Gastric cancer:An epigenetic view
INTRODUCTION
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common malignant tumors of the digestive tract and ranks as the fifth leading cause of morbidity and second leading cause of mortality worldwide,posing a serious threat to all human beings[1].Residents in South and East of Asia including China,Japan and Korea are reported to have a higher risk of GC[2].Due to the unconspicuous symptoms in the early stage of GC,many patients are first diagnosed as advanced GC accompanied by tumor infiltration and metastasis.Despite of combined treatment of surgery,chemotherapy,radiotherapy,and sometimes targeted therapy and immunotherapy,GC still shows a poor prognosis with the 5-year overall survival less than 30%[3,4].Currently routine screening for GC is endoscopy and histological examination,which is costly,invasive and often painful to patients.Therefore,development of new or alternative methods for screening,diagnosis and treatment to GC is of great clinical significance.
Epigenetics has been illustrated to be associated with the diagnosis and treatment of GC patients.GC is highly complicated and heterogeneous in nature and often genetically divided into familial and sporadic disease.Familial GC,constituting about 10% of GC patients,has a close connection to genetic alterations[5].Sporadic GC (90%of GC) is largely related to() infection and evolves in a canonical model of chronic inflammation,atrophy,intestinal metaplasia,dysplasia and finally adenocarcinoma,which is characterized by typically epigenetic alterations but scarce genetic changes across over the stages[6].With rapid progress in epigenomics,precise molecular classification towards GC seems admirable in research and clinical medicine.In 2014,The Cancer Genome Atlas identified GC into four molecular subtypes including Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) associated,microsatellite instable (MSI),chromosomal instability (CIN),and genomically stable (GS)[7].Apparently,GS means the genome is stable in this type of GC[8].Among the four classes,MSI patients have the best overall prognosis and the lowest frequency of recurrence with high incidence of gene mutations and DNA methylation.Patients in EBV-subtype are associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection and have extremely high DNA methylation status.In the patients with CIN subtype,the largest proportion of GC,is more prone to chromosomal diseases such as chromosome rearrangement and aberration.Radically distinct clinical outcomes are presented in different subtypes.
4. Middle-sized Bear: As the three bears transformed into a nuclear family through various retellings, the middle-sized bear acquired feminine traits and became the mother/wife in the family.Return to place in story. #p#
In this review,we mainly explore GC from an epigenetic view and summarize key epigenetic alterations and related functions and mechanisms,with special attention to histone modifications and the translational findings which guide us towards better clinical utility.
HISTONE MODIFICATIONS
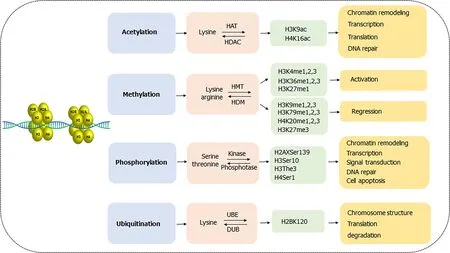
Nucleosome,as a major unit of chromatin,consists of wrapped DNA and a histone octamer formed by two copies of H2A,H2B,H3 and H4 proteins[9].Each histone contains an accessible amino terminal tail rich in lysine,arginine,serine and threonine residues,which is often modified post-translationally and the process is called posttranslational modifications (PTMs).Studies have shown that histone PTMs in GC mainly including acetylation,methylation,phosphorylation and ubiquitination are involved in various pathophysiological cellular functions such as carcinogenesis,inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (Figure 1)[10].In recent years,some new modifications,such as succinylation,sumoylation,butyrylation and crotonylation,have been discovered in the occurrence and progression of other gastrointestinal tumors,such as esophageal,colorectal,and hepatocarcinoma liver cancer[11-14],which provide new insights in functions and mechanisms and even therapeutic potential for cancer diagnosis and treatments.Notably,those new types of histone modifications remain a vacant field in GC and thereby it may be an innovative and interesting field to explore in the near future.
Histone acetylation
As the most common form of PTMs in GC,acetylation always occurs in N-terminal lysine residues of histone H3 and H4 and is associated with chromatin remodeling,regulation of transcription,translation and DNA repair.The acetylation of histones catalyzed by histone acetylase (HATs) transfers acetyl moieties from coenzyme A to lysine residues,opens the chromatin structure and makes it accessible to transcriptional factors,thus activating gene transcription.Instead,the histone deacetylase(HDACs) removes the acetyl groups from histone and results in repression of transcription.HATs consist of three families including GCN5,MYST and p300/CBP,while HDACs contain four classes including type I (HDAC 1,2,3,8),type II (HDAC 4,7,9,10),type III (SIRT 1-7) and type IV (HDAC 11)[15,16].The reversible acetylation and deacetylation processes mainly facilitate GC progression by activating oncogene expression and silencing tumor suppressor gene expression.
