shoulders, knees, hips, and ankles).The 25-min strength training involved upper and lower body exercises using external weights based on individual functional ability to estimate 1-RM (repetition maximum) at the baseline as well as at the end of every month, to assure a suitable training stimulus.During the first 4 weeks, light loads (20-30% 1-RM)were used to perform the exercises for appropriate adaption to resistance exercise,and thereafter the loads,if tolerated, were increased to 80% 1-RM.Balance training (10-30 min) involved decreased support(one-legged stand, both feet together, and standing on tips and heels), and the difficulty was increased gradually.The gradual increase in the complexity of movements was meant to challenge the balance of the participants as they progressed.Variable endurance exercises were performed throughout the study: during the second month, treadmill walking, and step-ups were introduced, and the training time was increased gradually.The exercise session was concluded with a 5-min cooling down breathing,stretching,and relaxing exercises.
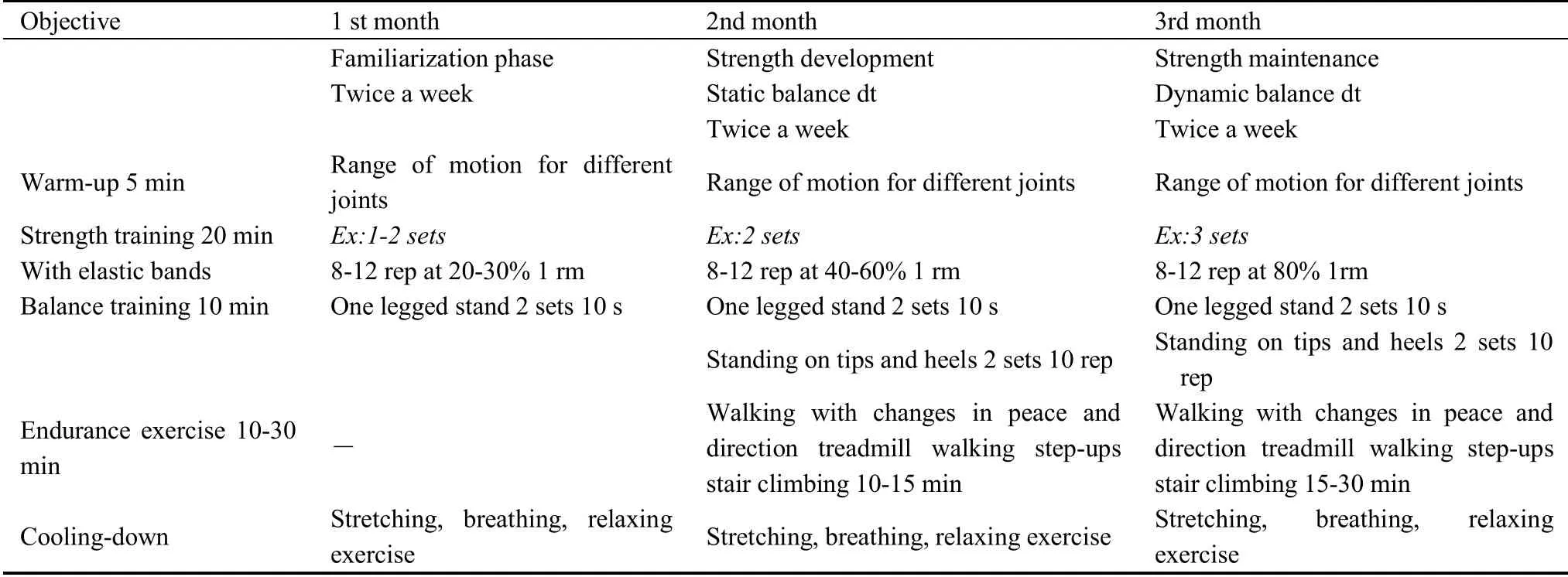
Table 1:Multicomponent exercise program for the 12 weeks
Modern online intervention
The service model of the sports and health platform was as follows: remote monitoring (mobile smart health station measurement) → automatic uploading(real-time evaluation, mobile phone evaluation report display) →sports and health education →establishment of sports and health archives → phase adjustment cycle.The system operation included detection, evaluation, prescribing the intervention,monitoring,and closed-loop movement management.The following four modules were involved in establishing and using an modern online platform: (1)Health knowledge module: this module would provide relevant knowledge, including text, voice, and video;(2) Health assessment module: this module would provide health reports, sports, physical, and psychological scales.Relevant scores could be obtained on filling appropriate data into the scales; (3)
Contact us module: the subjects could directly contact the person through this module; The subjects could directly go to the medical examination center with one-click navigation; the micro official website would introduce to the community platform; Learning points:Score points easily by reading and answering questionnaires; Gift exchange: the subjects could get the corresponding gift based on their points;(4) Group WeChat interaction: this module would include reminders,supervision and answer questions.
