Bit-Level Composite Signal Design for Simultaneous Ranging and Communication
Weigang Chen,Yalong He,Changcai Han,Jinsheng Yang,Zhan Xu
1 School of Microelectronics,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2 Key Laboratory of Modern Measurement and Control Technology,Beijing 100192,China
3 School of Information and Communication Engineering,Beijing Information Science and Technology University,Beijing 100192,China
Abstract:As the complexity of space exploration missions augments,how to enhance the overall performance of communication,ranging or other functions has become a challengeable problem.Considering the integration of communication and ranging,we present a bit-level composite signal for simultaneous ranging and communication.In this composite method,through a specially designed mapping scheme using low-weight codewords,the information sequence is converted to a sparse sequence which is then superimposed on the ranging code.For ranging,the correlation characteristics of the ranging code component can be maintained to calculate the transmitter-receiver distance.For communications,the sparse sequence can be extracted without interference by eliminating the ranging code component.Simulation results show that the proposed composite signal can support communication and ranging simultaneously with limited sacrifice of ranging performance,and the performance loss of ranging can be controlled and minimized by lowering the density of information sequences using different sparsification encoding methods.
Keywords:composite signal;spectrum sharing;lowweight codeword;regenerative PN ranging code
I.INTRODUCTION
With the requirements of space exploration missions escalating,the limited spectrum resources and energy are increasingly strained[1]and mutually independent ranging and communication systems are unable to meet the requirements.It is valuable to make one system have the capability to complete multitask,which can be achieved by designing composite signals for simultaneous transmission of information sequences and ranging codes.The Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems(CCSDS)has proposed a composite signal[2]for simultaneous ranging and telemetry based on the regenerative pseudo-random noise(PN)ranging code[3].The composite signal can use a single signal to support multiple functions,which can mitigate electromagnetic interference,save the transmission power consumption and alleviate the tension of spectrum resources[4].
There are several means to design a composite signal for simultaneous communication and ranging.The key difference between these approaches is how ranging codes and information sequences are combined or merged.In[5,6],the unbalanced quadrature-phase shift keying(UQPSK)modulation mode is adopted to support simultaneous transmission of telemetry and ranging.The in-phase(I)branch is applied to transmit the information sequence and the quadrature(Q)branch is used to transmit the PN ranging code.This system essentially conducts communication and ranging using the two orthogonal channels independently,which has the low bandwidth efficiency.The composite approach in[7]is embedding ranging information into communication signals as a separate ranging segment to realize the simultaneous transmission.The above methods actually combine the two signals at the level of signal-multiplexing,which are limited in improving spectrum utilization and the overall performance.Different from the above methods,there are also some contributions dedicated to the superimposed signal.In[2],the simultaneous transmission is obtained by combining the Gaussian filtered minimum shift keying(GMSK)modulated telemetry signal with a CCSDS standard regenerative PN ranging code which is phase-modulated on top of telemetry signals.It can meet the requirements of ranging and high-speed data transmission under the constraints of the space frequency coordination group(SFCG)[8].This scheme has been tested by engineering implementation[9,10].However,ranging code is actually an interference signal which degrades the performance of the telemetry subsystem,while errors in estimating telemetry symbols compromise the correct detection of the ranging chips[11,12].Similar to GMSK modulation,multi-h continuous phase modulation(multi-h CPM)is also suitable for simultaneous transmission of telemetry and ranging[4,13].Compared with the GMSK system,the multi-h CPM system can adjust the parameters,such as shaping pulse function,modulation index and modulation order,according to the actual requirements for the improvement on the overall performance[4].
Unlike the previous composite approaches,we propose a bit-level composite method of superimposing ranging codes and sparse information sequences,which can obtain communication performance enhancement with limited sacrifice of ranging performance.The encoded symbol is first transformed into a sparse sequence by using partial low-weight codewords selected from the Golay code.Then,the composite signal is generated by modulo-2 chip-by-chip adding the sparse sequence to the ranging code.That is,the chips of the ranging code are inverted according to the pulse position of the sparse sequence.On the one hand,due to the sparsity of the pulse position in the sparse information sequence,the flip ratio of the chips in the ranging code can remain moderate,thereby maintaining correlation characteristics of the ranging code component in the composite signal.On the other hand,the sparse information sequence can be perfectly extracted without interference by only identifying the start position of the composite ranging code,which outperforms the GMSK/PN scheme.In the proposed composite method,there is no need to allocate additional transmission power and frequency spectrums for information sequences,thereby effectively guaranteeing the overall performance and enhancing the link efficiency.
The remainder of this paper is arranged as follows.In Section II,we present the composite signal design method,and further study the promising application prospect of this proposed composite signal in deep space exploration.Section III details the composite signal receiving method.In Section IV,simulation results and analysis are reported.Section V concludes this paper.
II.PROPOSED DESIGN METHOD FOR THE MULTI-FUNCTION COMPOSITE SIGNAL
This section introduces the design method and principle of the proposed composite signal.Then,its promising application prospect in deep space exploration is investigated preliminarily.
2.1 Design Method of the Composite Signal
The integration of ranging and communication shows some potential advantages in performance and complexity.We propose a bit-level composite signal by superimposing the information sequence on the ranging code to share the same frequency band and transmission power.The generating procedure of the proposed composite signal mainly includes sparsifying the information sequence for communication and superposing with the ranging code,as shown in Figure 1(a).The information sequence is first encoded by outer multi-ary error-correction codes over GF(2m)or binary codes.Then,each encoded symbol or bit vector includingmbits is converted to a low-weight Golay codeword and then modulo-2 added to the ranging code for generating the composite signal.The outer code can adopt various error correction codes with excellent performance,such as extended irregular repeat-accumulate(eIRA)codes which are efficiently encodable LDPC codes with a low error floor[14]or non-binary low-density parity-check(NB-LDPC)codes which can provide better error performance than binary LDPC codes[15,16].
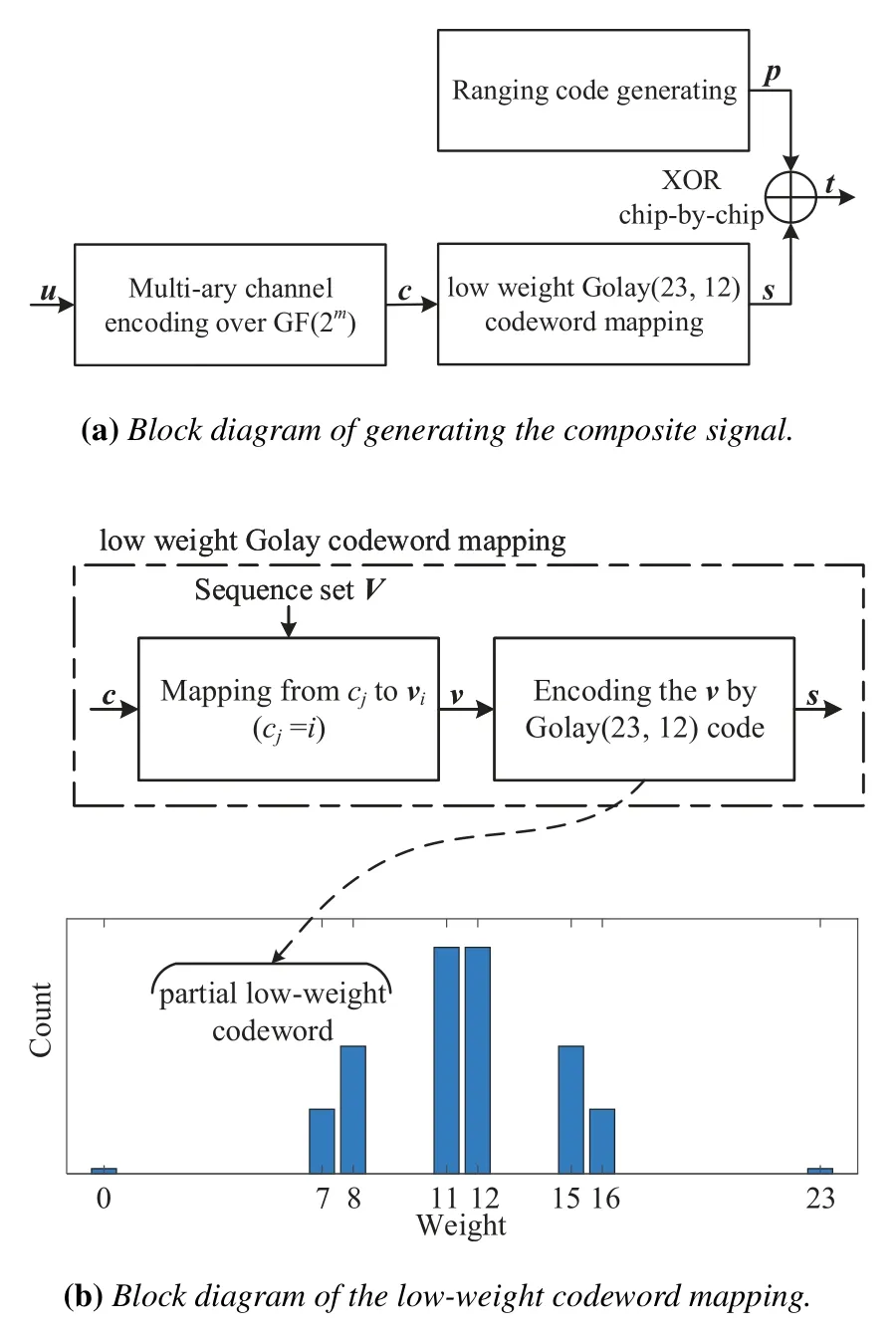
Figure 1.Proposed composite signal for simultaneous ranging and communications.