Histone phosphorylation frequently happens in H3 and H4 with a dual role in cancer progression[32,33].For instance,phosphorylated histone H3 at position of serine10 (H3S10) by MSK1 promoted cell proliferation during gastric tumorigenesisthe activation of downstream transcriptional factor NFATc2-related inflammatory pathway[37].H3S10 phosphorylation also played a vital prognostic role in defining negative resection margins in GC due to its lower expression in the surgical resection margins[38].A cohort of 122 GC patients further indicated phosphorylated histone H3 overexpression could be an independent prognostic factor[39].Moreover,repression of Aurora B-mediated H1.4 phosphorylation at Ser27,caused by Ras-ERK1/2 signaling,evidently participated in the progression of GC[40].
Histone methylation
Non-coding RNAs consist of microRNAs (miRNAs),long non coding RNAs(lncRNAs),circular RNAs (circRNAs),small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs),small interfering RNAs (siRNAs),.[63].Since the first two non-coding RNA lineage defective 4 (lin-4)[64] and lethal 7 (let-7)[65] were identified in 1993 and 2000,researchers realized that in addition to protein,some RNAs lacking of protein-coding regions,which are called non-coding RNAs,were still conserved functional molecules and required for many biological processes.Among non-coding RNAs,miRNAs,lncRNAs and circRNAs were found to have plenty of functions in GC (Figure 3),including cell proliferation,cell cycle arrest,apoptosis,migration,invasion and chemoor radio-sensitivity[66,67].
53.Miss Charlotte:The stepsisters are rarely named in any Cinderella tale. Perrault s use of a name comes from his literary embellishment of the tale and was a personal choice. The name he uses in the original French is Javotte.Return to place in story.
Specifically,repression of HDMs KDM5A and DPY300 subunits upregulated H3K4me level,inhibiting GC cell proliferation[27].However,overexpression of HDMs LSD1 declined methylation of H3K4 in p21 promoter and repressed the transcription of p21,resulting in progression of GC[28].An assay of familial GC patients identified INSR,FBXO24 and DOT1L as new susceptibility genes in diffuse gastric carcinoma,in which DOT1L was a histone methyltransferase involved in the mono,di and trimethylation of H3K79,suggesting the contributing role of H3K79 in gastric carcinogenesis[29].Methylation of H3K27 is well-investigated in GC.A paired-study of 117 GC patients showed that the level of H3K27me3 in GC and normal tissue was 56.4%and 7.25%,respectively,which negatively correlated with GC overall survival[30].Besides,knockdown of demethylases SETDB2 was found to accelerate the expression of tumor suppressor genes WWOX and CADM1,and significantly reduced cell growth,migration and invasion in GC cells[31].
Histone phosphorylation
Histone phosphorylation is a dynamical process mediated by histone kinases and phosphatases,in which the phosphate group is transferred from ATP to the histone serine and threonine residues.There are several accessible sites in histone phosphorylation including H1.4 Ser27,H2AX Ser139 ( also called γ-H2AX),H3 Ser10,H3 The3 and H4 Ser1[32,33].Particularly,histone H3 is phosphorylated at Ser10 during mitosis in all eukaryotes and induction of phosphorylation in interphase has been shown to correlate with chromosome condensation prior to mitosis[34].Histone phosphorylation functions as a switch on chromosomal folding,compression,segregation,transcriptional regulation,cell signal transduction,cell apoptosis,and DNA damage repair[35,36].
Studies revealed that high H3K9Ac positive cells were associated with undifferentiated GC,suggesting poor prognosis of GC[17].Further,BMP8B was highly expressed in GC tissues other than adjacent normal tissues,and reduced acetylation level of BMP8B loci on H3K9 and H4K16 influenced the development of poorly differentiated gastric tumors[18].Many genes encoding HATs,such as KAT2B and EP300,are often genetically depleted or mutated in GC,and are significantly correlated with TNM staging[19,20].IFN-γ-induced upregulation of histone H3 Lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9)level in gene promoter accelerates the expression of B7-H1,which contributes to tumor immune evasion in HGC-27 cells[21].Wisnieski[22] demonstrated hypoacetylation of histone H3 in the initiator domain of CDKN1A decreased its mRNA level and reduced antitumor effect in GC.Besides,-infection inhibited recruitment of HAT p300 to the p27 promoter which caused the hypoacetylation status in histone H4,then induced the downregulated p27 mRNA expression,and finally led to gastric carcinogenesis[23].