Measurements
Trained research assistants, who were blinded to the subject allocation scheme and were independent of the research investigators (exercise assistant and coach),recorded the study outcomes at baseline and at the end of week 12.Both objective and subjective criteria were considered while determining frailty.
Subjective measuresFrailty was measured using the FRAIL scale (0-5), which involved the following five components: fatigue, resistance, ambulation, illnesses,and loss of weight (one point for each component)[2].A 0, 1-2, 3-5 FRAIL score indicated robust, pre-frail,and frail status, respectively.The FRAIL scale can predict mortality and disability and has been tested in Chinese, African American patients, and other Asian populations.There are three components involved in the Tilburg Frailty Indicator(0-15 points)[2], which is used to assess the frailty in the older adults: physical frailty, psychological frailty, and social frailty.A score between 1-4 indicates pre-frail status, and 5 indicates frail status.The higher the score,the more severe is the frailty.
Objective measuresThe objective outcomes measured physical functioning using the “Short Physical Performance Battery” (SPPB), Timed Up & Go Test(TUG), Hand-grip strength, 1-legged balance tests,chair stands, and gait speed.The equipment was provided by Hefei Intelligent Machinery (IIM2010A),Chinese.SPPB is tested on a 12-point scale and includes balance test, gait speed test, and chair sitting test.A score of 0-6, 7-9, and 10-12 indicates poor,medium, and good physical ability, respectively [27].TUG test measures sensitivity and balance [28].The subjects were required to stand up from their seats as fast as possible, on hearing the signal, followed by walking towards a line at 3 meters and return to the original seat.The time taken to complete all the actions was recorded.A digital grip dynamometer was used to measure the hand-grip strength.The subjects stood upright with fully extended elbows and their feet forward-facing and shoulder-width apart.The higher of the two readings that were recorded from both arms was used for further analysis.Grip strength of < 26 kg for men and<18 kg for women was considered as low muscle strength [29].Standing on one foot with eyes closed is a simple test of balance.It is through the measurement of the human body in the absence of any visual reference,only rely on the brain vestibular organ balance receptors and the coordinated movement of muscles, to maintain the body center of gravity on the support surface of 1-legged balance time, to reflect the strength of balance ability.The shorter the standing time, the worse the balance and physical fitness.Muscle endurance in the lower extremities was examined through the chair stands.The subjects were asked to rise from a chair with their arms across their chest as rapidly as possible, five times, and the total time taken was recorded and used for further analysis.There exists no definite cut-off point for the chair stands.Various studies have used time values ranging from 10 to 15 seconds.Here, if ≥13 seconds was taken to complete five stands, then, it indicated low muscle endurance.A flat walkway of 6 meters was used to measure gait speed.The subjects were required to walk at twice their usual pace, and we used an average of two usual walking pace trials for further analysis.Low gait speed was defined as<0.8 m/s[30].Lung capacity is the simplest indicator of pulmonary ventilation function.It refers to the maximum amount of air a person can breathe out with all his strength after maximum deep inhalation.It is the maximum projection of the body's ability to perform lung ventilation.Currently, vital capacity has become the main index of medical examination of human aging.