Figure 1(b)illustrates a specially designed mapping scheme which adopts partial low-weight Golay(23,12)codewords to transform the encoded bitstream into a sparse sequence.In this paper,we use Golay(23,12)code as an example to generate the sparse sequence with a good minimum distance for error correction capability.The weight distribution of all the Golay(23,12)codewords is given in Table 1.It can be observed that there are 760 codewords with weight less than 8.Considering the number of low-weight codewords,we chose the 9-to-12 mapping to use 512 low-weight codewords.It is the main contribution in the sparsification process.In this case,the sparse sequence is generated by the low-weight Golay codeword set composed of 253 codewords of weight 7,258 codewords of weight 8 and the all-zero codeword.The average proportion of symbol‘1’in the sparse sequence is about 32.6% which is calculated according to the weight of these 512 codewords selected.The density of a binary vector is defined in[17]and a vector with density less than 1/2 is said to be sparse.One of the contributions of this paper is that we use low-weight Golay codewords as sparse sequences,which guarantee low density of the information sequence and also provide significant error correction capability due to the relatively large minimum distance.The proportion of ‘1’ in the sparse sequence mainly depends on the inner low-weight codewords or sequences and we can also construct a sparse sequence with less‘1’.For example,each encoded symbol with the length of 3 bits is converted to a sparse sequence with the weight of 1 and the length of 8 bits.It is the“one-hot”scheme and the density of the sparse sequence generated by this scheme is about 1/8.Unfortunately,the minimum distance of these sequences is not so significant.In the future,we will use more strong error correction codes or some explicit strategies of sequence design to generate low-weight sequences with satisfying error correction capability.

Table 1.The weight distribution of Golay(23,12)codewords.
We further introduce a mapping sequence setVto describe the low-weight codeword mapping process in detail.The mapping sequence setVin Figure 1(b)is constructed using the information bits of these 512 low-weight codewords selected.The setVis designed as follows.
Step 1:Calculate the weight of all the Golay(23,12)codewords.
Step 2:Select 2msequences with the smallest weight as shown in Table 1.
Step 3:Form the setVby choosing the information bits of the 2mlowest weight Golay(23,12)codewords and sort the setVascendingly.
Step 4:Build the mapping relations between multiary symbols and the information bit vector of the chosen low-weight Golay codewords according to the one-to-one correspondence,in order to utilize the efficient cyclic encoding structure of the Golay code.
In summary,the generating procedure of the composite signal can be summarized as Algorithm 1.

Algorithm 1.Generating algorithm of the composite signal.Step 1.Encoding of the outer code.1.1.Divide the binary information into a series of groups with the length of m bits to form a symbol sequence,m ≤9.1.2.Perform q-ary outer code encoding to generate a non-binary codeword c with a length of l symbols,q=2m.Step 2.Mapping from m bits to 12 bits.2.1.Construct the mapping sequence set V and determine the mapping rule form per q-ary channel encoded symbol with m bits to 12 bits.2.2.Map each q-ary encoded symbol ci with the length of m bits to a corresponding binary sequence vi of length 12 bits in V,ci= j,i=1,2,···,l,j=0,1,···,q ?1.2.3.Obtain an intermediate information bit sequence v after mapping all the symbols.Step 3.Encoding of the inner Golay(23,12)code.3.1.Encode the sequence v by Golay(23,12)code to generate a sparse sequence s with the length of 23l bits.Step 4.Superposing the two signals.4.1.Superimpose the sparse sequence s on the ranging code p by modulo-2 chip-by-chip addition operation to generate the composite signal t.
2.2 Principles of the Composite Signal
The superposition principle of the ranging code and the sparse codeword sequence is depicted in Figure 2,whereNsandNprepresent the length of the sparse sequence and the ranging code,respectively.The chips of the ranging code are inverted according to positions of the‘1’chips in the sparse sequence.The proposed composite method originates from the Davey-MacKay(DM)construction[17–19],in which the NB-LDPC codeword is transformed into a sparse sequence and then added modulo 2 to a watermark code.Due to the sparsifying of the LDPC codewords,the watermark code in DM construction can still be used as a reference to infer the position of insertion or deletion errors.Ranging codes in this paper play a similar role as the watermark.The ranging code is not used for identifying the insertions/deletions,but used for independent ranging function.Different from the DM construction,we choose partial low-weight codewords of the error-correcting codes(e.g.,the famous Golay code)to generate the sparse sequence.For communications,it also can exploit the error correction capability of the codes to offer a certain coding gain.It is one of the contributions.In addition,the period of the ranging code may be much longer than the sparse sequence.In these scenarios,we only need to superimpose sparse sequences on a partial of ranging codes,which can further decrease the influence on ranging codes,as shown in Figure 2.
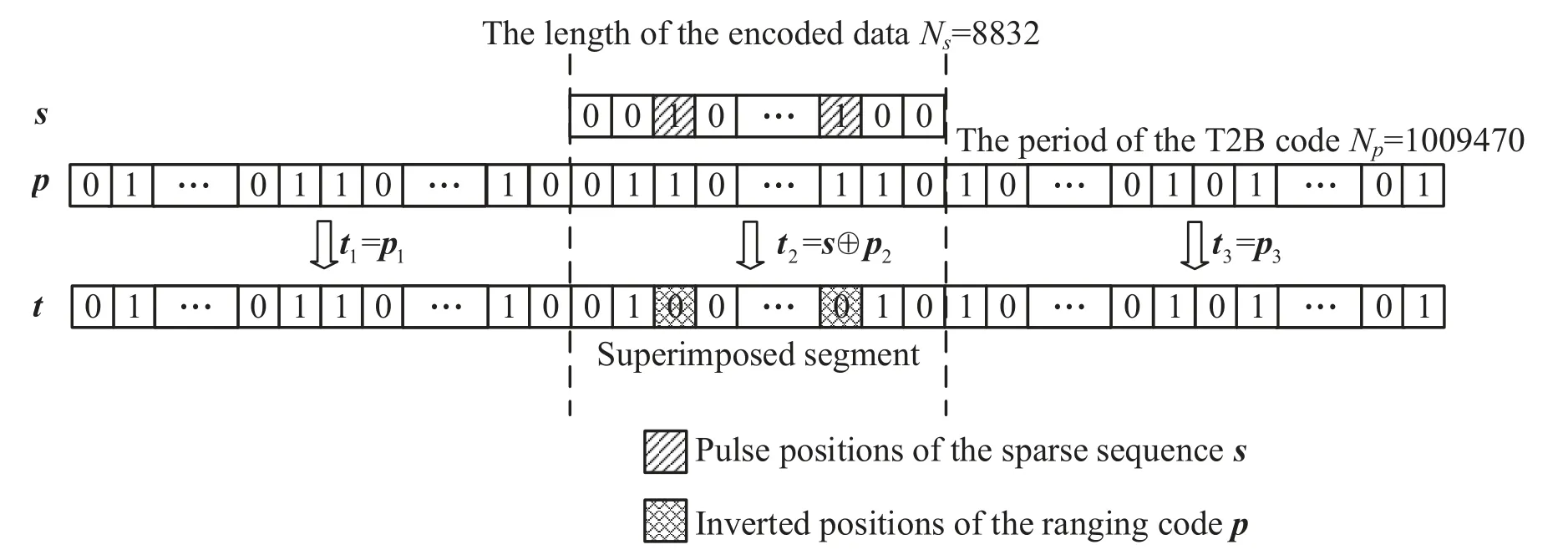
Figure 2.Principle of superimposing ranging codes and sparse information sequences.