Histone ubiquitination
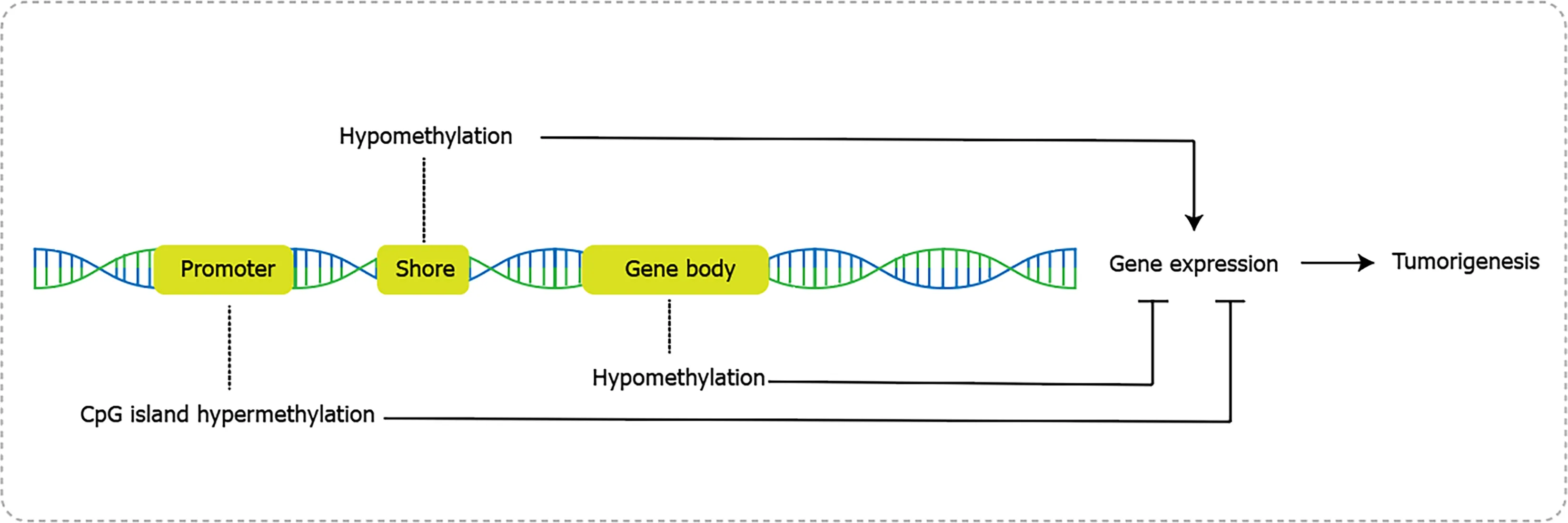
Aberrant DNA hypermethylation usually happens in the promoter of tumor suppressor genes in GC like p16,RASSF1A and hMLH1.Hypermethylation inhibits gene transcription by reducing binding to transcription factors,thereby impeding DNA readability and resulting in gene silencing[50].Specifically,alteration of methylation in p16 promoter inhibited the cell cycle in G1 phase and induced 5-fluorurazil chemo-resistance in GC[51].Abnormal methylation of RASSF1A gene promoter reduced RASSF1A expression,decreased cyclin D1 accumulation,and arrested cell cycle.Consistently,GC patients presented evidently higher frequency of aberrant methylation in RASSF1A promoter than control group,indicating the potential of methylated RASSF1A promoter as a molecular marker for the diagnosis of GC[52].In addition to methylation alterations in promoter,hypomethylation at gene body regions has a distinct association with transcription and gene hypomethylation also exerts profound effects on cancer progression[53].For instance,hypomethylation of SAT-α and L1 was associated with shortened survival in advanced GC patients[54].And Lineage-specific RUNX3 hypomethylation constituted the immune component in GC and was associated with the early inflammatory,preneoplastic and tumor stages[55].Genome-wide methylation sequencing studies in GC identified both hypo-and hyper-methylation events across the genome,suggesting a dual role of global genomic methylation in the stages of gastric carcinogenesis[56].
Hahn[45] identified that ring finger proteins RNF20 and RNF40 constituted a heterodimeric complex that functions as the E3 ubiquitin ligase for monoubiquitination of histone H2B at lysine 120 (H2B-K120) and the tumor suppressor CDC73 exerted antitumor effect in GC through the maintenance of H2B-K120 monoubiquitination.Besides,histone ubiquitination presents a therapeutic potential in GC as the expression of ubiquitinated-H2B was significantly lower in the malignant tissues and different differentiated tumors had variant levels of H2B ubiquitination[46].