Body compositionBody composition was measured using the principle of Bioelectrical impedance analysis.Non-invasive measurements of muscle, fat, and minerals were done at various stages to predict the electrical conductivity of the human body[31].
Psychological and social supportThe psycho-affective assessment was conducted using the Anxiety Self-rating Scale (SAS) and Self-rating depression scale (SD) and the UCLA Loneliness Scale[32].Social interaction, social network, instrumental support, and subjective support was examined using the Duke Social Support Index(DSSI)[33].
Covariates,adherence, and adverse eventsA standard questionnaire was used to record the demographic data(sex, age, marital status, employment, disposable income education level, and living arrangement) and lifestyle data (smoking habits, physical activity, and alcohol intake).Also, standardized methods were used to record anthropometric measurements.Body mass index (BMI) was calculated using the following formula: body weight (kg)/(height (m)2).We also recorded the level of adherence and any adverse events that occurred during the study.
Data Analysis
An independent researcher performed all data analyses using SPSS v25.0 (IBM Corp., Chicago, USA).The appropriateness of parametric analysis was evaluated using the Shapiro-Wilk test.Data normalization was assessed graphically.Here, categorical variables were expressed through descriptive data, including frequencies and continuous variables through mean standard deviation (SD).The chi-squared (2) test and the Kruskal-Wallis test was used for analyzing baseline differences in nominal data and ordinal data,respectively.The differences between the groups were compared based on the change value, which was calculated post-pre (Δ) with 95% confidence intervals(95% CI).The Wilcoxon and Mann-Whitney U tests were used to analyze the non-parametric data,whereas the Student’st-test was used for parametric data.A limit of significance of 5% (P< 0.05) was set for all statistical analyses.
Results
Of the 80 study volunteers,60 were randomly assigned to the control group (CG) and the intervention group(IG).Of these, 54 completed the 12-week exercise treatment program.Twenty frail older adults were excluded either due to noneligibility or their unwillingness to participate.Three of the 30 CG subjects discontinued the study due to their inability to participate in the intervention.Data from the remaining 27 CG subjects were included in the traditional offline analysis.Thus,the total number of subjects included in the final analysis were 27 in the IG(18 female,9 male)and 27 in the CG (17 female, 10 male) (Figure 1).There was a minimum of 90%treatment compliance in the IG.We observed no major health-related issues or serious adverse events due to the testing or training sessions.
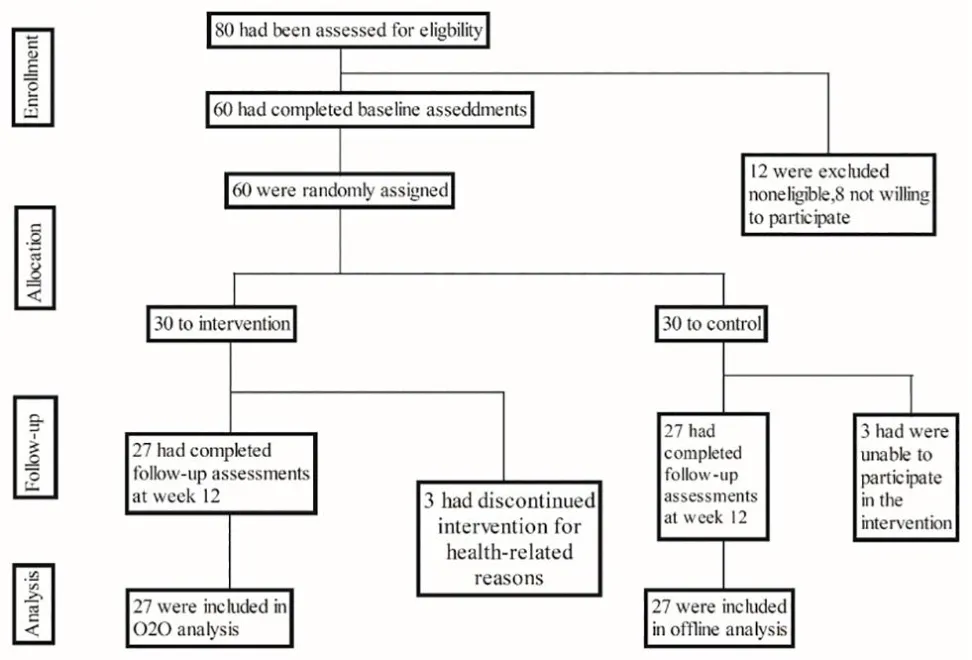