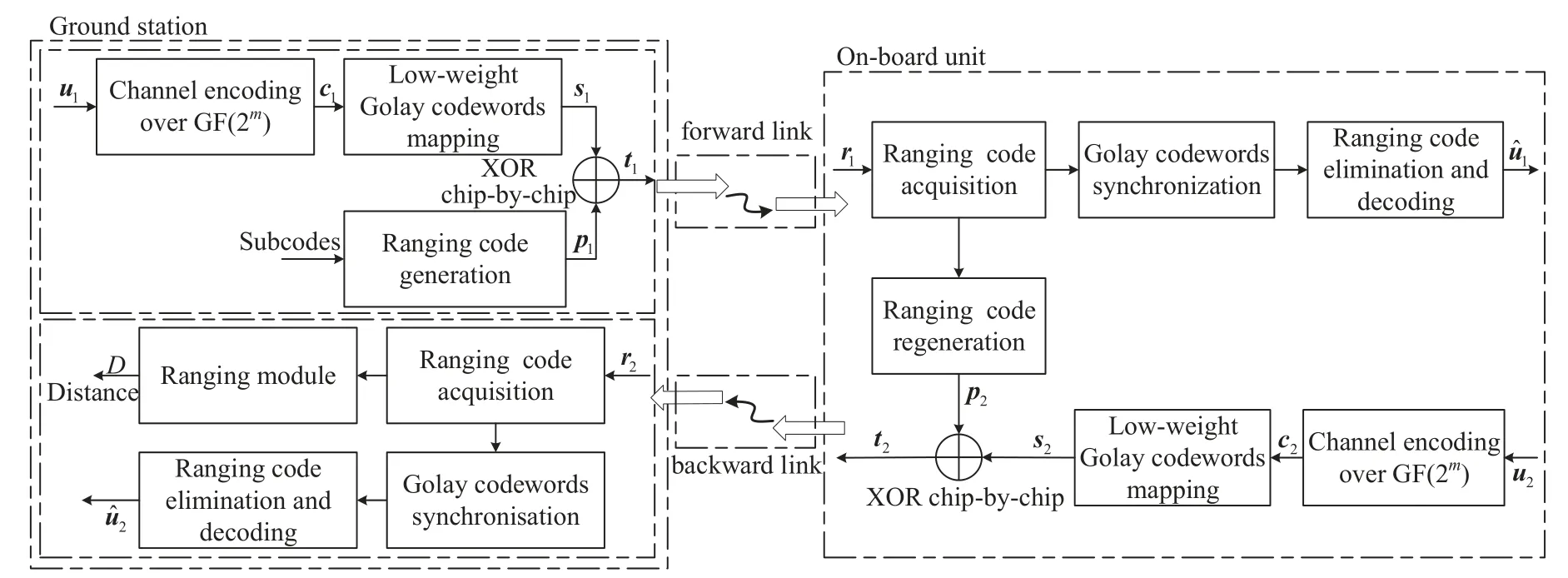
Figure 3.Block diagram of the composite signal transmission system in deep space exploration scenario.
2.3 Potential Application of the Composite Signal in Deep Space Exploration
In this subsection,the CCSDS standard regenerative PN ranging code,called weighted-voting balanced Tausworthe code,is adopted to construct the composite signal.This ranging code is built from logical combinations of six periodic component PN sequences(subcodes)of which the shortest one is the range clock component[3].The regenerative PN ranging code has a shorter acquisition time than the single PN ranging code.The deblurring ability of the regenerative PN ranging code is excellent attributed to the long period.Moreover,we can start to acquire the regenerative PN ranging code anywhere without knowing the initial position.Precisely owing to this advantage,the sparse sequence can be superimposed on any continuous position of the regenerative PN ranging code.Correspondingly,it is necessary to accomplish the synchronization of the superimposed sparse sequence,which is a precondition for restoring the information sequence.
The block diagram of the proposed composite signal transmission system in deep space exploration scenario is depicted in Figure 3.At the ground station,the forward information is first encoded using channel codes over GF(2m).Then,each encoded symbol in GF(2m)is converted to a sparse sequence using the low-weight Golay codewords.Finally,the composite signal is generated by modulo-2 chip-by-chip adding the sparse sequence to the ranging code.At the onboard unit after receiving the signal,the ranging code component acquisition process is performed to find the correct phase of each subcode and then the ranging code can be regenerated according to the phase of all the 6 subcode components.Next,the backward information is similarly encoded and superimposed on the regenerated ranging code for the backward link.Finally,the ranging code component in the received signal is eliminated to extract the superimposed coded bitstream which is further decoded to restore the forward information.At the ground station after receiving the returned signal,the round-trip time is obtained by comparing the phase difference between the returned signal and the local ranging code.Simultaneously,the backward information is recovered by processing the returned signal in the same manner as the on-board unit.During this process,how the parameters affect the two functions will be investigated.
Specifically,we futher investigate the relation of information transmission rate,the ranging code rate and the ranging S/N,and give the possible application condition of the purposed method according to the simulation results.
III.PROPOSED RECEIVING METHOD FOR THE COMPOSITE SIGNAL
The reception of the composite signal mainly includes the processing of the ranging code and the synchronization/decoding of the sparsified coded bitstream,as illustrated in Figure 4.The local subcodes are used to acquire the ranging code component.Then,the acquired phase of the entire ranging code is used to perform regenerative ranging-related operations in the ranging module and achieve the synchronization of the superimposed low-weight codewords which are further decoded to restore the original information.
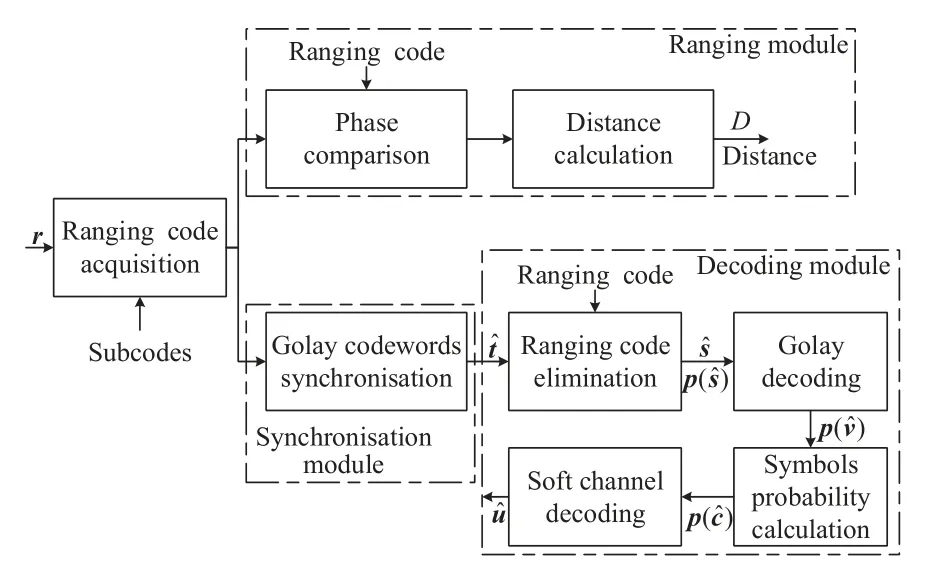
Figure 4.Block diagram of the composite signal reception at the ground station.
3.1 Processing of the Ranging Code
Ensuring the acquisition accuracy of the ranging code is the key to the subsequent steps.The received signal is first sent to the correlators to perform correlation with the local subcodes for acquiring the phase of the ranging code component.Then,the rangingrelated operations are performed under the ranging code tracking state in the ranging module,as depicted in Figure 4.At the ground station,the phase difference of the round-trip signal is compared for distance computation.At the on-board unit,the ranging code is regenerated for only forwarding.The maximum search algorithm represents the optimum approach for ranging code acquisition[3],which is adopted in this paper.The specific procedure of the algorithm is presented as follows.