DNA METHYLATION
In contrast to histone methylation,DNA methylation is a more frequent and comprehensive epigenetic modification (Figure 2),mediated by DNA methyltransferase(DNMTs) and demethylases.It refers to the transfer of the methyl group (CH3) from S.adenosylmethionine to C5 and forms 5-methylcytosine[47,48].DNA methylation occurs in the dinucleotide CpG sequence,which may form CpG islands and dispersed sequences.CpG islands exist in around 60%-70% of gene promoters in human and consist of CpG core and shore area[49].CpG core has a specific inhibitory effect on methylation,while the shore area,also known as transitional CpG region,is variable sites for dynamical alterations between hypomethylated and hypermethylated groups.In normal cells,CpG islands are non-methylated and other CpG sequence are methylated.Once stimulated by intrinsic or extrinsic factors,the methylation status changed and caused alterations in gene transcription,and consequently lead to tumorigenesis[48].
Unlike the three types of histone modifications described above,histone ubiquitination always works in the crosstalk with other modifications.Histone ubiquitination often acts subsequently after histone acetylation and methylation or modifies the stability and the activity of enzymes in these acetylation and methylation processes,which endures a synergic effect on cell division,cell cycle,DNA damage and cell apoptosis in GC[41].When the histone,usually H2A and H2B,binds to one or several ubiquitins on lysine residues,it is called mono-or poly-ubiquitination and tends to work in the following three ways:Alterations of chromosome structure,recruitment and activation of downstream proteins,and degradation in proteasome pathway[42].Ubiquitination is a reversible process in which ubiquitin is removed from polypeptides by deubiquitinases (DUBs),a superfamily of cysteine proteases and metalloproteases that cleave ubiquitin-protein bonds[43,44].
MicroRNAs are a class of small RNAs with 18-24 nucleotides and they repress translation process and silence target gene through complementary binding with 3’untranslated terminal region (UTR) of mRNA[68].A shaped understanding towards miRNAs has been established in the past two decades due to numerous miRNAs arrays conducted in GC.Taking the largest scale of GC miRNAs array cohort for example,a general miRNAs signature profiling was developed,in which 22 oncogenic miRNAs and 13 tumor suppressor miRNAs were identified in 353 primary Japanese gastric tumor samples.In this study,authors also revealed that different histological subtypes had different miRNA signatures[69] as diffuse-type showed 2 folds of proportion in upregulated miRNAs to intestinal-type GC.Specifically,low expression of let-7g and miR-433 and high expression of miR-214 were associated with unfavorable outcomes in GC patients[69].MiRNAs have an edge on GC diagnosis potential over other epigenetic factors because they alter quickly and are easy to be detected in the early stage of GC.Yu[70] performed a miRNAs microarray in early GC mouse model and the result showed that miR200-family promoted the initiation of GC and the integration of miR200-family’s 15 target gene would provide superior predictive sensitivity and specificity for overall survival compared with each early GC indicator alone.Here we summarized the up-or down-regulated miRNAs in GC(Table 1).
Steven Olderr s symbolic66 meanings of the sky include: the active male principal, the father, holiness, purity, the supreme67 being or his dwelling68 (Olderr 1986).
LncRNAs are longer than 200 nucleotides and exert profound influences on multiple biological functions through regulating transcription,chromatin remodeling and posttranscriptional process[71].They work mainly in three ways:(1) Interact with mRNA,control transcription and regulate cellular signaling pathways;(2) Act as regulators of splicing and mRNA decay;(3) work as molecular decoys for miRNAs;and (4) interact with chromatin-modifying complexes or being a scaffold to maintain the structure of nuclear speckles[72-74].Numerous lncRNAs have been uncovered the role and related mechanisms in GC.HOTAIR is a well-studied lncRNA and it is frequently overexpressed in GC,which may play a part in metastasis through following pathways:(1)Being a sponge of miR-330[75] and miR-331-3p[76] to upregulate the downstream targets;(2) Directly silencing HOXD[76] or miR34a expression[77];(3) Regulating Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt pathways[77];and (4) Inducing ubiquitination of Runx3[78].Therefore,HOTAIR was considered to be a potent diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in GC.Most of lncRNAs in GC were found to be oncogenic,like H19,MNX1-AS1,MALAT1,HULC,UCA1,However,some lncRNAs like CRNDE were identified to inhibit GC progression.Here we summarized the up-or down-regulated lncRNAs and the related targets and functions in GC (Table 2).