Figure 1.Study flow diagram
Table 2 displays the baseline characteristics of the study subjects.Except for age, no significant difference was observed between the two groups.The mean(SD)age of the IG subjects was 66.96(4.4)years,with 33.3% males, and a BMI of 16(59.3) kg/m2.Of these, 41.2% had a surgical history, and 78.9% had received adjuvant chemotherapy.The mean (SD) age of CG subjects was 65.9(5.6)years,with 37.0%males,and a BMI of 18(66.7)kg/m2.

Table 2.Baseline characteristics of the participants
Table 3 shows the results of physical function and body composition outcomes in both groups along with the differences between these groups after the 12-week program (Figure 2,3).A significant increase in the functional capacity tests was observed in the IG:SPPB total score (P< 0.001), Gait speed (P<0.001), chair stand test(P<0.001),one-legged balance(P<0.001),and TUG (P= 0.037).Additionally, a significant reduction in the FRAIL score(P<0.001)and fat mass(P< 0.001) was observed for the IG.Similarly, CG showed a significant improvement in functional capacity:SPPB total score(P<0.001),Gait speed(P<0.001),chair stand test(P<0.001),one-legged balance(P< 0.001), and TUG (P= 0.037) with a significant decrease in the FRAIL score (P< 0.001) and the fat mass(P<0.001).There was a significant difference in functional capacity between these two groups: SPPB total score (P< 0.001), chair stand test (P< 0.001),one-legged balance (P< 