Step 1:Calculate correlation values between the received binary phase shift keying(BPSK)signal and thei-th local subcode,denoted asRi(w,g)and calculated as follows,
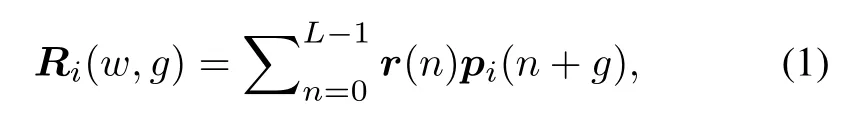
wherepi(n+g)is the extended sequence of thei-th subcode by shiftinggbits,r(n)is the received signal andLis the correlation length.i,nandwdenote the serial number of subcodes,digital samples and correlation values,respectively,1≤i ≤6.
Step 2:Search for the phase position of the maximum correlation values at each branch as follows,

where the maximum value defines the correlation peak andWirepresents the searched position in thei-th branch.The phase offset of each subcode can be obtained according to the acquired position,which is used to calculate the overall phase of the ranging code.
Step 3:The current phase of the ranging code can be calculated according to the Chinese remainder theorem(CRT).
3.2 Synchronization and Decoding of Superimposed Low-Weight Codewords
The synchronization and decoding process is illustrated in Figure 4.
First,since low-weight codewords may be superimposed on any continuous segment of the ranging code,it is necessary to find the starting position of superimposed low-weight codewords.After acquiring the ranging code,we can obtain the current position of the received signal in the entire ranging sequence,which is then used to locate the superimposed segments in the ranging code.
Then,the superposed ranging code is eliminated by inverting the sign of the composite signal according to the pulse position of the ranging code.After synchronizing and ranging code elimination,the separated data segment in the received signal is determined and divided into a series of groups,each of which is one low-weight Golay(23,12)codeword with a length of 23 bits.In the decoding module,the bit-level hard and soft decision information is first calculated for all the codewords.
Next,Golay decoding is performed using a simplified maximum-likelihood decoding algorithm[20]and the Golay decoding results are demapped into the symbols in GF(29)according to the specially designed mapping rule.Finally,the outer decoding is performed to restore the original information.The detailed decoding process is summarized in Algorithm 2.
IV.SIMULATION RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
In this section,we perform the computer simulation to evaluate the performance of the proposed composite signal.
4.1 Simulation Parameters

Algorithm 2.Decoding algorithm of the sparsified codewords.Step 1.Synchronization and eliminating the ranging code component.1.1.Identify the location of the received segments according to the embedded ranging code.1.2.Eliminate the ranging code component in the composite signal and obtain ^s from ^t by inverting the sign according to the pulse position of the ranging code.1.3.According to the code boundaries,divide the signal(excluding the ranging code component)into a series of groups with the length of 23 bits to form serials of Golay codewords and the number of groups denoted as lr.Step 2.Decoding of the inner Golay(23,12)code.2.1.Define the summation term as the correlation discrepancy between ^s and d,expressed as λ(^s,d)=images/BZ_230_692_1417_758_1463.png j:^s ⊕d=1|P(^s)j|,where d indicates a sequence mapped by an arbitrary Golay(23,12)codeword,j=1,2,···,23.2.2.Calculate the λi(^s,d)for all the Golay(23,12)codewords,and select a codeword with the smallest correlation discrepancy in each correlation discrepancy array as the i-th group decoding result,i=1,2,···,lr.Step 3.Mapping from 12 bits to m bits.3.1.Map each Golay(23,12)decoding result with the length of 12 bits to a symbol with the length of m bits according to the mapping rule for the hard channel decoder.3.2.Calculate the soft decision information of each symbol according to Golay(23,12)soft decoding information for the soft channel decoder.Step 4.Decoding of the outer code.4.1.Decode the outer code to restore the original information according to the hard and soft decision information from Step 3.
The simulations are performed over the additive white Gaussian noise(AWGN)channel using BPSK constellation.RS codes and NB-LDPC codes over GF(29)are chosen as the outer code,respectively.The inner code is the 512 low-weight Golay(23,12)codewords.Taking the outer RS(511,k)code as an example,the information sequence with the length ofksymbols is first encoded into 511 symbols.Then,each symbol is mapped to an intermediate information sequence of length 12 bits,which is then encoded into a low-weight codeword of length 23 bits using inner Golay(23,12)encoding.The code length and code rate of the concatenated code using RS codes are 11753 bits and 9k/11753.The hard decision decoding algorithm is performed for the RS code.Similarly,for the concatenated code composed of LDPC(384,192)code over GF(29)and Golay(23,12)code,the code length and code rate are 8832 bits and 9/46.The NB-LDPC code is decoded using the belief propagation algorithm based on fast Fourier transform.The inner Golay(23,12)code is decoded with a simplified maximum-likelihood decoding algorithm and then demapped into the symbols in GF(29).
4.2 Ranging Code Acquisition Performance
In this part,we give the simulation results to explain the feasibility of the proposed method and verify the acquisition performance of the ranging code component in the composite signal.
The acquisition performance is evaluated using the acquisition error probability which is defined as the probability of false acquisition of the ranging code.We select the regenerative PN ranging code(T2B)as the ranging code,where the T2B is the weightedvoting balanced Tausworthe code with the weightedvoting of 2 defined in the CCSDS recommended standard[3].The acquisition error probability of the T2B code superimposed with the sparse sequence is shown in Figure 5,whereLis the correlation length,fis the density of superimposed sparse sequences andNis the length of superimposed sparse sequences.The acquisition performance of proposed composite signals with the correlation length of 80000 chips is about 1.2 dB worse than that of the T2B code with the correlation length of 10000 chips,under the condition thatNis the same as the correlation lengthL.The composite signal with the correlation length of 20000 chips can achieve the same performance as that of the T2B code with the length of 10000 chips,under the condition thatNis 8832.This method retains the advantage of the T2B code,such as short acquisition time,long period and so on.
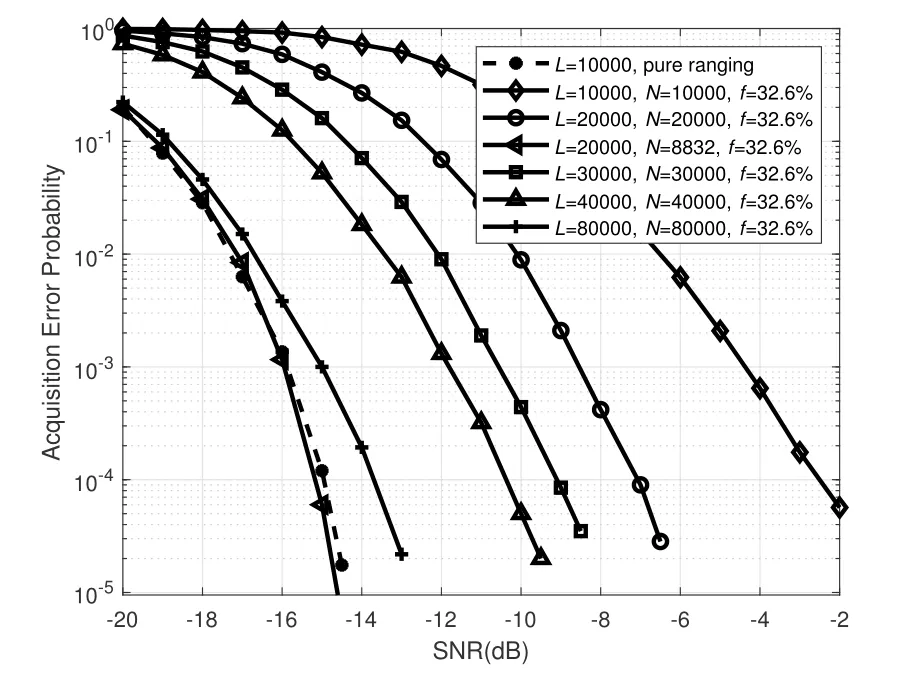
Figure 5.Acquisition performance of the T2B code superimposed with the low-weight Golay(23,12)codewords.
Moreover,m-sequences can also be chosen as the ranging code in the proposed method for their good correlation properties.The acquisition error probability of the m-sequence superposed with the sparse sequence under different SNR is illustrated in Figure 6.The acquisition performance of composite signals with the correlation length of 4095 chips has a gain of 1.0 dB compared with the order-8 m-sequence.