NON-CODING RNAS
Histone methylation usually takes place on H3 and H4 Lysine or arginine residues,catalyzed by histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and reversely controlled by histone demethylases (HDMs).The methylation could be single or multiple methylations to form mono-methylation (me1),di-methylation (me2) and tri-methylation (me3),participating in the formation and maintenance of chromatin structure,DNA repair,gene inactivation and transcription[24].Methylations on different sites have different functions in regulation of gene expression.In general,methylation of arginine residues,methylation of lysine H3K4 and H3K36,and monomethylation of H3K27 are associated with gene activation,while methylation of H3K9,H3K79 and H4K20,and dimethylation and trimethylation of H3K27 might cause gene silencing[25,26].

miRNAs
-induced DNA Methylation is a hot research area in the development of GC.Numerous researches revealed that,classified as Class I carcinogen by WHO,induced and accumulated aberrant DNA methylation through continuous chronic inflammation in gastric mucosae,and such high level of epigenetic field defects increased the risk of gastric carcinogenesis[57].For example,infection upregulated inflammatory response genes like IL-1β,Nos2,and Tnf,and promoted the infiltration of monocytes/macrophages with residual neutrophils in noncancerous mucosae,which induced a large number of aberrant DNA methylation in tumor suppressor genes and led to malignant transformation[58].Eradication ofhad subtle influence on the decrease of DNA methylation in gerbils,while application of immunosuppressive agent (cyclosporin A) and demethylation agent (5-Aza-2-deoxycytidine) could evidently reduce level of DNA methylation and prevent development of GC[59,60].Moreover,high levels of DNA methylation were found in gastric biopsies of inflammatory and precancerous lesions,comparing to adjacent normal tissue,and were also correlated with a greater risk of GC incidence[61].