0.001), and TUG (P= 0.003)as well as the FRAIL score (P< 0.001).There was no significant difference in TFI, lung capacity, BMI, left arm muscle, right arm muscle, left leg muscle, and right leg muscle(P>0.05)for both CG and IG.
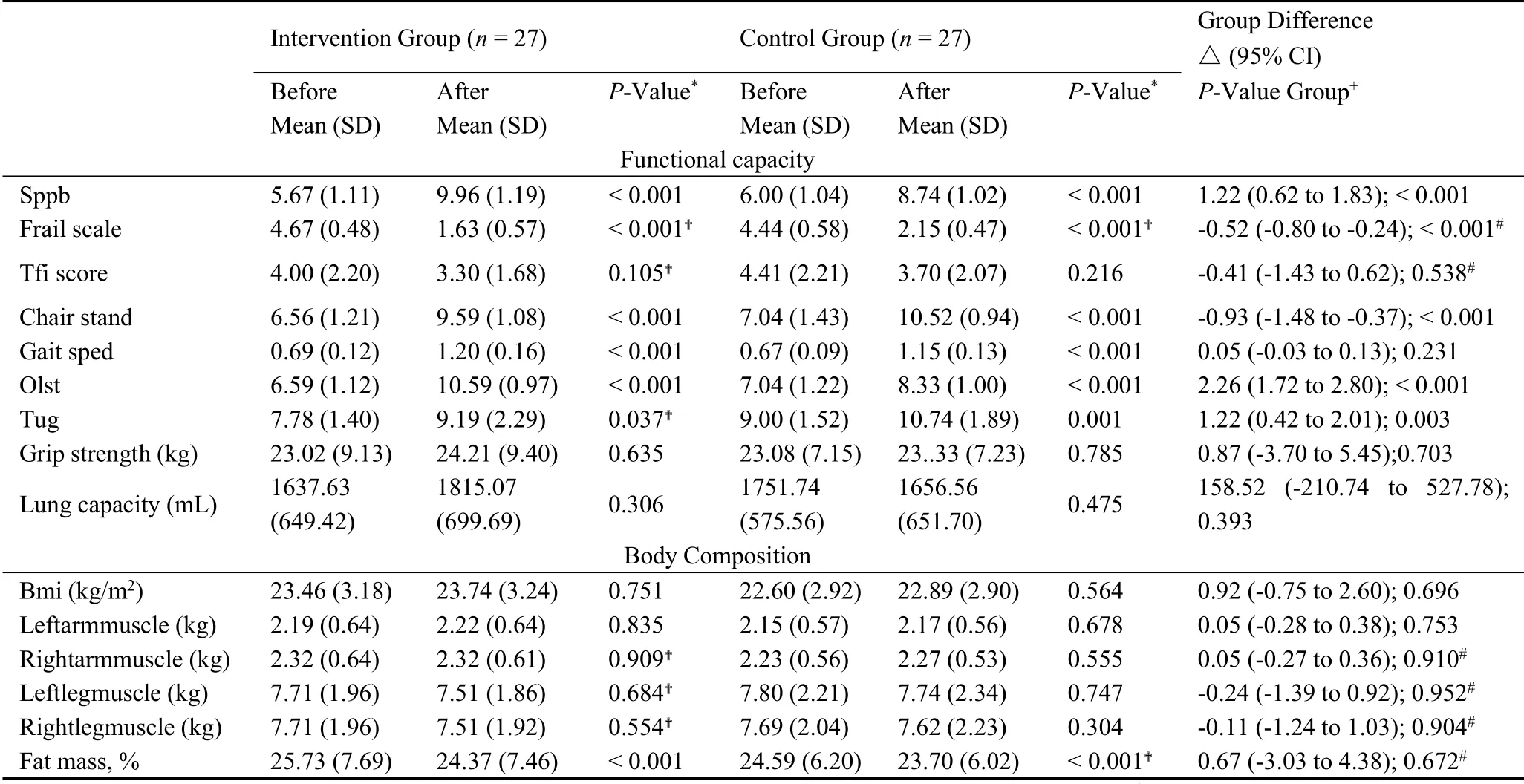
Table 3.Results of physical function,Body composition outcomes by group
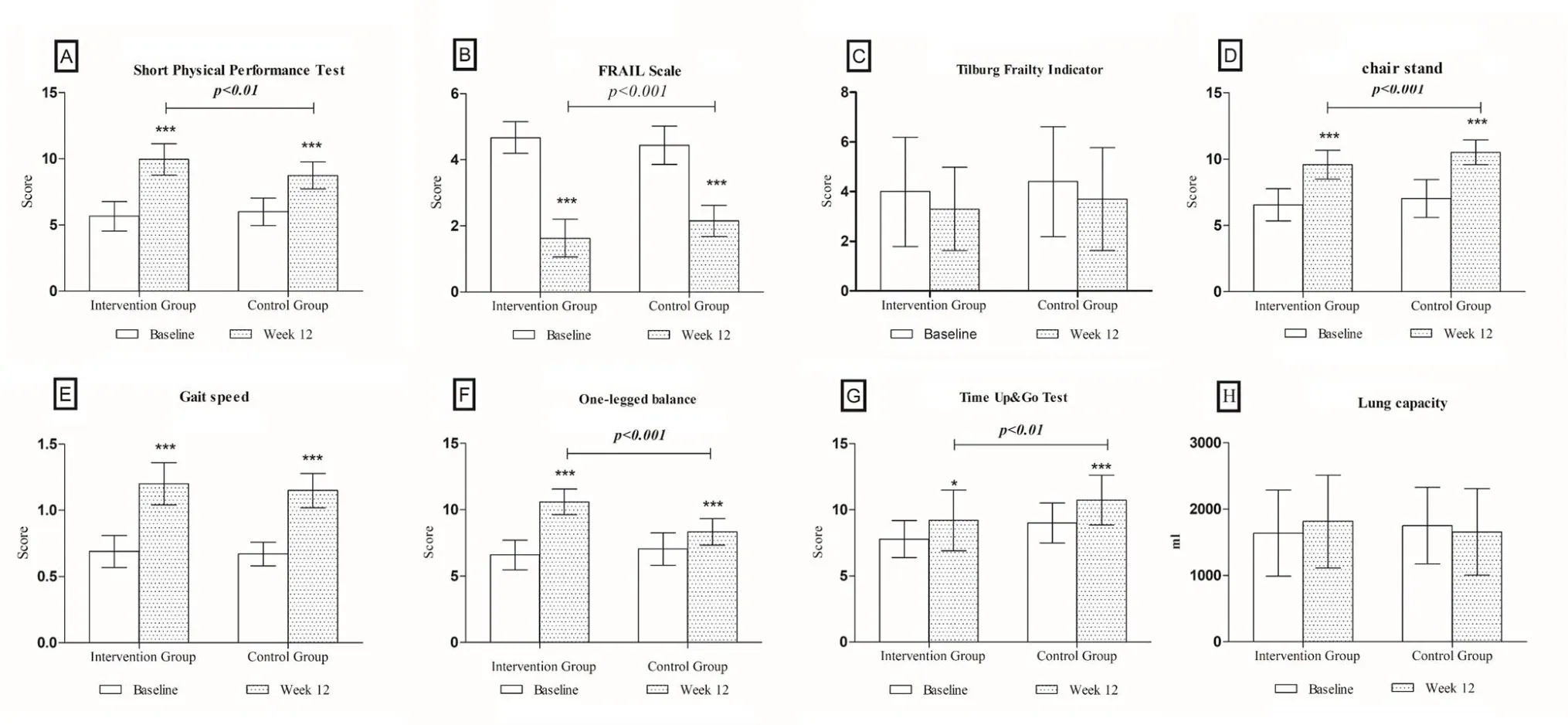
Figure 2.Changes in frailty measures from baseline to week 12.Changes in (A) Short Physical Performance Test(B)the FRAIL total score(C)the Tilburg Frailty Indicator(D)the chair stand(E)the Gait speed(F)the One-legged balance(G)the Time Up&Go Test(H)the Lung capacity,of frail older adults from baseline to week 12.*P<0.05;**P<0.01; ***P<0.001.

Figure 3.Changes in body composition from baseline to week 12.Changes in (A) BMI (B) left arm muscle (C)right arm muscle (D) left leg muscle (E) right leg muscle (F) fat mass percentage, from baseline to week 12.*P <0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.BMI,Body Mass Index.
Table 4 demonstrates the outcomes of emotional and social support for both groups.We observed a significant difference in DSSI in the IG (P< 0.001),which created a significant difference between these two groups (P< 0.001).Additionally, there was a significant difference in UCLE loneliness Scale between these two groups (P< 0.001).We did not observe any significant change in SAS and SD (P>0.05)in both IG and CG(Figure 4).