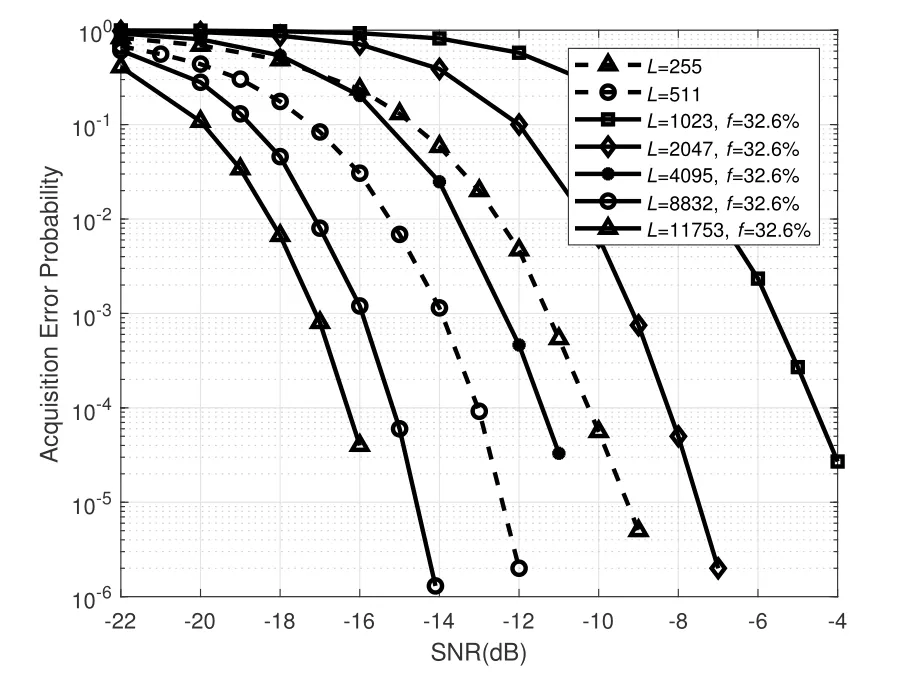
Figure 6.Acquisition performance of m-sequences superimposed with the low-weight Golay(23,12)codewords.
It can be observed from the two examples that due to the sparseness of the information sequence,the chip flip ratio of ranging codes is quite limited,thereby maintaining the correlation characteristics for successfully acquiring the ranging code.However,there is a certain acquisition performance loss of ranging codes in the proposed composite signal.The length of superimposed sparse sequences can affect acquisition performance and thus the acquisition performance can be compensated through increasing the correlation length.A tradeoff between complexity and performance can be achieved by adaptively adjusting the correlation length according to channel condition.
4.3 Information Transmission Performance
In this part,we demonstrate the simulation results to verify the information transmission performance of the superposed composite signals.
The bit error rate(BER)is used to evaluate the transmission property of communications use composite signal.Firstly,BER performance of proposed schemes with the outer RS codes is depicted in Figure 7,whereRis the overall code rate.RS(511,165),RS(511,311),RS(511,351)and RS(511,411)are chosen as the outer code to construct the concatenated code with the inner low-weight Golay(23,12)codewords.The overall code rate of these schemes is 0.126,0.238,0.269 and 0.345,respectively.It can be observed that the BER of the proposed scheme with the code rate of 0.238 achieves 10?5atEb/N0of 3.5 dB.Figure 7 also illustrates the BER of the proposed scheme with the outer NB-LDPC(384,192)code over GF(29)and the BER of this scheme achieves 10?5atEb/N0of about 0.9 dB.It also verified that the non-binary LDPC code achieves much better performance compared with the RS codes with the similar code rate.
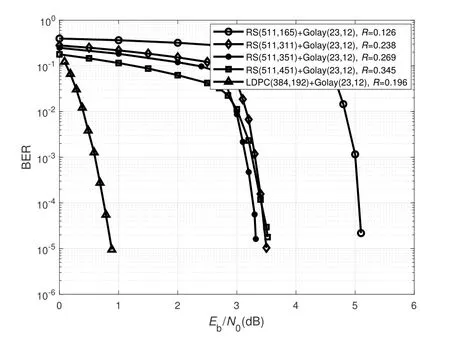
Figure 7.BER of composite signals with outer RS codes and NB-LDPC codes.
Then,we study the information transmission capability of the proposed method under extremely low signal-to-noise ratio conditions,for the regenerative ranging may work under extremely low signal-tonoise ratio than the data transmission function in many practical deep space application scenarios.In order to simultaneously achieve ranging and data transmission under extremely low signal-to-noise ratio,we need to adjust the parameter settings,such as reducing the code rate and extending the code length.In order to obtain better error correction capability,the direct method is to design a low-rate code.Here,we just take the repetition coding scheme as an example to reduce the overall code rate,though it is surely not the optimal scheme.Figure 8 presents the performance of the concatenated code composed of NB-LDPC(384,192)code over GF(29)and Golay(23,12)code with different repetition coding schemes,where n is the repetition parameter.It can be observed that the proposed method can transmit information even under very low SNRs by reducing the code rate.
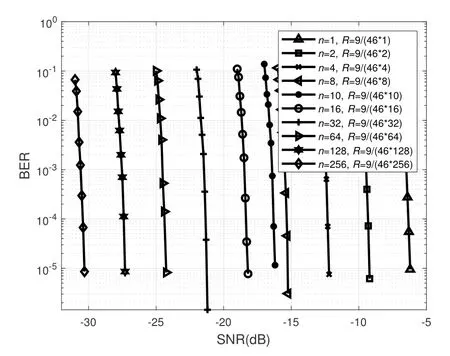
Figure 8.BER of concatenated codes composed of NBLDPC(384,192)code and Golay(23,12)code with different repetition coding schemes.
Finally,we analyze the information transmission capability of the proposed method under different parameters in the case ofFc=2.068 Mchip/s,whereFcis the chip rate.In the CCSDS information report[21],the chip signal-to-noise ratioSNRchipcan be calculated by[22]
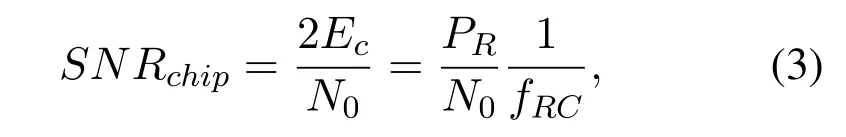
whereEcis the received chip energy,N0/2 is the two-sided noise power spectral density of the additive Gaussian noise,PR/N0is the ranging power over noise spectral density andfRCis the frequency of the ranging clock(half of the chip rate valuefRC=Fc/2).Due to the proposed bit-level composite signal generated by superimposing ranging code and sparsified coded bitstream chip-by-chip,the chip SNR of the ranging code is equal to the bit SNR of the sparsified coded bitstream.Table 2 lists information transmission capability of the proposed method under different parameters.It can be observed that the BER of the scheme achieves 10?5at-30.31 dB in the case ofn=256,PR/N0=30 dBHz.In this case,the overall code rate and information rate are 0.0008 and 1.618 Kbps,respectively.
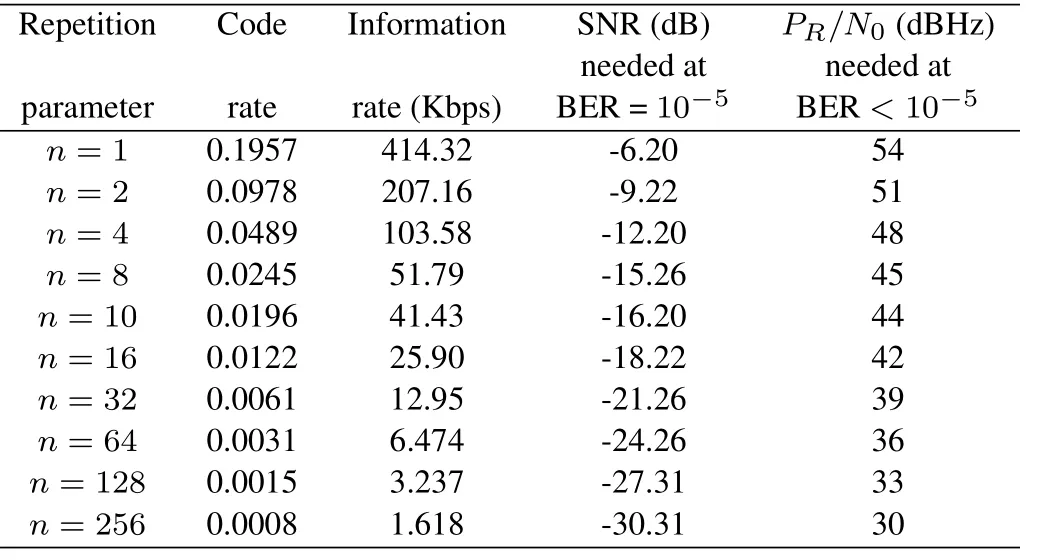
Table 2.The information transmission capability of the proposed method under different parameters.