-induced DNA methylation takes place in various genes involved in cell adhesion,cell cycle,DNA damage repair,inflammation,and autophagy,which allows intensive interfered targets of such epigenetic defects in diagnostic biomarker and cancer prevention[58,62].
LncRNAs
51.Loan of my horse: Horses are intelligent, strong animals highly valued and sometimes worshipped in numerous cultures. The lending of a horse is a sign of trust and faith. Horses are often considered lucky in folklore.Return to place in story.
4. Adopted daughter: The adopted has been added to this story once again to suit Victorian and modern sensibilities. In the original version by Perrault, Donkeyskin is the full-blooded daughter of the king and queen. If Donkeyskin is adopted, the marriage ceases to be incestuous and morally wrong, only undesirable60 to Donkeyskin herself.
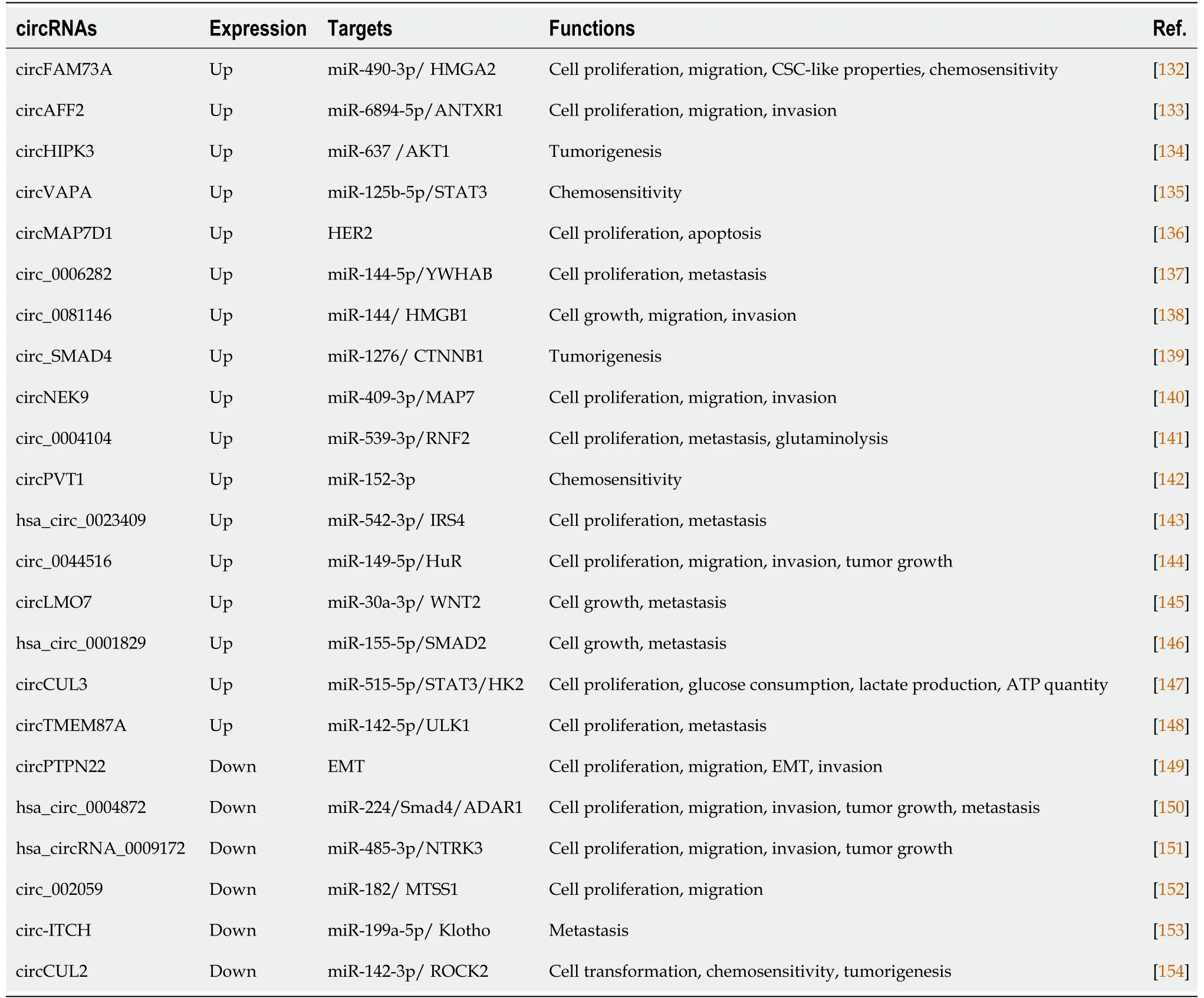
CircRNAs
CircRNAs are a novel class of conserved single-stranded RNA molecules derived from exonic or intronic sequences by precursor mRNA back-splicing[79].Compared to linear RNAs,the circular structure of circRNAs confers enhanced stability to exonuclease digestion[80].Partially similar to lncRNAs,circRNAs could also act as miRNAs sponge,regulators of alternative splicing and tools of sequestering functional proteins in gene expression and posttranscriptional modification[81].However,some circRNAs were identified to encode functional proteins[82].CircRNAs were reported to exert influences on tumor growth,therapeutic resistance,recurrence and metastasis[83].GC-related sequencing data revealed a variety of circRNAs with pro-or antitumor roles,including CircPVT1,CircRNA_001569,CircHIPK3,CiRS-7,one of the mostly investigated circRNAs,is a sponge of miR-7.MiR-7 was known as a tumor suppressor miRNA,while ciRS-7 was found to act in an oncogenic role by antagonizing