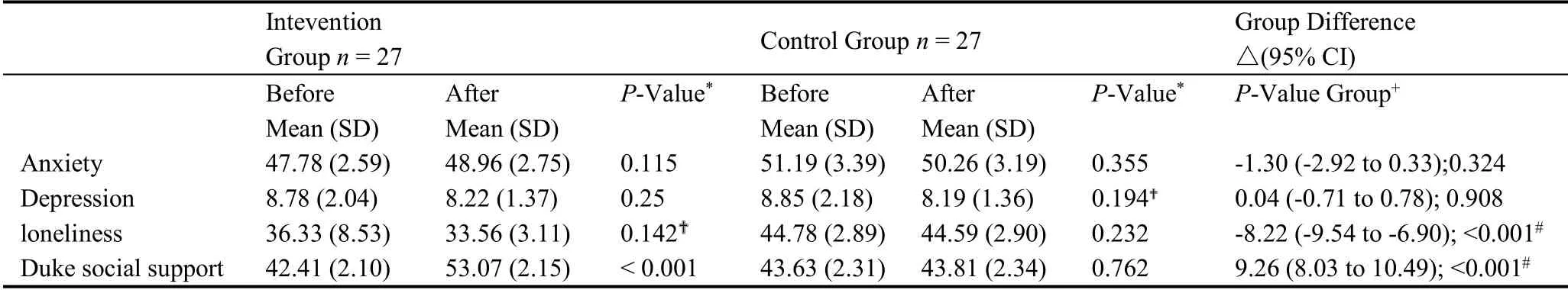
Table 4.Results of emotion and social support outcomes by group
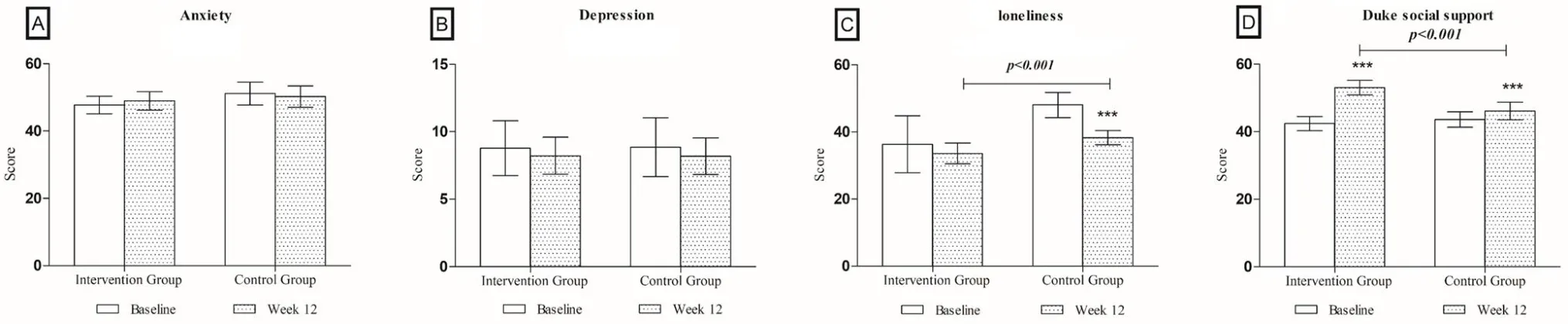
Figure 4.Changes in the emotional and social support from baseline to week 12.Changes in the (A) anxiety self-rating scale (B) self-rating depression scale (C) the UCLA loneliness scale (D) the Duke social support index,from baseline to week 12.*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
Discussion
This study showed that a sports health care scheme based on the combination of the modern online and traditional offline platform was effective in improving the physical function,psychological and social support,as well as the frailty status and exercise adherence in community-dwelling older adults.
We found that the modern online + traditional offline supervised exercise programs were more effective than the conventional center-based interventions for the older adults.These results were consistent with the results of a recent study that showed that following a physical activity program could result in a reduction in the frailty.Multicomponent exercise programs are known to improve functional activity scores [34,35].Overall,both traditional multicomponent training (12-week or longer,performed twice/week for 30 to 45 minutes per session) [36] and a combination of modern online and traditional offline training were capable of improving the frailty status; however, the latter showed a relatively significant improvement.