In the future,we can adopt more strong and efficient error correction codes of very low code rate,such as LDPC-Hadamard codes[23],to enhance the overall information transmission performance instead of the repetition code.In this case,the proposed method can support communication and ranging simultaneously with the ranging acquisition performance loss of about 10.5 dB.Considering the overall performance of the system,there is no need to work on extremely low SNR conditions.
4.4 Analysis of the Compatibility between Ranging Codes and Sparsified Coded Bitstream
Compatibility is a key problem that must be considered for the composite signal.Since the ranging code and the sparsified coded bitstream are superimposed,they will inevitably cause interferences between each other.It is necessary to analyze the compatibility between the two components of the proposed composite signal and the simulation results are summarized in the following sections.
4.4.1 Information Transmission Performance of the Composite Signal with Acquisition Failure
In the following,we give results to compare the BER performance of uncoded BPSK system between the proposed method and the pure communication method.
For the proposed composite signal,sparse sequence can be extracted by inverting the sign of the composite signal according to the chip‘1’position of the ranging code.The acquisition of the ranging code component is the key step to extract the sparse information sequence,which may influence the error performance of the information transmission,as shown in Figure 9.It can be observed that information transmission performance of the proposed method with acquisition failure(e.g.,L=1500)is worse than the pure communication method.As the correlation length increases,BER performance of the superimposed sparse sequence can be improved,since the acquisition performance is improved as shown in Subsection 4.2.It can also be observed that after successful acquisition of the ranging code component(e.g.,L=3000),the sparse sequence can be extracted without interference by eliminating the ranging code component.
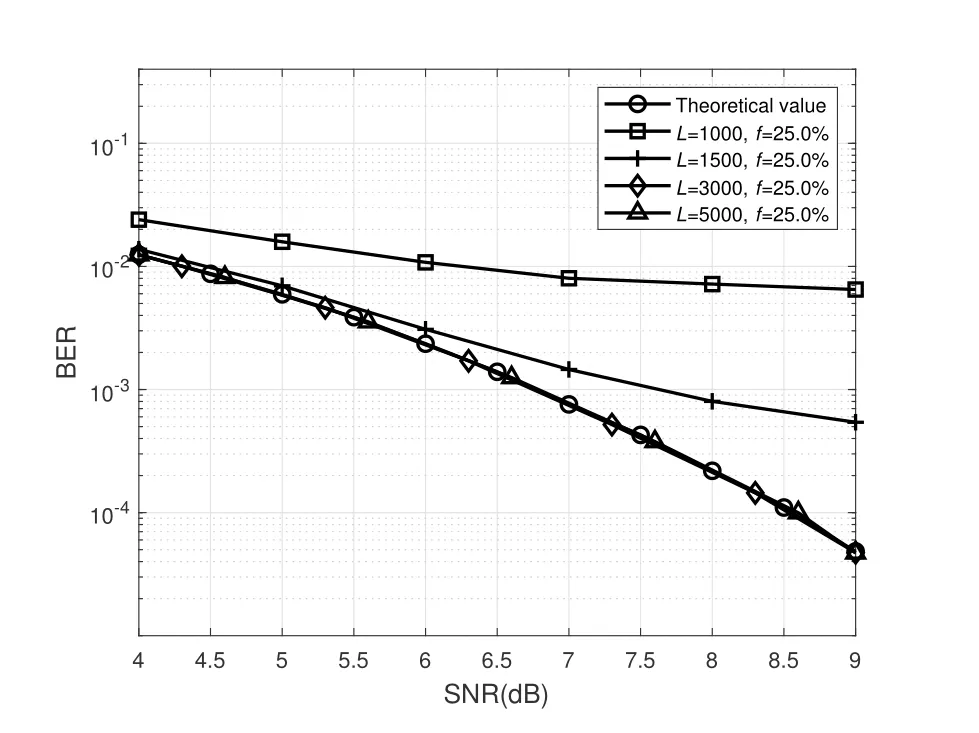
Figure 9.Comparison of the BER performance between the proposed method and the pure communication method.
4.4.2 Ranging Code Acquisition Performance under Different Superposition Densities
The sparsified coded bitstream may influence the acquisition performance of ranging codes,which can be controlled and minimized by adjusting the density of sparse sequences.As the density of the coded bitstream decreases,the impact on ranging code acquisition also decreases,as shown in Figure 10.Condition that the density of superimposed sparse coding sequences is 12.5% and 6.25%,the acquisition performance of the proposed method with the correlation length of 20000 chips and 15000 chips is better than that of pure ranging method with the correlation length of 10000 chips,respectively.The length of superimposed coded bitstream is also an important influence factor,which has been mentioned in Subsection 4.2.As the length of the superimposed segment decreases,the effect of coded bitstream on ranging code acquisition can also be weakened.
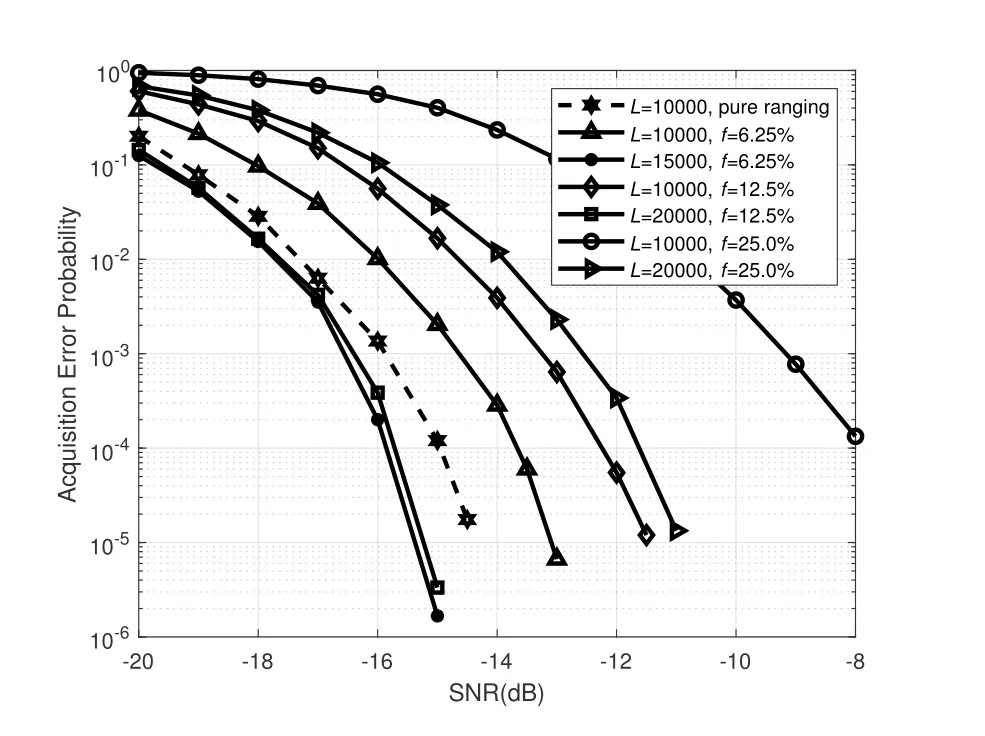
Figure 10.Acquisition performance of the T2B code superimposed with the sparse sequence of the different density.
Then,we compare the acquisition performance of the two methods under low superposition density(e.g.,f=6.25%)with the correlation length of 20000,40000 and 80000 chips,respectively.As illustrated in Figure 11,compared with the pure ranging method at the acquisition error probability of 10?4,the acquisition performance of the proposed method in the case off=6.25%has a loss of about 1.2 dB.