miR-7-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in GC.Overexpression of ciRS-7 accelerated the progression of GC[84].Undoubtedly,circRNAs are of great value in research and are emerging as a rising star in the field of cancer biology and therapy.We listed some important circRNAs,as well as their targets and functions in Table 3.
He spake to the King: Your loyalty46 shall be rewarded, and taking up the heads of the children, he placed them on their bodies, smeared the wounds with their blood, and in a minute they were all right again and jumping about as if nothing had happened
TRANSLATIONAL APPLICATION OF EPIGENETICS
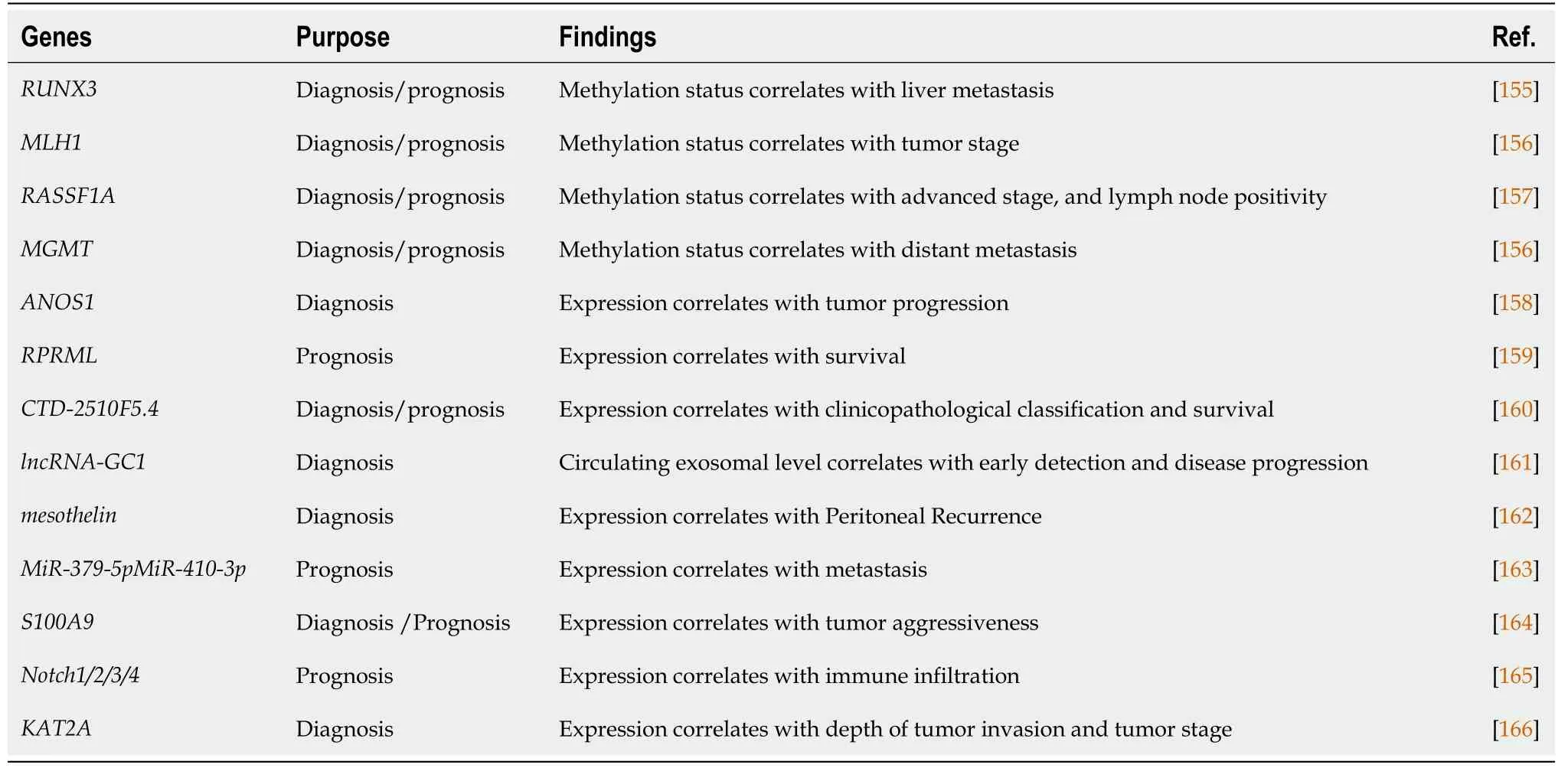
Researches on epigenetics not only revealed the underlying mechanism of cancer initiation and progression,but also provided novel diagnostic and prognostic candidate biomarkers and therapeutic targets.To the best of our knowledge,biomarkers in GC ranges from pivotal proteins,non-coding RNAs to plenty of modifications with various specificity and sensitivity,as well as epigenetic liquid biopsy,some of which have already shown favorable clinical utility (Table 4).Liquid biopsy is a simple,fast and non-invasive alternative to surgical biopsies,as blood or body fluid sample is always easy to collect.A sum of circulating tumor cells (CTCs)and cell-free nucleic acids (cfNAs) including DNA,mRNA and microRNAs could be detected in patient blood or body fluid[85].Available information obtained from liquid biopsy could help doctors with cancer diagnosis and evaluation of clinical outcomes.Up to now,most of epigenetic liquid biopsies in GC were aberrant DNA methylations such as 5-methylcytosine (5mC),5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC),CD40 and GHSR hypermethylation and they even could be used to identify specific cancer types[86-88].Moreover,CTCs were often detected based on miRNA or mRNA PCR assay due to its low concentration in blood.