Our study results demonstrated a substantial improvement in physical function.The IG subjects also showed significantly improved values of the functional parameters after the 3-month treatment period.There was a significant enhancement in the SPPB, TUG, chair stand test, gait speed, and one-legged balance test scores in both the IG and the CG subjects.Thus, the Multicomponent exercise program was also effective in improving the SPPB,TUG, Chair stand test, and in lowering the frailty.Furthermore, it has been reported that one in three people>65 y falls at least once a year worldwide[37].Studies have confirmed that Tai Chi [38], group exercise [39], balance training and strength training[34] are effective in reducing the risk of falls in the older adults.This study, like previous studies, found that the balance and strength of the frail older adults were significantly improved after exercise.More importantly,as the subjects in this study were the frail older adults, they were characterized by poor stability and high risk of falling [40,41].In this study, we observed a significant improvement in their balance after 12 weeks of modern online and traditional offline intervention.Therefore, the design of a sports rehabilitation program for frail older adults should be based on balance and strength training, supplemented by speed and agility, which is consistent with their actual physical status.
Additionally, our exercise program caused a significant reduction in fat mass, consistent with the results of a previous study that demonstrated that 12-week of progressive elastic band resistance exercises could reduce fat mass in elderly women[42].A recent study has shown a link between frailty (not age)and oxidative stress[43].Consequently,we found that exercise can lower protein oxidation.Moreover,several observational studies have shown an association between obesity/high waist circumference and frailty [44,45].Thus, frail older adults might benefit from weight loss and exercise interventions that have a positive impact on body composition.
This intervention resulted in a decrease in the loneliness index and an increase in the DSSI.Previous studies on frail individuals have shown that exercise has the potential to improve an individual’s frame of mind [46], cognitive function [47], and the quality of life.Here, we also observed an improved psychological state post-intervention.Furthermore, a significant improvement in social support occurred through joint modern online intervention, compared with a single multicomponent exercise intervention in the community, which could be attributed to the sharing, communication, and feedback of the modern online WeChat groups.This intervention targeted social networking because there exists a link between frailty and poor social functioning as well as with an increase in loneliness over time [48].Therefore, it is necessary to consider the social vulnerability of physically frail older adults while designing their care provisions.
The main strength of this study is to deal with public health promotion issues through the construction of networked organization coordination,relying on mobile phones, computers, cloud services and other technologies, and using the "one-to-many"fitness guidance mode, to provide scientific fitness guidance services for the frail people.Moreover, the overall scheme of the system implementation is to adopt wireless communication technology,establish an“Modern online + Traditional offline digital system”,and implement closed-loop exercise management of detection, evaluation, prescription, monitoring, and detection.
This study had several limitations.First, the research results were mainly collected from Chinese older adults who are socioeconomically and educationally disadvantaged. The smartphone ownership and utilization rates are low, and these results may not be extended to other groups.Second,due to the limited time and objective conditions,only a small sample of empirical research was conducted in this study.Additionally, the sample size could be further expanded to verify the clinical effect to understand deficiencies and obstacles in the implementation process of the program.Finally, it is necessary to further verify the long-term effects of modern online and traditional offline exercise intervention programs on the frail older adults in the community.
Thus, a complete platform system, which meets the criteria of aging and of the information age, is the next step in the development of elderly care provisions.The frail older adults in the community in this study had a high degree of adherence to the modern online and traditional offline joint exercise mode, which significantly improved their frailty status, physical function, body composition, as well as psychological and social support.
Conclusions
Thus, this sports health care program, combining modern online and traditional offline exercise modes,for the frail older adults was effective in improving exercise self-efficacy as well as enhanced physical condition, psychological, and social support.Also, the development of the modern online sports health information management model could result in an optimized sports rehabilitation framework by designing, implementing, and supervising the rehabilitation exercise program for the community-dwelling frail older adults.
- Nursing Communications的其它文章
- The application progress of auricular therapy in diabetes
- Neonatal Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome: A Case Report
- Comparison of Status of Mental Health of Male Nursing Students between China and Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Current Situation Analysis of Nursing Students' Professional Attitudes and Employment Intentions during COVID-19 Pandemic