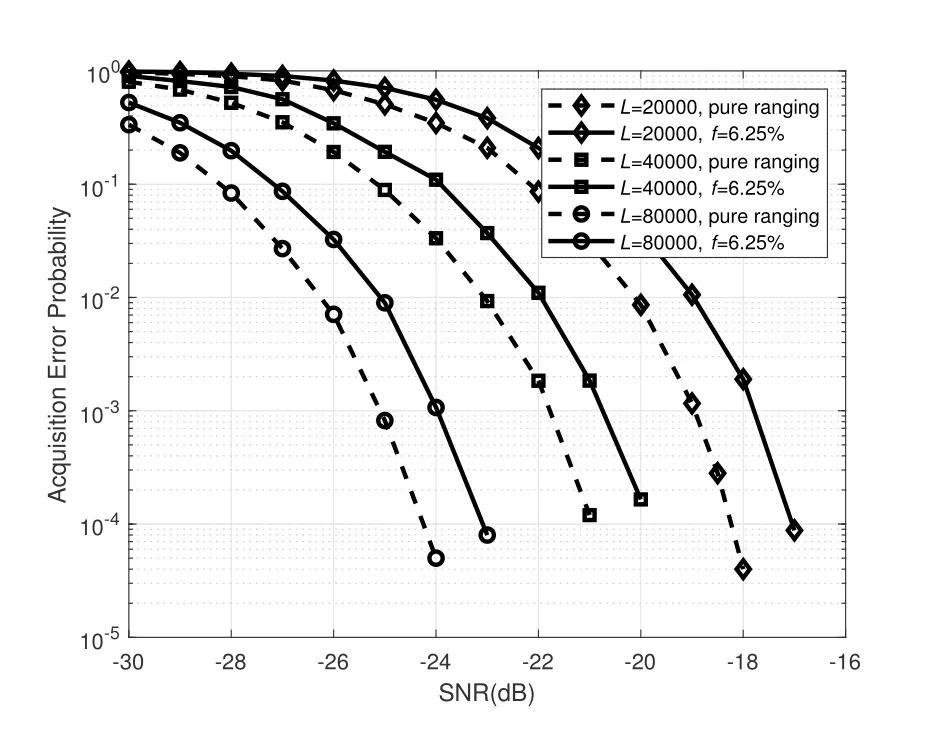
Figure 11.Comparison of the acquisition performance between the proposed method and the pure ranging method.
4.4.3 Ranging Accuracy of the Composite Signal
In this part,we give simulation results to compare the tracking performance of the chip tracking loop(CTL)and ranging accuracy between the proposed method and the pure ranging method.Specifically,we use the timing jitter and ranging jitter to evaluate the ranging performance.Their computation is presented as follows.
According to the CCSDS recommended standard for pseudo-noise ranging systems[21],in the ideal case of a square-wave shaped ranging signal and a matched receiver,the on-board PN tracking performance of the CTL in terms of timing rms error(called timing jitter)σεcan be expressed as
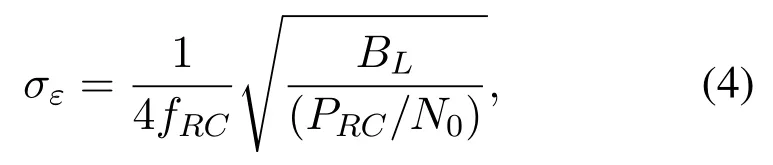
wherePRCis the power of the ranging clock component,N0is the one-sided noise power spectral density andBLis the one-sided loop noise bandwidth of the CTL.In the presence of thermal noise only,the timing jitter at the on-board unit is given by Eq.(4),leading to the one-way ranging rms error(called ranging jitter)σRangewhich can be written as[21,24]

wherecis the light speed.The ranging power of the ranging clock component over noise spectral density at CTL input can be expressed as[21]
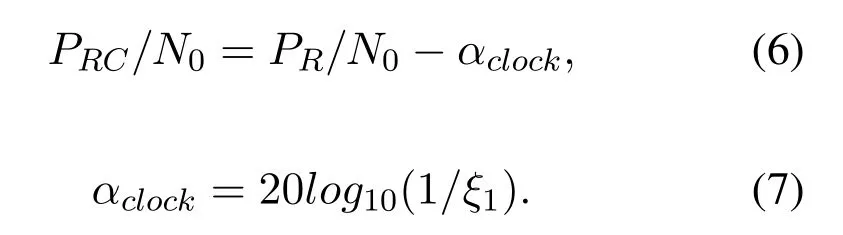
Here,PR/N0is the ranging power over noise spectral density as defined in Section 4.3.The range clock attenuation,αclock,is a measure of the strength of the range clock in the composite sequence relative to an unmodulated square-wave pattern.It has a direct effect on the ranging accuracy,which is determined by the in-phase correlation of the clock component,ξ1,as shown in Eq.(7).ξ1is defined as the in-phase fractional correlation for the range clock component,which is the ratio of in-phase correlation value of the range clock component to the length of the ranging code[21].
In the following analysis,we chooseBL=1 Hz andFc=2.068 Mchip/s,the same conditions indicated in the CCSDS recommended standard[3].
First,the timing jitter and ranging jitter are estimated using(4)-(7)whenPR/N0=30 dBHz,as summarized in Table 3.It is observed that,the lower the density of the superposed sparse sequence is,the better the ranging performance is.In the case off=6.25%,the timing jitter is 13.92 ns and the ranging jitter has a loss of about 0.26 m compared with the pure ranging method.
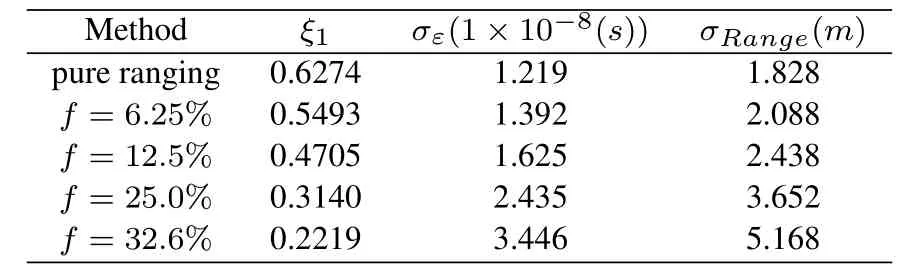
Table 3.The information transmission capability of the proposed method under different parameters.
Then,we analyze the timing jitter and the ranging jitter under differentPR/N0conditions,as depicted in Figure 12 and 13.Figure 12 illustrates the comparison of the timing jitter of the CTL between the proposed method and the pure ranging method.The proposed method has an increase in under the same timing jitter.At the timing jitter of 10?8,the proposed method has a loss of about 1.2 dBHz compared with the pure ranging method in the case off=6.25%.Figure 13 illustrates the comparison of the two methods in terms of ranging jitter.Compared with the pure ranging method at the ranging jitter of 1 m,the proposed method in the case off=6.25%has a loss of about 1.2 dBHz.
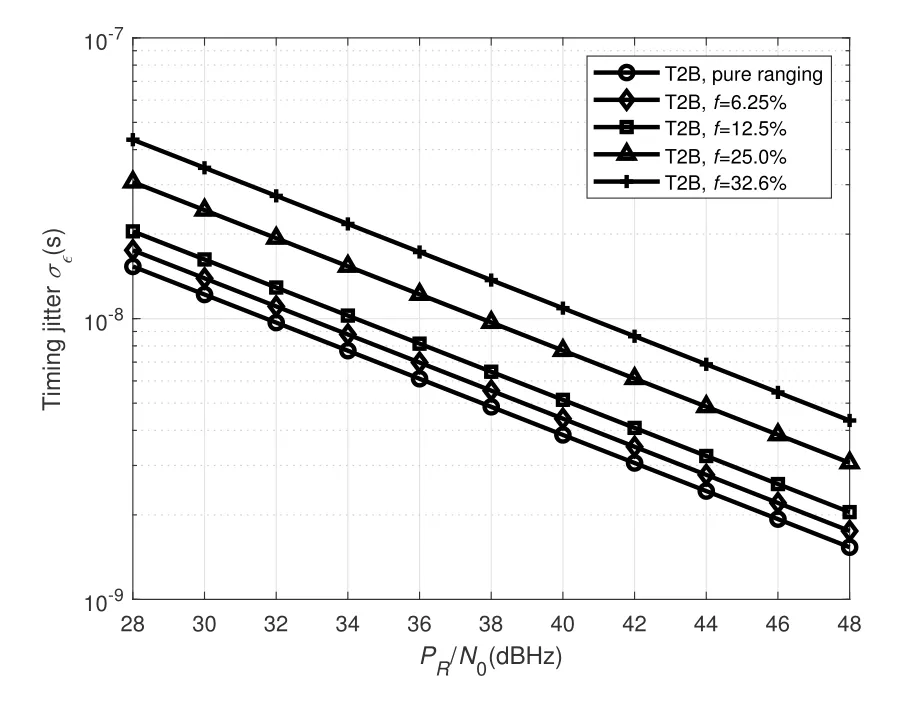
Figure 12.The timing jitter of the CTL using T2B code of the proposed method and the pure ranging method.