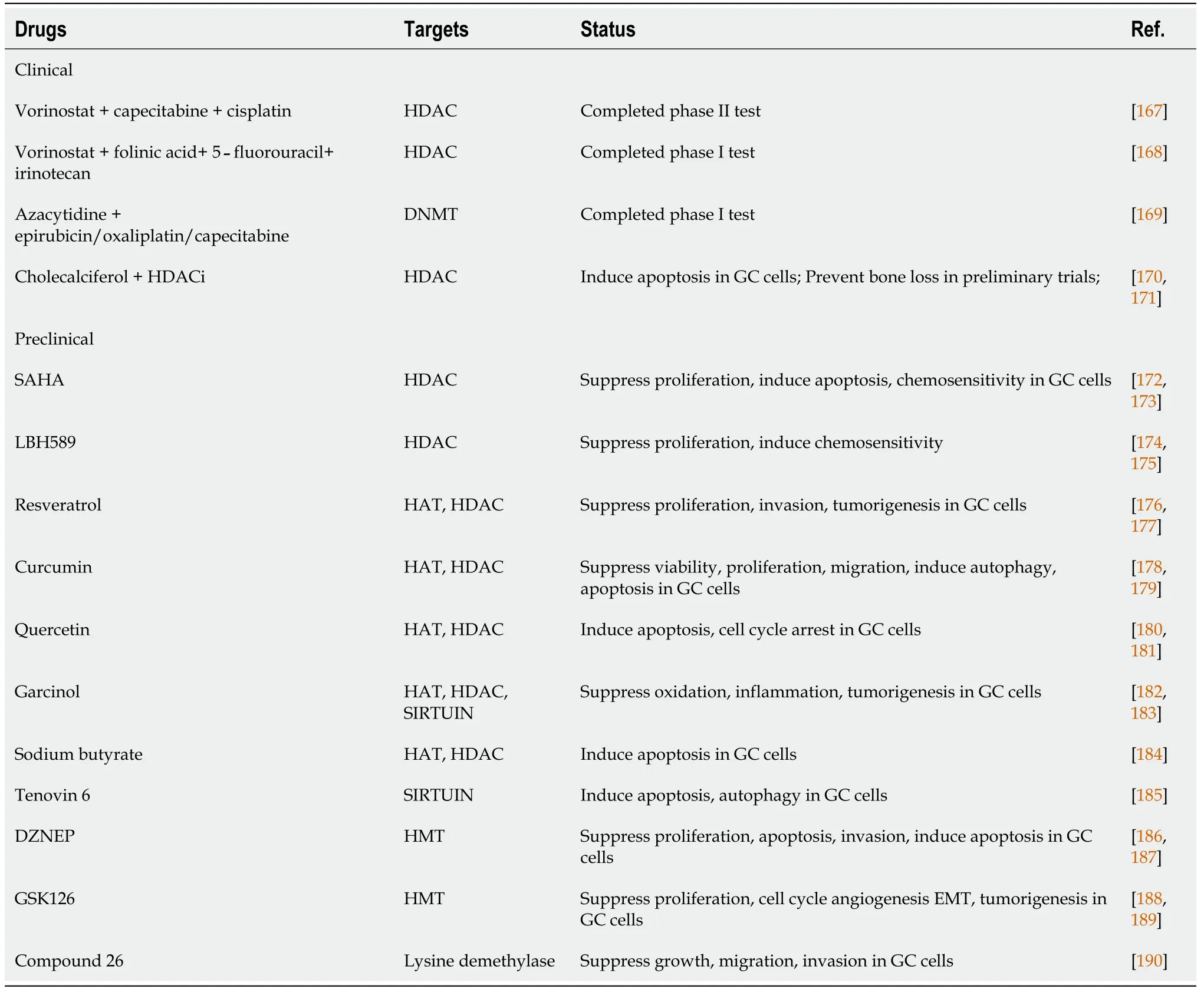
From the therapeutic perspective,targets involved in epigenetic modifications are potential drug targets and they are mainly divided into two groups including enzymes in histone acetylation (HAT or HDAC) and methylation (DNMT or DMT),and noncoding RNAs (miRNA or lncRNA).Some epigenetic drugs have been approved by FDA such as HDAC inhibitors (SAHA) in treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and DNMT inhibitors (vidaza,decitabine) in treatment of myelodysplatic syndromes[2].However,most of epigenetic drugs are undergoing clinical or preclinical tests and none of them were currently ready for clinical utility in GC.As the rapid development of GC epigenetics research in recent decades,it is of great significance to integrate existing findings to ensure efficient translation applications (Table 5).
CONCLUSION
Accumulating evidence revealed the critical role of epigenetic alterations in cancer initiation and progression.Herein,we comprehensively discussed the functions and mechanisms of epigenetic factors in GC.Drugs targeted HAT,HDAC,DNMT are undergoing preclinical and clinical trials,which is promising for improving the efficacy and survival to GC.However,epigenetic studies in GC are still challenged by lack of innovative findings in new types of histone modifications.Succinylation and sumoylation,for instance,have already been reported to participate in tumorigenesis and progression in other gastrointestinal cancers including esophageal,colorectal and liver cancer.We believe combined technologies like single cell sequencing and multiple protein omics sequencing will further broaden epigenetic investigation in gastric malignancy and GC patients will benefit from numerous epigenetic drugs in the future.
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2022年1期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2022年1期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Comment on “Outcomes of curative liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis”
- Liquid biopsy:Precise diagnosis and therapy for cholangiocarcinoma
- Increased risk of colorectal neoplasia in inflammatory bowel disease patients with post-inflammatory polyps:A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Exosomes as potential diagnosis and treatment for liver cancer
- Effects of cognitive behavior therapy combined with Baduanjin in patients with colorectal cancer
- Intertwined leukocyte balances in tumours and peripheral blood as robust predictors of right and left colorectal cancer survival