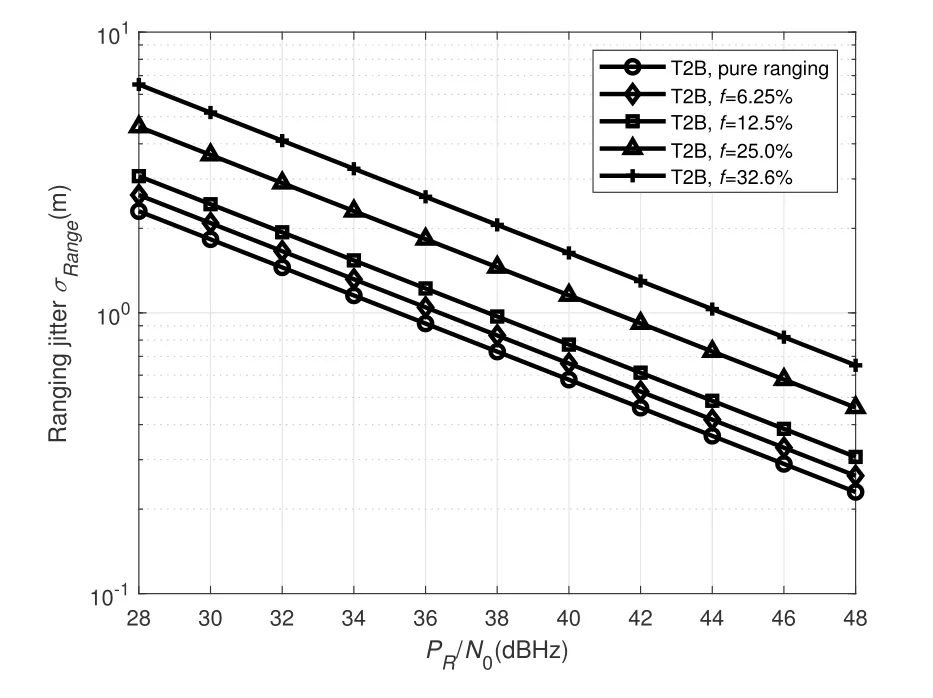
Figure 13.The one-way ranging jitter using T2B code of the proposed method and the pure ranging method.
4.5 Potential Application Condition for the Proposed Method
We summarized the simulation results above to present the possible application conditions of the proposed method compared with the example in[9].
In the link budget for Mars-M mission in[9],the information transmission rate is 150 kbps andPR/N0is 57.1 dBHz.In the case of telemetry-only,the transmission signal can be received at the SNR with a margin of 3.6 dB using the CCSDS standard turbo code of rate 1/6.01.If the conventional residual carrier modulation is used to perform ranging and telemetry simultaneously,the telemetry symbol rate is limited to 52.6 kbps,corresponding to the pure information transmission rate of 8.75 kbps.
Under the same parameter settings of the Mars-M,PR/N0=57.1 dBHz,the performance of our proposed method is shown in Table 2.It can be observed that the information rate is 414.32 kbps using the proposed concatenated code,which is higher than the reference system of 150 kbps[9].Even ifPR/N0decreases to 48 dBHz,the proposed method can still achieve information transmission rate of 103.58 kbps with the ranging accuracy loss of about 0.94 m.Compared with the pure ranging method,our proposed method is a good tradeoff which can transmit the information superimposed on the ranging signal simultaneously with a certain sacrifice of ranging performance.The acquisition time is extended by about 10 times and the ranging accuracy is also slightly reduced.In conclusion,the proposed method is feasible in application scenarios where the ranging distance and the signalto-noise ratio is moderate.
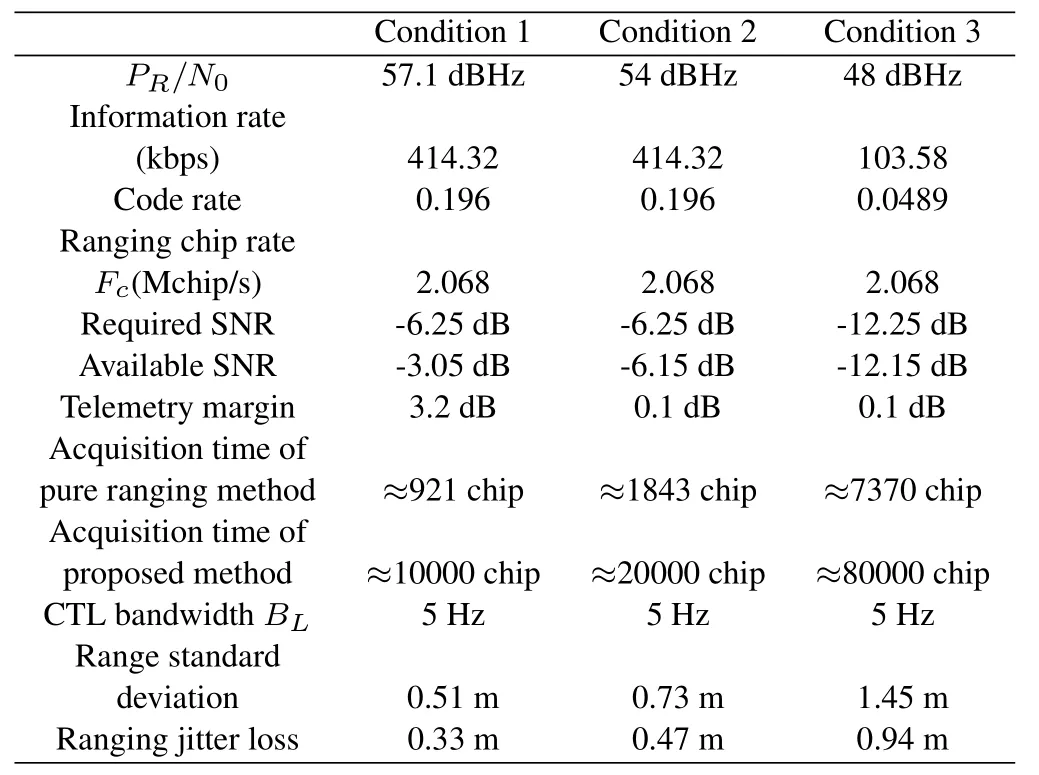
Table 4.The application conditions of the proposed method.
In the specific engineering implementation for our proposed paradigm,we have many freedoms to trade off the performance and parameter settings.On the one hand,the code rate and code length of the coding scheme can be adjusted to offer different error correction capabilities and sparsity levels.On the other hand,the performance degradation of ranging can be controlled and minimized by adjusting the density or the length of superimposed coded information sequences.
V.CONCLUSION
A bit-level composite signal for simultaneous ranging and communication is proposed in this paper.We study the potential application prospect of this composite signal in deep space exploration and analyze the compatibility between ranging codes and superimposed information sequences.On the one hand,the information sequence is transformed into a sparse sequence so that the influence on ranging performance of ranging codes can be minimized.On the other hand,the information sequence can be extracted without interference by adopting the simple modulo-2 addition operation.Simulation results validate that the proposed composite signal can transmit ranging codes and information sequences simultaneously in the low SNR regime.The parameters of sparse sequences can be adaptively adjusted according to the actual situation to satisfy the system requirements of communication and ranging.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable suggestions which have greatly improved the manuscript.This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China(61671324)and the Director’s Funding from Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology(Qingdao)(QNLM201712).Zhan Xu was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China(61620106001).
- China Communications的其它文章
- LED Adaptive Deployment Optimization in Indoor VLC Networks
- Reinforcement Learning-Based Sensitive Semantic Location Privacy Protection for VANETs
- Boosting Unsupervised Monocular Depth Estimation with Auxiliary Semantic Information
- Joint 3D Trajectory and Resource Optimization for A UAV Relay-Assisted Cognitive Radio Network
- A Blockchain-Based Credible and Secure Education Experience Data Management Scheme Supporting for Searchable Encryption
- Sparsity-Aware Channel Estimation for mmWave Massive MIMO:A Deep CNN-Based Approach

